ដំណាំបន្ថែមបំពេញចន្លោះដី ត្រប់វែង តាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ និងការពាររំហួតដោយ ប្រើចំបើងជាគម្របដី [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Navin Chea
- Editors: Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Reviewers: TOM SAY, SO Than
ការដាំដំណាំត្រប់វែងនៅក្រោមស្វាយ
technologies_2255 - Cambodia
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- ដំណាំបន្ថែមបំពេញចន្លោះដី ត្រប់វែង តាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ និងការពាររំហួតដោយ ប្រើចំបើងជាគម្របដី: Nov. 18, 2017 (inactive)
- ដំណាំបន្ថែមបំពេញចន្លោះដី ត្រប់វែង តាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ និងការពាររំហួតដោយ ប្រើចំបើងជាគម្របដី: Nov. 18, 2017 (inactive)
- ដំណាំបន្ថែមបំពេញចន្លោះដី ត្រប់វែង តាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ និងការពាររំហួតដោយ ប្រើចំបើងជាគម្របដី: Maart 1, 2018 (inactive)
- ដំណាំបន្ថែមបំពេញចន្លោះដី ត្រប់វែង តាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ និងការពាររំហួតដោយ ប្រើចំបើងជាគម្របដី: Sept. 2, 2019 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យកសិកម្ រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី:
សារ៉ាវុធ លី
(+855) 89 796 786)
saravuthly123@gmail.com
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី
ភូមិខ្សារ ឃុំដារ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Cambodia
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វទទួលបន្ទុករួម:
land user:
សុភ័ក្រ យ៉ាន
(+855)17 834 572
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
កសិករ
ភូមិកំបោរ ឃុំគោលាប់ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Cambodia
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
09/04/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
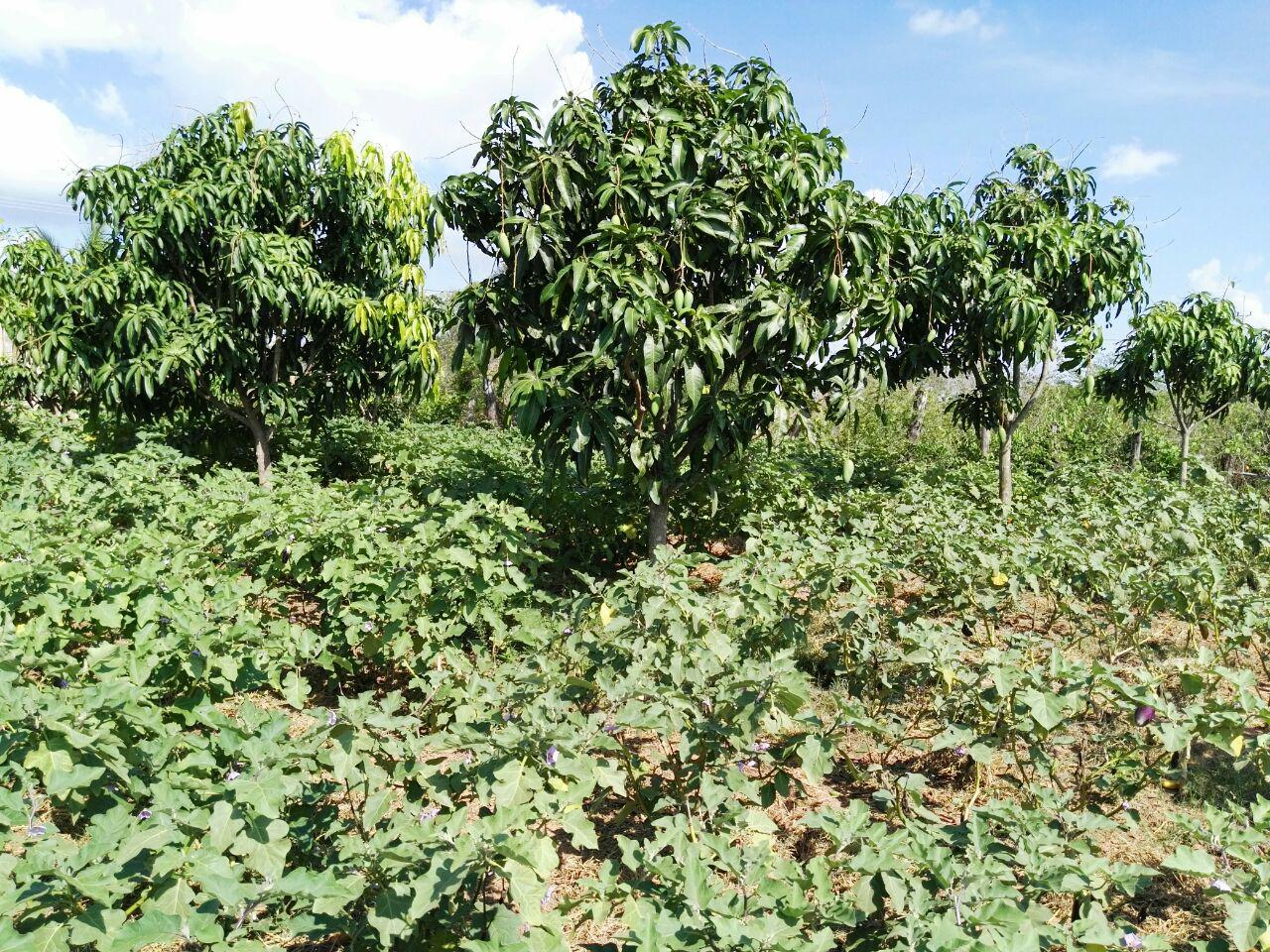
ការដាំដំណាំបន្ថែមបំពេញចន្លោះដីដោយដាំត្រប់វែងនៅចន្លោះដើមស្វាយប្រើចំបើងគ្របលើគល់ដំណាំ និង ពង្រាយពេញលើដីដើម្បីរក្សាសំណើម ការពាររំហួតដោយកម្តៅថ្ងៃ។ ពេលចំបើងរលួយក្លាយជាជី និងធ្វើ ឱ្យដីធូរ។ កសិករអាចប្រមូលផលបានពីការដាំដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លី ក្នុងរយៈពេលពី៣ ឆ្នាំដំបូងមុនពេលដើមស្វាយផ្តល់ផលពេញលេញ។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
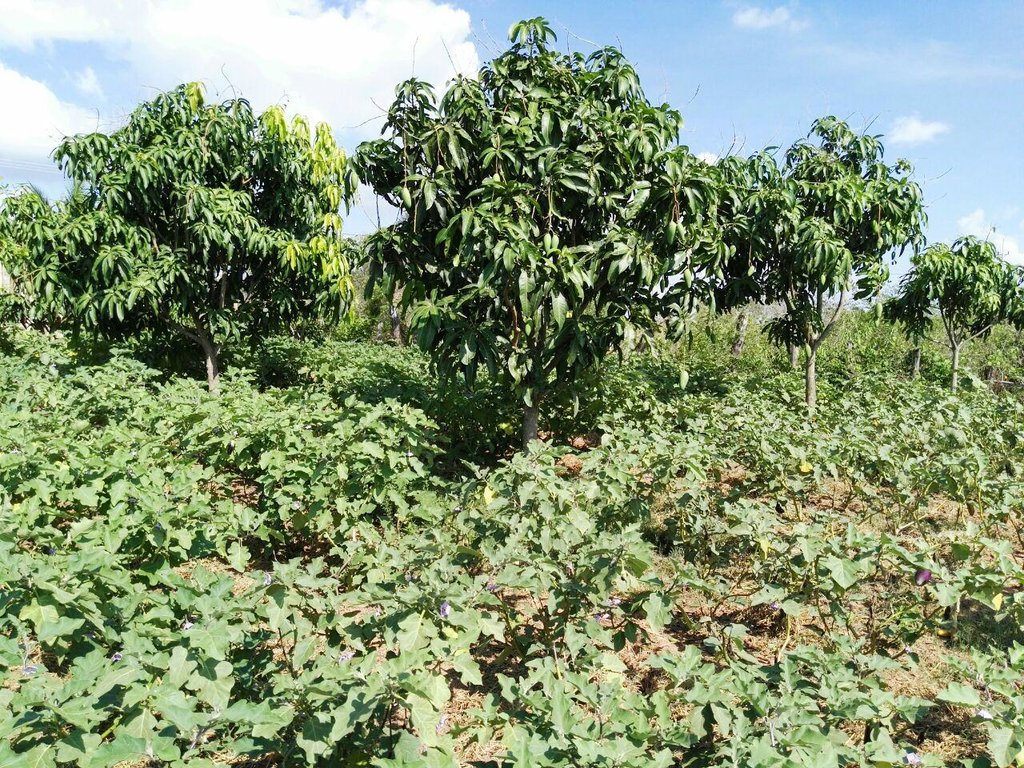
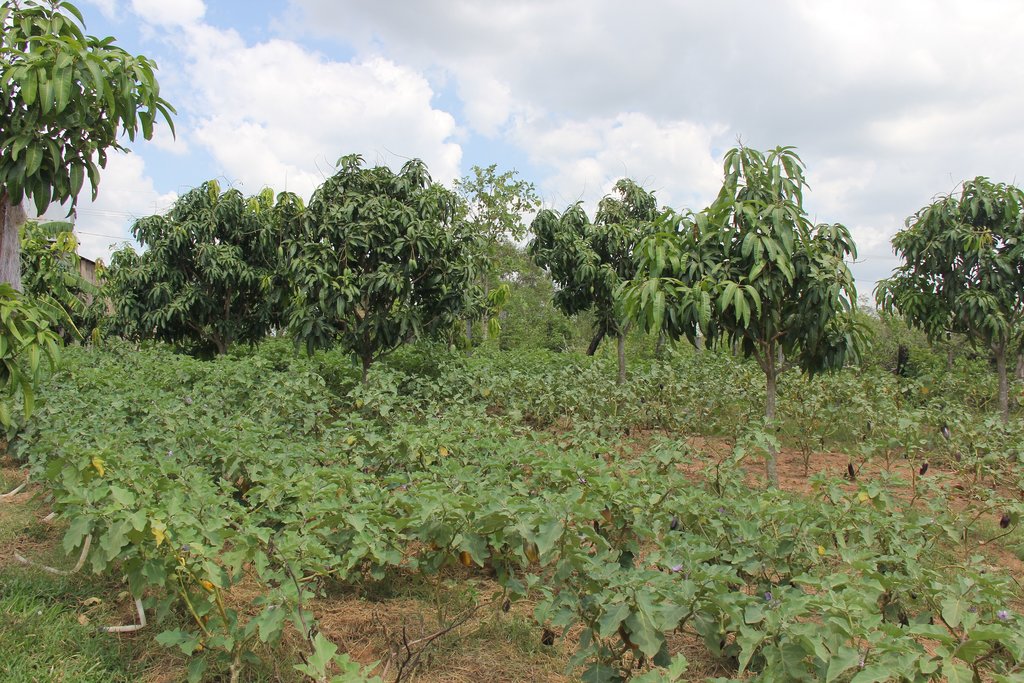
ការដាំដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លីលាយជាមួយដំណាំឈើហូបផ្លែដែលជាប្រភេទដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង (ដូចជាស្វាយដែលផ្តល់ផលនៅឆ្នាំទី៣អាស្រ័យទៅតាមប្រភេទពូជ និង ការថែទាំ) គឺ ជាការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស កសិរុក្ខកម្មមួយដ៏ល្អដែលផ្តល់អត្ថប្រយោជន៍ទាំងផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច និងបរិស្ថាន។ នៅពេលដែលកូនស្វាយនៅតូចមិនទាន់ផ្តល់ផលនៅចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ គឺមានសល់ចន្លោះដីធំទូលាយដើម្បីបានទទួលផល ប្រយោជន៍បន្ថែម និង ជៀសវាងស្មៅចង្រៃរាតត្បាត ធ្វើឱ្យរំខានដល់ការលូតលាស់របស់កូនស្វាយការដាំត្រប់វែង និងប្រើចំបើងជាគម្របដី គឺមិនត្រឹមតែកសិករបានទទួលបាន
ចំណូលបន្ថែមប៉ុណ្ណោះទេ ការដាំនិងថែទាំដំណាំត្រប់វែងអាច បំពេញបន្ថែមឱ្យការថែទាំ សំអាតស្មៅ ស្រោចទឹក ដាក់ជីដល់កូនស្វាយទៀតផង ។ ដំណាំត្រប់អាចផ្តល់ផលជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ចាប់ពីអាយុបាន៣ខែនិងបន្តផ្តល់ផលរាល់ថ្ងៃក្នុងរយៈពេលជាច្រើនខែកសិករអាចប្រមូលផលពីដំណាំត្រប់ជាច្រើនដងក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំដូច្នេះគាត់អាចទាញផលប្រយោជន៍ផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ចដោយ ទទួលបានប្រាក់ចំណូលបន្ថែមសម្រាប់ដោះស្រាយចំណាយប្រចាំថ្ងៃ មុនពេលស្វាយផ្តល់ផល ដែលធ្វើឱ្យជីវភាពគាត់ប្រសើរជាងមុន។
នៅក្នុងបច្ចេកទេសនេះដើមស្វាយ ត្រប់វែង និងចំបើងបានផ្តល់អត្ថប្រយោជន៍ឱ្យគ្នាទៅវិញទៅមក។ នៅរដូវប្រាំងស្វាយផ្តល់ជាម្លប់ខ្លះដល់ដំណាំត្រប់ ហើយត្រប់ និងចំបើងដែលគ្របលើគល់ដំណាំ និងរាយលើដីបាន ជួយរក្សាសំណើមដី កាត់បន្ថយរំហួត មិនធ្វើឱ្យដំណាំឆាប់ស្រពោននៅពេលមានកំដៅថ្ងៃខ្លាំង។ លើសពីនេះទៅទៀតនៅពេលដែលកសិករស្រោចទឹកលើដំណាំត្រប់វាក៏បានផលប្រយោជន៍ទៅដល់ស្វាយ ផងដែរ។ រីឯនៅរដូវវស្សា ចំបើង និងត្រប់ គឺជាគម្របដីដ៏សំខាន់សម្រាប់ទប់ស្កាត់ការហូរច្រោះពេលមានភ្លៀងខ្លាំង។ គម្របចំបើងធ្វើឱ្យដីសើមជានិច្ចនោះ គឺជាប្រភពអាហារយ៉ាងសំខាន់សម្រាប់ពពួកមីក្រូសរីរាង្គមានប្រយោជន៍ក្នុងដី ពិសេសពេលចំបើងពុកផុយ គឺវាជួយបង្កើនជីជាតិដី និងធ្វើឱ្យដីធូរ អំណោយផលដល់ការលូតលាស់របស់ដំណាំ។
ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះកសិករបានដាំស្វាយជាជួរដែលមានចន្លោះស្មើៗគ្នា ៦ម៉ែត្រ គុណ ៦ម៉ែត្រ ហើយត្រប់ត្រូវ បានដាំជាជួរនៅតាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយក្នុងចន្លោះគុម្ព ១ម៉ែត្រ និងចន្លោះរង ១,៥ម៉ែត្រ។ រណ្តៅ ស្វាយមានទំហំ ៧០x៧០x៧០ សង់ទីម៉ែត្រដោយមុនពេលដាំកសិករបានដាក់ផេះអង្កាមលាយជាមួយលាមកគោ និងស្លឹកទន្ទ្រានខែត្រនៅបាតរណ្តៅដែលជាជីដ៏សំខាន់សម្រាប់ការលូតលាស់របស់ ដំណាំស្វាយ។នៅពេលដាំកសិករក៏បានបន្ថែមជីកំប៉ុស្តដែលបានមកពីកាកសំណល់ឡជីវឧស្ម័ននៅនឹងគល់ស្វាយផងដែរ។
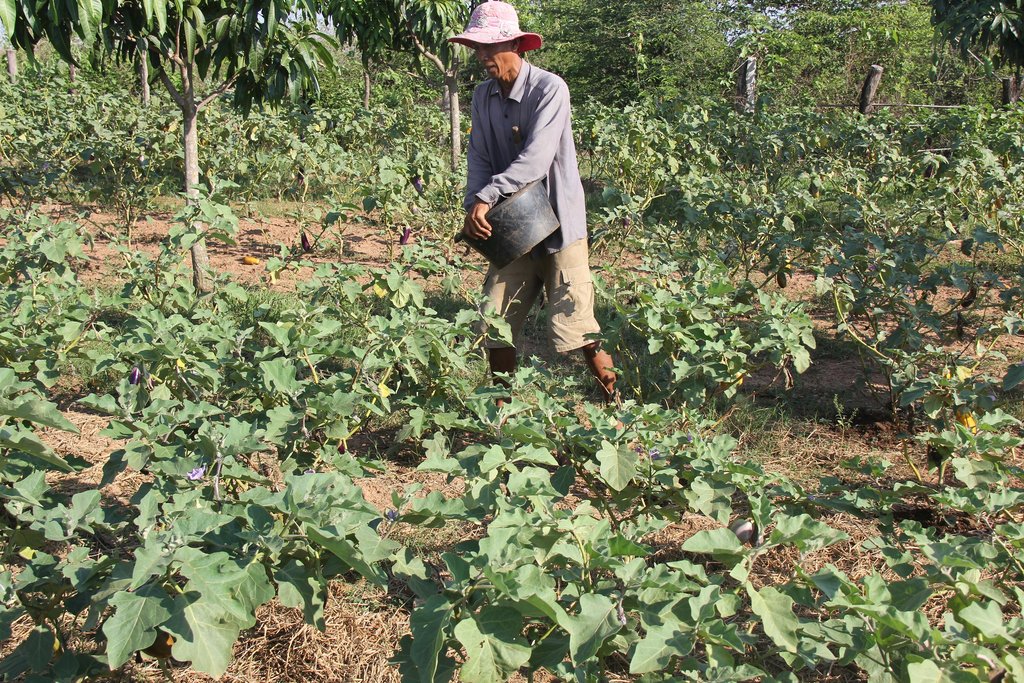
សម្រាប់ការដាំត្រប់វិញគាត់ជីករណ្តៅជម្រៅប្រហែល ១០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ហើយដាំកូនត្រប់ដែលបានសាបរួច អាយុ ២០-៣០ថ្ងៃ។ បន្ទាប់មក គាត់ពង្រាយចំបើងនៅតាមគល់ត្រប់គល់ស្វាយ និងពេញផ្ទៃដី។ កសិករធ្វើការស្រោចទឹកត្រប់ជារាងរាល់ថ្ងៃ និងស្រោចទឹកពីរដងក្នុងមួយសប្តាហ៍សម្រាប់កូនស្វាយ។ ការសំអាតស្មៅ ក៏ត្រូវបានយកចិត្តទុកដាក់ផងដែរ ទោះស្មៅមិនសូវដុះច្រើនក្រោមគម្របចំបើងក្តី។ ជាទូទៅគាត់ដាក់ជី កំប៉ុស្តនៅតាមគល់ដំណាំចំនួនពីរដងក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ គឺនៅដើម និងចុងរដូវវស្សានៅខែឧសភា និងខែតុលា។
នៅពេលដែលត្រប់ចាប់ផ្តល់ផល កសិករត្រូវការពេលប្រហែល ១ម៉ោងក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃក្នុងការប្រមូលផលត្រប់។ ពេលខ្លះការសំអាតស្មៅបានប្រព្រឹត្តទៅនៅពេលប្រមូលផលនេះដែរ។ ដើម្បីឱ្យការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះកាន់តែមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពគួរធ្វើការផ្លាស់ប្តូរមុខដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លីឱ្យបានញឹកញាប់ ព្រោះការដាំដំណាំដដែលៗ ដំណាំនោះនឹងស្រូបយកប្រភេទជីដូចៗ គ្នាពីដី ធ្វើឱ្យការដាំជាលើកទីពីរ
មិនសូវបានល្អ និងងាយក្នុងការផ្ទុះឡើងនូវជំងឺផ្សេងៗដល់ដំណាំ។ ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរមុខដំណាំនេះអាចដូរពីការដាំត្រប់វែងទៅជាសណ្តែកបាយពោត ឬត្រសក់ ដោយស្ទាបស្ទង់ទៅតាមតម្រូវការទីផ្សារផងដែរ។
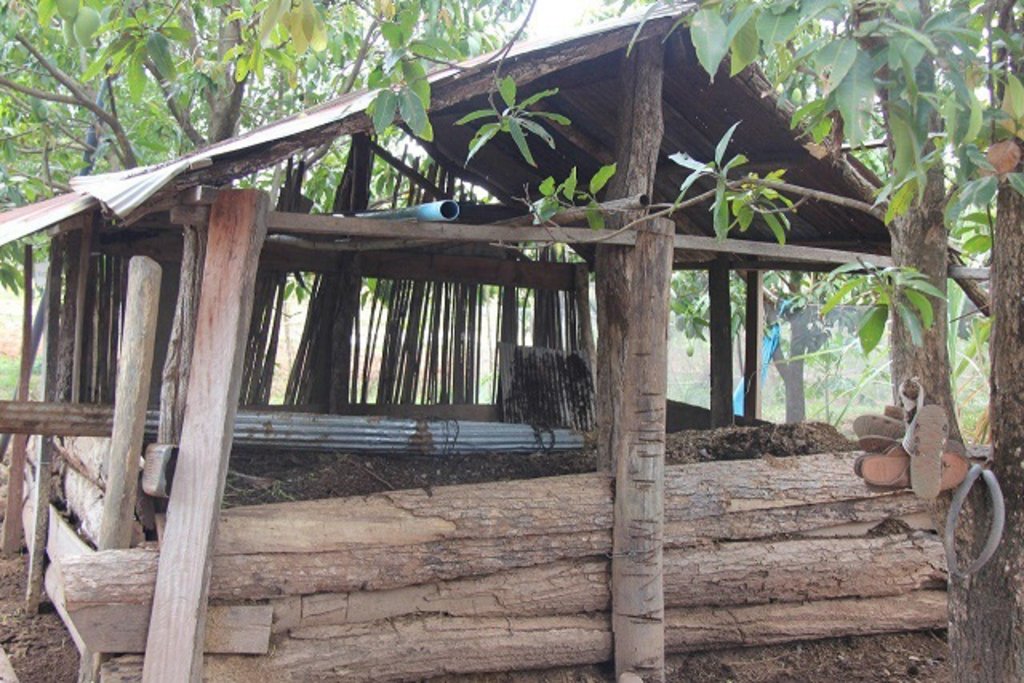
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិកំបោរ ឃុំគោលាប់ ស្រុកចិត្របុរី ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Further specification of location:
នៅទីវាល
Comments:
បច្ចេកទេសនេះអនុវត្តនៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោយផ្ទះរបស់កសិករ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2012
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
កសិករបានចូលរួមដំណើរទស្សនៈកិច្ចនៅទីវាលនៅខេត្តបាត់ដំបងដែលមានការឧបត្ថម្ភពី SNV ក្រោមគម្រោងសាកវប្បកម្មកម្ពុជា ដើម្បីបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូល និងអាហារូបត្ថម្ភសហការជាមួយការិយាល័យកសិកម្មស្រុកចិត្របុរី ហើយគាត់បានរៀនបច្ចេកទេសនេះ។
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
- ដាក់ចំបើងរក្សាសំណើម ហើយនៅពេលវារលួយវាកើតជាជី ។ ទទួលបានចំណូលបន្លែមពីដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លី មុនទទួលផលពេញលេញពីស្វាយ
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
- ស្វាយ និង ត្រប់វែង
Main crops (cash and food crops):
ស្វាយថៃ (៣ឆ្នាំបានផ្លែ) ត្រប់វែង (ក្រោយស្ទូងបាន ២ ខែ គឺអាចឱ្យផល។ កសិករឈប់ទទួលផលត្រប់វែងក្នុងរយៈពលេ ៦ខែ ទើបដាំជាថ្មី។ ប្រសិនកសិករចង់ទុកប្រមូលផលវារហូត ១ឆ្នាំក៏បានប៉ុន្តែប្រភេទផ្លែ និងទិន្នផល គឺទទួលបានទាប)

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
Main products/ services:
ស្វាយ និងត្រប់វែង
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
ដីព្រៃរេចរិល
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
ទឹកស្រះ និងទឹកអណ្តូង ស្រះធ្លាប់រីងឆ្នាំ ២០១៦
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
ស្វាយដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង ត្រប់អាយុកាល ៦ ខែ ពោតមានអាយុកាល ០២ ខែ សណ្តែកបាយមានអាយុកាល ០២ ខែ
Livestock density (if relevant):
ចិញ្ចឹមគោ ១៩ ក្បាល លាមកគោយកដាក់ឡជីវឧស្ម័ន និងប្រើសំណល់ឡសម្រាប់ដាក់ដំណាំ។ ចំនួនគោនេះ គឺគ្រប់ក្រាន់សម្រាប់ដាក់នៅក្នុងឡជីវឧស្ម័នជារៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃ។
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- integrated soil fertility management
- ចំបើងជួយរក្សាសំណើមនិងក្លាយជាជីសរីរាង្គពេលវារលួយ
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
បច្ចេកទេសនេះអនុវត្តលើផ្ទៃដីទំហំ ២៤៥០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ( ទទឹង៣៥ ម៉ែត្រ និងបណ្តោយ ៧០ ម៉ែត្រ) ។
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
- A3: Soil surface treatment

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
- Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bl: loss of soil life
- Bp: increase of pests/ diseases, loss of predators

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
បានដាក់ជីកាកសំណល់ពីឡជីវឧស្ម័ន ដីនៅតំបន់នេះពុំសូវមានជីជាតិ ប៉ុន្តែការដាក់បន្ថែមជីសរីរាង្គ និងដាំដំណាំវិលជុំបានជួយកែលំអដីនេះបានប្រសើរឡើង។
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
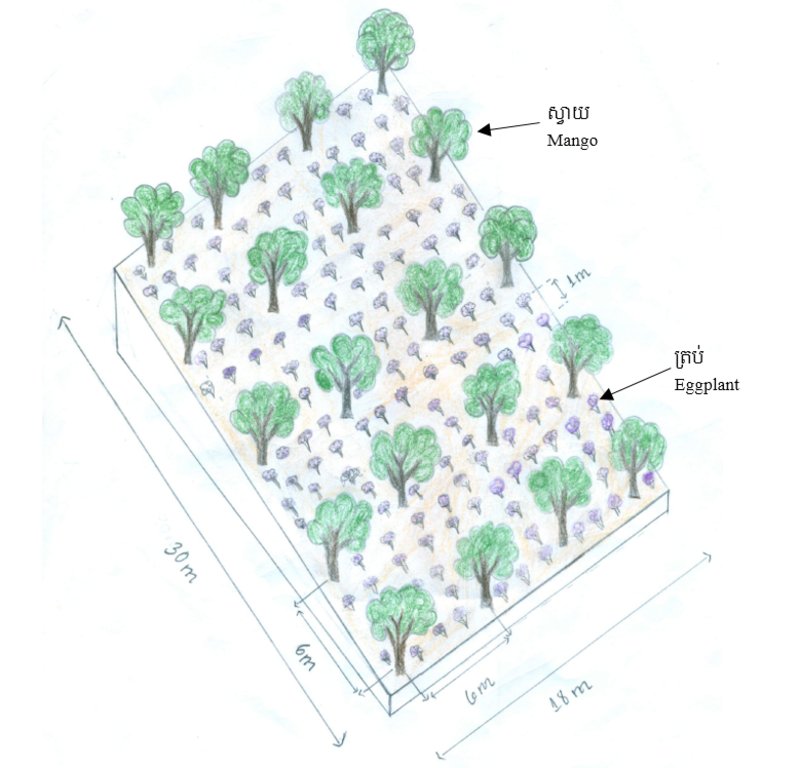
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
ស្វាយសរុបមានចំនួន ២៥ ដើម ត្រប់វែងមានចំនួន ៣៥០ ដើម និងផ្ទៃដីដាំត្រប់ក្រោមស្វាយមានទំហំ៦០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ(ទទឹង ១៥ ម៉ែត្រ បណ្តោយ ៤០ ម៉ែត្រ ) ។
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
៦០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
១ ហិិចតា = ១០០០០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
៣០០០០ រៀល
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ភ្ជួរដីហាល | Agronomic | ខែឧសភា |
| 2. | ជីករណ្តៅស្វាយ | Structural | ខែឧសភា |
| 3. | ដាក់លាមកគោ ផេះអង្កាម កន្ទ្រានខែត្រក្នុងរណ្តៅ | Agronomic | ខែឧសភា |
| 4. | ដាំកូនស្វាយ | Agronomic | ខែឧសភា |
| 5. | ដាក់ជីកាកសំណល់ឡនៅតាមគល់ស្វាយ | Agronomic | ខែមិថុនា |
| 6. | ភ្ជួរដីលាយលាមកគោ បាចកំបោរកម្ចាត់មេរោគ | Structural | ខែមិថុនា |
| 7. | បណ្តុះកូនគ្រាប់ត្រប់វែង | Agronomic | ខែឧសភា |
| 8. | ជីរណ្តៅ និងដាំកូនត្រប់វែង | Agronomic | ខែមិថុនា |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ភ្ជួរដីហាលចោល ១៥ ថ្ងៃ | ថ្ងៃ | 0.5 | 20000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ជីករណ្តៅដាំស្វាយ | រណ្តៅ | 35.0 | 5000.0 | 175000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ដាក់ជី និងបាចកំបោរ | ថ្ងៃ | 0.5 | 20000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | កូនស្វាយ | ដើម | 25.0 | 8000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ពូជត្រប់វែង | កញ្ចប់ | 1.0 | 8000.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | កំបោរ | គីឡូក្រាម | 25.0 | 2000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ជីកាកសំណល់ឡជីវឧស្ម័ន | ស្ពេត្រូ | 50.0 | 2000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ចបកាប់ | ផ្លែ | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | បង្គីរ | គូរ | 1.0 | 7000.0 | 7000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ត្រសេះជីកដី | ដើម | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 625000.0 | |||||
Comments:
កសិករប្រើលុយដែលចំណាយទាំងអស់បានមកពីការសន្សំ រីឯជីបានពីជីលាមកគោខ្លួនឯង និងជីកាកសំណលឡជីវឧស្ម័នដែលគម្រោងបានផ្តល់ឱ្យ។
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ត្រួតពិនិត្យដើមស្វាយកុំឱ្យដួល ឬដង្កូវស៊ីស្លឹក | Management | ៥ ថ្ងៃត្រួតពិនិត្យម្តង |
| 2. | ភ្ជួរដំណាំគម្របដីដូចជាសណ្តែកបាយពេលប្រមូលផលរួច | Agronomic | ពេលប្រមូលផល |
| 3. | ជីកបង្អូរជុំវិញស្វាយ | Management | ពេលស្វាយធំបន្តិច |
| 4. | ដាក់ជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ ជីកែងលាយ(15-15-15) | Agronomic | ដាក់ខែមិថុនា និងខែតុលា |
| 5. | ស្រោចទឹកត្រប់រាល់ថ្ងៃ | Agronomic | ពេលខែប្រាំង |
| 6. | ទិញម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹក | Management | ក្រោយពេលដាំស្វាយរួច |
Comments:
ម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹកមានតម្លៃ ១,៦០០,០០០ រៀល
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
If possible, break down the costs of maintenance according to the following table, specifying inputs and costs per input. If you are unable to break down the costs, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
2800000.0
Comments:
ម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹកមានតម្លៃ ១,៦០០,០០០ រៀល អំឡុងពេលថែទាំកសិករធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯងនៅពេលទំនេរ រីឯការប្រើប្រាស់ជីគឺប្រើលាមកគោ និងជីកាកសំណល់ដែលមានប្រសិនបើចំណាយប្រហែល ១២០០០០០ក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ។
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ម៉ាស៊ីនបូមទឹកមានមានតម្លៃខ្ពស់ ចំណាយប្រាក់លើការទិញកូនស្វាយ និងគ្រាប់ពូជត្រប់វែង ជួលពលកម្មបន្ថែមក្នុងការភ្ជួរដី ដោយឡែកមិនមានចំណាយលើការទិញជីទេ ដោយប្រើជីលាមកគោដែលខ្លួនមាន។
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1138.20
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
ឆ្នាំ 2015 បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងមាន 1138.2 ម.ម ឆ្នាំ 2014 មាន 1696.50 ម.ម និងក្នុងឆ្នាំ 2013 មាន 1661.8 ម.ម។
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧត្តុនិយម នាយកដ្ឋានឧត្តុនិយមឆ្នាំ ២០១៥
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
មានពីររដូវគឺ រដូវប្រាំង និងរដូវវស្សា
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
ពីមុនដីដែលគាត់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះគឺជាដីព្រៃរេចរិលខ្សោះជីជាតិសម្បូរទៅដោយថ្មនៅស្រទាប់ខាងក្រោម តែដោយសារលាមកគោ និងជីកាកសំណល់ឡជីវឧស្ម័នដីនេះល្អជាងមុន។
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
ទឹកដែលចេញពីអណ្តូងមានជាតិកំបោរដែលត្រូវបង្ហូរចូលក្នុងស្រះជាមុនសិន រីឯទឹកសម្រាប់បរិភោគគឺបានពីទឹកភ្លៀងបានត្រងទុក និងទិញទឹកស្អាតបន្ថែម។
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
កសិករអាយុ ៤៥ ឆ្នាំ
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
ជាដីព្រៃ
Quantity after SLM:
ដាំដំណាំដោយប្រើជីលាមកសត្វ កំប៉ុស្តិ៍
Comments/ specify:
ផលិតកម្មកើន
crop quality
animal production
Quantity before SLM:
គោ ៣០ ក្បាល
Quantity after SLM:
១៩ ក្បាល
Comments/ specify:
លក់គោ ១១ ក្បាលដើម្បីយកលុយធ្វើផ្ទះ ទុកខ្លះដើម្បីយកលាមកសត្វ។ បរិមាណគោល ១៩ ក្បាល គឺគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់យកលាមកវាមកធ្វើជាជីលើដំណាំ។
risk of production failure
Quantity before SLM:
ទុកចោល
Quantity after SLM:
មានដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទមិនទុកដីទំនេរចោល
Comments/ specify:
ដាំវិលជុំផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដំណាំ
product diversity
Quantity before SLM:
ទុកចោល
Quantity after SLM:
មានដំណាំ
Comments/ specify:
មានដំណាំទៅតាមទីផ្សារ
land management
Quantity before SLM:
ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
Quantity after SLM:
មិនទុកដីទំនេរ កែលំអរដីដោយប្រើជីធម្មជាតិ
energy generation
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
drinking water quality
water availability for livestock
water quality for livestock
irrigation water availability
irrigation water quality
demand for irrigation water
Quantity before SLM:
មិនមានដាំដំណាំ
Quantity after SLM:
មានដាំដំណាំពេញមួយឆ្នាំ
Comments/ specify:
ដំណាំក្រោមស្វាយត្រូវការស្រោចទឹករាល់ថ្ងៃ
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
មានគោខ្លួនឯង និងមានឡជីវឧស្ម័នមិនចំណាយទៅលើការទិញជីពីទីផ្សារ ។ កម្លាំងពលកម្ម ភាគច្រើនធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង។
farm income
Comments/ specify:
បានចំណូលជាប្រចាំពីការលក់ផ្លែត្រប់
diversity of income sources
workload
Comments/ specify:
ការគ្រប់គ្រងត្រួតពិនិត្យមើលស្វាយ មើលត្រប់វែងគឺធ្វើរួមគ្នា
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
បានហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ និងលក់បានប្រាក់ចំណូល
health situation
Comments/ specify:
ប្រើលាមកគោ ជីកំបុស្តិ៍ ជីកាកសំណល់ឡជីវឧស្ម័នដែលមិនប៉ះពាល់ដល់សុខភាពអ្នកដាំដុះ និងអ្នកទិញបរិភោគ។
recreational opportunities
Quantity after SLM:
មានគំនិតដាំដំណាំផ្សេងៗដូចជាទំពាំង
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
water quality
evaporation
Comments/ specify:
បានចំបើង និងស្វាយជាម្លប់
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil crusting/ sealing
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
ជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ និងជីកាកសំណល់ឡជីវឧស្ម័នបានជួយឱ្យដីធូរ
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
invasive alien species
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
សម្បូរសត្វកាឡនតន
pest/ disease control
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
drought impacts
impacts of cyclones, rain storms
micro-climate
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារមានដើមស្វាយ
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
មានអ្នកយកទៅអនុវត្តតាម កសិករផ្សេងចាប់អារម្មណ៍ច្រើន មានស្ថាប័នពាក់ព័ន្ធចុះមកទស្សនៈកិច្ច
Comments/ specify:
មានកសិករផ្សេងមកទស្សនៈកិច្ច តាមរយៈកម្មវិធី ASPIRE និងគម្រោង CHAIN។
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | dry season | increase | very well |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | well |
| other gradual climate change | ការប្រែប្រួលនៃរបបទឹកភ្លៀង | increase | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| heatwave | moderately |
| drought | well |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | well |
| insect/ worm infestation | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
៧ គ្រួសារ ចង់បានចំណូលបន្ថែម ទោះបីពួកគាត់មិនបានអនុវត្តទាំងអស់តែគាត់ក៏យកផ្នែកមួយនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅអនុវត្តផងដែរ
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- climatic change/ extremes
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| អាចដាំដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លីនៅតាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ |
| ស្រោចទឹកដល់ត្រប់វែងក៏បានប្រយោជន៍ដល់ស្វាយផងដែរ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| មិនឱ្យដីទំនេរចោលដែលខាតផលប្រយោជន៍ព្រោះស្វាយរយៈពេលប្រហែល០៣ឆ្នាំទើបអាចប្រមូលផលបាន |
| ចំបើងជួយរក្សាសំណើមដល់ដីកុំឱ្យហួត និងខ្សោះជីជាតិ |
| បានប្រាក់ចំណូលដល់គ្រួសារ |
| ដីមិនខ្សោះជីជាតិដោយសារដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លី វិលជុំ និងប្រើប្រាស់តែលាមកគោ ជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ និងកាកសំណល់ឡជីវឧស្ម័ន |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ដង្កូវរូងដើមត្រប់វែង | ដើរចាប់ពងដង្ហូវ មិនប្រើថ្នាំពុលដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់សុខភាព |
| ខ្វះទីផ្សារនៅពេលដែលដាំត្រប់វែងបានផលច្រើន | ដើរលក់គ្រប់ទីផ្សារដែលអាចទៅបានដើរលក់តាមផ្ទះ |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| នៅពេលស្វាយធំប្រមូលផលបានពេញលេញ គឺមិនអាចដាំដំណាំត្រប់វែងនៅក្រោមស្វាយបានទៀតទេ | អាចដាំជារំដេង រមៀត |
| ត្រូវការជីកំប៉ុស្តិ៍ និងឡជីវឧស្ម័ន | ជំរុញការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វគោ ក្របី មាន់ជ្រូកជាដើម។ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
៦ នាក់
- interviews with land users
១ នាក់
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules