Floating Vegetable Garden Using Water Hyacinth as Planting Medium [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Gulayan sa Gakit
technologies_7000 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Perez Mercy
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
菲律宾
土地使用者:
Cutao Arnel
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
菲律宾
土地使用者:
Osigan Marvin
Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
菲律宾
Project Implementer:
Acopiado Ma. Angelita Salome
Agusan del Sur Provincial Environment and Natural Resources Office (PENRO)
菲律宾
Project Implementer:
Dumaguit Dennis
LGU of Talacogon, Agusan del Sur
菲律宾
Project Implementer:
Asufre Gemma
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
菲律宾
Project Implementer:
Tabudlong Richard
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
菲律宾
co-compiler:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Plaza Marvin Emmanuel
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Talavera Ana Marie
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Manuel Paquito Jr.
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
Biodiversity Corridor Project staff who facilitated the interviews:
Barraca Jodel
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
菲律宾
Project Implementer:
Amante Romer
Department of Agriculture CARAGA
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Integrated Approach in Management of Major Biodiversity Corridors in the Philippines - GEF 6 Project (BD corridor)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
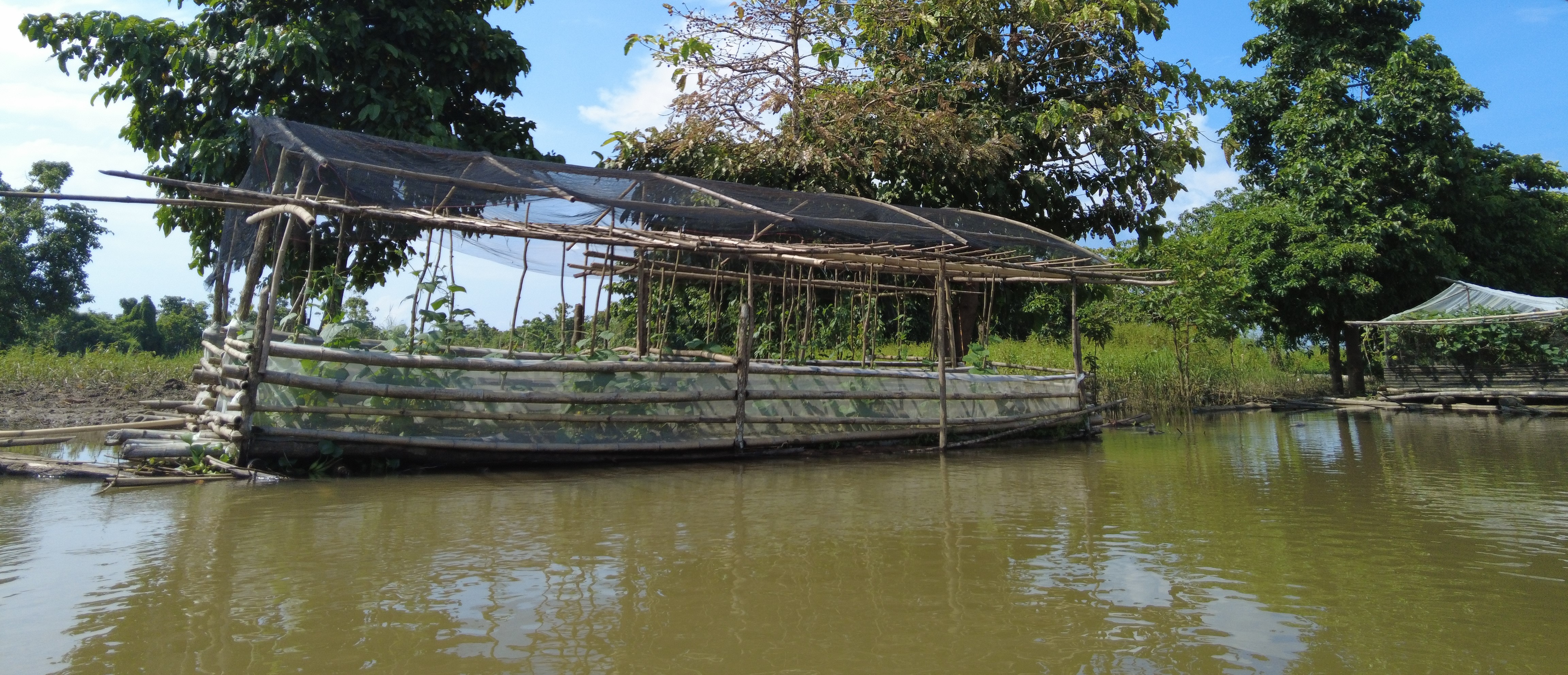
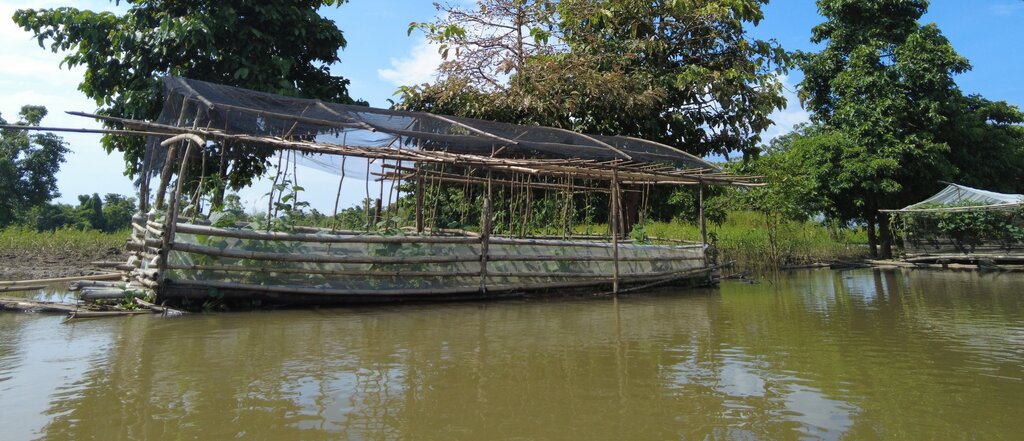
技术定义:
Floating vegetable garden as a climate change adaptation strategy for the indigenous communities living in the wetland of Agusan del Sur to grow vegetables during the flooding season.
2.2 技术的详细说明
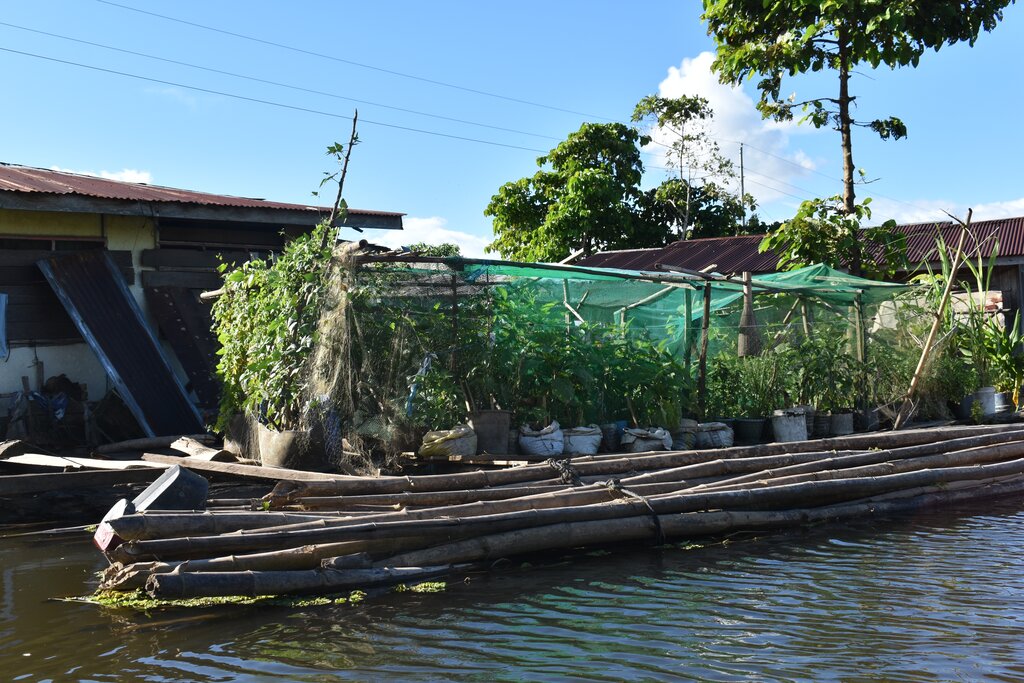
说明:
Agusan Marsh is considered one of the wetlands in the Philippines that experiences flooding all year round, and most areas are flooded, making it impossible to grow food for the communities living in the area. In order to address this issue, the construction of floating gardens were initiated by the Department of Agriculture CARAGA supported by various government agencies and Non Government Organizations (NGOs).
The floating garden technology and initiative, developed by the Foundation for the Development of Agusanons, Inc. (FDAI), was enhanced by the Department of Agriculture CARAGA and carried out by the Agricultural Program Coordinating Office (APCO) with the aim of establishing a sustainable agricultural system that promotes biodiversity and resilient farming practices. By using decomposed water hyacinth as a medium for growing crops, the technology helps mitigate its negative effects and transforms it into a valuable resource. Water hyacinths have a variety of negative impacts such as clogging waterways hampering boating and fishing, reducing local aquatic biodiversity and obstructing river flows which can aggravate flooding. The technlogy is being adopted by the Adaptation and Mitigation Initiative in Agriculture (AMIA) as a mitigation strategy against the impacts of climate change, enabling communities to better manage and adapt to climate-related risks. It also provides means for communities in flood-prone or coastal areas to engage in sustainable agri-fishery activities, ensuring food security and enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
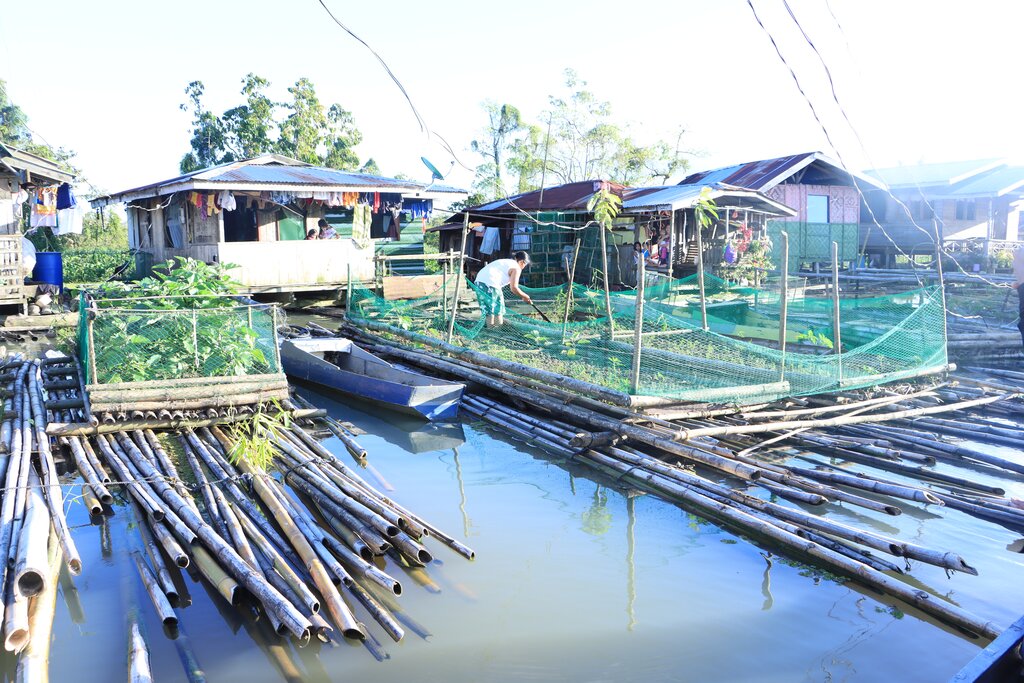
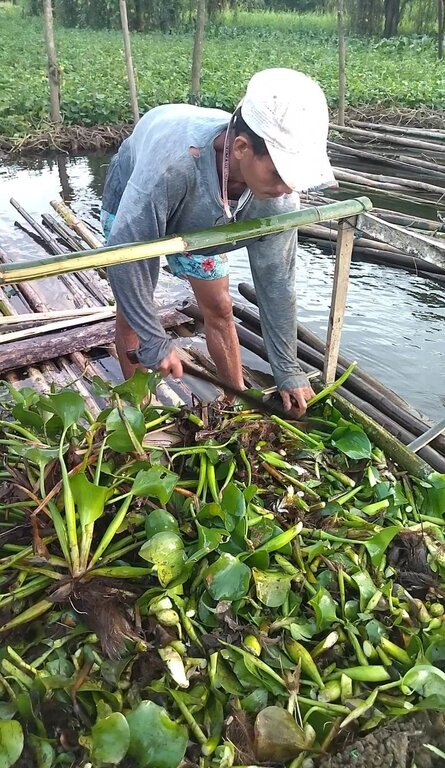
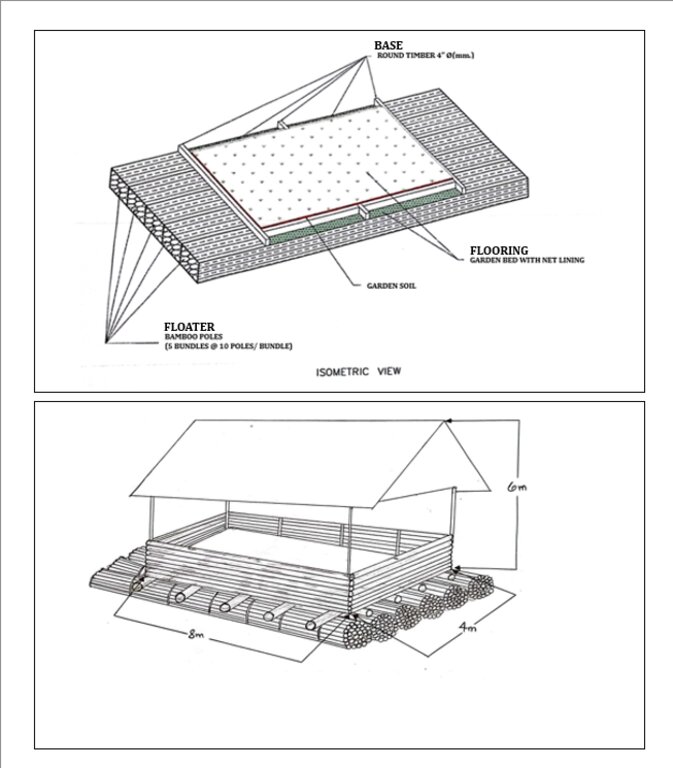
The components of the floating garden include a floater, a base (batangan), flooring (salug), growing substrate composed of layers of water hyacinth and layers of soil. Thewater hyacinths are collected from the river, chopped, and then mixed with the soil for composting before being used as a growing substrate in the floating garden. It is applied in layers as follows: composted hyacinth/soil mix, soil, composted hyacinth/ soil mix, and soil. The use of water hyacinth as substrate for the compost addresses the community’s concern about its proliferation, which causes obstruction in rivers, resulting in the destruction of boats and houses.
The standard dimension of a floating garden is 8 meters (length) by 4 meters (width), but this could be increased depending on the needs and financial capacity of the landusers. Crops planted are high-value vegetables such as pechay (pak choi), string beans, bitter gourd, tomato, bell pepper, cucumber, and eggplant, which were provided by the Department of Agriculture.
The FDAI played a pivotal role in project implementation, overseeing the construction of floating gardens and the provision of supplemental seedlings. The Binus-Ugan Farmers Association (BFA), as the recipient of the project, received 50 units of floating gardens through the Department of Agriculture's Adaptation and Mitigation Initiative in Agriculture (AMIA) Program.
Floating gardens were instrumental to the community in growing crops as their source of food and nutrients during the COVID-19 pandemic, where movement from barangay to barangay was restricted. A barangay is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines. The floating gardens became a source of income as the excess produce was sold to neighbors. The floating garden initiative did not only enhance economic conditions but also attracted local avian species, locally referred to as "pari-pari." Furthermore, it strengthened women's involvement in the community, particularly through their active participation in maintaining the gardens.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Province of Agusan Del Sur
有关地点的进一步说明:
Talacogon municipality
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The floating garden is within the Agusan marsh which is also considered as wildlife sanctuary.
Talacogon and Bunawan where most of the floating gardens are located. Only the Talacogon floating gardens were visited but during the interview with project implementers, they mentioned that they have also constructed floating garden in Bunawan.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The construction of floating garden at Barangay Sabang Gibong, Talacogon was funded by the Department of Agriculture in response to the needs of the community for food sources during flooding season when growing crops is not possible because the lands are submerged in water.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

水道、水体、湿地
- 沼泽、湿地
主要产品/服务:
Vegetables for own consumption and surplus is being sold
注释:
Floating gardens to grow vegetables are constructed in the wetlands when the area is flooded. For the past years, flooding occurred all year round.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
During rainy seasons, the landusers do not water the crops since the rainwater is already sufficient. When week passed and no rains occur, the landuser will water the crops from the river.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 湿地保护/管理
- 家庭花园
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S9:动植物庇护所

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Floating garden structure as shelter for plants
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Year round flooding (change in surface water quantity) limited agricultural activities on the land.
This technology address the decline of surface water quality due to the eutrophication of waterbody where water hyacinth is a contributor.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 适应土地退化
注释:
The community adapted to the state of land degradation in the area by transferring crop production from the year round flooded fields to floating gardens and using the available resource like the water hyacinth as substrate to produce compost used as substrate for plant growth
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The standard size for the floating garden has a length of 8 meters, width of 4 meters, and height of 6 meters. This could be decreased or increased depending on the the financial capacity and needs of the farmer. It is composed of floater, flooring, and base. The floater is made of bamboo poles (5 bundles at 10 poles/bundle). The flooring is the garden bed with net lining. The base is made up of wood that will act as the crossbeam. Plastic roofing could be added using UV plastic.
作者:
Jodel Barraca; Paquito Jr. C. Manuel; and DA CARAGA
日期:
09/01/2024
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
one floating garden unit
指定单位面积(如相关):
length-8 meters; width-4meters
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Pesos
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
55.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
350 Pesos
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of the floating garden | All year round |
| 2. | Collection of water hyacinth | All year round |
| 3. | Composting of water hyacinth and mixing with soil | All year round |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construction of the floating garden | person/day | 16.0 | 350.0 | 5600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Collection and composting of water hyacinth | person/day | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | vegetable seeds | cans | 3.0 | 1500.0 | 4500.0 | |
| 施工材料 | bamboo as floater | pieces | 200.0 | 40.0 | 8000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | wood for crossbeam | pieces | 4.0 | 200.0 | 800.0 | |
| 施工材料 | bamboo for floor joist | pieces | 10.0 | 30.0 | 300.0 | |
| 施工材料 | nails | kilos | 2.0 | 80.0 | 160.0 | |
| 施工材料 | wood as sidings | board feet (bd.ft) | 4.0 | 20.0 | 80.0 | |
| 施工材料 | bamboo as pole | pieces | 6.0 | 50.0 | 300.0 | |
| 施工材料 | rope | pieces | 16.0 | 25.0 | 400.0 | |
| 施工材料 | carabao rope for anchoring the garden | meters | 20.0 | 28.0 | 560.0 | |
| 其它 | UV plastic roofing | roll (12m x 5m) | 1.0 | 6000.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 27050.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 491.82 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The cost for the construction of the floating garden was subsidized by the Department of Agriculture
注释:
The materials used for the construction of the floating garden was subsidized by the government. The counterpart of the land user is the labor for the construction.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Change of the bamboo used as floaters | 1 to 2 years |
| 2. | Planting of vegetable seeds | All year round |
| 3. | Fertilizer application | All year round |
| 4. | Application of organic spray | All year round |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintenance of the floater | person/day | 3.0 | 350.0 | 1050.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting of vegetable seeds | person/day | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Fertilizer application | person/day | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Organic Spray application | person/day | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | cans | 3.0 | 1500.0 | 4500.0 | 50.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic Fertilizer | bag | 2.0 | 500.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic spray | liter | 4.0 | 250.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | bamboo | pieces | 200.0 | 40.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 16600.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 301.82 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The Department of Agriculture partially subsidized the seeds
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Availability of bamboo in the area which is heavily used as the floater
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
不可用
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
For the past three (3) years, the community has observed that flooding is all year round
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
其它(具体说明):
Houses are built with floaters which could be moved depending on the occurrence of floods
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Fishing is the main source of income of the landusers
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Less than 0.5 ha refers to the size of the floating garden itself
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
注释:
General characteristics of the situation in the area where the floating gardens are being implemented
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
There is an increase in production since floating garden made it possible for the landusers to grow crops in the absence of productive land for cultivation
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
The landusers planted other vegetables which were given by the Department of Agriculture.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
The production area increased since they could also produce using the floating garden.
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
The landuser will not only rely on fishing as source of income but also on vegetable production
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The community does not need to go to the mainland or to the town market to buy vegetables since they could grow their own produce.
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
Women's involvement in the community, particularly through their active participation in maintaining the gardens
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Trainings were conducted by the Department of Agriculture on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and vegetable production
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
The floating garden provided income to the indigenous people living in the area
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Attracted local bird species, locally referred to as "pari-pari."
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Utilized water hyacinth which is considered as an invasive aquatic weed
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
The establishment of the floating gardens reduced the invasive population of the water hyacinth in the Agusan Marsh.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热带风暴 | 适度 |
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 非常好 |
| 山洪暴发 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Serves as an efficient mode of resource utilization on a small productive land area like the Agusan Marsh. |
| Relatively sustainable use of environmental resources. |
| An additional source of sustenance/income from the floating garden's produce. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The floating garden technology could act as an additional tourist spot in Agusan Marsh. |
| There is strong support from various stakeholders, including the Municipal and Provincial Local Government Units, Department of Agriculture and Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) |
| Promote greater engagement within the community. |
| Reduce eutrophication by recycling water hyacinth |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital cost can be a hindrance for the community in Agusan Marsh. | The floating garden could be a project of the Local Government Unit (LGU) where they can subsidize the initial costs. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Erosion on river banks due to bamboo utilization for the construction of the floating garden. (Lack of resource sustainability program). | The community can initiate a bamboo planting program to ensure the sustainability of bamboo production and prevent soil erosion in riverbanks. |
| Some of the floating gardens constructed sunk because of the incorrect proportion of soil and compost ratio | Close monitoring during the land preparation to ensure the stability of floating garden. |
| Lack of monitoring of the technology by concerned government agencies due to the difficult accessibility of the community where the technology is being practiced. It will take three hours using pump boat to reach the barangay. | Government agency involved to look for possible source of funding for procurement of pump boats to be used for monitoring. The Department of Agriculture could train people from the barangay on how to do the monitoring and take measurements. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Number of field visits: 2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Number of informants: 8
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/12/2024
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Design, User, Experience, and Usability; Aaron Marcus, Elizabeth Rosenzweig, and Marcelo M. Soares (Eds.); 2023; ISBN: 978-3-031-35704-6
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Google Books; Free of charge
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Residents build flood-resilient floating gardens in Agusan Marsh
URL:
https://www.mindanews.com/top-stories/2021/07/residents-build-flood-resilient-floating-gardens-in-agusan-marsh/?fbclid=IwAR2PNh3GmiUKpk8JTWw5kHjcTRz4opsPxJGlWmvzjU33BWyHNR9jUb5ipnw
标题/说明:
Feature: Vegetable Garden floats in Agusan Marsh
URL:
https://issuu.com/caragainfocus/docs/october_15-21_2022/s/17258517?fbclid=IwAR0tLILkV0qGVCkcLJbMWcn5bAgBKJqxp4bfKKPzXDBBm9Zd3MmQTMlG0Wg
7.4 一般注释
The questionnaire, though it's lengthy, has all the relevant information that the interviewee must determine from the site. This incites a comprehensive documentation process, ensuring that all the subject's technology and adjacent information (i.e. community and environmental impacts) are captured.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块