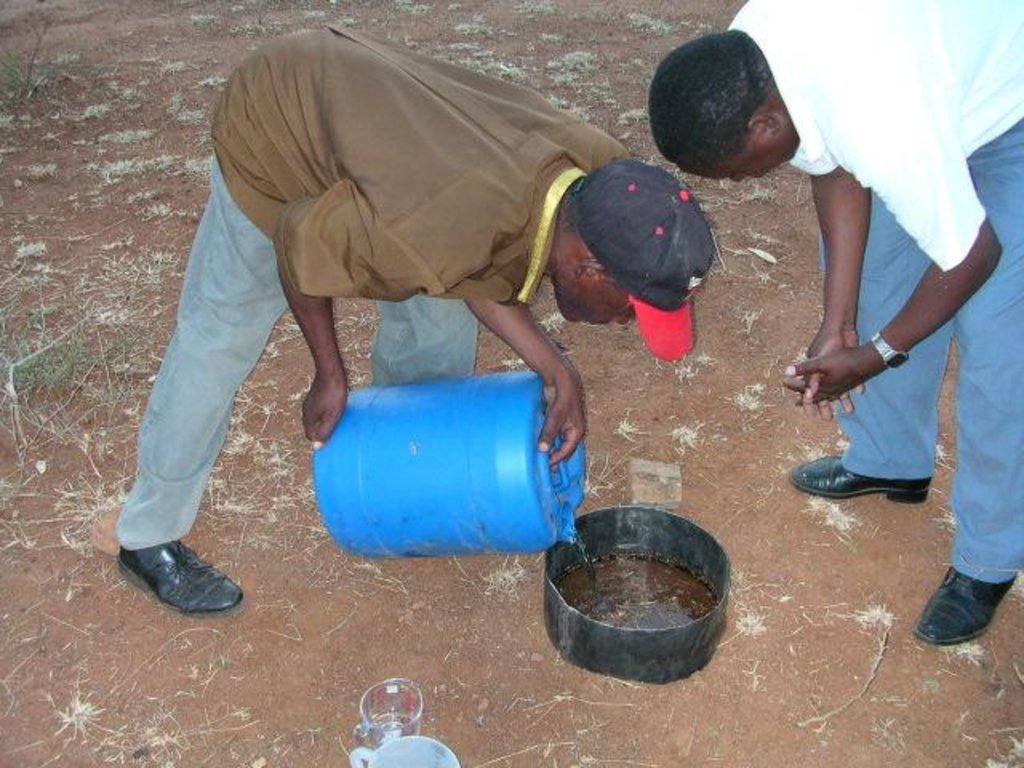
Farmer Field Schools [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Philippe Zahner
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2569 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Duveskog Deborah
deborah.duveskog@gmail.com
FAO
كينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Callejones de piñón con forrajes intercalados [المكسيك]
La tecnología consiste en un sistema agrosilvopastoril con árboles de Pinus cembroides (pino piñonero) alineados een bordos ─en un terreno con suelos calizos previamente subsoleado─ conformando melgas (callejones) para con cultivos anuales para grano y forraje, con pastoreo libre eventual por períodos muy breves.
- جامع المعلومات: BENJAMIN SANCHEZ BERNAL
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
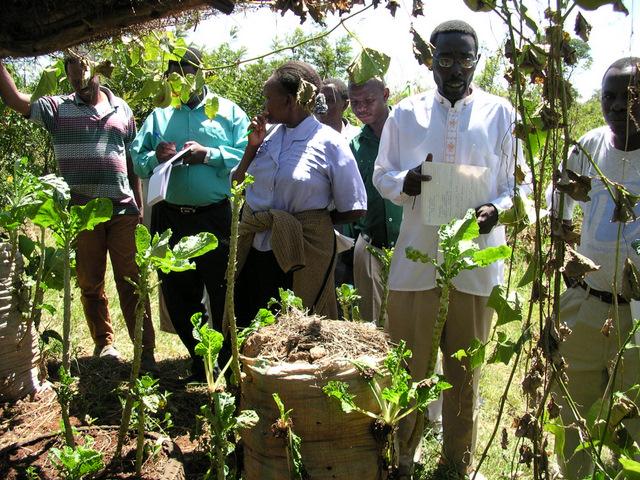
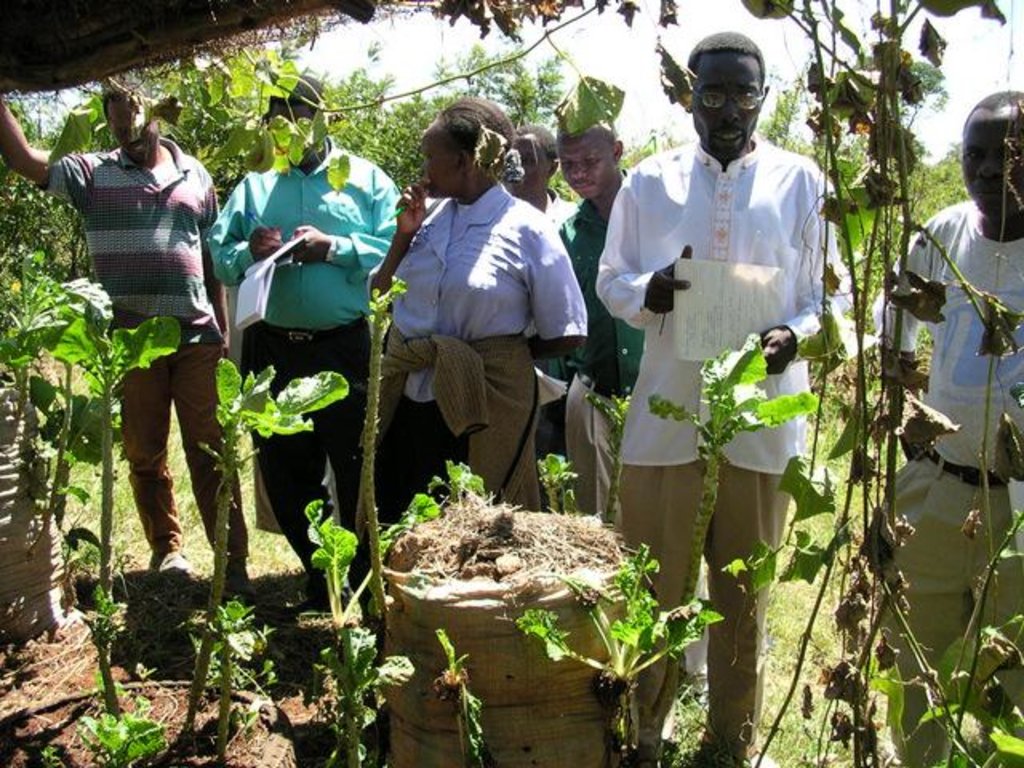
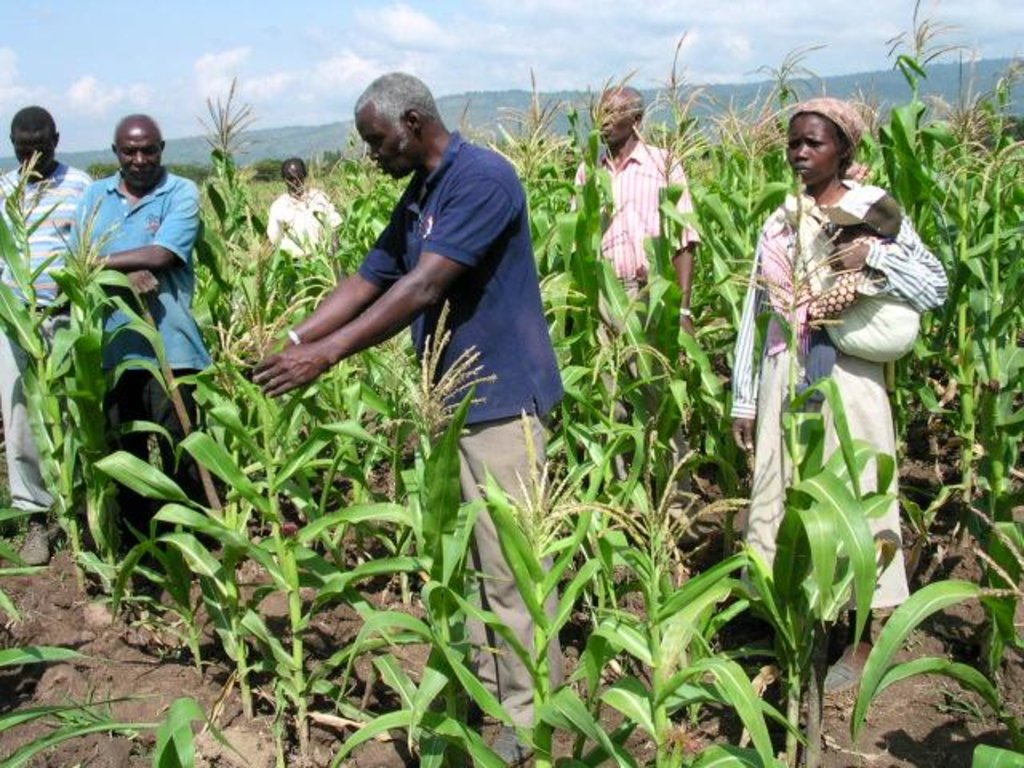
A Farmer Field School (FFS) is a community-based practically-oriented field study programme.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: It is usually a time-bound activity (generally one agricultural production cycle), involving a group (commonly 20-30) of farmers, facilitated by agricultural advisors or – increasingly – by other farmers. The FFS provides an opportunity for farmers to learn together, using practical, hands-on methods of discovery-based and participatory learning.
Methods: The methods emphasise observation, discussion, analysis, collective decision-making, presentation and taking appropriate action. Discussion and analysis are important ways to combine local indigenous knowledge with new concepts and bring both into decision-making. The aim is to develop participants’ decision-making and problem solving capacity among farmers. The process builds self-confidence (particularly for women), encourages group control of the process, and builds management and leadership skills. Although FFS are time-bound, many groups formalise their relations and continue study or action projects, including FFS on other subjects, after the FFS learning cycle is completed. The Farmer Field Schools on Integrated Land and Water Management (ILWM) in eastern and central Kenya focus on learning about how to improve management of land and water resources both on individual plot and farm level and within ‘landscapes’ and communal lands; including local watersheds, river-valleys, forested hill-tops, grazing lands, eroded gullies etc. Each FFS group experiments practically on selected SLM practices/ measures. All learning takes place in the field and farmers usually meet once per week at a selected host farm in their locality to monitor their field experiments and to discuss emerging issues. Trained facilitators, usually agricultural advisors, guide farmers in their observation and analysis of what is taking place in the field. Local farmer innovations are identified to feed indigenous knowledge into the FFS process: Innovators visit FFS groups or FFS members visit innovators farms to share their knowledge.
Other important information: The FFS process combined with the promotion of farmer innovation has proven to contribute to strong and cohesive groups that are able to make informed decisions and change cultural and practical behaviour in order to improve their production and land management. The process also builds self-confidence, and empowers especially women to take on leadership roles in the community. The impacts observed of FFS thus have strong biophysical and social dimensions.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Eastern and Central Kenya
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mwingi, Kitui and Nakuru Districts
Map
×2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (community organisational building for collective action and collective storage and marketing of products)
Support farmers’ knowledge levels and decision making capacity in relation to sustainable land and water management Raise farmers’ yields in a sustainable manner and ultimately contribute to increased net farm income Strengthen community organisation and collective efforts
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Land degradation, climatic variability and loss of agricultural biodiversity, Farmers focus on their own farms and income and lack of interest for wider watershed / environment
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
Ministry of Agriculture
- منظمة دولية
FAO
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | تفاعلي | |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | |
| الرصد/التقييم | غير موجود | |
| Research | غير موجود |
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي بشكل أساسي، بدعم من متخصصي الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
اشرح:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
شكل التدريب:
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- دورات
المواضيع المغطاة:
Agricultural advisors were trained in the FFS approach and in ILWM topics through a total of four weeks of training. Farmers were trained in FFS through season-long FFS learning where farmers meet at a host-farm weekly to carry study activities.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
Name of method used for advisory service: Participatory extension; Participatory extension with season-long regular interaction between farmers and agricultural advisors. At a later stage also strong farmer-to-farmer extension
The approach requires an attitude shift among agricultural extension workers to become more client-orientated.
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- 1,000000-100،000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international: 60.0%; government: 20.0%; local community / land user(s): 20.0%
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
yield increase of more than 200% has been recorded frequently
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
the applied practices have spread from participants to neighbours in the community
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
improved gender relations and division of farm workload, resistance to drought and improved livelihoods and life satisfaction in general
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
all participants fall in the poor or medium poor category and therefore the project has contributed to reduced poverty levels
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
- الوجاهة والضغط الاجتماعي/التماسك الاجتماعي
- الانتماء إلى حركة/ مشروع/ مجموعة/ شبكات
- friendship and collective spirit among group membe
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
Graduated FFS groups have organised themselves into a network and farmer organisations that have taken on collective activities following the end of the initial project. In some cases this has included starting up self-financed new FFS groups.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The collective action created in communities to deal with and manage their own resources. |
| Improved capacity of farmers for problem solving and innovation in ISWM. |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| A top-down and patronising attitude towards farmers are common among agricultural staff and experts, which prevents equal and trustful relationships | Institutionalisation of participatory extension is thus needed with a change in mindset among government and other agricultural support staff. |
| The various government bodies and ministries responsible for land and water issue often operate individually without strong synergie | A stronger collaboration is needed between ministries especially Ministry of Water and Ministry of Agriculture in order to deal effectively with land and water aspects in an integrated manner. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Duveskog D. 2001. Adapted from A Study Guide for Farmer Field Schools: Water Harvesting and Soil Moisture Retention.FAO-IIRR. 2006. Discovery-based Learning on Land and Water Management: Practical Guide for Farmer Field Schools.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Callejones de piñón con forrajes intercalados [المكسيك]
La tecnología consiste en un sistema agrosilvopastoril con árboles de Pinus cembroides (pino piñonero) alineados een bordos ─en un terreno con suelos calizos previamente subsoleado─ conformando melgas (callejones) para con cultivos anuales para grano y forraje, con pastoreo libre eventual por períodos muy breves.
- جامع المعلومات: BENJAMIN SANCHEZ BERNAL
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية