Sistema de tratamiento de aguas mieles (STAM) [Nicaragua]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Carlos Marín
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Johanna Jacobi, Alexandra Gavilano
Filtro de aguas mieles
technologies_4579 - Nicaragua
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
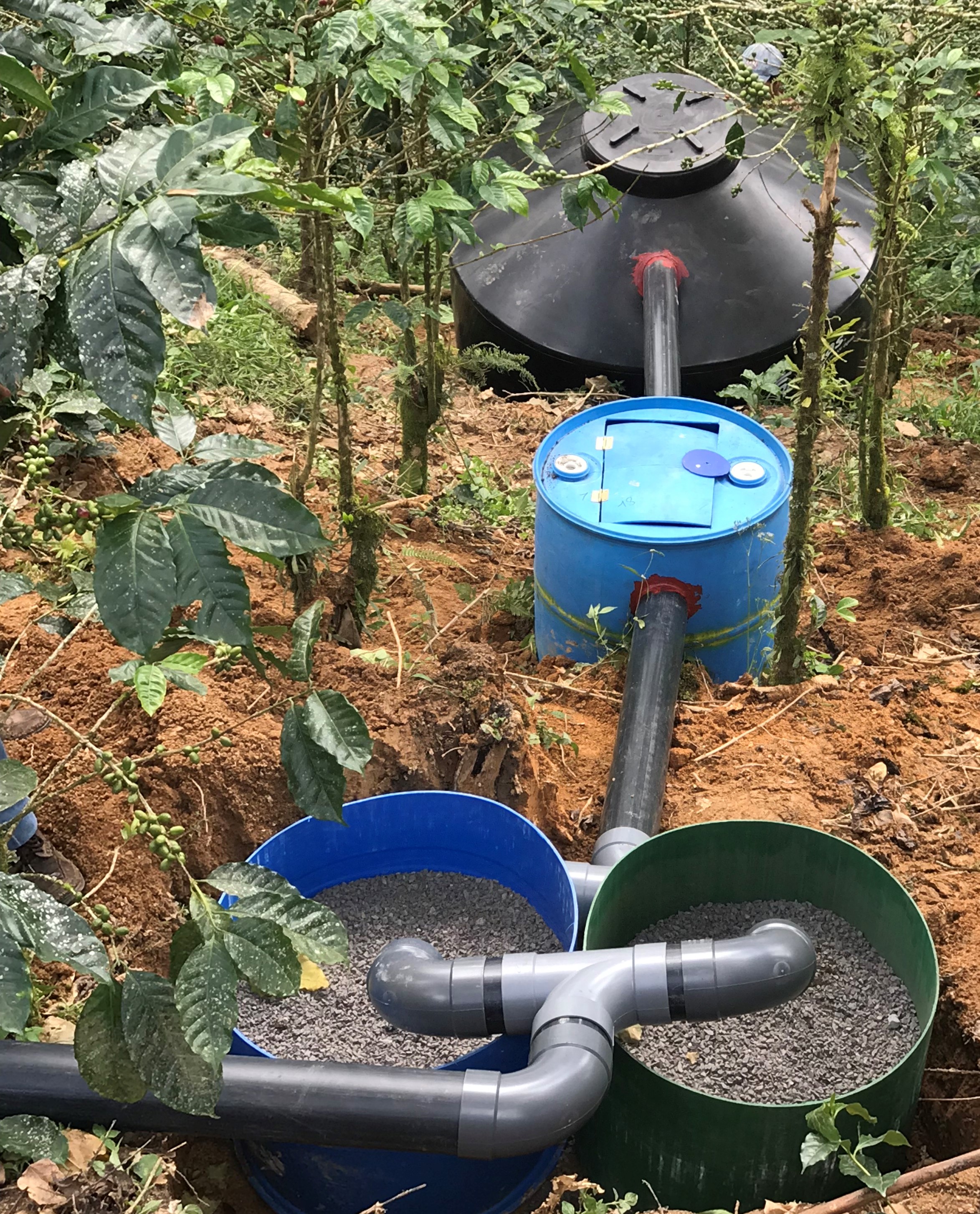
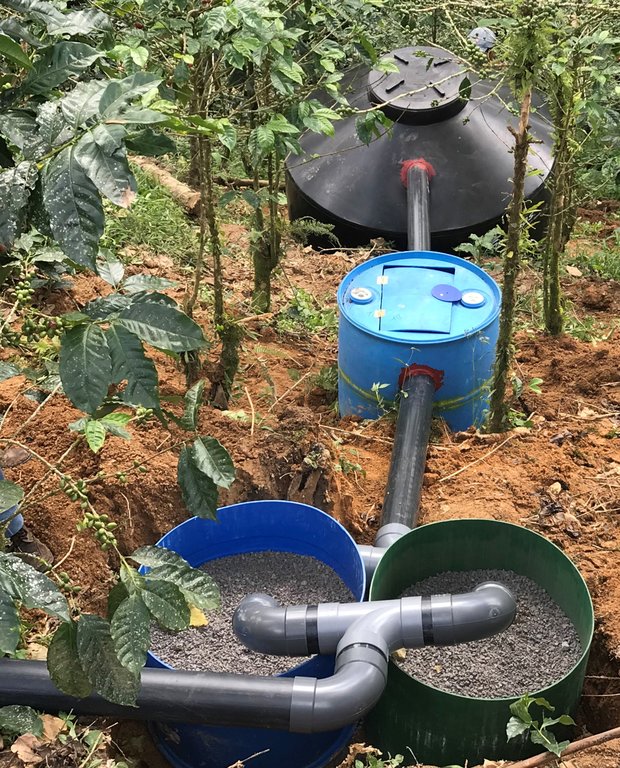
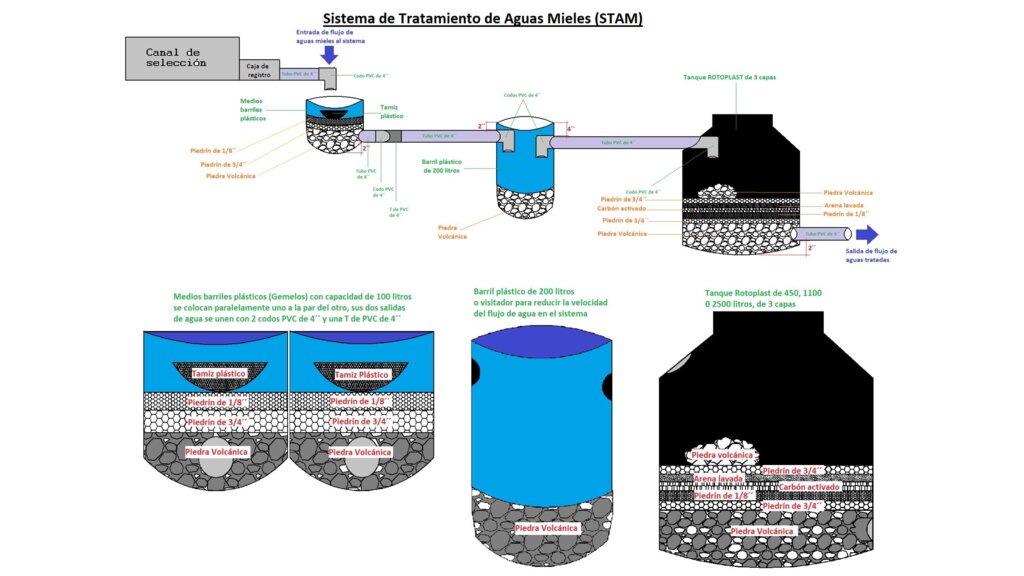
El Sistema de Tratamiento de Aguas Mieles (STAM) del procesamiento del café es compuesto por materiales naturales: piedrín, arena de río, piedra volcánica y carbón activado, que se colocan en capas dentro de depósitos plásticos, barriles y tanques.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
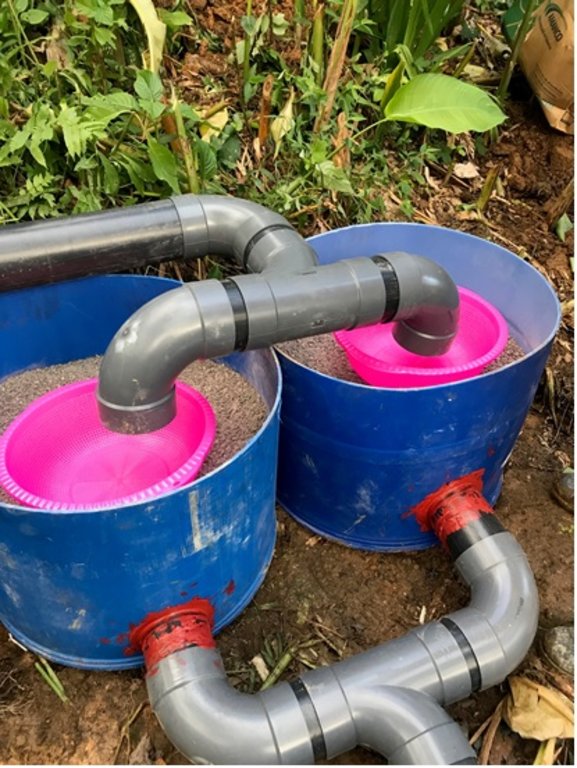
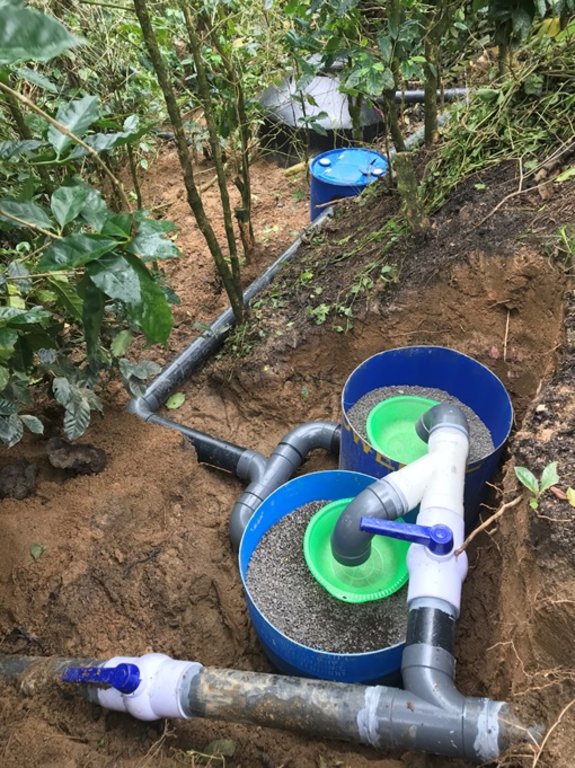
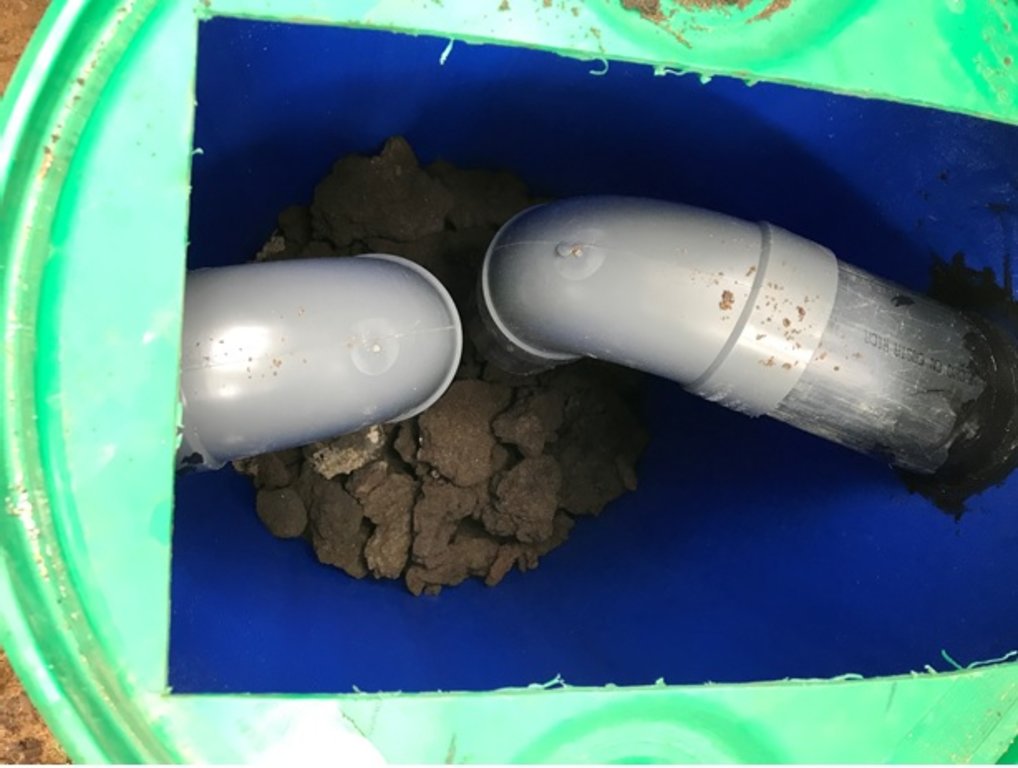
El agua miel sale del proceso del beneficio húmedo del café, y muchas veces sale a los ríos sin tratamiento. Los Sistemas de Tratamiento de Aguas Mieles (STAM) se instalan a la salida del canal de lavado del café y están compuestos por: 1 barril de 200 litros, cortado a la mitad, como primer módulo de retención de sólidos con las dos mitades del barril; 2 canastas de plástico para retener los sólidos; 1 barril de 200 litros; 1 tanque plástico que puede ser de 750, 1100 o 2500 litros dependiente de la cantidad de café que se beneficiará; tubos PVC de 4”, Codos PVC de 4” y tapagoteras (p. ej. IMPERFAST). Los módulos están separados hasta 3 metros para evitar que el peso del agua mueva los tubos. Los materiales filtrantes que se utilizan son: Piedra volcánica, piedrín grueso de ½”, piedrín fino de 1/8”, arena de río y carbón activado. El carbón se quiebra hasta tamaño de 1”, se lava y se seca 3 días, y se vuelve a lavar. Cuando ya no desprende el polvillo está listo. Los materiales se colocan en capas dentro de cada uno de los barriles y dentro del tanque. El primer filtro está formado por un par de medios barriles que se colocan lado a lado y retienen los sólidos del primer lavado. En el primer filtro se coloca una primera capa de piedra volcánica con un espesor de 6” equivalente a medio saco de piedras. Se coloca la segunda capa compuesta por una lata de piedrín de ½”, la capa queda con un espesor de 2”. Se coloca como tercera capa una lata de piedrín de 1/8”, la capa queda con un espesor de 2”. El segundo filtro está compuesto por un barril que tiene una entrada de agua que entra en la parte de arriba a 2” del borde del barril y una salida colocada a 4” del borde superior hacia el tanque. La función del segundo filtro es reducir la velocidad del flujo de agua. Se coloca en el fondo del barril una capa de medio saco de piedra volcánica que ocupa una cuarta parte del barril. El tercer filtro o tanque plástico tiene la función de refinar más el filtrado del agua, reducir su acidez, cambiar el color, el olor y el sabor del agua. El tercer filtro contiene una primera capa de 6” de piedra volcánica colocadas en el fondo del barril, equivalente a 2 sacos de piedra. Se coloca una segunda capa de piedrín de ½”, formando una capa de 4”, una tercera capa de 2” de piedrín de 1/8”, una cuarta capa de carbón activado de 6” equivalente a un saco quintalero de carbón, una quinta capa de 4” formada con tres latas de arena de río, otra capa de 2” de piedrín grueso, y finalmente se coloca piedra volcánica de tamaño mediana, en el punto donde cae el chorro de agua, para evitar que se remueva la arena a la superficie. Los materiales filtrantes ocupan la mitad del tanque. Se requiere mantenimiento del primer filtro lavando el piedrín fino en tamices plásticos y ubicarlo nuevamente después de cada lavada de café. También se requiere reemplazar los materiales del tanque plástico cada dos años. Los STAM generan mejores condiciones en las fincas al reducir el vertido de aguas mieles, menos proliferación de insectos y evitan que las aguas mieles contaminen los ríos o quebradas.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Nicaragua
Region/ State/ Province:
La Tablazón, municipio de Dipilto, departamento de Nueva Segovia, Nicaragua
Further specification of location:
Parte media y alta de la cuenca del río Dipilto.
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
Ja
If yes, specify:
Cuenca del Río Dipilto, Área de Amortiguamiento del Área Protegida Serranías Dipilto y Jalapa
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2017
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Ja
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- coffee, shade grown
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Algunos cultivos como las Musaceas se cosechan todo el año
Is intercropping practiced?
Nee
Is crop rotation practiced?
Nee
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Ja
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Waterways, waterbodies, wetlands
Main products/ services:
Tratamiento de agua
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- manejo de subproductos del cultivo de café
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S8: Sanitation/ waste water structures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover

water degradation
- Hq: decline of groundwater quality
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Dos medios barriles plásticos con altura aproximada de 40 cm, 1 barril plástico de 200 litros con 80 cm de altura, 1 tanque plástico con capacidades de 450, 1100 o 2500 litros. Las conexiones entre filtros se hacen con tubos PVC de 4" y se pueden utilizar opcionalmente llaves de pase de 4" en la entrada al sistema. La distancia máxima entre filtros es de 3 m con una pendiente de 1%.
Author:
Carlos Ramón Marín
Date:
21/03/2019
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
metros cuadrados
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
18
other/ national currency (specify):
Córdoba
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
32.59
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
150
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparación de los materiales (corte y perforación de barriles y tanque, lavado de arena y piedrín, activación de carbón) | None |
| 2. | Delimitación, limpieza y trazado del área | None |
| 3. | Ubicación de barriles y tanques | None |
| 4. | Conexión de tuberías | None |
| 5. | Disposición o acomodamiento de los materiales por capa | None |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 7.0 | 150.0 | 1050.0 | |
| Equipment | STAM con tanque de 450 litros | Sistema | ||||
| Equipment | STAM con tanque de 1100 litros | Sistema | ||||
| Equipment | STAM con tanque de 2500 litros | Sistema | ||||
| Construction material | None | None | 2.0 | 1210.0 | 2420.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 6.0 | 66.0 | 396.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 2.0 | 66.0 | 132.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 3.0 | 242.0 | 726.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 1.0 | 260.0 | 260.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 2.0 | 120.0 | 240.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 1.0 | 14000.0 | 14000.0 | |
| Other | None | None | 2.0 | 30.0 | 60.0 | |
| Other | None | None | 5.0 | 30.0 | 150.0 | |
| Other | None | None | 4.0 | 10.0 | 40.0 | |
| Other | None | None | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | |
| Other | None | None | 18.0 | 275.0 | 4950.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 24824.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 761.71 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Programa de Gestión comunitaria de la cuenca del río Dipilto.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Limpieza de materiales del primer filtro que consiste en sacar y lavar el piedrín fino para volver a acomodar | Después de cada lavada de café |
| 2. | Reemplazo de los materiales del filtro (excepto la piedra volcánica) | Cada 2 años |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Lavado de materiales | días/hombre | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | piedrín de 1/8´´ | None | 2.0 | 30.0 | 60.0 | |
| Construction material | Piedrín de 3/4´´ | None | 5.0 | 30.0 | 150.0 | |
| Construction material | arena | None | 4.0 | 10.0 | 40.0 | |
| Construction material | Carbón | saco | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 700.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 21.48 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
La disponibilidad de los materiales del filtro en la zona y el transporte hacia las comunidades.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
En la zona solo hay disponibilidad de aguas superficiales
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
La zona corresponde a un área protegida de la cordillera de Dipilto y Jalapa.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Los usuarios de la tierra que implementan esta tecnología son todos productores de café.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
Ja
Specify:
Escrituras públicas
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Water availability and quality
irrigation water availability
Socio-cultural impacts
health situation
land use/ water rights
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quality
surface runoff
excess water drainage
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| landslide | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
Todos los productores que cuentan con infraestructura productiva de beneficio húmedo en la cuenca implementan el sistema de tratamiento de aguas mieles.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
Solo aplican la tecnología los beneficiarios del Programa de Gestión Comunitario de la cuenca del Rio Dipilto.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Permite mejorar las condiciones de higiene en la finca |
| Reduce la contaminación de las fuentes de agua por el vertido de aguas mieles. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Materiales del sistema de fácil manejo para instalación del sistema. |
| Adaptación a todo tipo de condiciones topográficas. |
| Aceptación de usuarios de la tierra. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Requiere mantenimiento permanente por lo que el usuario de la tierra debe adaptarse a su uso | Una vez que el productor conoce sobre el uso y mantenimiento del sistema el sistema trabaja correctamente. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| No siempre se realiza el manejo adecuado del sistema. | Apropiando al productor y trabajadores de la finca sobre el uso del sistema |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1
- interviews with land users
1
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
3
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
21/03/2019
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Manual sobre el uso y mantenimiento de los STAM, Juan Carlos Plama, 2018
Available from where? Costs?
Programa de Gestión comunitaria de la cuenca del Río Dipilto
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links