Geocoding of Million Fruit Trees for Monitoring and Tracking [Bhoutan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Nima Dolma Tamang
- Rédacteur : Haka Drukpa
- Examinateurs : William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Not Applicable (NA)
technologies_6829 - Bhoutan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Agriculture Extension Officer:
Penjor Thuji
Geog Renewable Natural Resources (RNR) Center, Agriculture Office, Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag
Bhoutan
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Bhoutan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
The technology enables remote monitoring of the growth and development of fruit trees ensuring the sustainable use of land and its resources. Further, the technology aids in the success of the Million Fruit Tree Plantation Project reducing the risk of converting cultivable land to fallow.
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Geocoding of fruit trees allows remote monitoring and progress tracking of the growth of seedlings. The Smart App MoDA (Mobile Operation and Data Acquisition) is used in geocoding.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Geocoding of the “million fruit trees” initiative has been carried out across Bhutan. Different fruit trees suitable for particular agroecological zones were planted in farmers' fields in twenty districts and each sapling was geocoded.
The main elements of geocoding fruit trees involve assigning unique geographical codes or coordinates to individual trees within an orchard, utilizing technical specifications and equipment such as handheld GPS to accurately determine the location. The potential benefits of this form of geocoding include:
1. Location Mapping: Geocoding allows fruit trees to be accurately located on a map, providing a visual representation of their spatial distribution. This mapping can help identify patterns, clusters, and gaps in tree distribution.
2. Data Integration: Geocoded data can be integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) and other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and topography. This integration provides a holistic view of the factors influencing fruit tree growth and productivity.
3. Precision: Geocoding provides precise coordinates for each fruit tree, enhancing the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This precision is crucial for making informed decisions regarding tree management and resource allocation.
4. Monitoring and Management: Geocoded fruit tree data enables efficient monitoring of tree health, growth, and potential issues. It facilitates targeted interventions, such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on the specific needs of individual trees or clusters.
5. Yield Estimation: By combining geocoded data with relevant environmental and growth information, it's possible to estimate the potential fruit yield in specific areas. This information aids in resource planning and harvest predictions.
6. Disease and Pest Management: Geocoded data can help identify patterns of disease or pest infestations. Early detection through geocoded monitoring can enable prompt intervention and prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
7. Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoding allows researchers to study the diversity of fruit tree species in different regions. This analysis can be useful for conservation efforts and understanding the ecological impact of specific tree species.
8. Research and Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data serves as a valuable resource for scientific research. Researchers can study the effects of climate change, urbanization, and land use changes on fruit tree populations and ecosystems.
9. Decision-Making: Geocoded data assists farmers, agricultural agencies, and policymakers in making informed decisions about land use, tree planting initiatives, and resource allocation for sustainable agriculture.
10. Community Engagement: Geocoded maps of fruit trees can be shared with communities, promoting awareness of local resources, fostering community engagement, and encouraging initiatives like urban orchards or community gardens.
11. Data Visualization: Geocoded data can be visualized using maps and spatial tools, making it easier to interpret and communicate information to various stakeholders.
12. Long-Term Tracking: Geocoded data allows for long-term tracking of changes in fruit tree populations, aiding in the assessment of the success of planting initiatives and the overall health of the environment.
The major activity of the technology is marking the fruit trees with the help of GPS so that these geocoordinates can be useful in tracking down the exact location of the plant. Geocoding is labour-intensive as the field workers need to be physically present in the field while carrying out the activity. Then the data recorded in GPS is transferred to the computer and analyzed using ArcGIS. This information is available to the policymakers and Agriculture officers and is shared with the Extension Agents through which it is disseminated to the land users.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
The Photo does not directly depicts the technology described here.
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Bhoutan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Thimphu Dzongkhag
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Sigay Chiwog, Mewang Gewog
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The geocoding of fruits are in the land users field. Therefore, the area does not fall under any of the protected area or national parks.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2022
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The geocoding of the million fruit trees in the country was initiated as per the directives of His Majesty the 5th King of Bhutan where all the saplings are funded by the Royal Government of Bhutan. Plantation and geocoding were done by the Desuups (Desuup is the highest form of the voluntary act in Bhutan. They wear orange uniforms and are also known as the Guardians of Peace).
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- préserver l'écosystème
- créer un impact économique positif
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agroforesterie

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - riz (de milieux secs)
Système de cultures annuelles :
Riz de terres humides - blé
- Apple
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Paddy in summer is followed by winter wheat or vegetables
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Oui
Si oui, précisez quelles cultures sont produites en culture intercalaire:
They intercrop vegetables with lugumes.
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
The land used for paddy cultivation is used for planting vegetables such as potatoes.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Non (Passez à la question 3.4)
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- agroforesterie
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes
Commentaires:
The technology aids in maintaining land cover by ensuring vegetative coverage of the land in which geocoding enhances easy management and improved health of the fruit trees such as apples, dragon fruit, banana, areca nut, kiwi, avocado and others.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Fruit tree plantations will potentially prevent land degradation in the long term by giving cover and strengthening soil structure by its roots.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
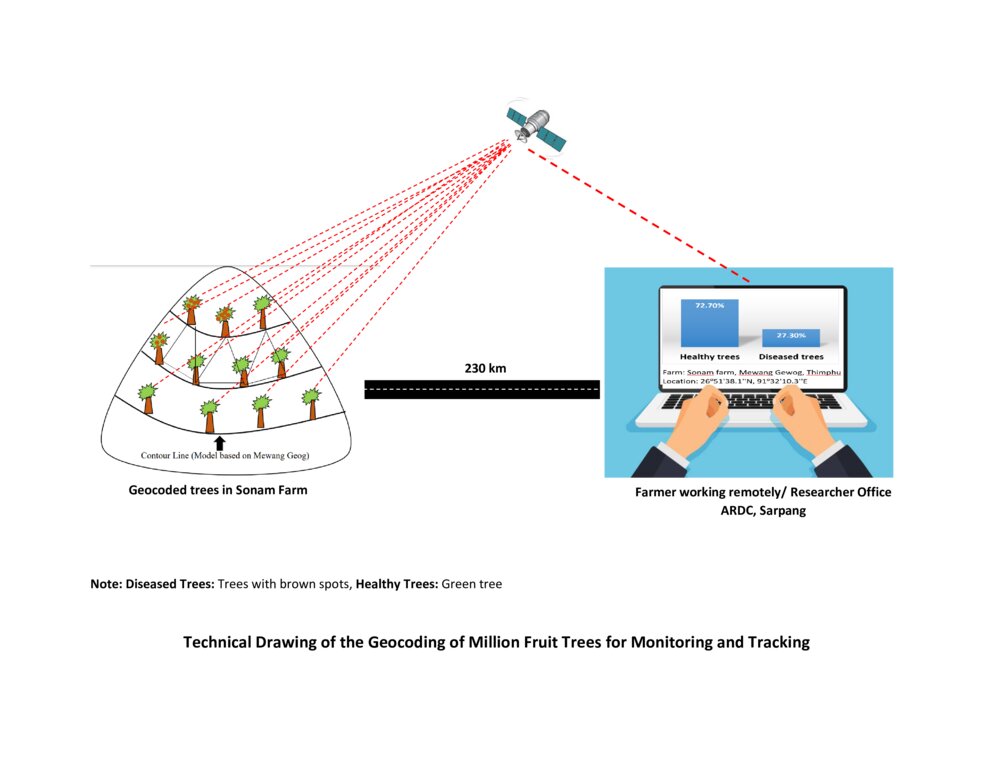
The technical drawing represents the general method of million fruit tree plantation and geocoding done on each tree. It depicts how geocoding enables the researcher or farmer to remotely check the health of the trees using satellite data. ARDC stands for Agriculture Research and Development Center.
Auteur:
Nima Dolma Tamang, Singye Dorji, Tshering Gyeltshen
Date:
07/07/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
No of Seedlings
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
8000 seedlings (Only in Mewang Geog)
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
82,62
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
800
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting between Gewog leaders and land users | NA |
| 2. | Identified a village for planation | NA |
| 3. | Identified households that wanted the seedings and number of seedlings | NA |
| 4. | Site identification | NA |
| 5. | Orchard layout | NA |
| 6. | Pit digging | NA |
| 7. | Plantation | March- April |
| 8. | Basin making | After planation |
| 9. | Geocoding | After one month of orchard establishment |
| 10. | Growth Tracking | After every six months |
Commentaires:
The above information is limited to only Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Desuup (Guardians of peace) - Volunteers | Person-days | 6,0 | |||
| Main d'œuvre | Farmers | Person-days | 10,0 | 800,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Shovel | No. | 10,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipements | crow-bar | No. | 5,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipements | Spade | No. | 20,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Equipements | GPS remote | No | 6,0 | 12000,0 | 72000,0 | |
| Equipements | Tabs/ mobile phones | No. | 6,0 | 15000,0 | 90000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Apple | No. | 3500,0 | 70,0 | 245000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Walnut | No. | 1000,0 | 120,0 | 120000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Almond | No. | 500,0 | 120,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Peach | No. | 1000,0 | 70,0 | 70000,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | Pear | No. | 2000,0 | 70,0 | 140000,0 | |
| Engrais et biocides | Manure and fertillizers | Metric Tonnes | 16,0 | 1600,0 | 25600,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 830600,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 10053,26 | |||||
Si le coût n'est pas pris en charge à 100% par l'exploitant des terres, indiquez qui a financé le coût restant:
Almost all the cost were covered by the Million Fruit Tree Project of Desuung National Service and Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock jointly.
Commentaires:
The total cost calculated is for planting and geocoding. The actual costs borne by land users are very minimal. The only cost the land users have to bear is labour cost and fertilizer cost. The high cost of the project is contributed mainly by seedling cost, GPS remote, tablets and mobile phones which was used during the marking position of fruit trees.
Cost for shovel spade and crowbar is not included as they are available at the farm and are reused.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Twice a year |
| 2. | Fertillizer application | Twice a year |
| 3. | Irrigation | Once a week |
| 4. | Replacement of dead plants | After 6 months from plantation |
| 5. | Growth tracking | After every six month |
Commentaires:
The information obtained are through verbal communication with the Agriculture Extension Officer of Mewang Gewog.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Weeding and fertilizer application | Per year | 4,0 | 1600,0 | 6400,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Irrigation | Litres | ||||
| Main d'œuvre | Geocoding | per plant | 8000,0 | |||
| Matériel végétal | Replacement of plants | per plant | 10,0 | 70,0 | 700,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 7100,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 85,94 | |||||
Commentaires:
The geocoding was done by the Desuung volunteers. so, the exact costs cannot be deduced.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Most important factors affecting the costs are seedling and labour cost.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
2076,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
The rainfall data for Mewang Gewog is not available. The provided data is for Thimphu Dzongkhag as Mewang Gewog is under Thimphu Dzongkhag (Gewog is one of the geographic units below Dzongkhag). Thimphu falls under a temperate region and experiences minimal rainfall compared to the other parts of Bhutan. Thimphu had the wettest month in July with 497 mm and experienced the least rainfall in December with 5 mm.
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
National Center for Hydrology and Metoerology, Thimphu.
Zone agro-climatique
There are six Agro-ecological Zones (AEZ) in Bhutan and the current place of study falls under warm temperate zone which occurs between 1,800 – 2,500 m. Rainfall is low but the temperature is moderately warm in summer with frost in winter.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations convexes
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The area was characterized by a steep valley near the river with minimal slope as the valley widened.
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
moyenne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
eaux de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Non
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
The availability of water in Mewang Gewog was a concern since a decade ago. Irrigation water was not enough for every farmers which resulted in delayed paddy plantation.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- faible
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
The species of flora and fauna diversity cannot be quantified under "high" as per the field observation. The area was surrounded by coniferous forest which generally has low biodiversity.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- femmes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
The majority of the land users who were part of the Geocoding of million fruit plantation had already established apple orchards.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
An average land holding capacity for Bhutanese household as per the Land Act is 3 acres. The land holding that exceeds 3 acres are categorized in large scale in Bhutanese context.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, avec titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Oui
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Internet:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Commentaires:
The drinking water is insufficient as some households face scarcity of drinking water.
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology aids in the monitoring and improves health and ease management of the already established orchard. Therefore, it indirectly increases crop production.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Remote or constant monitoring ensures timely management to prevent biotic and abiotic factors deteriorate the crop quality.
production fourragère
qualité des fourrages
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Geocoding enables land user to determine potential risk so that the land user can use appropriate methods to prevent crop failure.
diversité des produits
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology is not directly related to the product diversity. However, it provides data on existing fruit tree diversity so that the land user can plan and plant different fruit trees based on the market need which indirectly increases diversity.
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Geocoding enables the land user to remotely view the cropped area and the area where the crop failed (could be due to dying of the seedlings/diseased). It enables the land user to narrow their focus on the specific area, learn about the issues causing the crop loss, provide appropriate management, and conduct plantation in that area which indirectly increases production area.
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
disponibilité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to increased production area with no increase in the quantity of irrigation water, water availability is likely to reduce.
demande pour l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
There is increased demand for irrigation water for new plantations. However, with the use of technology land users can monitor the water requirement and use efficiently based on the need of the tree whereby the land users can avoid watering the trees that require less water and provide to those that require more water.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Minimal increase in expenses on agriculture inputs as planting materials (except manure) were provided to the land users for free of cost.
revenus agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Once the fruit trees starts bearing fruits, income is expected to increase.
diversité des sources de revenus
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It adds to farmers sources of income other than vegetable and dairy product sale.
disparités économiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology is expected to reduce economic disparity by providing equal opportunity for the land users to generate income.
charge de travail
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Workload for the project implementors or land users are significantly reduced as they need not go to the actual site to determine the progress of the Million Fruit Trees Plantation Project.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology indirectly aids in the increased production making an individual land user and the nation self-sufficient in fruits.
possibilités de loisirs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
With reduced workload, land users can engage in recreational activities.
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology will enable the project implementors to determine specific knowledge gaps and provide training in that particular field to the land users. Improving knowledge of both project implementors and land users.
situation des groupes socialement et économiquement désavantagés
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Land users willing to be involved in fruit tree plantation are supported without discrimination of their social status or economic background and geocoding services are provided. This leads to the improved situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The total water quantity remains same. However, the available water per tree or sapling is reduced.
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to the absorption of water by the roots of the fruit trees, surface run-off is decreased.
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Evaporation will be decreased due to an increase in the vegetation cover from the plantation of the fruit trees.
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Slight increase in the soil moisture in long run due to addition of soil organic matter and monitored irrigation.
couverture du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology enhances easy monitoring of the trees and encourages increased soil cover.
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology enhances soil cover reducing the soil loss from erosion.
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Geocoding enables the land user to have overview of the nutrient content of the production area aiding land users to add nutrient based on the need.
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Generally, there will be an increase in the soil organic matter due to an increase in production area and management practice such as the addition of manures by the land user.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Increase due to the scheduled irrigation applied to the fruit trees.
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Slight increase due to proper management and care provided to the orchard.
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Animal diversity in the case of pollinators such as bees increases as the fruit trees mature and start flowering.
espèces bénéfiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Beneficial species such as bees are attracted to the orchards.
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Pest and diseases control improves with the use of remote monitoring facilitated by this technology.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
glissements de terrains/coulées de débris
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Once the fruit trees establish themselves, landslides can be reduced significantly due to vegetation cover.
émissions de carbone et de gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
This technology could potentially reduce greenhouse gas as trees utilize carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In the long run, a well-established orchard can act as a windbreak and reduce wind velocity and damage it poses to the property.
microclimat
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
An orchard can act as a micro-climate harbouring many plants and insect species.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
disponibilité de l'eau
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Fruit trees require irrigation which reduces the availability of water for other purposes.
impact des gaz à effet de serre
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Having a land cover with vegetation compared to barren land reduces greenhouse gases.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| températures saisonnières | été | augmente | très bien |
| précipitations annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | été | décroît | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| averse de grêle locale | très bien |
Catastrophes biologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| maladies épidémiques | très bien |
Commentaires:
The technology copes very well with gradual climate change because it sends rapid messages to farmers on actions to take (e.g., concerning pests and diseases). In a way it’s a form of early warning systems (EWS).
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Although the initial establishment of the orchard is costly considering the labour charge, it is expected to have positive income and impact once the fruit trees start bearing.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
Total 8000 fruit trees are planted in the five Chiwogs (third level administrative division under Gewog) under Mewang Gewog.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
Almost all those who adopted the technology are funded by the government.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Non
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| 1. Precision Mapping: Geocoding allows for accurate mapping and identification of fruit trees. By assigning specific geographic coordinates to each tree, it becomes easier to locate and monitor individual trees or orchards. |
| 2. Efficient Resource Allocation: Geocoding helps optimize resource allocation by providing information on tree density and distribution. Land users can identify areas with high fruit tree concentrations and strategically allocate resources such as labour, water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to improved productivity and reduced costs. |
| 3. Data-driven Decision Making: Geocoded data on fruit trees can be analyzed to gain insights into their distribution patterns, growth rates, and health status. This information enables land users, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding fruit tree cultivation, pest control, and disease management. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| 1. Conservation and Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data aids in the conservation and analysis of biodiversity. By mapping the locations of different fruit tree species, experts can assess the distribution and abundance of specific varieties, identify endangered local or traditional landraces varieties, and develop strategies for their preservation. |
| 2. Targeted Marketing and Distribution: Geocoded fruit tree data facilitates targeted marketing and distribution strategies. By understanding the location of fruit trees and their yields, producers can identify potential markets and plan transportation logistics more effectively, minimizing waste and ensuring timely delivery to consumers. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Geocoding large numbers of fruit trees can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive task, particularly when manual processes are involved. It may require extensive fieldwork and manual data entry, making it impractical or costly for large-scale fruit tree inventories. | |
| Privacy Concerns: Geocoding fruit trees raises privacy concerns, particularly when tree locations are associated with specific individuals or properties. Care must be taken to ensure that privacy is respected and sensitive information is appropriately handled | An updated and secured security-protected website can be used. |
| Lack of knowledge of geocoding by the farmers. | Provide awareness trainings |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The higher expense of the geocoding in terms of labour cost for geo-coding | Train land users on geocoding, instead of using trained professionals. |
| Difficult to constantly update information on time. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
The information documented was from the field visit to orchards near the RNR center.
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
The information collected are from first-hand interview with the Agriculture Extension Officer who was engaged fully during the implementation of the technology.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
07/07/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
De-suung National Service (DNS). (n.d.). Million Fruit Trees Plantation
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://desuung.org.bt/25978-2/#:~:text=In%20order%20to%20monitor%20the,from%20the%20date%20of%20plantation.
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched
URL:
http://www.bbs.bt/news/?p=166763
Titre/ description:
Kuensel. (2022). Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched. Thimphu.
URL:
Website: https://kuenselonline.com/414000-fruit-trees-planted-in-45-days/
Titre/ description:
Geocoding of trees from street addresses and street-level images
URL:
https://www.fs.usda.gov/psw/publications/vandoorn/psw_2020_vandoorn001_laumer.pdf
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé