គេហសួន (ក្រូចថ្លុង ក្រូចឆ្មារ និងដំណាំរួមផ្សំផ្សេងៗ) [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Be Gechkim
- Editors: Navin Chea, Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Reviewers: Nicole Harari, Nimul CHUN, Ursula Gaemperli
ដំណាំចម្រុះ
technologies_2099 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
សុភឿន អ៊ុក
(+855) 31 45 444 46 / មិនមាន
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
មិនមាន
ភូមិសំរោង ឃុំសំបូរ ស្រុកសំបូរ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Cambodia
ប្រធានទទួលបន្ទុករួមការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ:
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី:
សារ៉ាវុធ លី
(+855) 89 796 786
saravuthly123@gmail.com
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី
ភូមិខ្សារ ឃុំដារ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
07/04/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
ដោយសារតែការដាំមិនមានប្រើជីគីមី និងទទួលបានទិន្នផលខ្ពស់
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
គេហសួនក្នុងករណីនេះ គឺជាការអនុវត្តការដាំដំណំាដូចជា ក្រូចថ្លុង ក្រូចឆ្មារ និងដំណាំរួមផ្សំផ្សេងៗទៀតនៅជុំវិញផ្ទះ ដោយប្រើលាមកគោ មាន់ និងមិនប្រើប្រាស់ជី ឬថ្នាំពុលគីមី។ គោលបំណងនៃការអនុវត្តនេះ គឺដើម្បីទទួលផលដំណាំចម្រុះជាប្រចាំ បង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលប្រចាំថ្ងៃជាពិសេសពីក្រូចឆ្មារ ព្រោះជាប្រភេទដំណាំមានអាយុកាលវែងអាចប្រមូលផលបានរាល់ថ្ងៃរយៈពេលច្រើនឆ្នាំ និងងាយស្រួលថែទាំ ព្រមទាំងផ្តល់នូវបរិយាកាសល្អសម្រាប់ការរស់នៅ។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
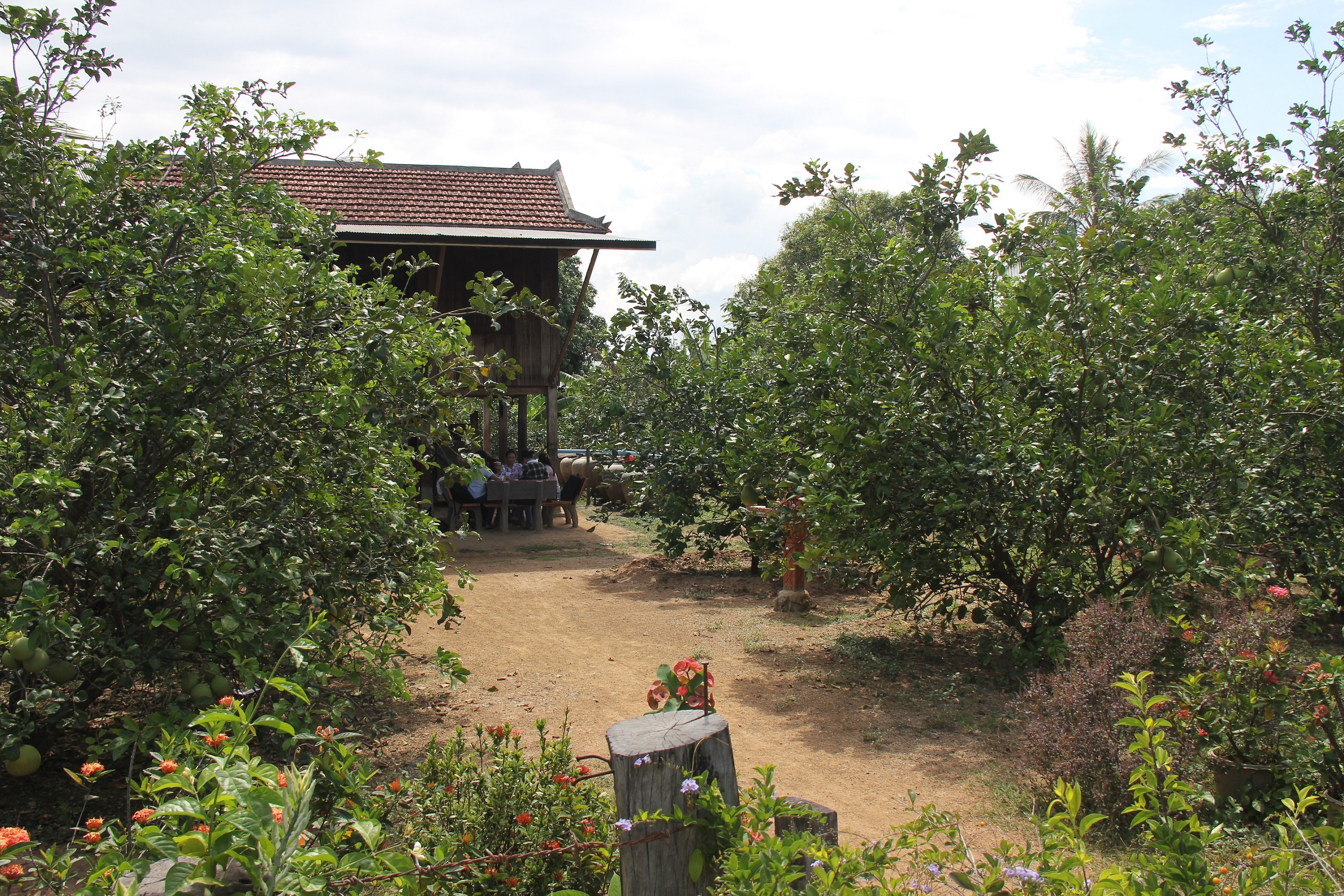
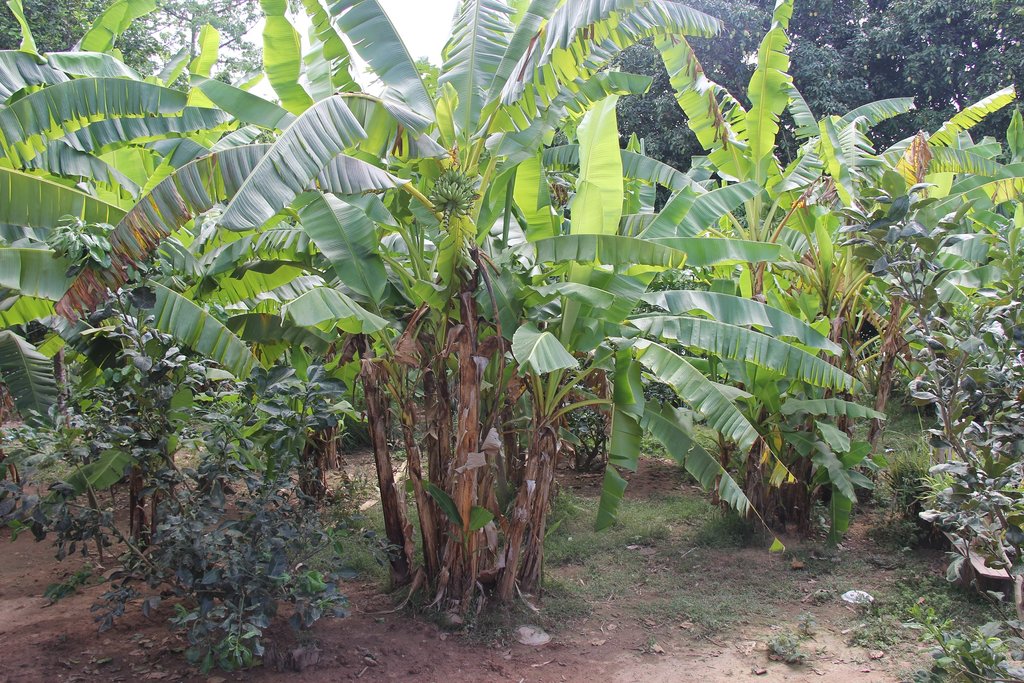
គេហសួន ត្រូវបានគេស្គាល់ថាជាការដាំដំណាំក្នុងបរិវេណផ្ទះដែលមានដំណាំចម្រុះគ្នាដូចជា ដំណាំបន្លែ ពពួកជី ដំណាំហូបផ្លែ និងដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំផ្សេងទៀត សម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងគ្រួសារប្រចាំថ្ងៃ និងសម្រាប់ពាណិជ្ជកម្មជាលក្ខណៈគ្រួសារ។ គេហសួនត្រូវបានអនុវត្តជាច្រើនក្នុងប្រទេសកម្ពុជា និងនៅប្រទេសនានាលើពិភពលោក ហើយអាចត្រូវបានហៅឈ្មោះផ្សេងៗគ្នា (Helen Keller International/Cambodia., 2003)។ បច្ចេកទេសនេះផ្តល់នូវអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ទាំងផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ចគ្រួសារ និងបរិស្ថានដូចជាការកាត់បន្ថយកំដៅក្នុងបរិវេណគេហដ្ឋានរស់នៅ។ ជាពិសេសផ្តល់ឱកាសដល់ស្ត្រី កុមារ មនុស្សចាស់ និងអ្នកបាត់បង់កាយសម្បទាមួយចំនួនក្នុងការអនុវត្តការងារកសិកម្មបានដែលចូលរួមចំណែកបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលក្នុងគ្រួសារ (Landon-Lane C., 2012; Helen Keller International, 2010)។
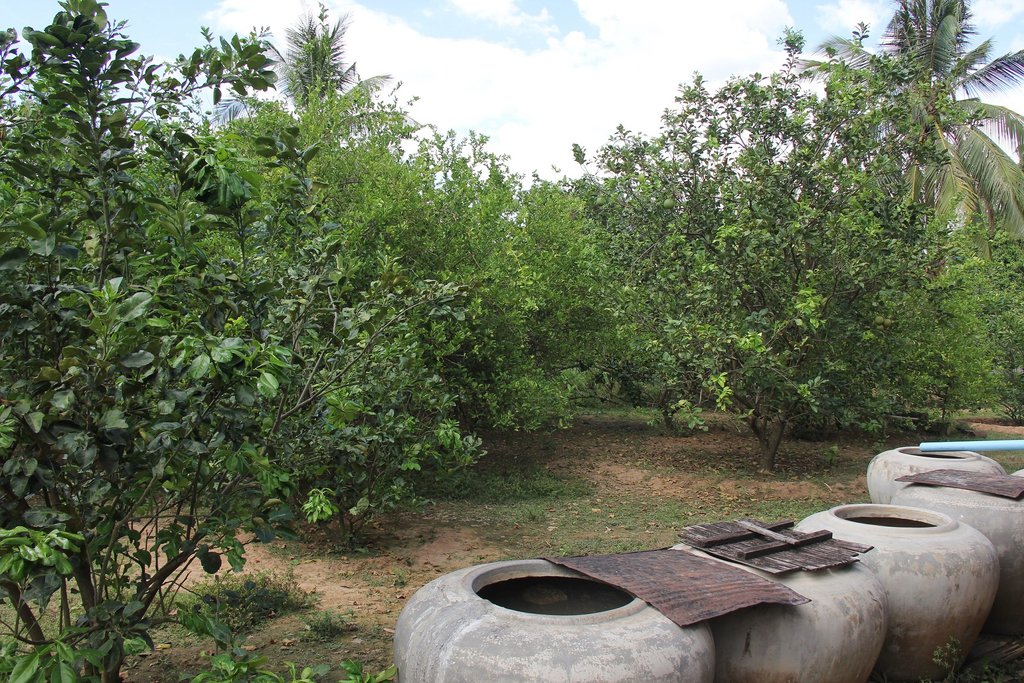
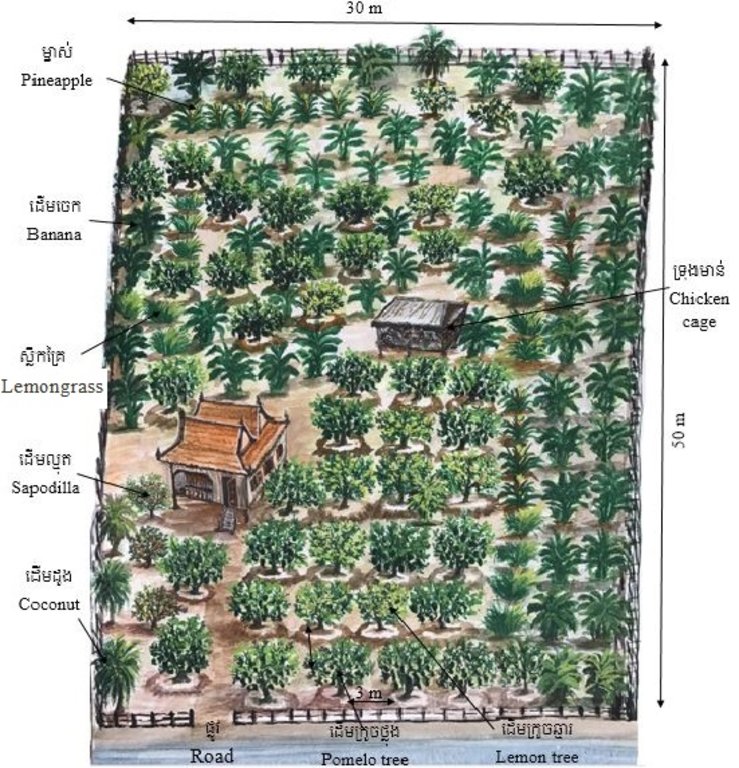
បច្ចេកទេសគេហសួន ត្រូវបានអនុវត្តយ៉ាងល្អនៅក្នុងភូមិសំរោង ឃុំសំបូរ ស្រុកសំបូរ ខេត្តក្រចេះ ដែលក្នុងនោះកសិករដាំក្រូចថ្លុង (ចំនួន ៣០ដើម) និងក្រូចឆ្មារ (ចំនួន ១០ដើម) ជាដំណាំចម្បងសម្រាប់លក់ និងមានដំណាំបន្ទាប់បន្សំច្រើនមុខផ្សេងទៀត ដូចជាចេក ម្នាស់ ទទឹម ស្លឹកគ្រៃ ដូង ស្វាយ និងខ្នុរសម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ។ បច្ចេកទេសនេះបានអនុវត្តលើផ្ទៃដីភូមិទំហំ ៣០ x ៥០ ម៉ែត្រ ស្មើនឹង ១៥០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ ដែលមានទន្លេមេគង្គនៅខាងក្រោយផ្ទះ។
ចំពោះបច្ចេកទេសក្នុងការដាំកូនក្រូច គេប្រើរណ្តៅ ទំហំ ០,៦ ម៉ែត្រ X ០,៦ ម៉ែត្រ រាងការ៉េ និងជម្រៅ ០,៥ ម៉ែត្រ ដោយមានដាក់ជីលាមកសត្វទ្រាប់បាតរណ្តៅ ហើយចន្លោះពីដើមមួយទៅដើមមួយមានប្រវែង ៣ម៉ែត្រ ដើម្បីទុកចន្លោះល្មមឱ្យក្រូចអាចបែកមែកសាខាបានល្អ។ ក្រៅពីនោះ នៅតាមគល់ក្រូចនីមួយៗកសិករបានលើកជាភ្លឺរាងរង្វង់ជុំវិញគល់ដើម្បីកុំឱ្យមានការហូរច្រោះពេលស្រោចទឹកម្តងៗ និងអាចជួយស្ទាក់ទឹកពេលមានភ្លៀងធ្លាក់។ ការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះ គឺប្រើប្រាស់តែជីលាមកគោ ក្របី មាន់ និងមិនមានប្រើជីគីមីនោះទេ។
ការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសគេហសួនដោយមានដំណាំក្រូចឆ្មារ ក្រូចថ្លុងជាដំណាំចម្បង និងដំណាំរួមផ្សំផ្សេងទៀតនេះ កសិករទទួលបានអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ជាច្រើន។ អត្ថប្រយោជន៍ទាំងនោះរួមមាន បង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលប្រចាំថ្ងៃ បង្កើតរុក្ខជាតិបៃតងនៅជុំវិញផ្ទះដែលផ្តល់នូវបរិយាកាសល្អសម្រាប់ការរស់នៅដែលអាចបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការឡើងកំដៅនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ ដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាការហូរច្រោះ និងបង្កើតបរិស្ថានដែលអំណោយផលសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វបក្សីនានា។ ការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះមិនតម្រូវឲ្យមានការចំណាយច្រើននោះទេ ព្រោះកសិករអាចចាប់ផ្តើមអនុវត្តវាជាដំណាក់កាលទៅតាមកំលាំងពលកម្ម និងធនធានដែលមាន ឬឆ្លៀតអនុវត្តវានៅពេលទំនេរ។
កសិករអាចប្រមូលផលក្រូចឆ្មារជារៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃតាមការបញ្ជាទិញ (ប្រហែល ១០ ទៅ ១៥គីឡូក្រាម ក្នុង១ថ្ងៃ) រួមជាមួយនឹងដំណាំរួមផ្សំផ្សេងទៀត។ ក្រូចថ្លុងវិញផ្តល់ផល ១ដងក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ (ជាមធ្យមប្រហែល ៣០ផ្លែ ក្នុងមួយដើម)។ លើសពីនេះ ភាពចម្រុះគ្នានៃដំណាំក្នុងបច្ចេកទេសនេះ ក៏បានបង្កើតនូវជម្រកធម្មជាតិដល់ពពួកសត្វក្នុងដីដែលជាភ្នាក់ងារដ៏សំខាន់ក្នុងការបង្កើនវត្តមានសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹមរបស់ដី ជួយឱ្យដីផុសល្អ ចៀសផុតពីការប្រើប្រាស់សារធាតុគីមីដែលអាចប៉ះពាល់ដល់សុខភាពគ្រួសារ។
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Name of videographer:
មិនមាន
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិសំរោង ឃុំសំបូរ ស្រុកសំបូរ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Further specification of location:
ជាប្រភេទដីភូមិ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2010
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
Comments (type of project, etc.):
ឃើញគេដាំក៏ព្យាយាមអនុវត្តតាមគេ
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
ក្រូចថ្លុង និងក្រូចឆ្មារ (ចាប់ផ្តើមទទួលផលពីឆ្នាំទី៣ ហើយបន្តទទួលផលបានប្រហែល ១៥ឆ្នាំ)។
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
ពីមុនជាដីដាំស្វាយ
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
បូមទឹកពីទន្លេក្រោយផ្ទះ
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
ជាដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង
Livestock density (if relevant):
មានមាន់ចំនួន ២០ក្បាល ដែលមានទ្រុងទំហំ ១៥ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated pest and disease management (incl. organic agriculture)
- home gardens
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
Comments:
ចំពោះវិធានការរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ ដោយធ្វើភ្លឺជារាងរង្វង់ ១០សម ជុំវិញដំណាំ
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

biological degradation
- Bl: loss of soil life

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
បានម្លប់ដល់ដី និងបង្កើនសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
ផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះសរុបមានទំហំ ១៥០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ (ទទឹង ៣០ម៉ែត្រ x ៥០ម៉ែត្រ) ដែលទទួលបានទឹកប្រើប្រាស់ពីទន្លេមេគង្គក្រោយផ្ទះ។ នៅជុំវិញផ្ទះមានដាំដំណាំក្រូចថ្លុងចំនួន ៣០ដើម ក្រូចឆ្មារ ១០ដើម និងដំណាំផ្សេងៗដូចជា ចេក ដូង គល់ស្លឹកគ្រៃ និងម្នាស់។ ចន្លោះដើមក្រូចមួយទៅដើមក្រូចមួយគឺ ចំងាយ ៣ម៉ែត្រ និងមានការលើកជាភ្លឺរាងរង្វង់ជុំវិញគល់ក្រូចកុំឱ្យហូរទឹកនិងជីចេញ។ ដំណាំរួមផ្សំផ្សេងៗត្រូវបានដាំនៅតាមចន្លោះដើមក្រូចពាសពេញបរិវេណសួនជាពិសេសនៅខាងក្រោយ និងតាមរបង។
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1500 ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20000រៀល/ថ្ងៃ
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ទិញកូនក្រូចថ្លុងនៅកោះទ្រង់ | Other measures | ខែប្រាំង |
| 2. | ទិញកូនក្រូចឆ្មារ | Other measures | ខែប្រាំង |
| 3. | ទិញសម្ភារៈ ម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹក ទុយោ | Other measures | ខែប្រាំង |
| 4. | ទិញចបកាប់ ចបជីក បង្គី | Other measures | ខែប្រាំង |
| 5. | ជីករណ្តៅដាំ | Structural | ខែវស្សា |
| 6. | ការដាំដំណាំ | Agronomic | ខែវស្សា |
| 7. | លើកភ្លឺជុំវិញដំណាំ | Structural | ខែប្រាំង |
Comments:
ដាំនៅរដូវវស្សាអាចត្រូវភ្លៀងរលួយ (ពេលចាប់ផ្តើម)
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ជីករណ្តៅ (ខ្លួនឯង) | ថ្ងែ | 10.0 | 20000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ម៉ាស៊ីនទឹក និងទុយោ | ឈុត | 1.0 | 2000000.0 | 2000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបកាប់ | ផ្លែ | 4.0 | 20000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបជីក | ផ្លែ | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | បង្គី | ផ្លែ | 5.0 | 10000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ទិញដីចាក់ | ឡាន | 100.0 | 25000.0 | 2500000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | កូនក្រូចថ្លុង | ដើម | 30.0 | 40000.0 | 1200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | កូនក្រូចឆ្មារ | ដើម | 10.0 | 15000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | លាមកគោ ក្របី | បាវ | 20.0 | 3000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 6255000.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ដាក់ជី | Agronomic | ដើមឆ្នាំ កណ្តាលឆ្នាំ និងចុងឆ្នាំ |
| 2. | បោចស្មៅ | Agronomic | រៀងរាល់សប្តាហ៍ |
| 3. | ស្រោចទឹក | Agronomic | រៀងរាល់ 3 ថ្ងៃម្តង |
| 4. | បេះក្តិបក្រូចពេលផ្លែច្រើនជ្រុល | Agronomic | នៅពេលចេញផ្លែដំបូង |
| 5. | បាញ់ថ្នាំមូសកុំឱ្យស្រមោច | Agronomic | នៅខែវស្សារាំងភ្លៀង |
| 6. | ការប្រមូលផលក្រូចថ្លុង | Management | នៅខែឧសភា |
| 7. | ការប្រមូលផលក្រូចឆ្មារ | Management | រៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃ |
Comments:
ពេលដើមក្រូចថ្លុងធំបន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងការធ្វើស្មៅ
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ដាក់ជី (ខ្លួនឯង) | ថ្ងៃ | 10.0 | 20000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | បោចស្មៅ (ខ្លួនឯង) | សប្តាហ៍ | 32.0 | 14000.0 | 448000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ប្រមូលផល | ម៉ោង | 635.0 | 2500.0 | 1587500.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ប្រើសាំងសម្រាប់បូមទឹកស្រោចស្រព | លីត្រ | 608.0 | 3000.0 | 1824000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | លាមកសត្វ | បាវ | 30.0 | 3000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 4149500.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
អត់មាន
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
គាត់ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្មផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ដូចនេះធ្វើឱ្យគាត់ទទួលបានចំណូលបន្ថែម ម៉្យាងវិញទៀតគាត់ប្រើតែជីធម្មជាតិ។
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1138.20
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១៥ គឺ ១១៣៨,២ មម ឆ្នាំ ២០១៤ គឺ ១៦៩៦,៥ មម និងឆ្នាំ ២០១៣ គឺ ១៦៦១,៨ មម។
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧតុនិយមឆ្នាំ (២០១៥)
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
អាកាសធាតុក្តៅហើយសើមដែលចែកជាពីរដូវ គឺរដូវប្រាំង និងវស្សា ហើយមិនមានការប្រែប្រួលអ្វីពិសេសនោះទេ
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
ដីល្បាយលាយដីកណ្តែងជម្រាលតាមមាត់ទន្លេ
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
ជាប្រភេទដីល្បាយ ល្បាប់ និងល្បាយកណ្តែងដែលមានកម្រិត pH ៥-៦
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Ja
Regularity:
episodically
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
ប្រភពទឹកប្រើប្រាស់បានមកពីទឹកទន្លេដែលអាចប្រើសម្រាប់ហូប និងកសិកម្ម រីឯប្រភពទឹកផ្សេងទៀតដូចជាអណ្តូង គឺមិនអាចទទួលបានទឹកប្រើប្រាស់នោះទេ។
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
គាត់មានអាយុ 45 ឆ្នាំ
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
ដីស្រែ និងដីចម្ការមានប្រមាណ ១០ ហិកតា តែទុកចោល ១០ ឆ្នាំហើយ។
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
កើនឡើងប្រមាណ 20% បើធៀបនឹងទិន្នផលដំណាំស្វាយដែលដាំដំបូង។
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
គុណភាពដំណាំទាំងក្រូចថ្លុង និងក្រូចឆ្មារ គឺកើនឡើងតិចតួចព្រោះមានទឹកគ្រប់គ្រាន់បើប្រៀបធៀបទៅតំបន់ផ្សេង។
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
ក្រូចថ្លុង និងក្រូចឆ្មារ គឺមានតម្រូវការច្រើនដែលនាំឱ្យបង្កើនចំណូលដោយដំណាំទទួលបានតម្លៃថ្លៃជាងមុន។
product diversity
land management
Comments/ specify:
លើកភ្លឺជុំវិញដំណាំដើម្បីរក្សាទឹកឱ្យបានយូរជាងមុន។
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Comments/ specify:
តម្រូវការទឹកស្រោចស្រព គឺនៅតែដដែលដោយសារពីមុនក្រៅពីដំណាំក្រូចថ្លុង និងក្រូចឆ្មារគាត់បានដាំដំណាំផ្សេងៗដែរ ដូចជាស្វាយជាដើម។
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
មិនប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំពុល
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ចំណេញបន្ថែម 20%
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
អាចទទួលចំណូលបន្ថែមបន្ទាប់ពីការដាំដំណាំបែបនេះ
workload
Comments/ specify:
បន្ទុកការងារត្រូវបានថយចុះដោយសារពីមុនគាត់ស្រោចស្រពដោយដៃតែឥលូវគាត់ស្រោចស្រពដោយប្រើម៉ាស៊ីនភ្ជាប់ជាមួយទុយោ។
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
ទទួលបានទិន្នផលខ្ពស់ជាងមុន
health situation
Comments/ specify:
មិនប្រើសារធាតុគីមី ឬធាតុពុលផ្សេងៗ
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
កសិករទទួលបានចំណេះដឹងពីការរក្សាទឹកដោយធ្វើភ្លឺទប់ទឹកនៅគល់ដំណាំ និងប្រើប្រាស់លាមកសត្វ។
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារការធ្វើភ្លឺទប់ទឹកនៅគល់ដំណាំ និងស្លឺកឈើដែលជ្រុះ
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
ដោយប្រើប្រាស់ជីធម្មជាតិ
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
ដោយប្រើប្រាស់ជីធម្មជាតិ
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
ទទួលបានជីជាតិដោយសារស្លឹករុក្ខជាតិជ្រុះ
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
ទទួលបានពីការប្រើប្រាស់លាមកសត្វជំនួសថ្នាំគីមី
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
កត្តាចង្រៃ និងជំងឺនៅធម្មតាដោយសារបច្ចេកទេសមិនបានផ្តោតទៅលើ ហើយមិនមានការប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំគីមី ឬធម្មជាតិឡើយ។
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
groundwater/ river pollution
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local thunderstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | moderately |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | moderately |
| flash flood | moderately |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | moderately |
| insect/ worm infestation | moderately |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extended growing period | moderately |
| reduced growing period | moderately |
| sea level rise | moderately |
Comments:
ប៉ុន្មានឆ្នាំចុងក្រោយនេះមិនមានគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត និងទឹកជំនន់ទេ
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
ដោយសារដំណាំត្រូវការរយៈពេលរហូតដល់ 3 ឆ្នាំទើបទទួលផល តែបន្ទាប់ពីទទួលបានផលហើយ គឺអាចទទួលបានរាល់ថ្ងៃ និងទទួលបានរយៈពេលវែងអាចរហូតដល់រយៈពេលប្រហែល ១៥ឆ្នាំ។
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Comments:
គ្រួសារដែលអនុវត្តនេះគ្រាន់តែមានគេសុំចែកយកទៅដាំប្រហែលពី ១០ ទៅ ២០ គ្រួសារ ប៉ុន្តែដាំត្រឹមតែ ១ ទៅ ២ ដើម ប៉ុណ្ណោះ។
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| មានទីផ្សារល្អសម្រាប់ក្រូចឆ្មារ និងមិនមានគូរប្រជែងច្រើនក្នុងការដាំចំពោះក្រូចថ្លុង។ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ជាប្រភេទដំណាំមានអាយុកាលវែង ប្រមូលផលបានច្រើន និងអាចប្រមូលផលបានជារៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃចំពោះដំណាំក្រូចឆ្មារ |
| នៅតំបន់នេះមិនមានអ្នកដាំក្រូចថ្លុង និងក្រូចឆ្មារច្រើនទេ ដែលធ្វើឱ្យមានតម្រូវការទីផ្សារល្អ។ |
| ការប្រើប្រាស់តែជីលាមកសត្វដែលធ្វើឱ្យទទួលបានទិន្នផលខ្ពស់ និងគុណភាពល្អ ដោយកាត់បន្ថយថ្លៃដើមចំពោះការប្រើជីគីមីផងដែរ។ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ត្រូវការកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើនក្នុងការថែទាំដំណាំ និងស្រោចទឹករាល់ថ្ងៃ | នៅពេលរវល់ខ្លាំងទុកតាមដំណើរ/ អាចឆ្លៀតខ្លះជាពិសេសនៅពេលព្រលឹម ឬល្ងាចបន្ទាប់ពីការងារចម្បង។ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
មួយកន្លែង
- interviews with land users
កសិក ១ នាក់
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
៣ នាក់
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Helen Keller International/Cambodia. (2003). Handbook for Home Garden in Cambodia: The Complete Manual for Vegetable and Fruit Production. Phnom Penh: Helen Keller Worldwide.
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Landon-Lane C. (2012) Livelihoods grow in gardens. Rome: Rural Infrastructure and Agro-industries Division Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Galhena D.H, Freed R., and Maridia K.M. (2013) Home Gardens: a promising approach to enhance household food security and wellbeing.
URL:
https://agricultureandfoodsecurity.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/2048-7010-2-8
Title/ description:
Helen Keller International (2010) Homestead Food Production Model Contributes to Improved Household Food Security, Nutrition and Female Empowerment-Experience From Scaling-up Programs in Asia (Bangladesh, Cambodia, Nepal and Philippines). Nutrition Bullein 8 (1).
URL:
http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/wa_workshop/docs/Homestead_Food_Production_Nutrition_HKI.pdf
Title/ description:
World Vegetable Center (2016) Home Garden in Cambodia. Retrieved on May 14 2017 from
URL:
https://avrdc.org/home-gardens-cambodia/
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules