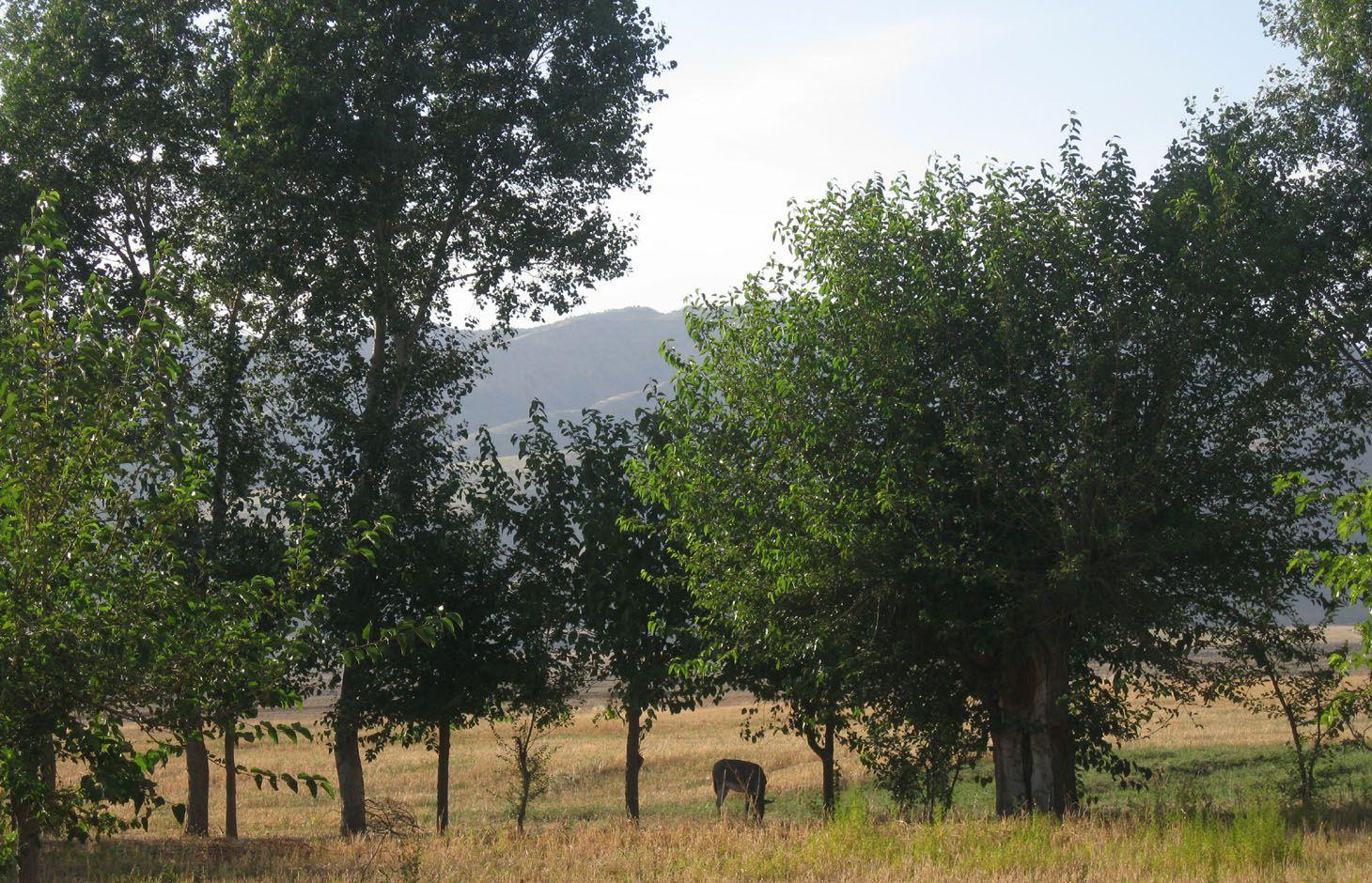
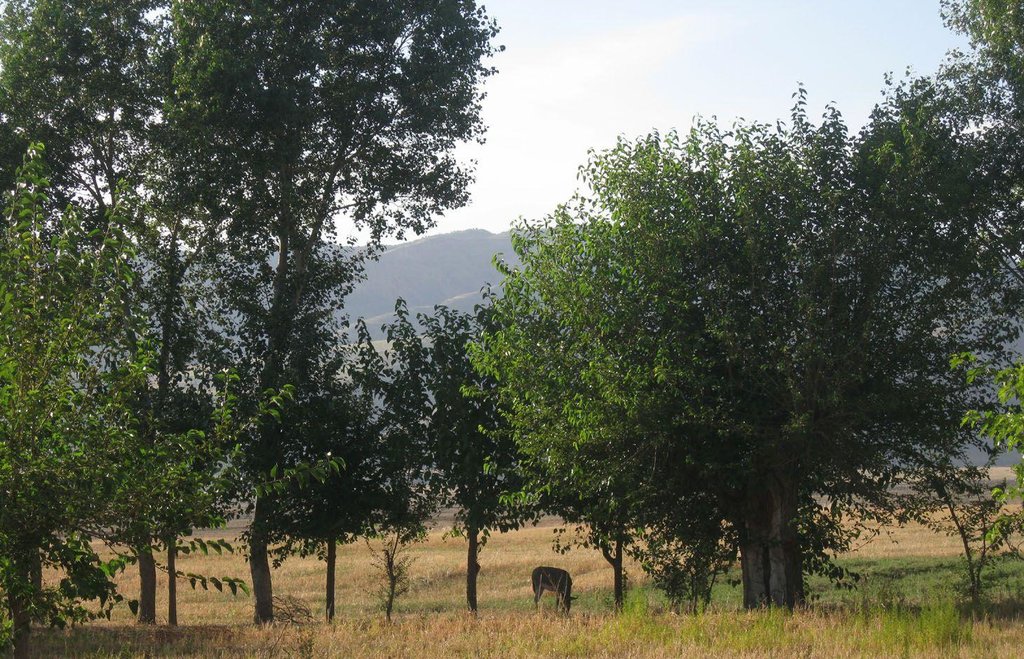
Current agroforestry: orchard with wheat intercropping [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Malgorzata Conder
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1134 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/08/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Current agroforestry of a degraded mulberry and apple orchard with wheat intercropping
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Since 1992 an area of around one ha has been owned by the farmer. He planted mulberry trees the same year. At that time, orchards were established in the whole surrounding area because the government decreed that a territory should have plenty of mulberry trees. Despite the government plan, all the land users of that area began to switch their orchards into wheat crops. Five years later the farmer planted apple trees within the mulberry orchard. The orchard had 200 mulberry and 100 apple trees. The motivation was to feed the working farmers of the fields around. Five years later the apple trees gave fruits. But only the first two years gave a good yield and income from selling them. Later on the fruits were just eaten by the farmer’s family. After another seven or eight years the farmer grew a wheat crop in between the tree lines. Nowadays it's the only remaining orchard in that area. Due to the lack of proper maintenance and water availability the orchard is degraded and the output is very low.
Purpose of the Technology: The government established a large territory of mulberry orchards, for three reasons: First to reduce the impact of natural hazards, second to increase silk production and last to improve fire wood availability. The planting of apple trees should be beneficial for farmers working in the surrounding crops and well as for the family, who sell the fruits and the mulberry leaves. As the yield started to decrease the wheat crop was established to have a bigger output for that crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Due to the government’s order to establish orchards, the local authorities provided the mulberry trees. Hence, it was in the responsibility of the farmer to plant the trees and to look after them by soil loosening and pruning. The latter activity must be done once in the first five years after planting. The farmer bought the apple trees himself as they were cheap at that time. To establish the wheat crop, ploughing, seeding, fertilizing and finally harvesting must be done. One person is supposed to guard the orchard and wheat crop every day. Yearly maintenance consists of soil loosening around the fruit trees and the above mentioned task for cropping. The maintenance of the orchard seems to be abandoned more and more, probably because the output decreases year by year.
Natural / human environment: The orchard is situated below Momandion village, on the very last foot slope before the valley plain begins and, hence, it has a slight slope,. In the past, orchards were numerous, but nowadays wheat crops have mostly replaced the orchard. As there is no fence and no one to control it regularly, livestock invades the property. During its first two years there was a water source, which had dried up by the time. The orchard is a relic being the only and last one in that area. Broken branches, unpruned trees and a trampled crop, show signs of insufficient control and maintenance and therefore of a gradual abandonment of the orchard.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Muminabad
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
- government
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Since 1992 it's property of the farmer
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Orchard with crop: Mulberry leaves, apples and wheat and mulberries
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Trampled and degraded soil as a consequence of no fences or control. Soil crusting and compaction because of lack in organic matter resulting in a low infiltration rate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): water scarcity and low soil moisture, small yield of the fruit trees
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: In the past the wheat and apple yield was much higher thereby they were cash crops. As the yield decreased by then and he gets low yield the use them as food crops.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept/Oct
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
According to farmer it's 1 ha, according to GoogleEarth around 1.6 ha
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (monocropping, lack of maintenance)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Because if no fence), education, access to knowledge and support services (More agronomic/ technical advice needed)
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เขียน:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Location: Muminobod, South of Momandion, Obishur Watershed. Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (How to regenerate the poor soil and water conditions, which species are useful to plant etc)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat intercropping within orchard
Agronomic measure: vertical plowing
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, apple
Change of land use type: Mulberry and apple orchard combined additionally with wheat crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level: More pressure on natural resources because of additional wheat crop in the orchard
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Somoni
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
4.83
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
12.40
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying, transport and planting of mulberry trees, 10 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once, 1992 |
| 2. | Buying, transport and planting of apple trees, 5 days (7 hours/day), 3 people | ด้วยวิธีพืช | once, 1997 |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 497.4 | 497.4 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 311.0 | 311.0 | 33.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 808.4 | |||||
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing vertically, 4 hours of labour, tractor and petrol | จัดการพืช | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 2. | Buying (200 kg) and sowing wheat, 2 hours, 3 persons | จัดการพืช | every year, spring (since 2007) |
| 3. | Applying fertilizer, 2 hours, 1 person, 2 bucks à 50 kg | จัดการพืช | once a year, september |
| 4. | Cutting wheat, 4-5 days (6 hours/ day), 4 people | จัดการพืช | September, once a year |
| 5. | Guardening | จัดการพืช | every day |
| 6. | loosening around trees (ca. on 1/3 of the trees), 4-5 trees a day | ด้วยวิธีพืช | every year, spring |
| 7. | pruning (ca. 1/2 of mulberry trees), 7-8 days (2-3 hours/ day), 3 persons | ด้วยวิธีพืช | every year, autumn |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 572.2 | 572.2 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 24.8 | 24.8 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Petrol | l | 25.0 | 28.5 | 712.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 82.8 | 82.8 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 76.6 | 76.6 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 1468.9 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The cost were calculated for 1 ha, but one have to consider that an orchard and wheat crop is on the same plot. This means that there's not fully a wheat crop of 1 ha.
Mulberry seedling were paid by the government, apple trees by the farmer.
Machine use and petrol, are all included in the labour input in the establishment phase, as it was not separately mentioned by the farmer.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour is the most important input, but as it is done mostly by the farmer or the family itself it's mainly agricultural material as seedlings, seeds and fertilizer. Latter particularly as recurrent costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked1, mostly) and rolling (ranked 2)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, no rainfall from July to August) and medium (ranked 2, winter and spring season with frequent rainfalls (700mm))
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1) and mechanised (ranked 2, only for plowing)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, mainly subsistent, depending on yield more or less commercial) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Based on land user's Certificates
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
less apple and wheat production
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
First 2 years water source, which dried out later on
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More fertilizer and pesticides needed than in the past
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced crop production and fruit yield
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
less maintenance work
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mulberries were shared with other people working next to the field (no fence)
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
negligible thanks to a little slope
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Higher vegetation cover, which would make the land use more resistant to drought, more stable in case of floods and heavy rainfalls.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The orchard gave by-product as leaves for silk production and branches. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
It is the only orchard in the neighbourhood, which is why it would be worthy to maintain it. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Put more effort and labour into the orchard, currently only the wheat crops seems to be of interest for the farmer. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Currently the orchard is too old to get a good yield and maintenance activities are comparatively high. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of maintenance and guarding or fencing. | More focus on the orchard as it has also ecological benefits. Enhance the farmer to put more labour into the orchard. |
| Show good examples of orchards and their resulting benefits. Round tables by and for farmers to share experiences. |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล