Geocoding of Million Fruit Trees for Monitoring and Tracking [不丹]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Nima Dolma Tamang
- 编辑者: Haka Drukpa
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Shingdrey Changm Saya Zukchong Tatok Gi Dhoen lu Sa Chhai Dhadhoen Dhulen (ཤིང་འབྲས་ལྕངམ་ས་ཡ་འཛུགས་སྐྱོང་བལྟ་རྟོག་གི་དོན་ལུ་ས་ཆའི་བརྡ་དོན་བསྡུ་ལེན།)
technologies_6829 - 不丹
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
Agriculture Extension Officer:
Penjor Thuji
Geog Renewable Natural Resources (RNR) Center, Agriculture Office, Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag
不丹
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - 不丹1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology enables remote monitoring of the growth and development of fruit trees ensuring the sustainable use of land and its resources. Further, the technology aids in the success of the Million Fruit Tree Plantation Project reducing the risk of converting cultivable land to fallow.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Geocoding of fruit trees allows remote monitoring and progress tracking of the growth of seedlings. The Smart App MoDA (Mobile Operation and Data Acquisition) is used in geocoding.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
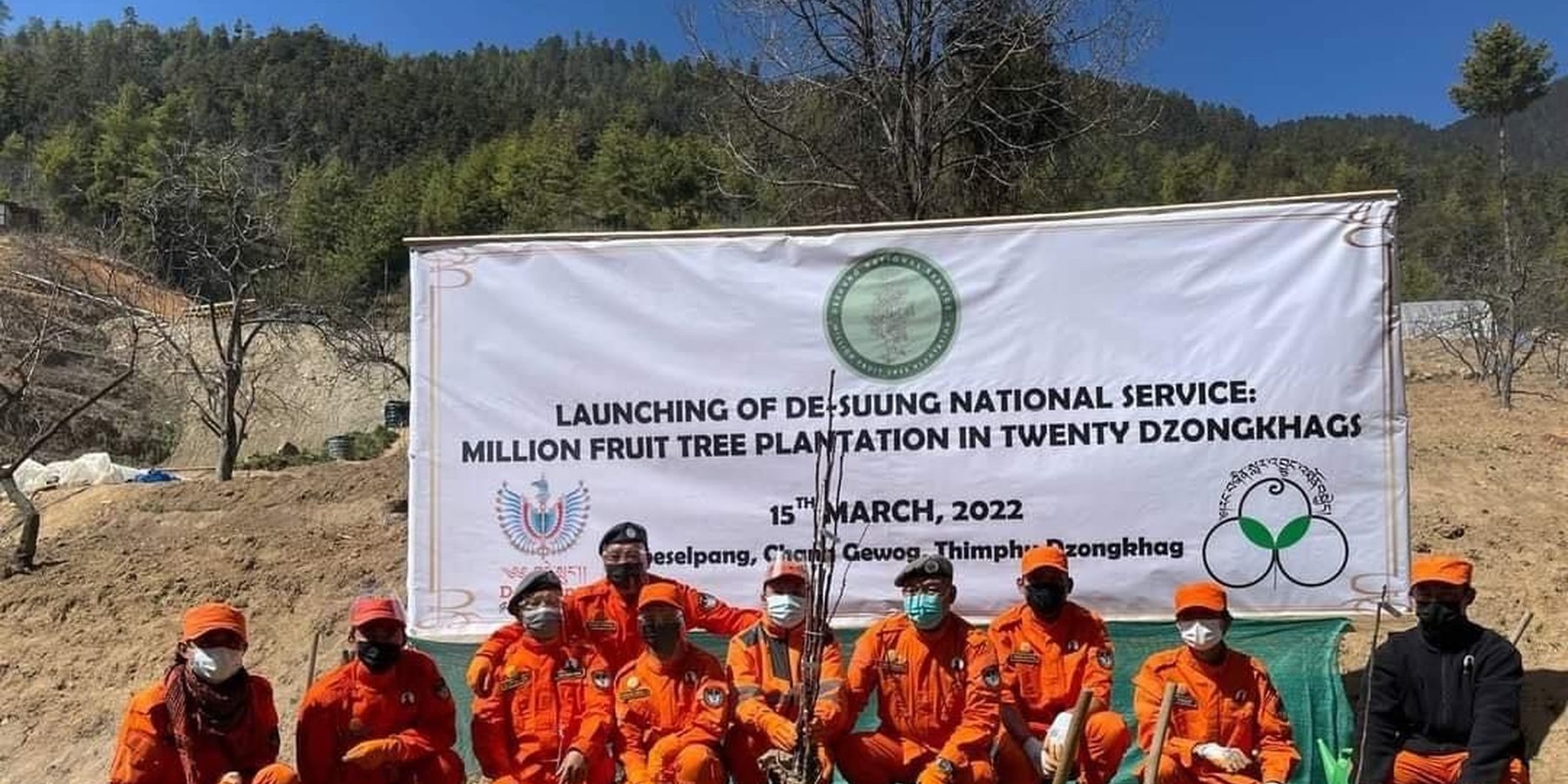
Geocoding of the “million fruit trees” initiative has been carried out across Bhutan. Different fruit trees suitable for particular agroecological zones were planted in farmers' fields in twenty districts and each sapling was geocoded.
The main elements of geocoding fruit trees involve assigning unique geographical codes or coordinates to individual trees within an orchard, utilizing technical specifications and equipment such as handheld GPS to accurately determine the location. The potential benefits of this form of geocoding include:
1. Location Mapping: Geocoding allows fruit trees to be accurately located on a map, providing a visual representation of their spatial distribution. This mapping can help identify patterns, clusters, and gaps in tree distribution.
2. Data Integration: Geocoded data can be integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) and other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and topography. This integration provides a holistic view of the factors influencing fruit tree growth and productivity.
3. Precision: Geocoding provides precise coordinates for each fruit tree, enhancing the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This precision is crucial for making informed decisions regarding tree management and resource allocation.
4. Monitoring and Management: Geocoded fruit tree data enables efficient monitoring of tree health, growth, and potential issues. It facilitates targeted interventions, such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on the specific needs of individual trees or clusters.
5. Yield Estimation: By combining geocoded data with relevant environmental and growth information, it's possible to estimate the potential fruit yield in specific areas. This information aids in resource planning and harvest predictions.
6. Disease and Pest Management: Geocoded data can help identify patterns of disease or pest infestations. Early detection through geocoded monitoring can enable prompt intervention and prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
7. Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoding allows researchers to study the diversity of fruit tree species in different regions. This analysis can be useful for conservation efforts and understanding the ecological impact of specific tree species.
8. Research and Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data serves as a valuable resource for scientific research. Researchers can study the effects of climate change, urbanization, and land use changes on fruit tree populations and ecosystems.
9. Decision-Making: Geocoded data assists farmers, agricultural agencies, and policymakers in making informed decisions about land use, tree planting initiatives, and resource allocation for sustainable agriculture.
10. Community Engagement: Geocoded maps of fruit trees can be shared with communities, promoting awareness of local resources, fostering community engagement, and encouraging initiatives like urban orchards or community gardens.
11. Data Visualization: Geocoded data can be visualized using maps and spatial tools, making it easier to interpret and communicate information to various stakeholders.
12. Long-Term Tracking: Geocoded data allows for long-term tracking of changes in fruit tree populations, aiding in the assessment of the success of planting initiatives and the overall health of the environment.
The major activity of the technology is marking the fruit trees with the help of GPS so that these geocoordinates can be useful in tracking down the exact location of the plant. Geocoding is labour-intensive as the field workers need to be physically present in the field while carrying out the activity. Then the data recorded in GPS is transferred to the computer and analyzed using ArcGIS. This information is available to the policymakers and Agriculture officers and is shared with the Extension Agents through which it is disseminated to the land users.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
不丹
区域/州/省:
Thimphu Dzongkhag
有关地点的进一步说明:
Sigay Chiwog, Mewang Gewog
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The geocoding of fruits are in the land users field. Therefore, the area does not fall under any of the protected area or national parks.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The geocoding of the million fruit trees in the country was initiated as per the directives of His Majesty the 5th King of Bhutan where all the saplings are funded by the Royal Government of Bhutan. Plantation and geocoding were done by the Desuups (Desuup is the highest form of the voluntary act in Bhutan. They wear orange uniforms and are also known as the Guardians of Peace).
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(旱地)
年作制度:
湿地稻 - 小麦
- Apple
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Paddy in summer is followed by winter wheat or vegetables
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
They intercrop vegetables with lugumes.
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The land used for paddy cultivation is used for planting vegetables such as potatoes.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
The technology aids in maintaining land cover by ensuring vegetative coverage of the land in which geocoding enhances easy management and improved health of the fruit trees such as apples, dragon fruit, banana, areca nut, kiwi, avocado and others.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Fruit tree plantations will potentially prevent land degradation in the long term by giving cover and strengthening soil structure by its roots.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
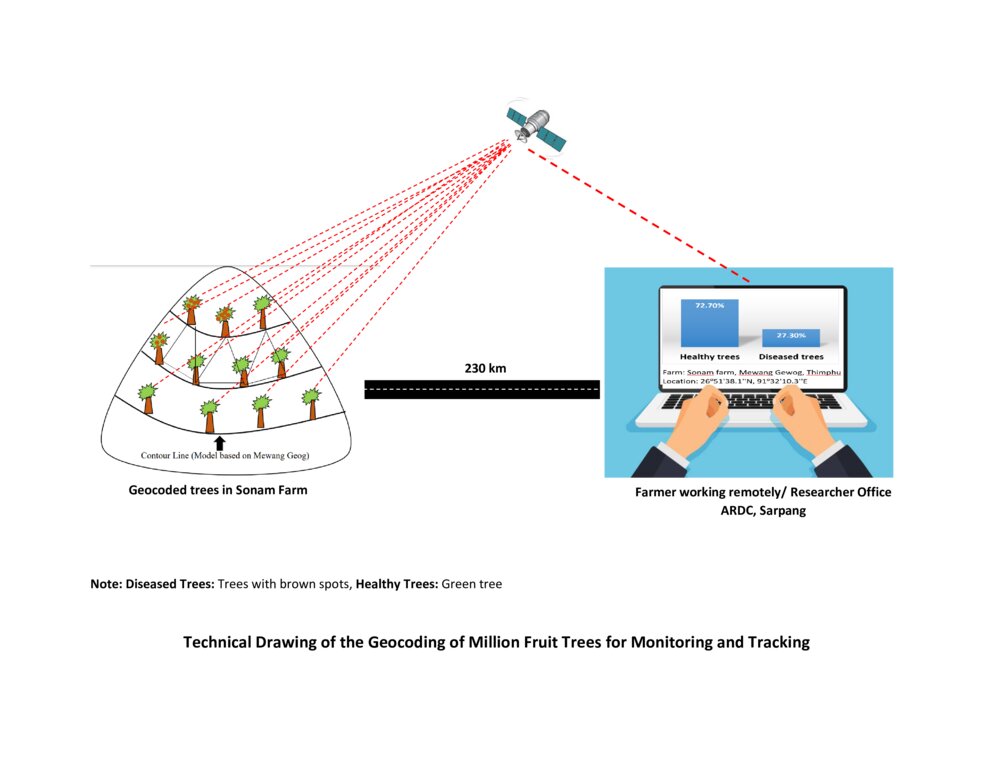
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The technical drawing represents the general method of million fruit tree plantation and geocoding done on each tree. It depicts how geocoding enables the researcher or farmer to remotely check the health of the trees using satellite data. ARDC stands for Agriculture Research and Development Center.
作者:
Nima Dolma Tamang, Singye Dorji, Tshering Gyeltshen
日期:
07/07/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
No of Seedlings
指定单位面积(如相关):
8000 seedlings (Only in Mewang Geog)
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
82.62
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
800
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting between Gewog leaders and land users | NA |
| 2. | Identified a village for planation | NA |
| 3. | Identified households that wanted the seedings and number of seedlings | NA |
| 4. | Site identification | NA |
| 5. | Orchard layout | NA |
| 6. | Pit digging | NA |
| 7. | Plantation | March- April |
| 8. | Basin making | After planation |
| 9. | Geocoding | After one month of orchard establishment |
| 10. | Growth Tracking | After every six months |
注释:
The above information is limited to only Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Desuup (Guardians of peace) - Volunteers | Person-days | 6.0 | |||
| 劳动力 | Farmers | Person-days | 10.0 | 800.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Shovel | No. | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | crow-bar | No. | 5.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | Spade | No. | 20.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | GPS remote | No | 6.0 | 12000.0 | 72000.0 | |
| 设备 | Tabs/ mobile phones | No. | 6.0 | 15000.0 | 90000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Apple | No. | 3500.0 | 70.0 | 245000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Walnut | No. | 1000.0 | 120.0 | 120000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Almond | No. | 500.0 | 120.0 | 60000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Peach | No. | 1000.0 | 70.0 | 70000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Pear | No. | 2000.0 | 70.0 | 140000.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Manure and fertillizers | Metric Tonnes | 16.0 | 1600.0 | 25600.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 830600.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 10053.26 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Almost all the cost were covered by the Million Fruit Tree Project of Desuung National Service and Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock jointly.
注释:
The total cost calculated is for planting and geocoding. The actual costs borne by land users are very minimal. The only cost the land users have to bear is labour cost and fertilizer cost. The high cost of the project is contributed mainly by seedling cost, GPS remote, tablets and mobile phones which was used during the marking position of fruit trees.
Cost for shovel spade and crowbar is not included as they are available at the farm and are reused.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Twice a year |
| 2. | Fertillizer application | Twice a year |
| 3. | Irrigation | Once a week |
| 4. | Replacement of dead plants | After 6 months from plantation |
| 5. | Growth tracking | After every six month |
注释:
The information obtained are through verbal communication with the Agriculture Extension Officer of Mewang Gewog.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Weeding and fertilizer application | Per year | 4.0 | 1600.0 | 6400.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Irrigation | Litres | ||||
| 劳动力 | Geocoding | per plant | 8000.0 | |||
| 植物材料 | Replacement of plants | per plant | 10.0 | 70.0 | 700.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7100.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 85.94 | |||||
注释:
The geocoding was done by the Desuung volunteers. so, the exact costs cannot be deduced.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Most important factors affecting the costs are seedling and labour cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
2076.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The rainfall data for Mewang Gewog is not available. The provided data is for Thimphu Dzongkhag as Mewang Gewog is under Thimphu Dzongkhag (Gewog is one of the geographic units below Dzongkhag). Thimphu falls under a temperate region and experiences minimal rainfall compared to the other parts of Bhutan. Thimphu had the wettest month in July with 497 mm and experienced the least rainfall in December with 5 mm.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
National Center for Hydrology and Metoerology, Thimphu.
农业气候带
There are six Agro-ecological Zones (AEZ) in Bhutan and the current place of study falls under warm temperate zone which occurs between 1,800 – 2,500 m. Rainfall is low but the temperature is moderately warm in summer with frost in winter.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The area was characterized by a steep valley near the river with minimal slope as the valley widened.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
The availability of water in Mewang Gewog was a concern since a decade ago. Irrigation water was not enough for every farmers which resulted in delayed paddy plantation.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The species of flora and fauna diversity cannot be quantified under "high" as per the field observation. The area was surrounded by coniferous forest which generally has low biodiversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The majority of the land users who were part of the Geocoding of million fruit plantation had already established apple orchards.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
An average land holding capacity for Bhutanese household as per the Land Act is 3 acres. The land holding that exceeds 3 acres are categorized in large scale in Bhutanese context.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
Internet:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
The drinking water is insufficient as some households face scarcity of drinking water.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The technology aids in the monitoring and improves health and ease management of the already established orchard. Therefore, it indirectly increases crop production.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Remote or constant monitoring ensures timely management to prevent biotic and abiotic factors deteriorate the crop quality.
饲料生产
饲料质量
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Geocoding enables land user to determine potential risk so that the land user can use appropriate methods to prevent crop failure.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
The technology is not directly related to the product diversity. However, it provides data on existing fruit tree diversity so that the land user can plan and plant different fruit trees based on the market need which indirectly increases diversity.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Geocoding enables the land user to remotely view the cropped area and the area where the crop failed (could be due to dying of the seedlings/diseased). It enables the land user to narrow their focus on the specific area, learn about the issues causing the crop loss, provide appropriate management, and conduct plantation in that area which indirectly increases production area.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Due to increased production area with no increase in the quantity of irrigation water, water availability is likely to reduce.
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
There is increased demand for irrigation water for new plantations. However, with the use of technology land users can monitor the water requirement and use efficiently based on the need of the tree whereby the land users can avoid watering the trees that require less water and provide to those that require more water.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Minimal increase in expenses on agriculture inputs as planting materials (except manure) were provided to the land users for free of cost.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Once the fruit trees starts bearing fruits, income is expected to increase.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
It adds to farmers sources of income other than vegetable and dairy product sale.
经济差异
注释/具体说明:
The technology is expected to reduce economic disparity by providing equal opportunity for the land users to generate income.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Workload for the project implementors or land users are significantly reduced as they need not go to the actual site to determine the progress of the Million Fruit Trees Plantation Project.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The technology indirectly aids in the increased production making an individual land user and the nation self-sufficient in fruits.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
With reduced workload, land users can engage in recreational activities.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The technology will enable the project implementors to determine specific knowledge gaps and provide training in that particular field to the land users. Improving knowledge of both project implementors and land users.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Land users willing to be involved in fruit tree plantation are supported without discrimination of their social status or economic background and geocoding services are provided. This leads to the improved situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
The total water quantity remains same. However, the available water per tree or sapling is reduced.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Due to the absorption of water by the roots of the fruit trees, surface run-off is decreased.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Evaporation will be decreased due to an increase in the vegetation cover from the plantation of the fruit trees.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Slight increase in the soil moisture in long run due to addition of soil organic matter and monitored irrigation.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
The technology enhances easy monitoring of the trees and encourages increased soil cover.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
The technology enhances soil cover reducing the soil loss from erosion.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Geocoding enables the land user to have overview of the nutrient content of the production area aiding land users to add nutrient based on the need.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Generally, there will be an increase in the soil organic matter due to an increase in production area and management practice such as the addition of manures by the land user.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Increase due to the scheduled irrigation applied to the fruit trees.
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Slight increase due to proper management and care provided to the orchard.
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Animal diversity in the case of pollinators such as bees increases as the fruit trees mature and start flowering.
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Beneficial species such as bees are attracted to the orchards.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Pest and diseases control improves with the use of remote monitoring facilitated by this technology.
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
Once the fruit trees establish themselves, landslides can be reduced significantly due to vegetation cover.
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
This technology could potentially reduce greenhouse gas as trees utilize carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
风速
注释/具体说明:
In the long run, a well-established orchard can act as a windbreak and reduce wind velocity and damage it poses to the property.
微气候
注释/具体说明:
An orchard can act as a micro-climate harbouring many plants and insect species.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Fruit trees require irrigation which reduces the availability of water for other purposes.
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Having a land cover with vegetation compared to barren land reduces greenhouse gases.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 减少 | 非常好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地雹灾 | 非常好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 非常好 |
注释:
The technology copes very well with gradual climate change because it sends rapid messages to farmers on actions to take (e.g., concerning pests and diseases). In a way it’s a form of early warning systems (EWS).
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Although the initial establishment of the orchard is costly considering the labour charge, it is expected to have positive income and impact once the fruit trees start bearing.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Total 8000 fruit trees are planted in the five Chiwogs (third level administrative division under Gewog) under Mewang Gewog.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Almost all those who adopted the technology are funded by the government.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| 1. Precision Mapping: Geocoding allows for accurate mapping and identification of fruit trees. By assigning specific geographic coordinates to each tree, it becomes easier to locate and monitor individual trees or orchards. |
| 2. Efficient Resource Allocation: Geocoding helps optimize resource allocation by providing information on tree density and distribution. Land users can identify areas with high fruit tree concentrations and strategically allocate resources such as labour, water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to improved productivity and reduced costs. |
| 3. Data-driven Decision Making: Geocoded data on fruit trees can be analyzed to gain insights into their distribution patterns, growth rates, and health status. This information enables land users, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding fruit tree cultivation, pest control, and disease management. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| 1. Conservation and Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data aids in the conservation and analysis of biodiversity. By mapping the locations of different fruit tree species, experts can assess the distribution and abundance of specific varieties, identify endangered local or traditional landraces varieties, and develop strategies for their preservation. |
| 2. Targeted Marketing and Distribution: Geocoded fruit tree data facilitates targeted marketing and distribution strategies. By understanding the location of fruit trees and their yields, producers can identify potential markets and plan transportation logistics more effectively, minimizing waste and ensuring timely delivery to consumers. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Geocoding large numbers of fruit trees can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive task, particularly when manual processes are involved. It may require extensive fieldwork and manual data entry, making it impractical or costly for large-scale fruit tree inventories. | |
| Privacy Concerns: Geocoding fruit trees raises privacy concerns, particularly when tree locations are associated with specific individuals or properties. Care must be taken to ensure that privacy is respected and sensitive information is appropriately handled | An updated and secured security-protected website can be used. |
| Lack of knowledge of geocoding by the farmers. | Provide awareness trainings |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The higher expense of the geocoding in terms of labour cost for geo-coding | Train land users on geocoding, instead of using trained professionals. |
| Difficult to constantly update information on time. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
The information documented was from the field visit to orchards near the RNR center.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
The information collected are from first-hand interview with the Agriculture Extension Officer who was engaged fully during the implementation of the technology.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
07/07/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
De-suung National Service (DNS). (n.d.). Million Fruit Trees Plantation
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://desuung.org.bt/25978-2/#:~:text=In%20order%20to%20monitor%20the,from%20the%20date%20of%20plantation.
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched
URL:
http://www.bbs.bt/news/?p=166763
标题/说明:
Kuensel. (2022). Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched. Thimphu.
URL:
Website: https://kuenselonline.com/414000-fruit-trees-planted-in-45-days/
标题/说明:
Geocoding of trees from street addresses and street-level images
URL:
https://www.fs.usda.gov/psw/publications/vandoorn/psw_2020_vandoorn001_laumer.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块