Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ahmad Khalid Wiyar
- 编辑者: Megha bajaj, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy, Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
د ځنګل رغونی او کرنیزی ځنګلداری لپاره د پمپ په واسطه د ابه خور سیستم
technologies_7473 - 阿富汗
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: March 5, 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: March 24, 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: May 18, 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: July 9, 2025 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Safi Sharifullah
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
阿富汗
土地使用者:
Safi Mohammad Afzal
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
阿富汗
土地使用者:
Safi Qiamuddin
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
阿富汗
土地使用者:
Safi Farhad
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
阿富汗
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistan有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - 阿富汗1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
No, the technology described here is not problematic with regard to land degradation. In fact, it promotes sustainable land management by enhancing soil health, preventing erosion, and supporting afforestation efforts. This technology contributes to the restoration and conservation of forest ecosystems.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
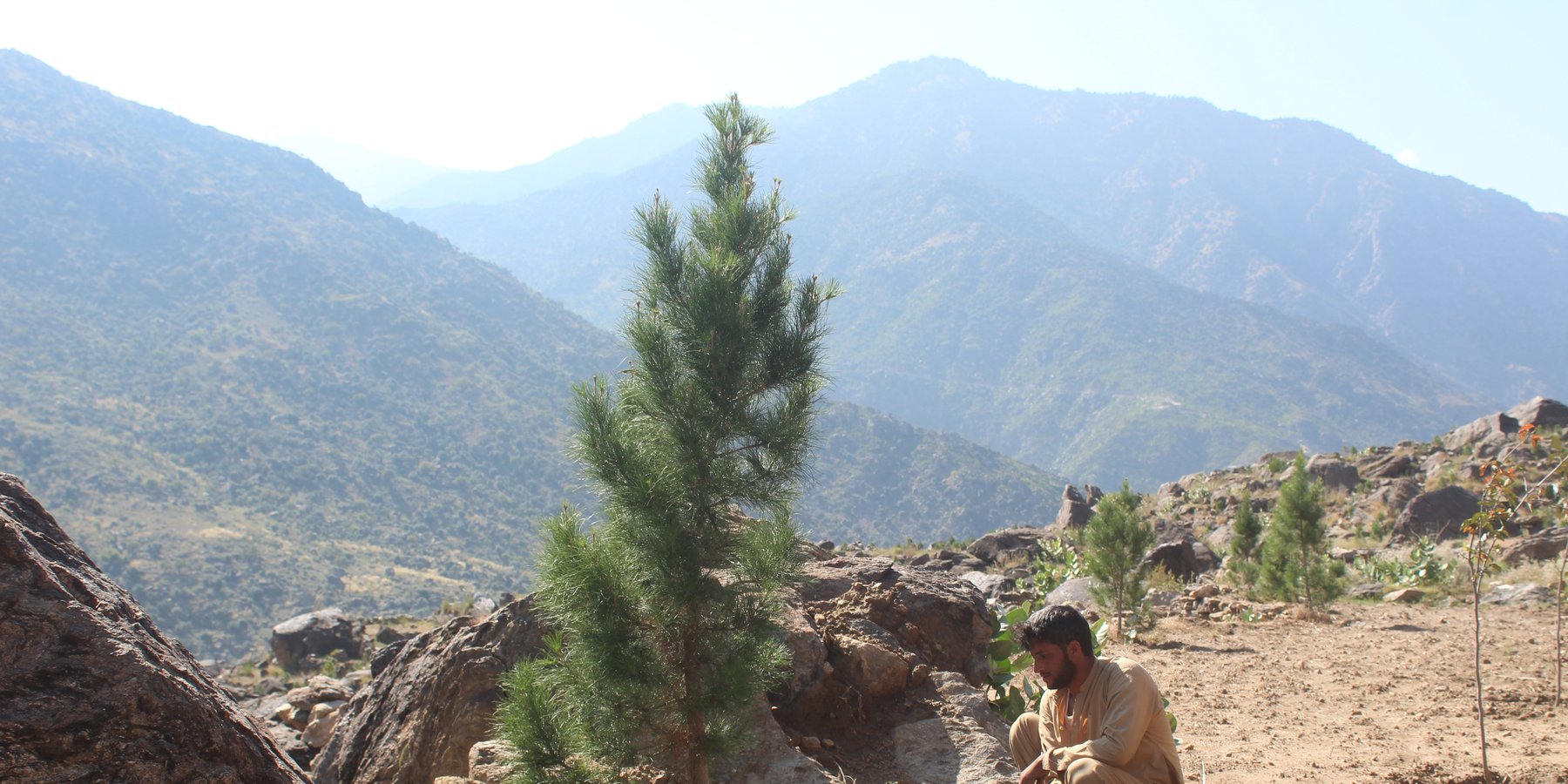
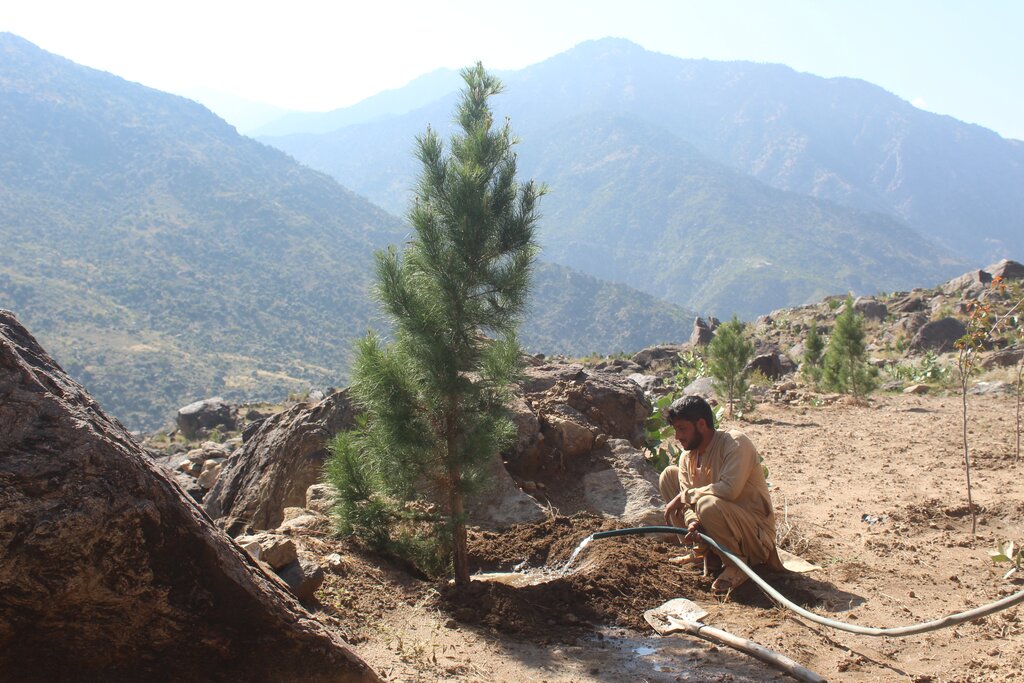
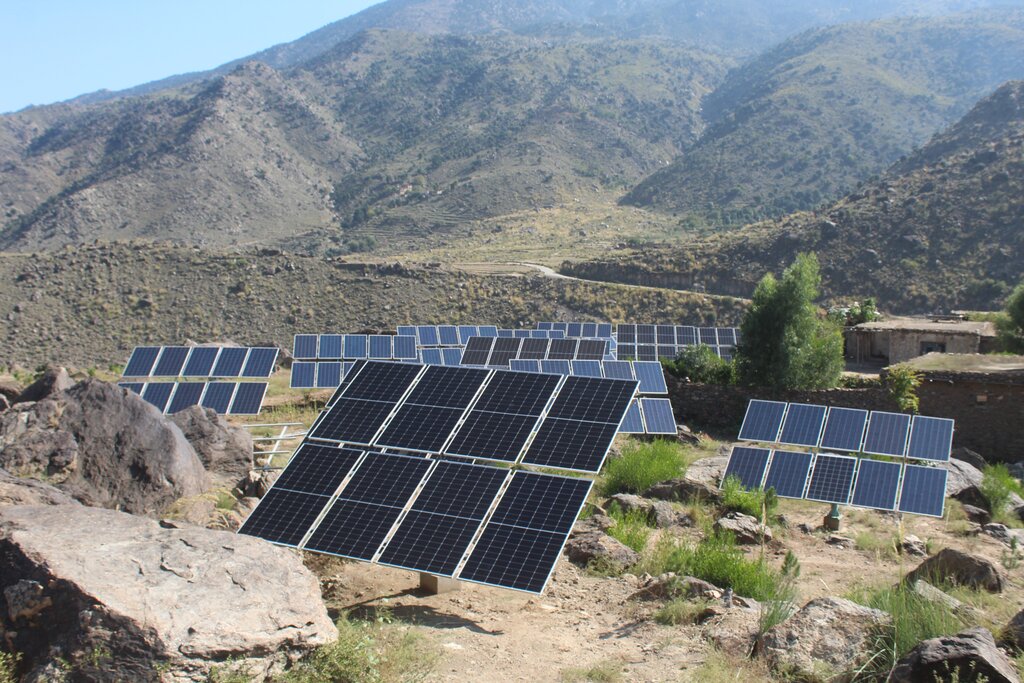
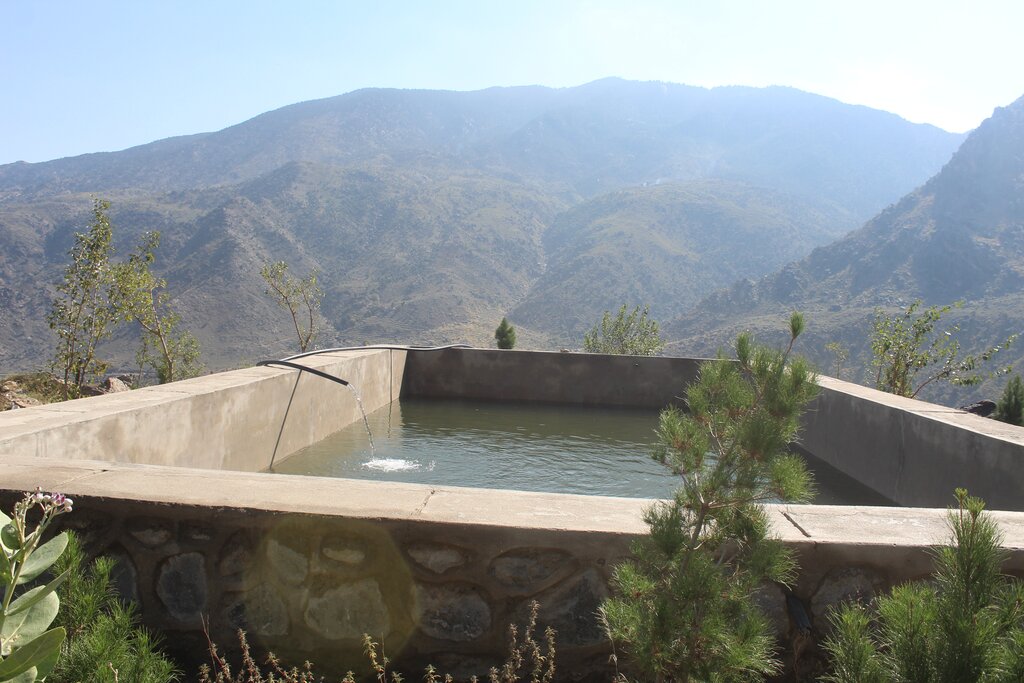
Water exploitation is a major issue in Afghanistan. The lift irrigation technology helps to irrigate an afforestation/agroforestry area (demonstration plot) using surface water (rivers) and solar-powered submersible pump. The construction of reservoirs at the demo plot ensures efficient water storage and use for irrigation purposes without relying on groundwater. A well-designed pipe irrigation scheme is implemented to distribute water evenly across the site, supporting plant irrigation and growth.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
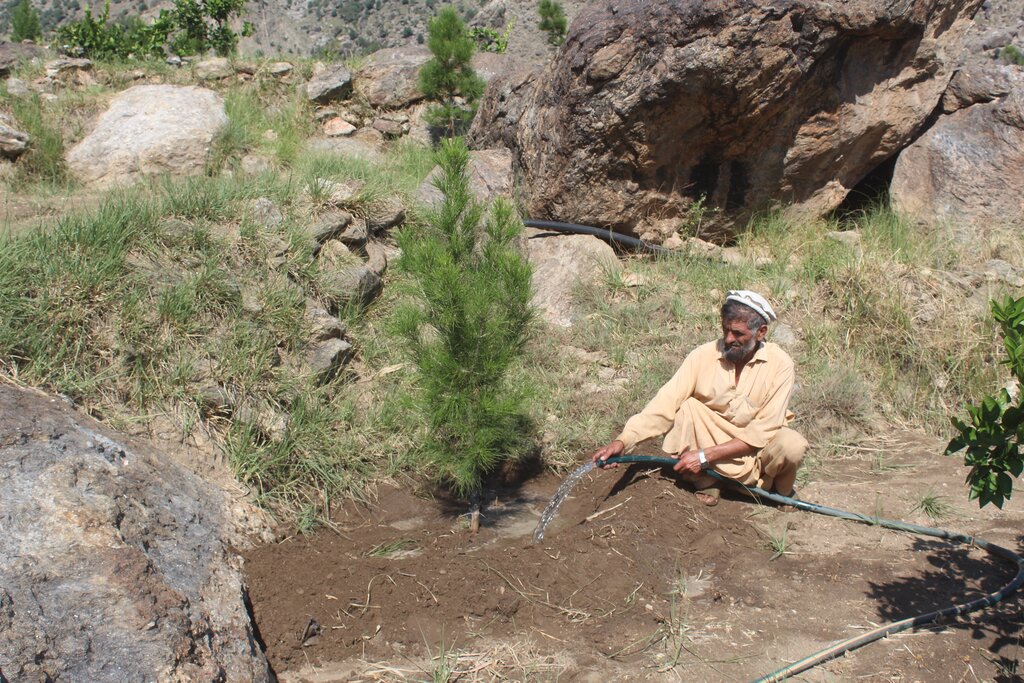
Water exploitation is a critical issue in Afghanistan, and the project aims to address this challenge through innovative and sustainable technology. The technology involves the use of solar panels and submersible water pumps to efficiently lift water from a nearby river to reservoirs constructed uphill, which is then distributed by gravity with the help of a pipe system to irrigate planted saplings in the afforested and agroforestry area. For afforestation, Pinus eldarica (Afghan pine) was planted due to its adaptability and soil stabilization properties. Additionally, citrus and persimmon trees are introduced for agroforestry, combining tree cultivation with agricultural benefits. This integrated technology promotes biodiversity, soil health, and sustainable land use, making the site a model/ demonstration site for afforestation and agroforestry practices. This is a significant advancement in the local area, utilizing clean energy to promote sustainable land and forest management and environmental restoration. The project is implemented on communal land, covering 50.25 hectares of land.
The primary purpose of this technology is to create an efficient irrigation system that extracts and transports water to support afforestation and agroforestry activities. By doing so, it aims to restore forest cover, mitigate environmental challenges such as land degradation, and promote long-term ecological and socio-economic sustainability. The technology includes key components such as solar panels, water pumps (submersible), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, water reservoirs, and saplings. Additionally, it requires labor, technical assistance, capacity-building programs, and construction materials for its establishment and maintenance.
The benefits of this technology are substantial. It has successfully irrigated previously barren land, achieving an impressive 85% survival rate for the saplings that were planted in the plot, while preventing land degradation and improving soil health. Without this technology, survival rates would drop to zero due to the arid conditions. Furthermore, the project has enhanced the capacities of local farmers/community members, enabling them to replicate and demonstrate the technology within their community. This has fostered a sense of ownership and empowerment among land users.
Land users have expressed both appreciation and concerns regarding the technology. On the positive side, they value its efficiency and reliability, as the solar panels provide a consistent water supply, especially during the hot/sunny season, leading to increased greenery and healthier trees. The cost-effectiveness of solar energy, with its low operational costs compared to traditional diesel pumps, has also been a significant advantage. Additionally, the environmentally friendly nature of the technology aligns with their desire for sustainable practices. The capacity-building programs provided by organizations like FAO have further empowered users to manage the system effectively.
However, some challenges have been noted. The initial investment costs for purchasing, installing and construction of the technology are high, making it difficult for smallholder farmers to replicate. Technical issues, such as inverter failures or battery malfunctions during extreme weather conditions (e.g., cloudy weather), can disrupt operations. Additionally, not all community members are equally informed about the technology’s benefits, highlighting the need for increased outreach and engagement efforts to ensure broader adoption and understanding.
In summary, this solar-powered irrigation technology represents a groundbreaking innovation in the area, combining clean energy with sustainable land management practices. While it has demonstrated significant environmental and agricultural benefits, addressing the challenges of initial costs, technical reliability, and community engagement will be crucial for its long-term success and scalability.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
位置:
N/A
摄影师的名字:
N/A
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Kunar
有关地点的进一步说明:
Managi village of Manogi district
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
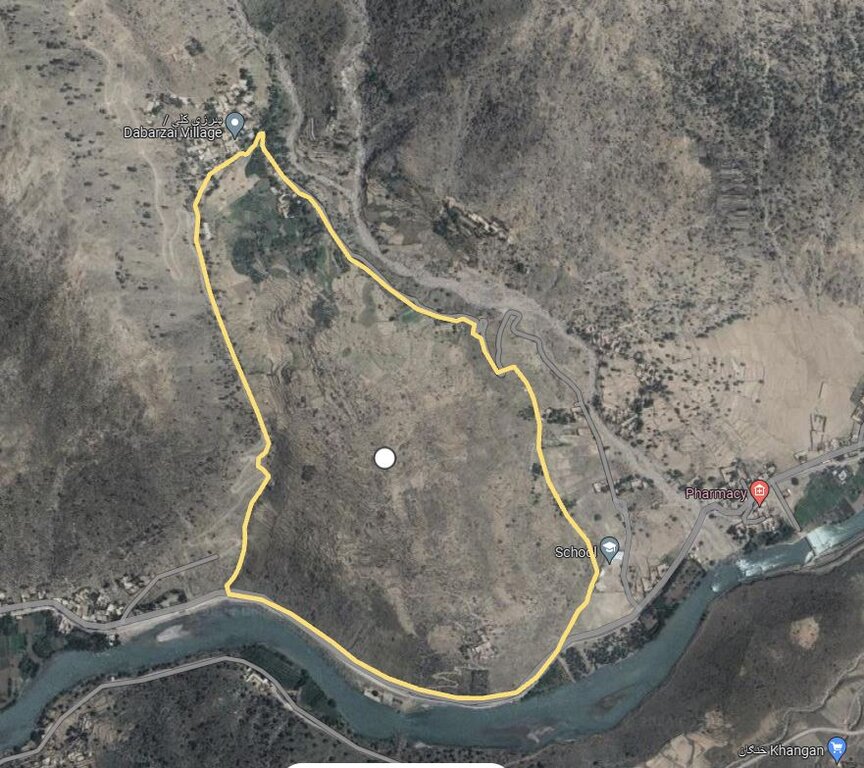
The area is about 50.25 ha, and the coordinate has been taken from the center of the site, where technology has been implemented:
34.9419930°N71.0119714°E
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
GEF-06 Community based Sustainable Land and Forest Management in Afghanistan
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 柑橘属
- Persimmon
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 单一栽培的本地品种
植树造林类型:
- 亚热带干林人工林 - 松树属
树木类型:
- 松属物种(松)
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

不毛之地
具体说明:
5 decades ago, the area was a forest area, but due to war, smuggling and drought the area become barren land.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
The saplings planted in the area have been supplementary irrigated. Prior to the implementation of this technology, the land was barren, and seasonal rains led to soil erosion.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 森林种植管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 节能技术
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
- S10:节能措施

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
注释:
The project has successfully implemented afforestation by planting trees and promoting agroforestry through the cultivation of fruit trees. To improve irrigation management, the project installed a 1-inch underground pipeline system with connected taps, enabling the attachment of flexible hoses. This efficient setup ensures optimal watering of saplings while significantly reducing water waste. By implementing this approach, the project has enhanced vegetative cover and successfully planted approximately 32,000 saplings. Additionally, the project constructed 14 rotating mounting structures for solar panels, installed 134 solar panels, established pipe schemes for manual irrigation of saplings, and constructed 6 water reservoirs with different capacities. The integration of trees at optimal spacing, combined with regular cultural practices, has further supported the project's goals.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
The planting pits are specially designed for planting of saplings. Additionally, farmers construct small barriers near plants (eye-brows and trenches), known as micro-catchments, to collect and retain water. It is important to note that these micro-catchments are distinct structures, separate from pits and reservoirs, and are specifically built to support water retention for plants. The enhanced vegetation cover and the establishment of micro-catchments for water collection significantly reduce soil erosion. Soil improvement and enrichment, as well as habitat enhancement, are supported through these practices. Additionally, they contribute to groundwater recharge and help control runoff.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
The human-induced causes of land degradation include deforestation, overgrazing of livestock, and unsustainable agricultural practices. In response, following the implementation of a specific technology, local communities established regulations rooted in their customs and traditions to protect the site, which is quarantined for five years. These regulations prohibit herders from grazing animals, cutting trees, engaging in unsustainable agricultural practices, and uprooting bushes for fuelwood. Additionally, the community has constructed rainwater harvesting structures, such as eyebrows and trenches, across the site to address natural causes of land degradation through runoff by enhancing water infiltration. As a result, the site is now effectively protected from both human-induced and natural land degradation.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
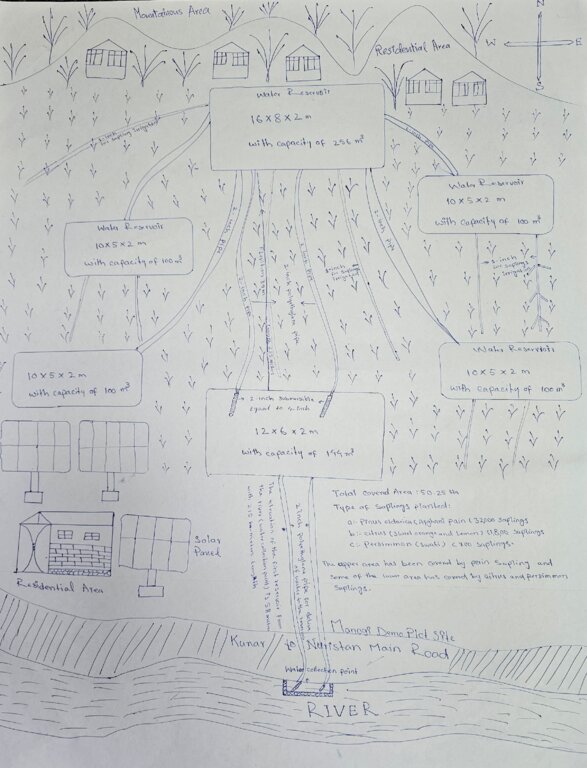
According to the technical specifications from the project engineer, 6 reservoirs have been constructed with varying dimensions and water holding capacities as follows:
1.First reservoir: Dimension of 12x6x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 144 m³.
2.Central reservoir: Dimensions of 16x8x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 256 m³.
3.Four additional reservoirs: Each measuring 10x5x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 100 m³
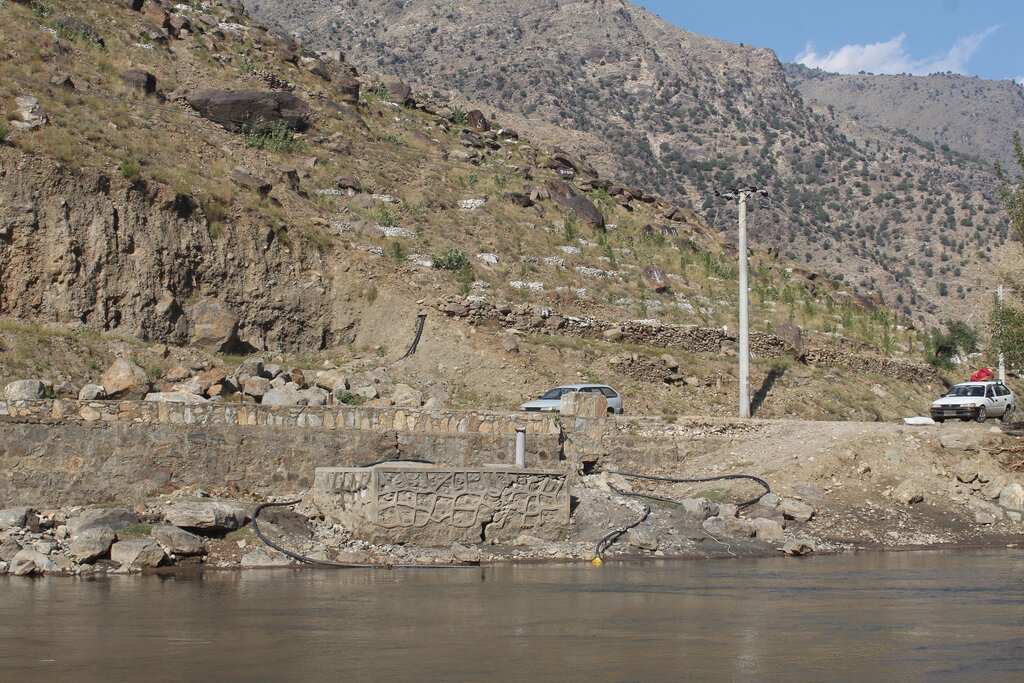
In total, the reservoirs will hold 800 m³ of water, ensuring a reliable water supply for irrigation of the area. Two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs by gravity.
Furthermore, excavation and backfilling for 2-inch polyethylene pipes should be done to a depth of 80 cm with a width of 50 cm. For 1.5-inch pipes, excavation and backfilling should be 40 cm deep. The installation of 1.5-inch polyethylene pipes, including all elbows, joints, connectors, and valves, should be carried out every 30 meters on both sides, connecting to 1-inch pipes, in accordance with specifications and to satisfaction.
Additionally, 32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghan Pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings were planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. The saplings are spaced 5 meters apart, both plant-to-plant and row-to-row, as part of afforestation and agroforestry initiatives. This effort aims to restore ecosystems, enhance biodiversity, and improve soil conservation.
作者:
Hafizullah Naeemy
日期:
01/03/2022
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
50.25 Hectares
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5 USD
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Awareness and mobilization of the community | Aug-2021 |
| 2. | Survey and site selection followed by feasibility study | Sep to Oct-2021 |
| 3. | Stakeholder consultation | Aug-2021 till Sep-2022 |
| 4. | Preparation of technical design, drawings, and Bill of Quantities (BoQ). | Nov to Dec-2021 |
| 5. | Initiation of procurement process for required tools and equipment | Jan to Feb-2022 |
| 6. | Excavation and construction of water reservoirs, setting up pipe system and installation of solar panels for irrigation. | Mar to Sep-2022 |
| 7. | Capacity building of the target communities | Aug- 2021 till date |
| 8. | Practical interventions: production or purchase of saplings, digging planting pits, transplatation and irrigation of saplings and establishment of micro-catchments | Feb to Mar-2023 |
注释:
The awareness-raising session on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) was successfully held to improve understanding of land and forest management practices and conservation efforts. Community members were actively mobilized to support the project, aiding in the completion of construction and installation work.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Unskilled labor for planting of saplings | Man/day | 450.0 | 5.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Skilled labor for installation of irrigation system and constuction of reservoirs | Man/day | 50.0 | 10.0 | 500.0 | |
| 设备 | Water Pump 2 inch - 10HP/7500w | Number | 4.0 | 450.0 | 1800.0 | |
| 设备 | Solar Panel minimum size 400W and 270W | Number | 132.0 | 82.0 | 10824.0 | |
| 设备 | DC to AC Inverter 7.5-11KW | Number | 4.0 | 450.0 | 1800.0 | |
| 设备 | Polyethylene Pipes 2 Inch and 1.5 Inch with all elbows, joints, connectors and valves after 30 meter for both sides to connect pipes. | Meter | 4300.0 | 2.75 | 11825.0 | |
| 设备 | Rotating PV panels mounting structure (manual) | Number | 28.0 | 270.0 | 7560.0 | |
| 设备 | DC and AC current wire | Meter | 1800.0 | 2.5 | 4500.0 | |
| 设备 | Distribution board | Number | 2.0 | 70.0 | 140.0 | |
| 设备 | Flexon 1 inch rubberize pipes | Meter | 5500.0 | 1.4 | 7700.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Saplings procured & transported | Sapling | 32000.0 | 0.775 | 24800.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Planting tools | lump sum | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic fertilizers for transplanted saplings added through community | Kg | 16000.0 | 0.1 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | 6 reservoirs constructed by a construction company (cement, stone, sand excavation, etc.. | lump sum | 1.0 | 35000.0 | 35000.0 | |
| 其它 | Patrolling, irrigating and quarantine of the site | lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 111799.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 111799.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The remining cost were covered by the project.
注释:
The first two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs through gravity.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Patrolling | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump (submersible) | Ad hoc /Annually |
| 4. | Plot maintenance (Pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding,). | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacement of failed saplings | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing micro-catchments | Spring/annually |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labor for cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Man/day | 60.0 | 5.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Labor for patrolling | Man/day | 360.0 | 5.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Labor for repairing micro-catchments | Man/day | 20.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Manage the solar system operations | Man/day | 360.0 | 2.77 | 997.2 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Labor for weeding and mulching | Man/day | 30.0 | 5.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pump submersible, PVC pipe, fittings | lumpsum | 3.0 | 500.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Shovels | lumpsum | 1.0 | 140.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | saplings | Sapling | 2000.0 | 0.6 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic fertilizers (cows dungs) | Kg | 16000.0 | 0.1 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 7787.2 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 7787.2 | |||||
注释:
The community has hired an individual to manage the solar system operations. This person is responsible for both operating the solar system for lifting water and overseeing the distribution of water for irrigation purposes among community members.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
All equipment are imported and has resulted into higher cost.
Natural hazards, floods and windstorms will increase the costs of repairs and replacement
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
300.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Most of rain occur in the months of Feb, Mar, Apr, July and Aug.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
The data has been collected based on the farmers observation and local practices.
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
The area where the technology is applied covers 50.25 hectares and is managed by 112 land users.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
In Afghanistan, the traditional land use system involves the equitable distribution of deserts and barren land among the local residents. The decisions made by the elders are respected and adhered to by all members of the community.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
fruit production (citrus and persimmon)
注释/具体说明:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as part of the agroforestry system and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people. Based on the production, the socio-economic status of the community members is expected to improve.
木材生产
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
A total of 32,000 forest saplings (Pinus species) were successfully planted
注释/具体说明:
32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghani pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. Following agronomic practices, the four Ds—dead, diseased, damaged, and dying—branches will be pruned and utilized for shelter and fuel.
生产区域
SLM之前的数量:
0 fruit trees
SLM之后的数量:
Approximately 1,200 fruit trees, including sweet orange and persimmon species, have been planted
注释/具体说明:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as a agroforestry and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
The area was once barren and occasionally used for rainfed cultivation, where most farmers grew wheat. Now, with the introduction and implementation of the technology farmers can also intercrop beans, mung beans, and others. Farmers who have more than 1 hectare of land hire labor for agronomical practices.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
With the adoption of this technology, irrigation for planted saplings is now available 100% throughout all seasons of the year.
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Timber Production, Non-Timber Forest Products, Ecotourism, Agroforestry, Wildlife Conservation and Fuelwood and Biomass
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Recreational opportunities that benefit both local communities and visitors such as nature trails allowed individuals to engage with nature, promoting physical activity and wellness. The reforestation efforts have led to the restoration of habitats for various wildlife species, this provides opportunities for wildlife observation and photography, and contributing to local ecotourism.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Improved due to workshops and on job trainings
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Due to better soil coverage by plantation of saplings and micro-catchment structures
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Due to the availability of irrigation water and the establishment of micro-catchments to harvest water and enhance water infiltaration soil moisture for sapling growth has increased
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Due to natural regeneration and plantation of saplings and intercrops
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Due to better soil coverage and less water runoff
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
better soil cover reduced water runoff and ultimately flooding
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Soil erosion was reduced and has been better controlled
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Due to plantation
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季雨量 | 春季 | 增加 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
The community economic condition is not good. So, without receiving incentives they are not able to adopt such technology easily.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improved water availability with minimized fuel cost and decreased pollution as well as minimum operational cost |
| Opportunities/ potential for upscaling of the technology |
| Use of clean energy to contribute to mitigate climate change |
| Reduce greenhouse emission through carbon sequestration |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is highly efficient and suitable for adoption by land users. It promotes clean energy, reduces greenhouse gas emissions through carbon sequestration, and contributes to climate change adaptation. |
| The area has been successfully afforested, restoring its natural beauty and original landscape. |
| The vegetation cover on the previously degraded land has been significantly enhanced. |
| This technology with its approach for implementation represents an effective solution for the restoration of degraded soils. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Inadequate maintenance and repair services of the technology | Linkage to the service provider and maintenance services. Nation wide technology transfer |
| Solar water lifting relies on fully sunny days for operation, which can sometimes be a limitation, especially when weather conditions are cloudy or during periods of low sunlight. This can result in insufficient water being lifted to meet the irrigation needs of the site. | Backup charging system/battery system |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Solar water lifting depends on sunny days for operation, which can sometimes fall short of meeting irrigation needs during cloudy periods. | Combining solar power with backup energy (like batteries or grid connection) |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
10
- 与土地使用者的访谈
15
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
2
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/11/2024
注释:
The data has been collected during Oct and Nov 2024
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块