Vetiver grass soil conservation system [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli
Vetiver system
technologies_938 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Stranic Rowan
South African Sugar Association
南非
SLM专业人员:
Grimshaw Dick
The Vetiver Network
美国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
The Vetiver Network International (TVNI) - 美国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
South African Sugar Association (SASA) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
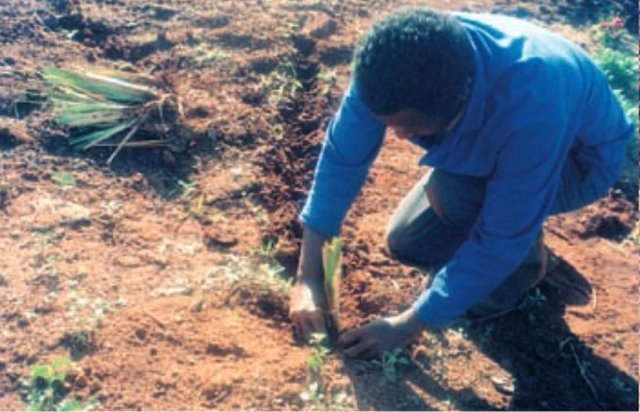

Self teaching [南非]
Learning how to use vetiver grass as a vegetative conservation barrier through instructions from a booklet and hands-on practical experience.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
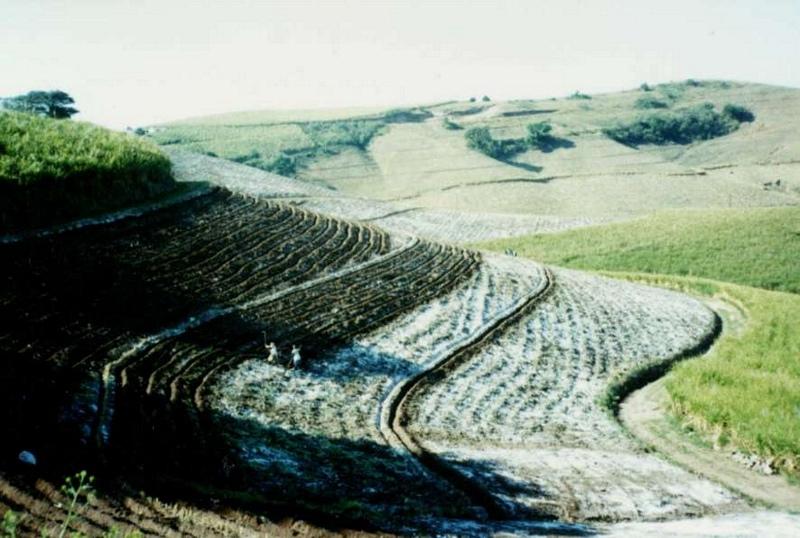
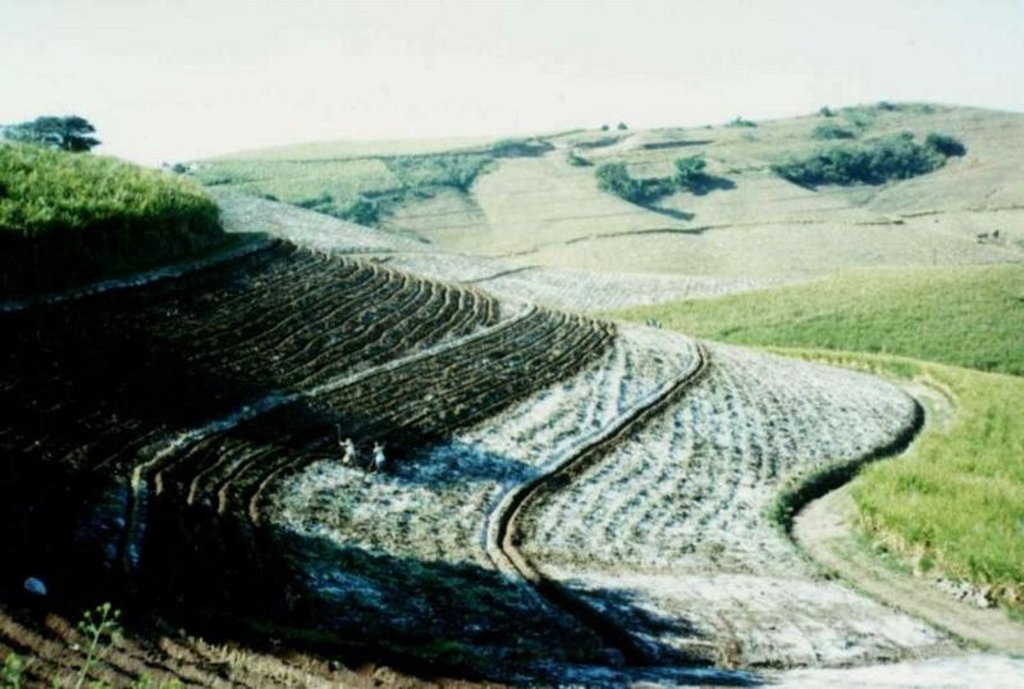
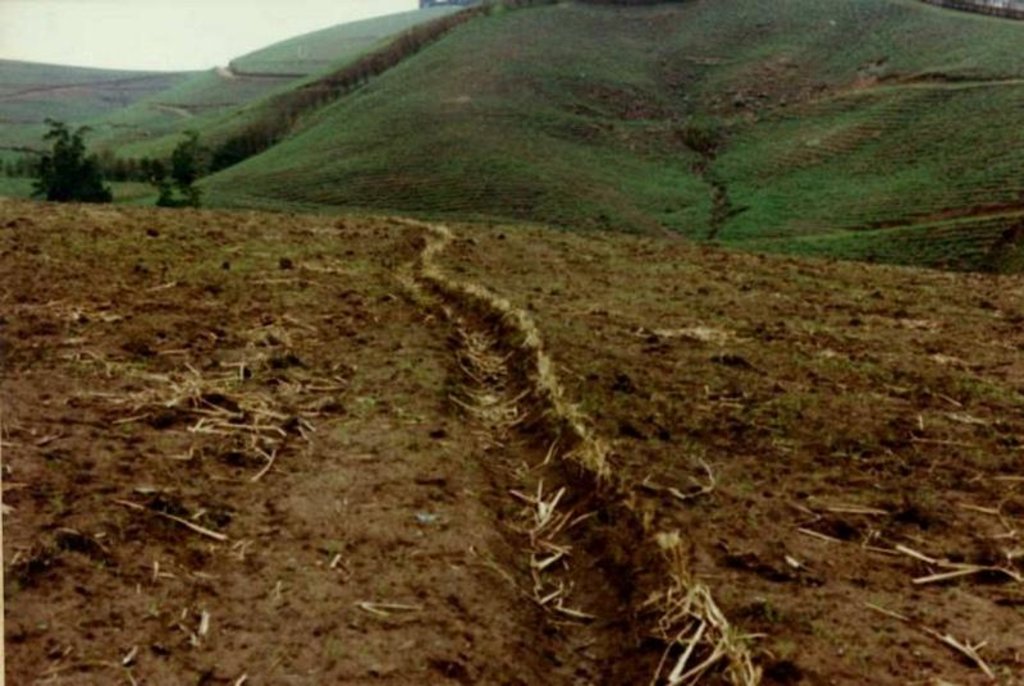
Contour lines of vetiver grass planted within fields of sugar cane, on stream banks and roadsides, to act as ‘hedges against erosion’.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
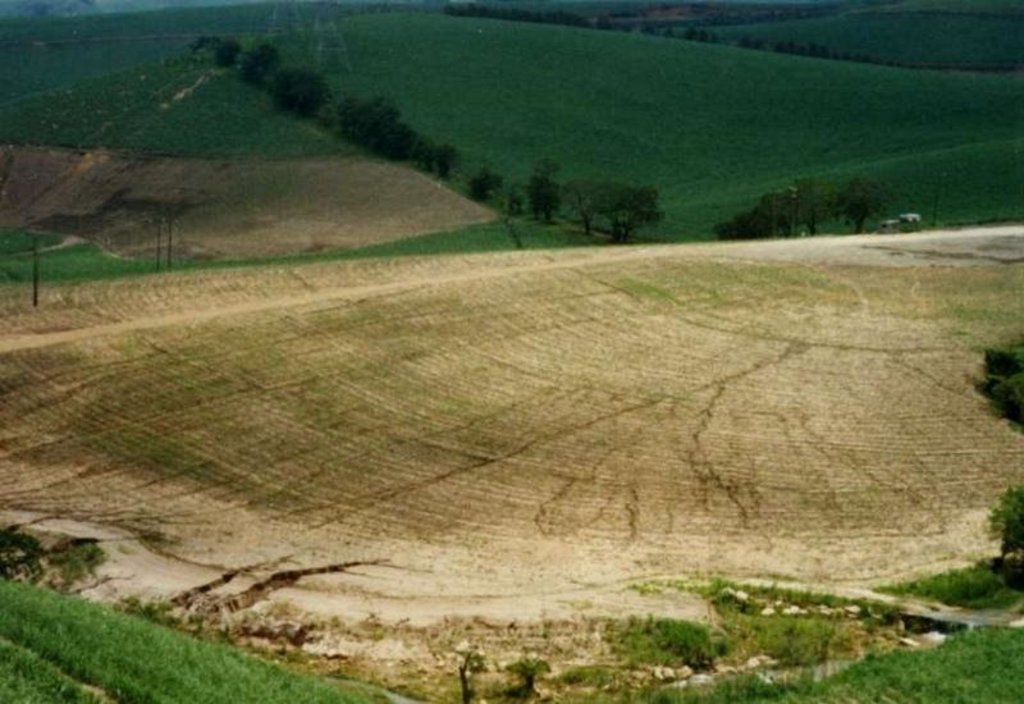
This example of vetiver grass barriers comes from a commercial farm in Kwa-Zulu Natal, South Africa, where sugar cane is grown on a large scale under a rainfall regime of around 1,000 mm per year. Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides), which had been growing naturally on the farm for years in isolated clumps, began to be used in 1989 to form vegetative hedges along the contour.
The purpose of these hedges is to protect the land from surface erosion by creating semi-permeable barriers, allowing excess runoff to filter through but holding back sediment. Infiltration is thus increased and moisture conserved in-situ. Although sugar cane in itself protects the soil quite well when the canopy is closed, after harvest on the moderate to steep slopes (10% to >30%) and erodible soils of the north coast of Kwa-Zulu Natal, extra protection is required. The vetiver system is supplemented by other soil conservation measures such as strip cropping, terraces, mulching and minimum tillage – all of which are used to some extent on this farm. Vetiver also helps by permanently marking the contour line, which then guides land preparation. In common with other vegetative barriers, vetiver lines lead to the formation of terraces over time, through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips.
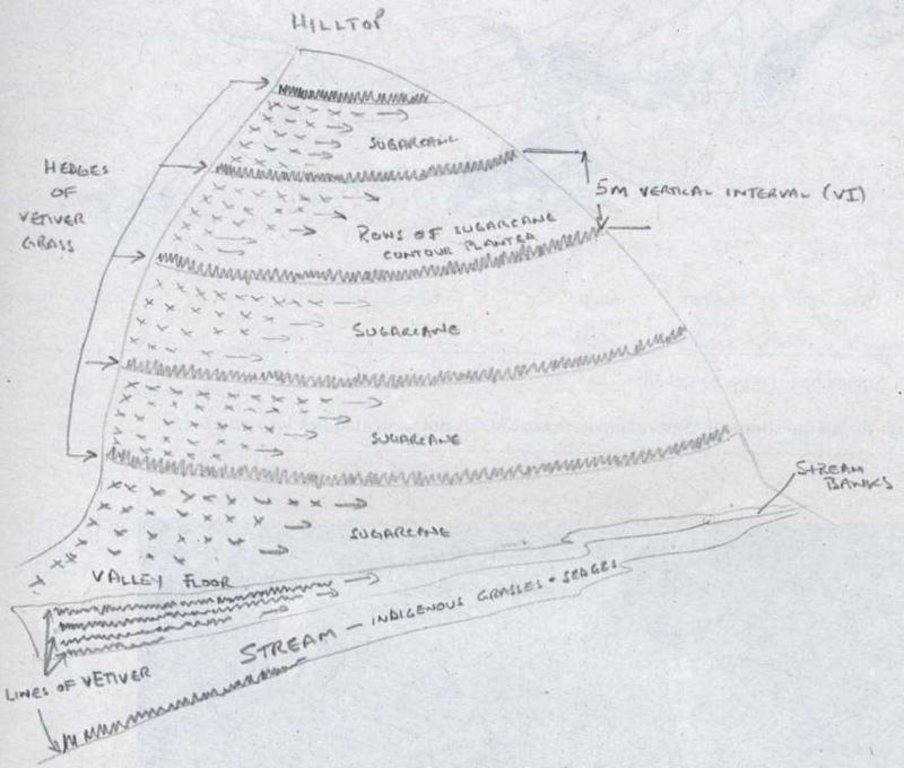
Vetiver clumps are dug up and separated into slips (tillers), cut to a length of 10 cm and then planted 10–15 cm apart along the contour, also by stream banks, and by roadsides, just before the rains. This ensures good establishment. Single lines are used in this farm, though double lines are more effective at creating a hedge, and are the normal recommendation. Work starts at the top of the slope, and continues downwards. The cross-slope grass hedges are sited at 5 m vertical intervals on slopes of more than 10%, in lines about 200 m long. The cost of vetiver grass planting depends very much on slope (and thus the number of lines to be planted), availability of materials and labour.
Maintenance is very important, as vetiver often requires ‘gapping-up’ to keep the barrier dense, and it needs also to be cut back before the dry season to prevent it burning. The cut material can be used for mulching. Vetiver is poorly palatable, and therefore not useful as fodder. The maximum height of a vetiver hedge is kept down to approximately 50 cm. This minimises shading and competition, keeps the fire risk low, increases tillering (for production of vegetative splits) and ensures adequate density.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
KwaZulu/Natal
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lower Tugela district
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
8.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 8 km2.
The vetiver system has been applied on my own properties. Neighbouring farms have adopted other methods of conserving the soil. i.e. vegetative, agronomic and structural in various combinations (= farm)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The grass originally came to this country from Mauritius.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 甘蔗
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 200; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - April
注释:
Major cash crop: sugar cane
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The steep topography and shallow soils limit the types of land use possible e.g.. perennial grass cover (sugarcane or grazing) or commercial timber production. Annual cropping is not possible without major alteration to the landscape e.g. terracing.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V5:其它
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, structural measures, management measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: grass strip as hedges
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, minimum tillage, contour ridging
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Vetiver grass is planted as a vegetative barrier (hedge), on the contour at 5 metre vertical intervals within fields of sugarcane.
Location: Lower Tugela district. KwaZulu/Natal
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: Sugarcane
Remarks: Full ground cover
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Chemical crop eradication
Contour ridging
Material/ species: Planting lines ridged on contour
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Vetiver grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Other type of management: Cane is planted on suitability (slope, soil depth)
作者:
Marie Joseph Maxime Robert
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant with fertilizer & water | Rainy season (Sept - Mrch) |
| 2. | Weed & gap plant | |
| 3. | Cut back to promote tillering | |
| 4. | Crop gradication | Nov-Jan |
| 5. | Ridging of planting furrows | +- 1-2 months before |
| 6. | Planting of sugarcane - fertiliser in furrow | |
| 7. | Top dress fertiliser | 9 week after planting |
| 8. | Herbicide application | Anytime necessary after planting |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Plant and fertilize | persons/day/ha | 15.0 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | hoe | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Vetiver | cubic meter | 1.0 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 140.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 140.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | minimum tillage | mulching at harvest |
| 2. | minimum tillage | |
| 3. | mulching at harvest | April-Dec / Every year |
| 4. | Weed | /3 times |
| 5. | Gap plant | /Once |
| 6. | Weed | /When required |
| 7. | Spray for creeper grasses | /When required |
| 8. | Plaint unwanted trees etc. | /When required |
| 9. | Harvest sugarcane | / Annual |
| 10. | Trash management (mulch spreading) | After harvest completed / Annual |
| 11. | Fertiliser application | 1-2 months after harvest / Annual |
| 12. | Herbicide application | Required / Annual |
| 13. | Hand weeding | / Annual & when required |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintaining plot | persons/day/ha | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | hoe | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Slips | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 25.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 25.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: 1 hoe
1) Labour,
2) Transport,
3) Price of grass,
4) Fertiliser,
5) Equipment
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1) Labour,
2) Transport from nursery to field,
3) The steeper the gradient the more contour lines of vetiver grass will be used,
4) Fertiliser
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Not usually less than 900 and not usually more than 1200
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Also moderate, mostly in footslopes & valleys (steep sides)
Landforms: Also ridges
Altitudinal zone: 360 - 380 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Als very shallow. But mostly moderately deep
Soil texture: Mostly medium
Soil fertility is medium
Topsoil organic matter: Mostly medium and high in very small areas
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Market orientation of production system: All commercial
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for fertilising, weeding, planting, harvesting and mechanised for crop extraction
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Per farm where SWC technology is used
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Contains a lot of oil, only when mature (after 2 years) but does not affect the roots
风速
注释/具体说明:
Row spacing
其它生态影响
demarcates the contour
注释/具体说明:
The planting is aligned for next planting
longer last of crop (sugarcane)
注释/具体说明:
From 8-12 cuttings before replanting sugarcane (+-15 years); 3000-3500 R/ha cost for replanting the sugarcane.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
风力搬运沉积物
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
3 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some local growers are experimenting with the vetiver system or with vetiver grass used in other applications (gullies, road embankments, etc.)
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The author is the land user |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
When planted correctly, vetiver forms a dense, permanent hedge which retains soil and water so increases crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make sure there are no gaps between slips in order to maintain a dense vegetative barrier. |
|
It has a strong fibrous root system that penetrates and binds the soil to a depth of up to 3 meters and can withstand the effects of tunnelling and cracking. Its many uses e.g.. Thatching, mulching etc. |
| Vetiver grass seed is sterile so it doesn’t spread. |
| Not very competitive to crops growing alongside. |
|
The cut material can be used for mulching and has multiple secondary uses (thatching, basket making, etc). Once established it can withstand periods of drought and waterlogging. It is also resistant to grazing and to most pests and diseases. Adaptability: can be planted in various environments and grows well in most soil types. Depending on the availability of planting materials and the spacing adopted, can be relatively cheap and easy to establish and – once well established – vetiver requires minimal maintenance. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The author is the land user |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Sugarcane residue is often blown against the hedges & this can form a thick blanket thus preventing ratooning of crop | Strategic/controlled burning at end of growing season or trimming back |
| The grass burns very easily when mature, due to its density | Keep chemicals off vetiver. |
| Susceptible to certain chemicals used in sugar cane | Establish own nursery. |
| Planting material expensive to buy: therefore costs increase considerably unless farmer has own nursery | |
| Takes time to plant a large area (in this case 2.5 ha per year). |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Self teaching [南非]
Learning how to use vetiver grass as a vegetative conservation barrier through instructions from a booklet and hands-on practical experience.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
模块
无模块