Participatory technology development [الجمهورية العربية السورية]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Francis Turkelboom
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2631 - الجمهورية العربية السورية
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Tubeileh Ashraf
A.Tubeileh@cgiar.org
الجمهورية العربية السورية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bruggeman Adriana
The Cyprus Institute (CyI)
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Cyprus Institute (The Cyprus Institute) - قبرص1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
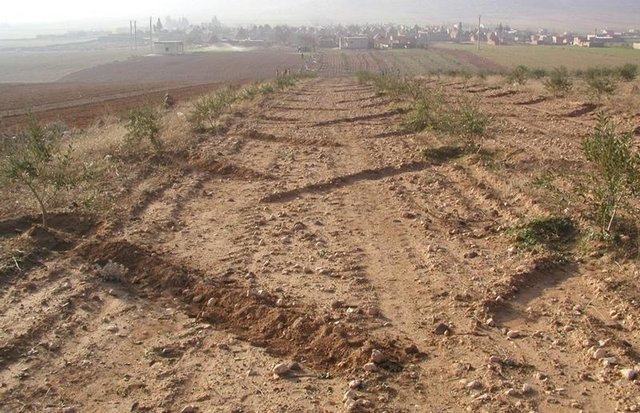

Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [الجمهورية العربية السورية]
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
- جامع المعلومات: Francis Turkelboom
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
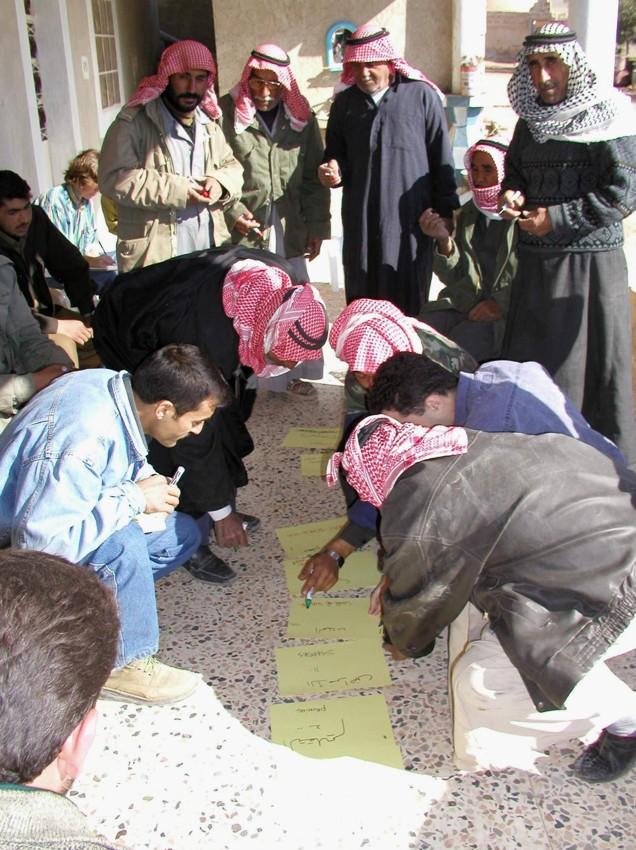
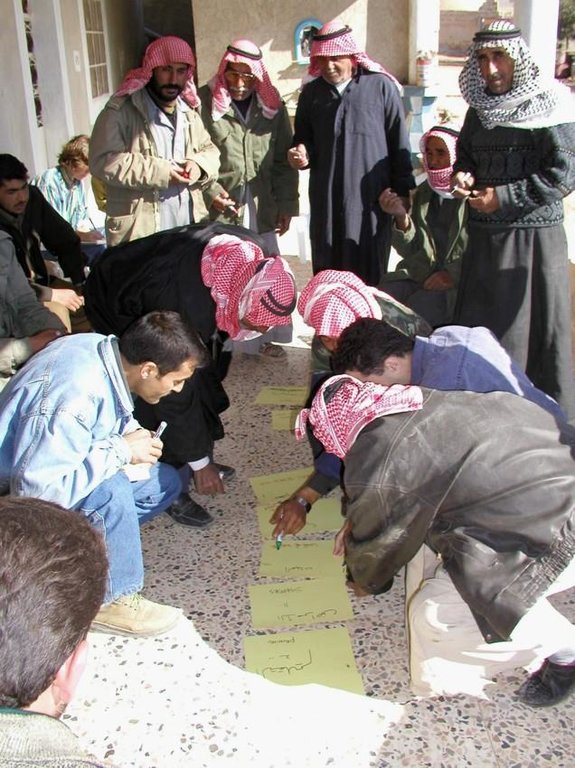
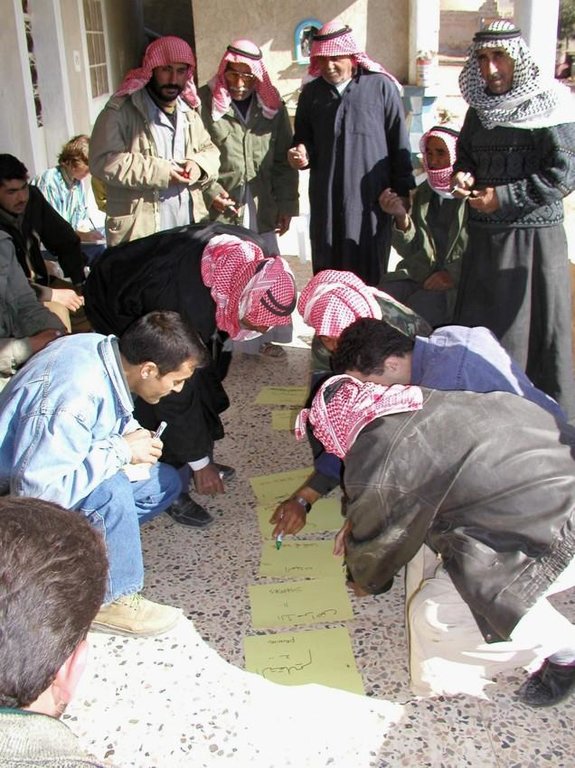
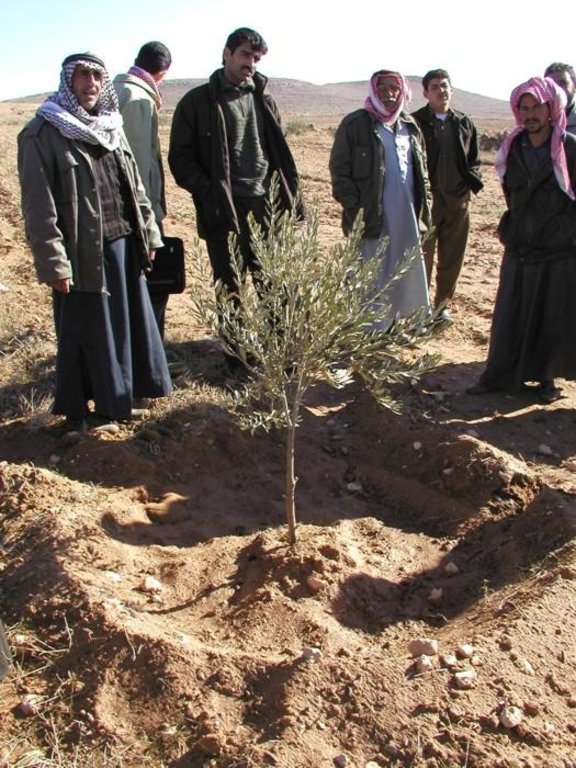
Participatory technology development, through close researcher-farmer interaction, for sustainable land management of olive orchards in dry marginal areas.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
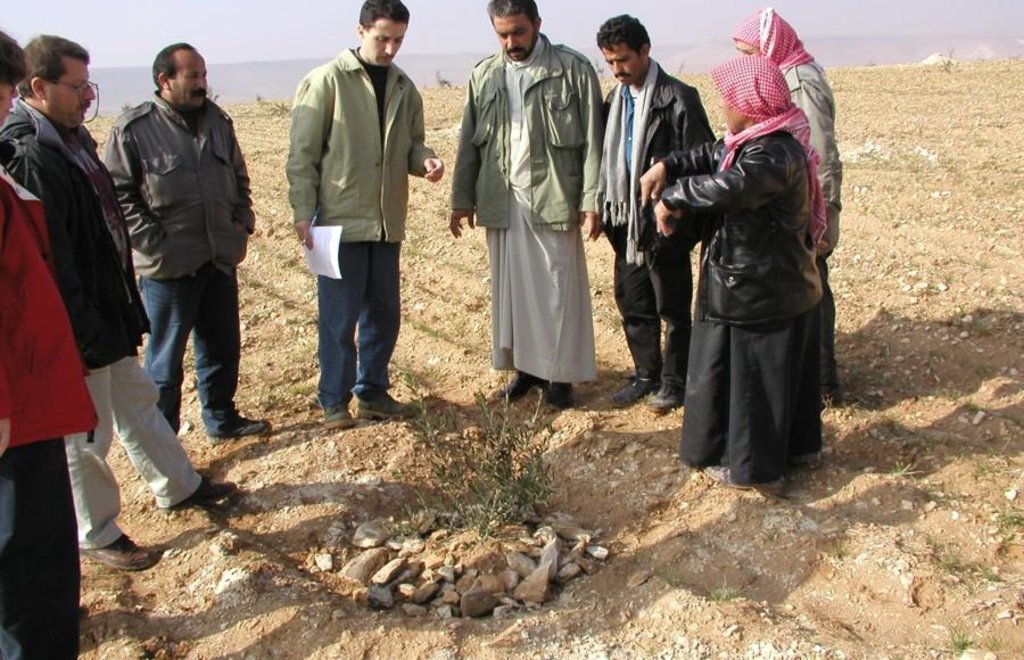
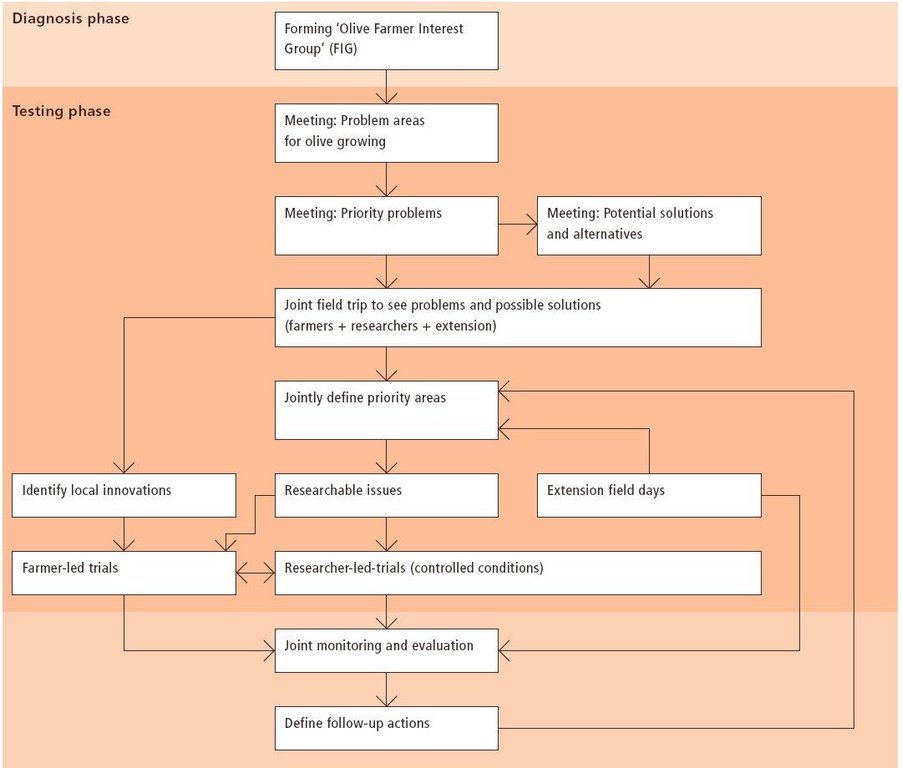
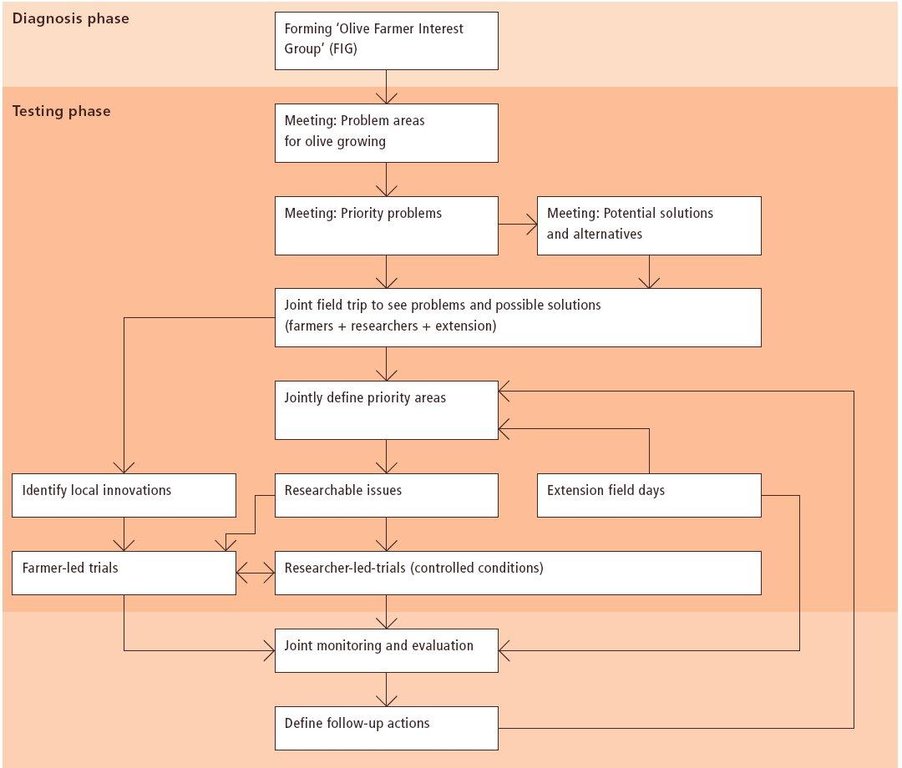
Aims / objectives: The purpose of participatory technology development is to gain from the synergy between indigenous knowledge and scientific expertise. The specific objective in this case was to develop and test water and land management techniques in order to sustainably improve olive production in a semi-arid area, while ensuring that the techniques were well adapted to local farming practices. The approach consists of group meetings, joint field trips, identification of local innovations, extension days, monitoring of farmer practices, and researcher-controlled experiments. The approach consists of a cycle with three major stages: a diagnostic phase, a testing phase, followed by monitoring and evaluation. In this case study, farmers were invited based on their interest in growing olives. Participation throughout the learning cycle was completely voluntary: no material or financial incentives were used (although they expected them in the beginning of the process). The role of farmers was to identify priority problems and potential solutions, to test new technologies on their farms, and to evaluate their suitability. Farmers observed the research experiment with water harvesting, and then adapted the technology to their needs. As shown, they built V-shaped bunds around their olive trees to capture rainwater runoff, but - contrary to the researchers??? suggestion - they continued to plough the olive orchards, as this is their standard weed control practice. Weeds attract sheep, lead to fires and compete for water with the olives. This simple runoff harvesting system is well adapted to farmers??? objectives, and their modification -the up-and-down slope furrows created through ploughing - actually serves to increase the efficiency of the water harvesting. The system is now being monitored by researchers to assess its technical and economic efficiency.
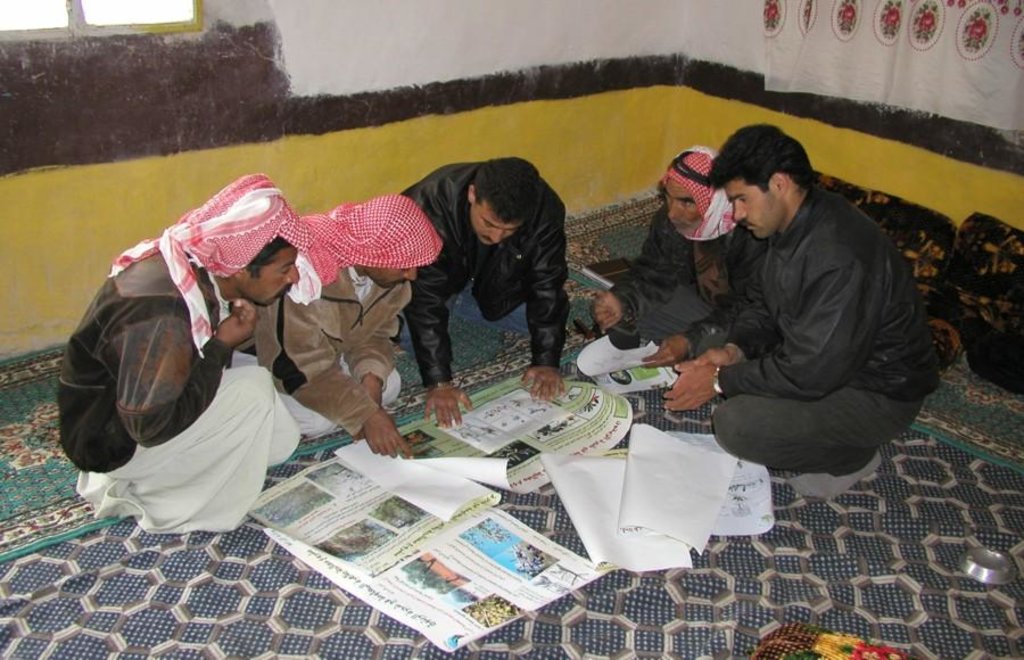
Methods: Improved farmer-researcher interaction helps farmers learn about a useful basic technique from researchers, while researchers learn in turn about potential improvements to the technology from local innovators. A community facilitator of ICARDA (International Centre for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas) facilitated the group discussions, and the researchers were asked to be open-minded to new approaches while conducting and monitoring field trials. The approach was tested by an interdisciplinary team of ICARDA as part of the ???Khanasser Valley Integrated Research Site???. This project aimed to develop local-adapted options for agriculture in dry marginal areas alongside a generally applicable integrated approach for sustainable land management in these zones.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
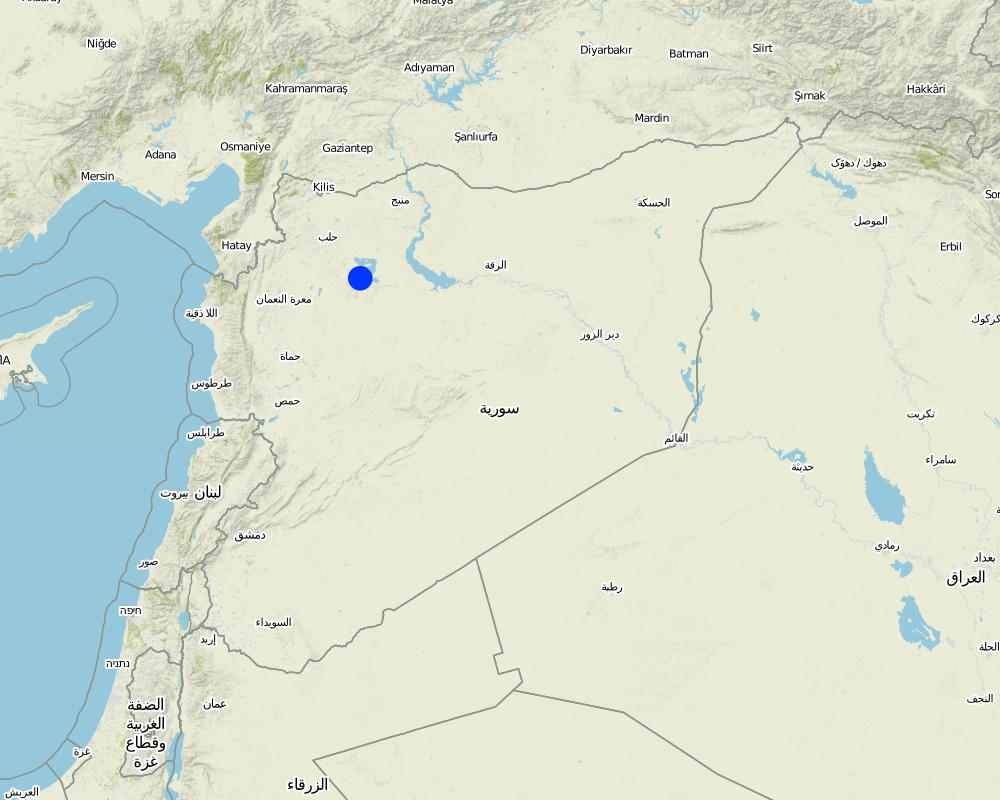
الجمهورية العربية السورية
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khanasser Valley
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
NW Syria
Map
×2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
- design, test and disseminate alternative technologies adapted to local conditions - strengthen local knowledge of SWC measures - strengthen joint learning by farmers and researchers
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The lack of appropriate ways to develop sustainable technologies to remedy loss of runoff water and poor olive growth -in the context of low-input agriculture on gentle undulating land in water scarce areas with an absence of soil conservation measures.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Water harvesting is considered expensive due to labour cost.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Identification of a low-cost water harvesting measure, which can be implemented during the off-season. Cost-benefit analysis.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
Difficulty in tilling the land when water harvesting structures are in place.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Integrating local innovations into the water harvesting system.
غير ذلك
- معيق
Uncertainty about appropriate size of micro-catchment area. Uncertainty about the amount of water harvested. Lack of technical expertise for olive crop husbandry in dry areas.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Researcher-controlled research and carry out farmer field days, desseminate and elaborate extension leaflets as a help.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Mainly men were involved, as most activities in olive orchards are managed by men. In addition, culturally bound gender segregation in public makes it difficult to organise gender-mixed meetings. Therefore, separate meetings were organised for women. In the case of one household, the de facto partner was a woman who takes most of the orchard-related decisions and does the work herself.
- researchers
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | سلبي | public meetings |
| التخطيط | تفاعلي | public meetings |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | completely conducted by land-users |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | interviews/questionnaires, public meetings; |
| Research | تفاعلي | on-farm; farmer experiments and controlled on-farm experiments |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي بشكل أساسي، بدعم من متخصصي الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
اشرح:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
شكل التدريب:
- في العمل
- من مزارع إلى مزارع
- اجتماعات عامة
المواضيع المغطاة:
Demand-driven training of olive husbandry techniques (eg pruning, grafting, pest management)
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
Farmer-to-farmer extension; Key elements: innovative farmers showed their technique to other olive farmers during farm visits
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- لا
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: soil moisture
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: water harvesting structures and management measures
technical aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: perceptions of the technology
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements; indicators: cost and benefits
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements; indicators: annual field survey using GPS
area treated aspects were regular monitored by None through measurements; indicators: annual farmer interview
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: There were few changes: interest in the farmers??? orchards and questions about the technology stimulated some other farmers to apply water harvesting.
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- علم الاجتماع
- الاقتصاد / التسويق
- تكنولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
Research was an important part of this approach. Technical and socio-economic topics were treated as follows: (1) Researcher-controlled on-farm experiments: this helped evaluate the impact of water harvesting design on the amount of water harvested and the olive crop response. (2) Monitoring of farmer-managed trials: to evaluate the performance of water harvesting under on-farm conditions. (3) Cos
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - ICARDA, Atomic Energy Commission Syria): 10.0%; international non-government (BMZ (Germany)): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 40.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Adoption of the furrow-enhanced runoff-water harvesting technique resulted in a concentration of scarce rainwater and nutrients in the basins around the olive trees. The consequence is a significant reduction of soil loss and runoff at the field level.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
This approach is now being applied in other ICARDA-coordinated projects in the region.
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
The complete PTD process/learning cycle needs outsider facilitation, but lack of outsiders will not stop farmers experimenting further by themselves. In terms of the technology itself, farmers can continue independently with water harvesting structures, as the system is very simple and relatively cheap.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Engagement of researchers with local innovators and thus interaction between scientific and indigenous knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: This approach can only be sustained if it is mainstreamed into national research and extension services.) |
| Attitude changes by researchers about farmers??? knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Building on local knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Capacity building of both land users and researchers (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Demand-driven technologies (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Time demanding | Less time needed after the first experience. |
| Appropriate facilitating skills required | Mainstreaming facilitation skills. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Tubeileh A and Turkelboom F (2004) Participatory research on water and soil management with olive growers in the Khanasservan Veldhuizen L, Waters-Bayer A, Abd de Zeeuw H (1997) Developing technology with farmers:
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [الجمهورية العربية السورية]
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
- جامع المعلومات: Francis Turkelboom
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية