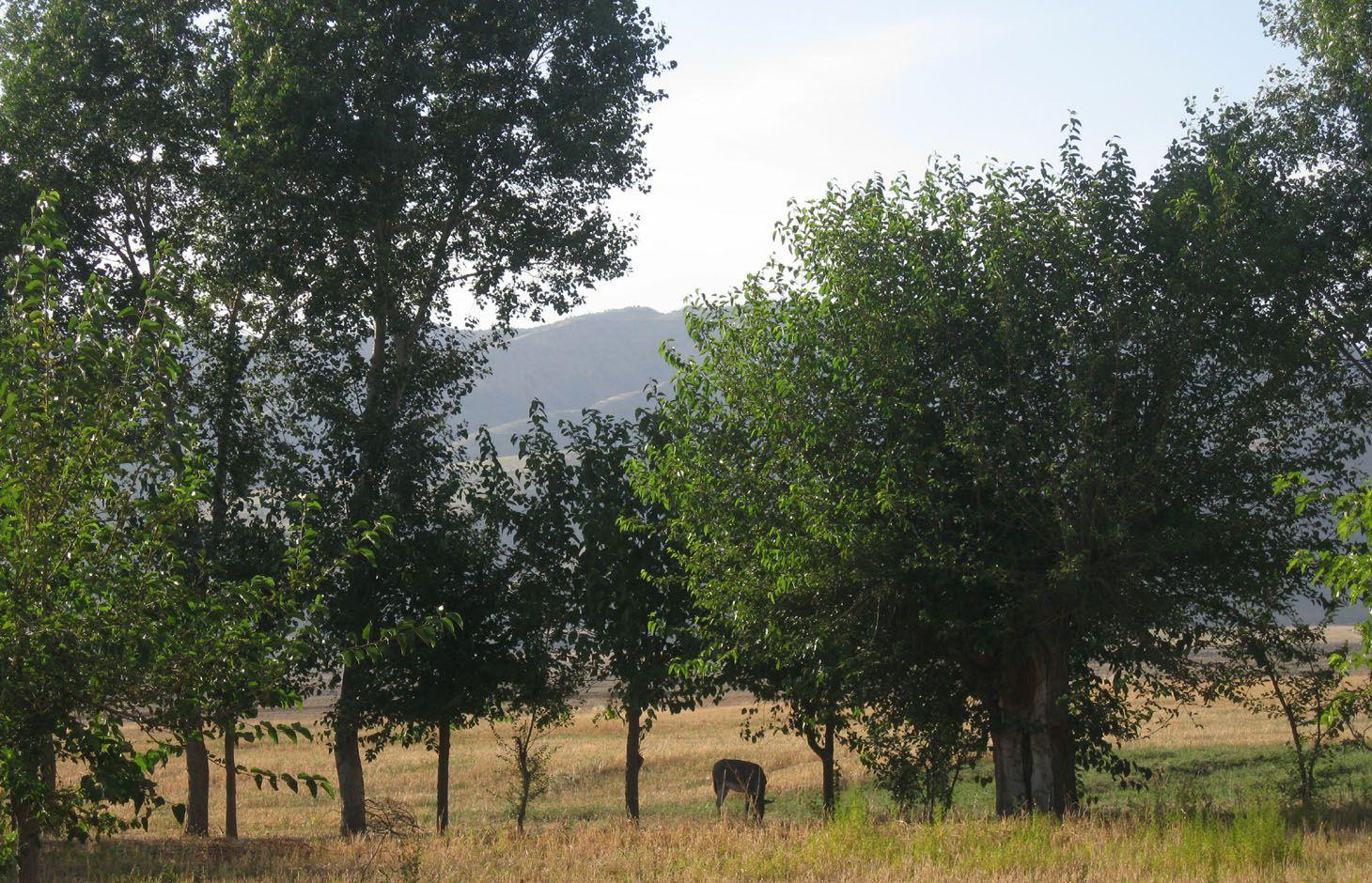
Current agroforestry: orchard with wheat intercropping [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Malgorzata Conder
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1134 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/08/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Current agroforestry of a degraded mulberry and apple orchard with wheat intercropping
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Since 1992 an area of around one ha has been owned by the farmer. He planted mulberry trees the same year. At that time, orchards were established in the whole surrounding area because the government decreed that a territory should have plenty of mulberry trees. Despite the government plan, all the land users of that area began to switch their orchards into wheat crops. Five years later the farmer planted apple trees within the mulberry orchard. The orchard had 200 mulberry and 100 apple trees. The motivation was to feed the working farmers of the fields around. Five years later the apple trees gave fruits. But only the first two years gave a good yield and income from selling them. Later on the fruits were just eaten by the farmer’s family. After another seven or eight years the farmer grew a wheat crop in between the tree lines. Nowadays it's the only remaining orchard in that area. Due to the lack of proper maintenance and water availability the orchard is degraded and the output is very low.
Purpose of the Technology: The government established a large territory of mulberry orchards, for three reasons: First to reduce the impact of natural hazards, second to increase silk production and last to improve fire wood availability. The planting of apple trees should be beneficial for farmers working in the surrounding crops and well as for the family, who sell the fruits and the mulberry leaves. As the yield started to decrease the wheat crop was established to have a bigger output for that crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Due to the government’s order to establish orchards, the local authorities provided the mulberry trees. Hence, it was in the responsibility of the farmer to plant the trees and to look after them by soil loosening and pruning. The latter activity must be done once in the first five years after planting. The farmer bought the apple trees himself as they were cheap at that time. To establish the wheat crop, ploughing, seeding, fertilizing and finally harvesting must be done. One person is supposed to guard the orchard and wheat crop every day. Yearly maintenance consists of soil loosening around the fruit trees and the above mentioned task for cropping. The maintenance of the orchard seems to be abandoned more and more, probably because the output decreases year by year.
Natural / human environment: The orchard is situated below Momandion village, on the very last foot slope before the valley plain begins and, hence, it has a slight slope,. In the past, orchards were numerous, but nowadays wheat crops have mostly replaced the orchard. As there is no fence and no one to control it regularly, livestock invades the property. During its first two years there was a water source, which had dried up by the time. The orchard is a relic being the only and last one in that area. Broken branches, unpruned trees and a trampled crop, show signs of insufficient control and maintenance and therefore of a gradual abandonment of the orchard.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Muminabad
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
- government
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Since 1992 it's property of the farmer
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Orchard with crop: Mulberry leaves, apples and wheat and mulberries
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Trampled and degraded soil as a consequence of no fences or control. Soil crusting and compaction because of lack in organic matter resulting in a low infiltration rate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water scarcity and low soil moisture, small yield of the fruit trees
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: In the past the wheat and apple yield was much higher thereby they were cash crops. As the yield decreased by then and he gets low yield the use them as food crops.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- أنظمة التناوب (تعاقب المحاصيل، البور، الزراعة المتنقلة)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
According to farmer it's 1 ha, according to GoogleEarth around 1.6 ha
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (monocropping, lack of maintenance)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Because if no fence), education, access to knowledge and support services (More agronomic/ technical advice needed)
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Location: Muminobod, South of Momandion, Obishur Watershed. Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (How to regenerate the poor soil and water conditions, which species are useful to plant etc)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat intercropping within orchard
Agronomic measure: vertical plowing
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, apple
Change of land use type: Mulberry and apple orchard combined additionally with wheat crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level: More pressure on natural resources because of additional wheat crop in the orchard
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Somoni
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,83
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
12.40
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying, transport and planting of mulberry trees, 10 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | نباتية | once, 1992 |
| 2. | Buying, transport and planting of apple trees, 5 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | نباتية | once, 1997 |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 497,4 | 497,4 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 311,0 | 311,0 | 33,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 808,4 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing vertically, 4 hours of labour, tractor and petrol | زراعية | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 2. | Buying (200 kg) and sowing wheat, 2 hours, 3 persons | زراعية | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 3. | Applying fertilizer, 2 hours, 1 person, 2 bucks à 50 kg | زراعية | once a year, september |
| 4. | Cutting wheat, 4-5 days (6 hours/ day), 4 people | زراعية | September, once a year |
| 5. | Guardening | زراعية | every day |
| 6. | loosening around trees (ca. on 1/3 of the trees), 4-5 trees a day | نباتية | every year, spring |
| 7. | pruning (ca. 1/2 of mulberry trees), 7-8 days (2-3 hours/ day), 3 persons | نباتية | every year, autumn |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 572,2 | 572,2 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 24,8 | 24,8 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Petrol | l | 25,0 | 28,5 | 712,5 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 82,8 | 82,8 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 76,6 | 76,6 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 1468,9 | |||||
التعليقات:
The cost were calculated for 1 ha, but one have to consider that an orchard and wheat crop is on the same plot. This means that there's not fully a wheat crop of 1 ha.
Mulberry seedling were paid by the government, apple trees by the farmer.
Machine use and petrol, are all included in the labour input in the establishment phase, as it was not separately mentioned by the farmer.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour is the most important input, but as it is done mostly by the farmer or the family itself it's mainly agricultural material as seedlings, seeds and fertilizer. Latter particularly as recurrent costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked1, mostly) and rolling (ranked 2)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, no rainfall from July to August) and medium (ranked 2, winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm))
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1) and mechanised (ranked 2, only for plowing)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, mainly subsistent, depending on yield more or less commercial) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
التعليقات:
Based on land user's Certificates
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
less apple and wheat production
خطر فشل الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
نوعية مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
More fertilizer and pesticides needed than in the past
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced crop production and fruit yield
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
less maintenance work
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Mulberries were shared with other people working next to the field (no fence)
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
negligible thanks to a little slope
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
Higher vegetation cover, which would make the land use more resistant to drought, more stable in case of floods and heavy rainfalls.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The orchard gave by-product as leaves for silk production and branches. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
It is the only orchard in the neighbourhood, which is why it would be worthy to maintain it. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Put more effort and labour into the orchard, currently only the wheat crops seems to be of interest for the farmer. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Currently the orchard is too old to get a good yield and maintenance activities are comparatively high. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Lack of maintenance and guarding or fencing. | More focus on the orchard as it has also ecological benefits. Enhance the farmer to put more labour into the orchard. |
| Show good examples of orchards and their resulting benefits. Round tables by and for farmers to share experiences. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية