Пчеловодство в горных регионах [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: German Kust
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Beekeeping in uplands (English)
technologies_1040 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Community Agriculture and Watershed Management project in Tajikistan (WB / CAWMP)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
22/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Contributing to biodiversity conservation and land rehabilitation in uplands through beekeeping. (Содействие сохранению биологического разнообразия и восстановлению земель горных территорий с помощью пчеловодства)
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
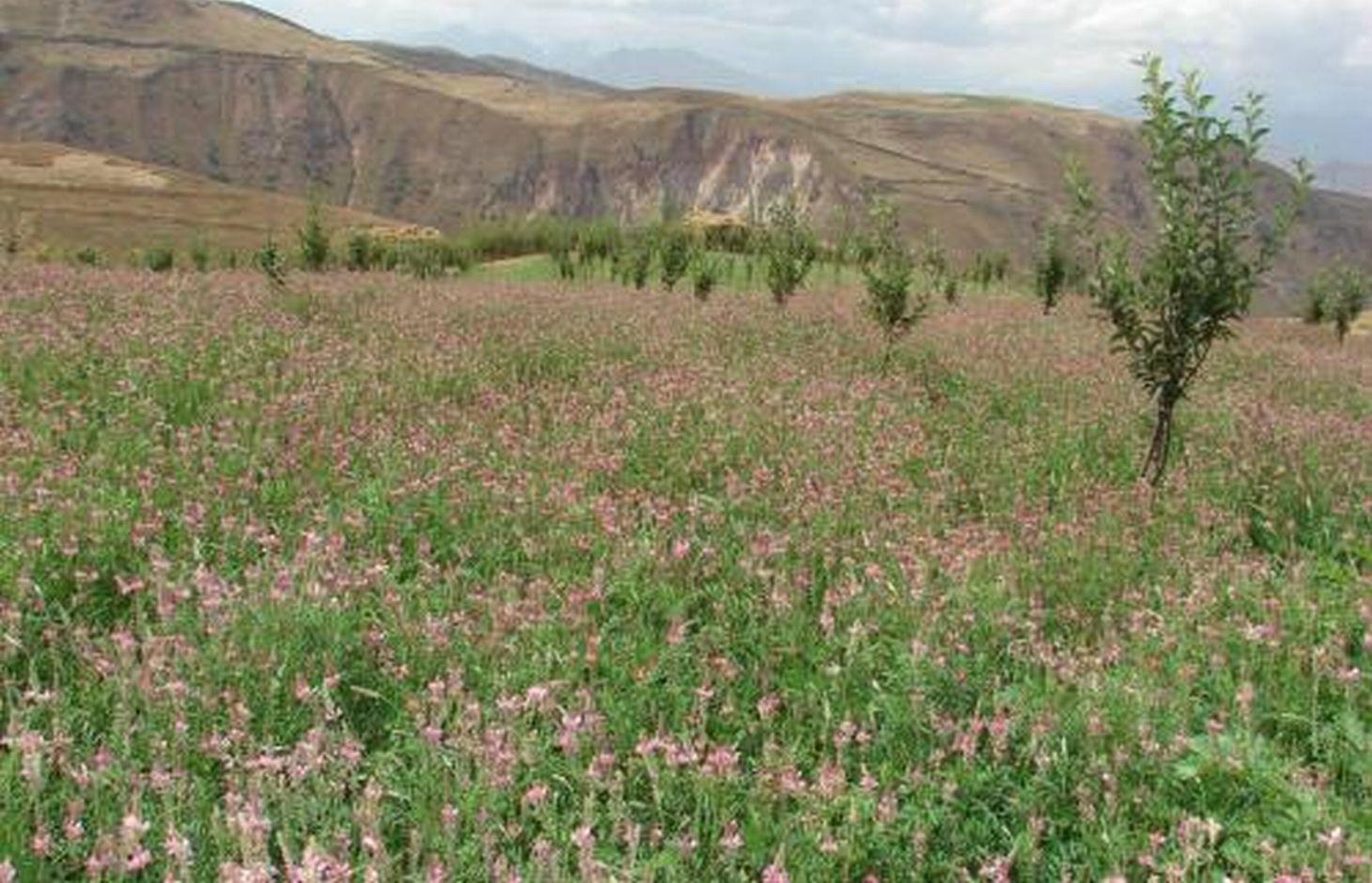
В целом технологические задачи решаются косвенно двумя основными путями: (1) перенос пыльцы растений на дальние расстояния пчелами в процессе передвижения ульев по медоносным участкам в высокогорьях и расширение этих участков; (2) создание посевов медоносных трав (преимущественно эспарцет и люцерна) на деградированных пастбищах и богарных землях, а такжи в междурядьях садов, что способствует улучшению почвенной структуры, накоплению органического углерода и увеличивает урожайность высококалорийных кормов для животных, тем самым косвенно также снижая нагрузку на ближние (зимние) пастбища
Purpose of the Technology: Более полное использование природных ресурсов. Косвенное содействие сохранению биоразнообразия и восстановлению деградированных земель. Повышение уровня жизни местного населения
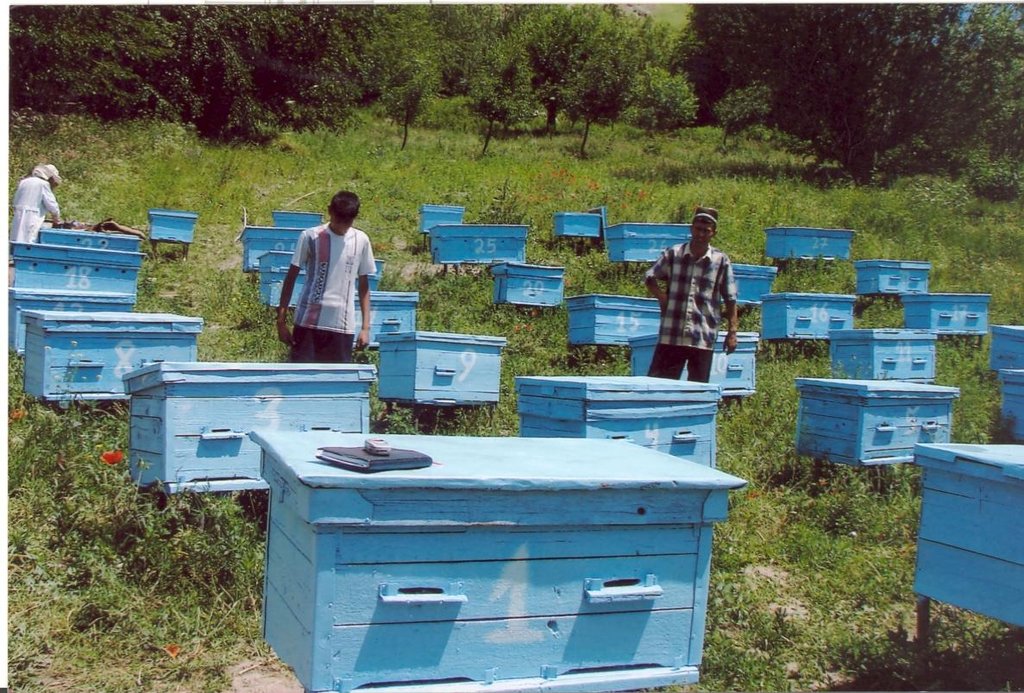
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: закупка ульев, пчелосемей и специального оборудования (рамок, сепараторов, и пр)
Natural / human environment: В природном отношении подходят любые регионы Таджикистана. Для использования технологии требуются специальные знания, которые можно получить в местных ассоциациях пчеловодов, созданных во всех регионах
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Зарафшан, Сурхоб, Ванж и водораздел Тоирсу
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
Comments (type of project, etc.):
2006
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agro-pastoralism
- Agro-silvopastoralism
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): бедный состав растительности, недостаток воды для орошения в некоторых регионах
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): эрозия почв, незначительный растительный покров, недостаток воды для орошения
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Other grazingland: агро-лесо-скотоводство
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Water supply: богарное, смешанное богарно-орошаемое
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- beekeeping, aquaculture, poultry, rabbit farming, silkworm farming, etc.
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- > 10,000 km2
Comments:
Технология была реализована в рамках 156 подпроектов (малые гранты) проекта CAWMP (проект Мирового Банка в 4 водоразделах)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants

structural measures
- S11: Others

management measures
- M5: Control/ change of species composition
Comments:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: более лучшее покрытие культур, смешанное возделывание / междурядное возделывание, посадка бобовых в междурядьях
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bh: loss of habitats
- Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Бр (Bc): уменьшение растительного покрова, Бо (Bh): потеря среды обитания, Бв (Bs): качественный и видовой состав /снижение разнообразия
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Вв (Wt): потеря верхнего слоя почвы / поверхностная эрозия
Main causes of degradation: чрезмерный выпас
Secondary causes of degradation: управление землеи, управление с/х культурами (однолетние, многолетние, деревья/кустарники), обезлесивание / удаление естественной растительности (включая лесные пожары), нарушение водного цикла (инфильтрация / поверхностные стоки), засуха, бедность / богатство, образование, доступ к знаниям и поддерживающие услуги, война и конфликты
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: средний
Technical knowledge required for land users: средний
Secondary technical functions: улучшение структуры верхнего слоя почвы (прессование), стабилизация почвы (например, с помощью корней деревьев против оползней), повышение органического вещества, повышение наличия питательных веществ (снабжение, переработка отходов,...), повышение инфильтрации, повышение биомассы (количество), содействие росту видов и сортов растительности (качество, например поедаемые кормовые культуры), пространственное урегулирование и разнообразие использования земель
Change of land use practices / intensity level: дополнительное использование растительности в качестве медоносов
Control / change of species composition: контроль состояния медоносных видов в естественной среде обитания (на горных лугах) и сеяных участках бобовых культур
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
other/ national currency (specify):
сомони
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | закупка ульев и пчелосемей | Structural | |
| 2. | работа по подготовке пасек и ульев | Structural | |
| 3. | работа по перемещению пасек | Structural | |
| 4. | закупка оборудования по уходу за пчелами | Structural | |
| 5. | обучение пчеловодству | Management | |
| 6. | организация закупок материалов, оборудования и инструментов | Management | |
| 7. | организация транспортировки пасек в течение сезона | Management | |
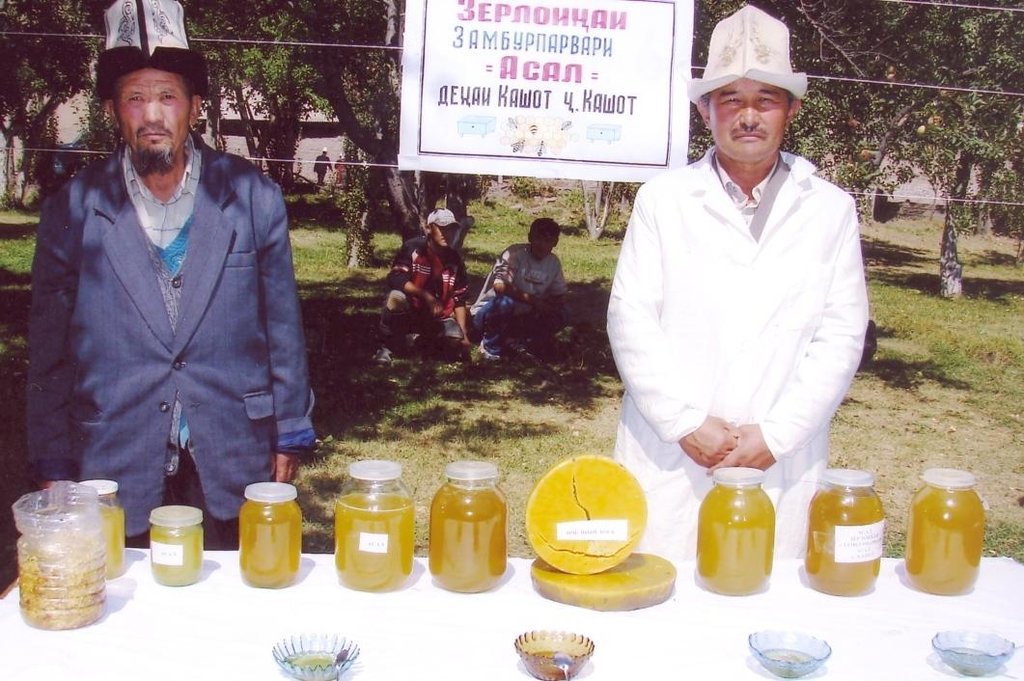
| 8. | сбор меда | Management | |
| 9. | продажа продуктов пчеловодства и распределение доходов | Management |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | |
| Equipment | None | None | 10.0 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 65.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ремонт ульев | Structural | |
| 2. | содержание пчел | Structural | |
| 3. | транспортировка пасек в течение сезона | Structural |
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Продолжительность вегетационного и медоносного сезона, суровость холодного периода (вымирание пчел), болезни и вредители, способ транспортировки пасек, количество мест локализации пасек в вегетационный период, дальность и условия транспортировки, наличие и доступность рынков сбыта продукции, и др
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
- semi-arid
- arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder quality
product diversity
production area
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
health situation
community institutions
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
nutrient cycling/ recharge
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
beneficial species
habitat diversity
Climate and disaster risk reduction
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
| local windstorm | not well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
при сохранении высоких рыночных цен на продукцию пчеловодства это будет очень выгодное вложение всегда
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2584 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: приведены данные по результатам проекта CAWMP, хотя точно известно, что данная технология применяется в значительно более широких масштабах, по экспертной оценке - не менее чем в 20-25 раз больше в целом по Таджикистану
Comments on spontaneous adoption: точные данные не известны, но эта технология очень популярна в Таджикистане
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| повышение здоровья |
| стало больше денег |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
сохранение и расширение биоразнообразия в горных регионах How can they be sustained / enhanced? регулярный мониторинг |
|
получение дополнительных кормов How can they be sustained / enhanced? расширение посевов эспарцета и люцерны |
| укрепление здоровья населения |
| увеличение благосостояния населения |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| высокие цены на оборудование для пчеловодства и пчело-семьи | расширение рынка материалов для пчеловодства, создание стимулов кустарного и мелкотоварного производства инструментов и материалов |
| отдаленность медоносных площадей |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| слабая организованность транспортировки пасек | развитие ассоциаций пчеловодов |
| отсутствие инвентаризации медоносных площадей на республиканском/областном уровнях | поддержка государством деятельности ассоциаций пчеловодов по инвентаризации медоносных площадей |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
База данных по общинному сельскому хозяйству и управлению водоразделами (Нарзимурод Холов, Рустам Ракимов)
Available from where? Costs?
Душанбе, пр. Рудаки 44, CAWMP PMU, безплатно
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules