Direct Payment System [سويسرا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Deborah Niggli
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Direktzahlungssystem
approaches_2602 - سويسرا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Bern, Institute of Geography (GIUB) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
23/06/2015
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
Financial aid of the government to land users to compensate for loss of financial output of crops.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
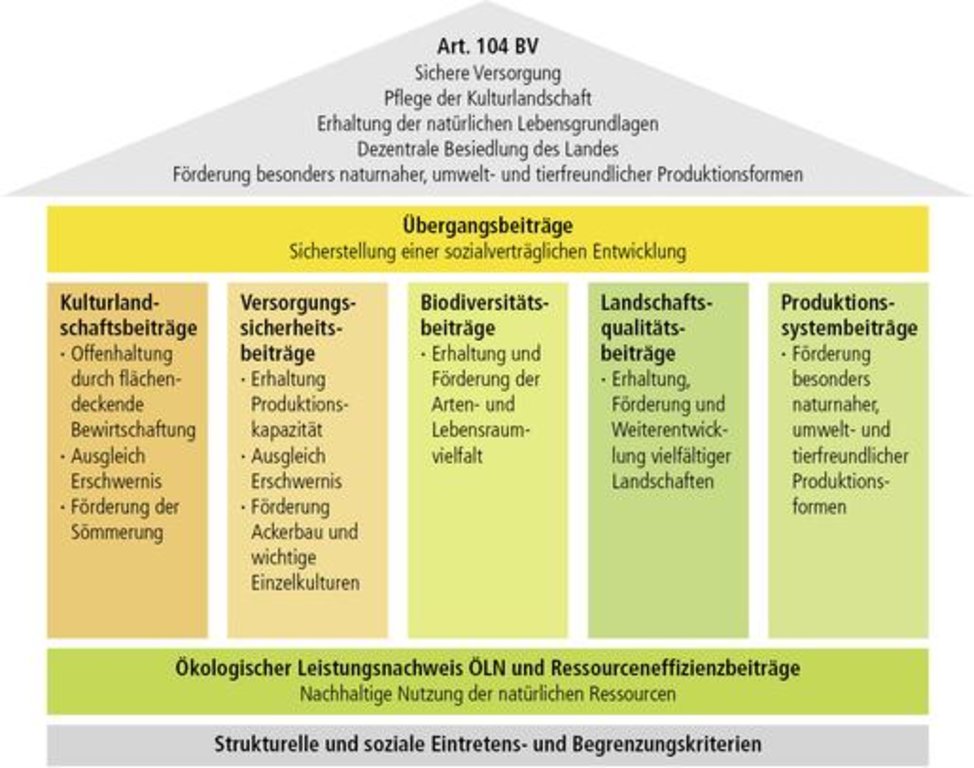
Aims / objectives: The main aim is to maintain agriculture and its production of goods. Because of the small amount of financial output for a land user and its products in Switzerland, there are direct payments to the land user paid per area size. These payments are substantial for every land user but especially in mountain regions of Switzerland to compensate land users for their work for nature and environment. Another goal is to keep the nutrient security of Switzerland alive. This goal can only be reached by supplementary payments in order to produce agricultural goods competitively.
Methods: Direct payments mean financial sums paid to a land user per area size. They differ from position of the field. A land user must apply for the direct payments in autumn. During winter the land user must mark his fields and their use online. Payments are reached three times during the following year: in June, autumn and winter.
Stages of implementation: The beginning of direct payments is in the 1980s when there were payments for livestock owners. Before there were never direct financial payments to land users but the agricultural products were financed by the government itself and land users got a fixed price for their products. 1989 land users got direct payments for the first time under the programs IP Suisse and ÖLN. Today payments are calculated by area size.
Role of stakeholders: The direct payment system is mainly a political issue. Politicians make budgets for the total amount of direct payments each year. Moreover, they can make new rules and obligations for land users. The land user must always adopt himself and his technology and crop rotation to these changes. This can be very difficult. Land users are represented by their unions but there is no space for individual opinions or direct participation in the system.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
سويسرا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bern
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Frienisberg
التعليقات:
Total Switzerland
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
1989
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Maintenance of a good financial situation for Swiss land users)
The system wants to support Swiss Agriculture on a financial basis. Because agricultural products are produced under swiss conditions regarding wages, soil prices etc. the products can not compete against other products from abroad. The direct payments close the gap between the theoretical value of a product and its end price in stores.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The system of direct payments gives wrong appeals to the land users. Because payments are made by area size land users want to expand their farm size even more. But there is also more work to do if a farm is bigger. The system also provokes cultivation of fields that are at risk for erosion or other consequences because it does not differ from fields that are at risk and fields that are not. It is only the size that matters.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Rentability of conservational agriculture and its technologies were often discussed because there may be losses at the beginning.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Because of financial payments losses of financial capital can be compensated.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
- منظمة غير حكومية
- الحكومة المحلية
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
إذا كان هناك العديد من الأطراف المعنية، قم بالإشارة إلى الوكالة الرائدة:
government
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | سلبي | |
| التخطيط | سلبي | |
| التنفيذ | الدعم الخارجي | |
| الرصد/التقييم | تفاعلي | |
| Research | غير موجود |
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي بشكل أساسي، بدعم من متخصصي الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
اشرح:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
شكل التدريب:
- في العمل
- مناطق العرض
المواضيع المغطاة:
There was also an overthinking on the side of land users. Some of them did not change environmentally good technologies after there were less payments for this technology because they saw the advantages of their technology. However, without a financial support at the beginning they would not have implemented new technologies.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
- في مراكز دائمة
وصف/تعليقات:
Advisory service is very adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- لا
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through measurements; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- الاقتصاد / التسويق
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
Research was carried out on station
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- > 1,000,000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (projects): 50.0%; national non-government (soil support program): 10.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc): 40.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| بذور | ممول بالكامل | |
- غير ذلك
| غير ذلك(حدد) | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| area size | ممول بالكامل | cultivation per ha |
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
There are payments for conservational agriculture and technologies. Therefore, SLM is applied there. However, there are also payments for conventional agriculture and technologies and the attractiveness to change a cultivation system is not very high.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
about 97%
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
- زيادة الربح (القدرة)، وتحسين نسبة التكلفة إلى العائد
- انخفاض عبء العمل
- المدفوعات/ الإعانات
- الوعي البيئي
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- لا
إذا كان الجواب لا أو غير متأكد، حدد ذلك وعلق عليه:
The current agricultural system in Switzerland can not run without direct payments and financial support of the land users.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The payments are a security of income for the land users. Therefore he continues his production of agricultural products. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The payment must be enough high so that it is accurate for the labour and work of a land user on the fields. This must also be a point regarding future payments.) |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| It is a fair system: a land user only gets paid for his work on a field. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: A good life for a land user and his family is possible through the financial aid of the direct payment system. This must be maintained.) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| A fixed product price would be the solution to higher payments. The situation from the beginning of the system was much better. | Product prices must be on a similar level. However, this is not possible. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The system provides some dependence for the land user. He can not produce competitively without supplementary payments. | Fair product prices and competitiveness would be the solution, but this is impossible to reach. |
| There are many differences during short time regarding the sum and conditions of direct payments. A land user has thereby no chance of adopting himself to the new conditions. | Payments must be stable during a longer time. Only then a land user is able to change his cultivation system. |
| The system leads to wrong cultivation of fields because a land user wants as much area size as possible. This endangers soil and can lead to erosion. | The system should be reduced to only not-endangered fields and provide payments for the non-cultivation of endangered fields. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية