Cолнечные теплицы [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Гармхонаи офтоби
technologies_1032 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Выращивание культур в закрытом грунте, получение урожая круглый год
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
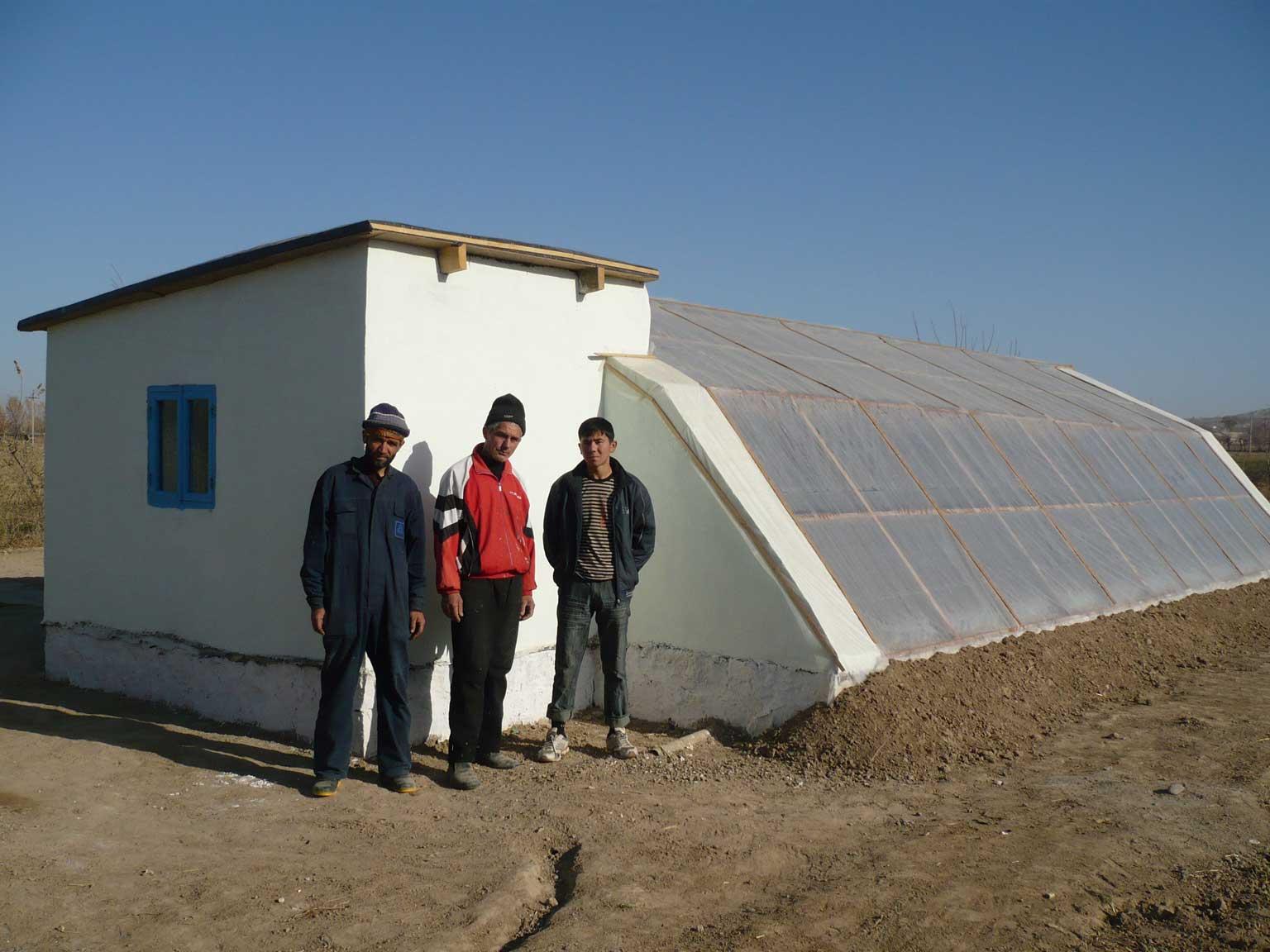
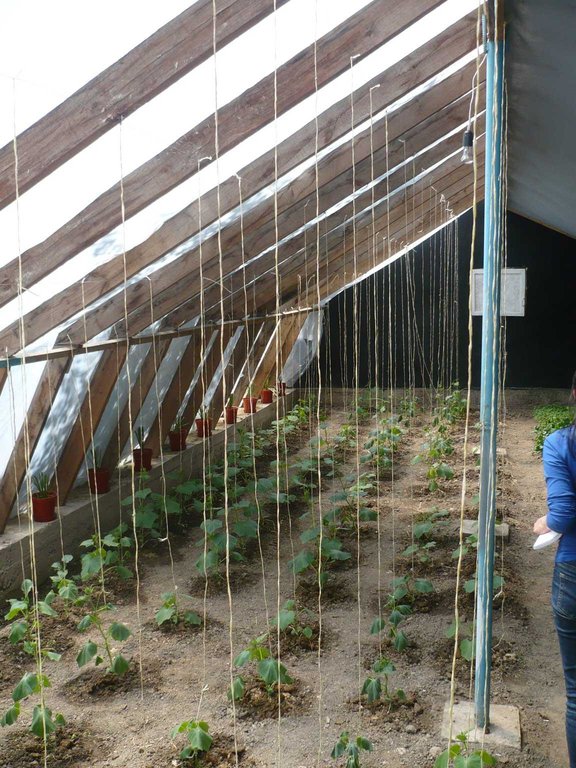
Производство овощей в закрытом грунте, при снижении тепло потерь за счёт применения теплоизоляции и максимального использования пассивной солнечной энергии. В этом теплицы можно использовать круглый год не зависимо от погодных условиях особенно зимой можно выращивать овощных культур за счёт тепло хранение самого теплицы без использование горючих материалов.За вегетационный пириди можно получит 3 - 4 урожая.
Назначение технологии: Предохранение высаженных растений от весенних и осенних похолоданий и даже заморозка, естественное продления вегетативного периода для созревания растений и получении продукции круглый год.
Основные действия и вложения: Выбор конструкции теплицы, выбор культур, эффективное проветривание и полив, ведение агротехники, борьба с заболеваниями против вредителей и болезней. Уход за почвой: обновление, дезинфекция почв, мульчирование, биогумус и капельное орошение в теплицах.
Природная\социальная обстановка: В условиях экстремального климата, засолённых почв, непредсказуемой погоды (заморозков), дефицита воды эксплуатируется много лет этот вид теплицы.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Хатлонская область, Носири Хусравский рн
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
2005 г. построена первая экспериментальная теплица на основе чертежей интернета. в дальнейшем технология была адаптирована фермерами с применением новаций- дождевания, более выгодного дизайна и пр.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Вегетативный период (дни): 150Вегетативный период по месяцам: декабрь- апрель. Второй вегетативный период (дни) : 180. Второй вегетативный период по месяцам: март - август

Settlements, infrastructure
Comments:
Основные проблемы землепользования (по мнению составителя): Это технология пользуется в условиях засолённой почвы, дефицит воды для полива растении, также предусмотрено при изменение климата
Основные проблемы землепользования (по мнению землепользователя): Способ интенсивного землепользования и получения раннего урожая
Будущее землепользование (после внедрения УЗП технологии): Пашня: Ca: выращивание однолетних
Ограничение поселения
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Cropland
- Annual cropping

Settlements, infrastructure
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Водопотребление: смешанное богарно-орошаемое, смешанное богарно-орошаемое, полностью орошаемое
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
- A3: Soil surface treatment
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.1: No tillage

vegetative measures
- V5: Others

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences

management measures
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level
Comments:
Основные мероприятия: инженерные
Второстепенные мероприятия: агрономические, связанные с использованием растительности, управленческие
Тип агрономических мероприятий : ранняя посадка, сменное возделывание культур, мульчирование, навоз / компост / остатки, ротация / под паром, разрушение уплотненного верхнего слоя почвы, обработка почвы без оборачивания пласта
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

physical soil deterioration
- Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities

biological degradation
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
Comments:
Основные типы деградации: Фб (Pu): потеря биопродуктивной функции из-за других деятельностей
Второстепенные типы деградации: Эв (Et): потеря верхнего слоя почвы, Бк (Bq): уменьшение количества / биомассы
Основные причины деградации: изменение температуры (адаптации к изменению климата), засуха (в случае засухи экономия воды), бедность / богатство (доход от теплицы), наличие работы
Второстепенные причины деградации: управление землей
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Основная цель: реабилитация / восстановление голых земель
Второстепенные цели: предотвращение / сокращение деградации, предупреждение деградации земель
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
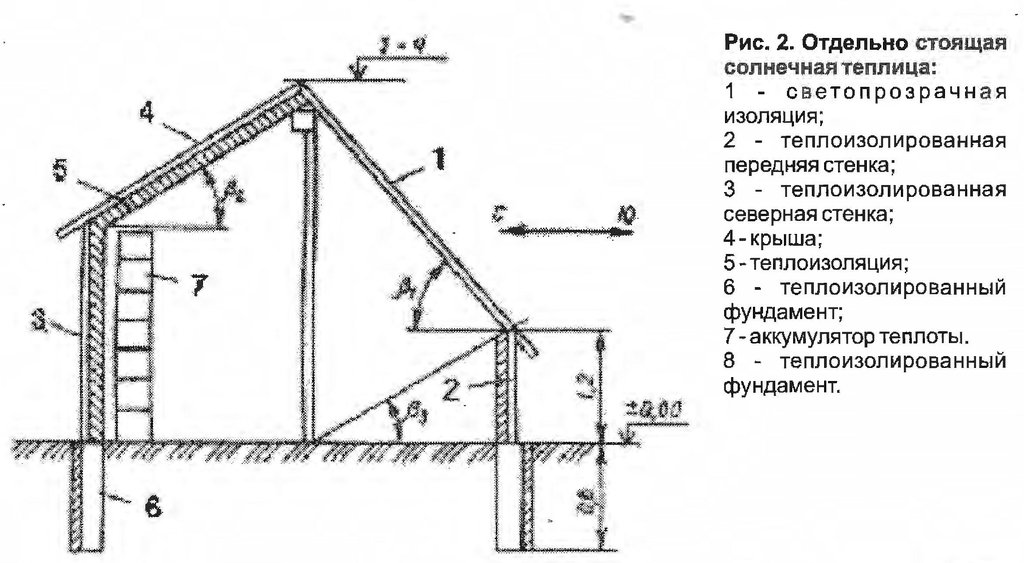
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
На рисунке отображена схема солнечной теплицы. Так ,как это теплица отличается от других обычных тем что у этого ест три стены по назначению. Каждая сторона стенки должно правильна расположенный точна как по схеме по направлению солнце. Основная стена является как тепло сохраняющий покрашено чёрным краской. боковая стена покрашен белым краской это как отражатель солнечного луча . Крыша покрывается полиэтиленовым пленкой.
Место расположения: Южный таджикистан. Н.Хисравский район
Дата: 2011. 05.0 5.
Необходимые технические навыки для работников: средний
Необходимые технические навыки для землепользователей: средний (нужны базовые знания по агротехнике)
Основные технические функции: исскуственная консервация почвы
Вторичные технические функции: контроль дождевых брызг, улучшение земляного покрова, повышение органического вещества, повышение наличия питательных веществ (снабжение, переработка отходов,...), сбор воды / повышение водоснабжения, повышение биомассы (количество)
Ранняя посадка
Пояснение: практически круглогодично
Следующие посадки
Пояснение: 3-4 раза в году
Ротация
Пояснение: обновление раз в 3 года
Выравнивание: -по контуру
Растительный материал: Др: другие
Расстояние по вертикали между рядами / полосами / участками (м): 0.3
Расстояние между рядами / полосами / участками (м): 0.7
Изменение типа землепользования
Author:
Каландаров Р., г.Душанбе. ул.Герцина 3.
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | выращивание рассады в горшочках | |
| 2. | выращивание рассады в горшочках | |
| 3. | высадка рассады | |
| 4. | высадка рассады | |
| 5. | полив, агроуход | |
| 6. | полив, агроуход | |
| 7. | борьба с заболеваниями | None |
| 8. | борьба с заболеваниями | |
| 9. | вертикальная подвязка | |
| 10. | обучение фермеров | периодически |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | высадка рассады | человек/день | 100.0 | 5.0 | 500.0 | 50.0 |
| Labour | борьба с заболеваниями | человек/день | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| Labour | обучение фермеров | человек/день | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 |
| Labour | Полив, ремонт теплицы | теплица | 10.0 | 130.0 | 1300.0 | |
| Plant material | семена | теплица | 10.0 | 50.0 | 500.0 | 50.0 |
| Plant material | компост, навоз | теплица | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| Plant material | пестициды | теплица | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| Construction material | Материал | теплица | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 50.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 4000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4000.0 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | проветривание, полив, температурный режим | постоянно |
| 2. | смена почвы, улучшение плодородия | раз в 3 года |
| 3. | борьба с заболеваниями растений | по сезонно |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | проветривание, полив, температурный режим,смена почвы, улучшение плодородия,борьба с заболеваниями растений | теплица | 10.0 | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 50.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 2000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2000.0 | |||||
Comments:
Инструменты: оборудование для сбора воды, опрыскиватели
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
труд- добровольный вклад
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Термический класс климата: субтропики
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Землепользователи, применяющие данную технологию, в основном среднестатистические
Плотность населения: 50-100 человек/км2
Годовой прирост: 2% - 3%
Ориентация производства: пропитание (для собственного потребления), смешанное (пропитание/ продажа)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- leased
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
risk of production failure
product diversity
Income and costs
farm income
diversity of income sources
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
evaporation
Soil
soil cover
nutrient cycling/ recharge
soil organic matter/ below ground C
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | not well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not known |
| local windstorm | not known |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
| понижению температуры | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
100% семей землепользователей применяют эту технологию без дополнительной материальной поддержки
15 семей землепользователей применяют эту технологию без дополнительной материальной поддержки
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
быстрые выгоды для получение овощных культур зимних и неблагоприятных погода Как можно сохранять устойчивость или усилить? по мере возможности использования теплиц по расчету от 10 до 15 лет |
| защита от изменения климата |
|
технология разработан на долгосрочный использования для адаптации к изменения климата Как можно сохранять устойчивость или усилить? при случаях дефицита воды или повешения или понижения температур максимально можно использовать для получении продукции |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| высокая стоимость конструкции и материалов | компромисс между стоимостью и неэффективностью |
| теплица рассчитан для вырашивание овощных культур | разрабатывается другая технология |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
www.ecocentre.tj
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules