Usage of Gher boundary for cropping [بنغلاديش]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Gherer bunder upar nana prokar shakshabjee uthpadon
technologies_1171 - بنغلاديش
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Shaha Tapan Kuma
SRDI
بنغلاديش
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bhander Bidhan Kumar
SRDI
بنغلاديش
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI) (Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI)) - بنغلاديش1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
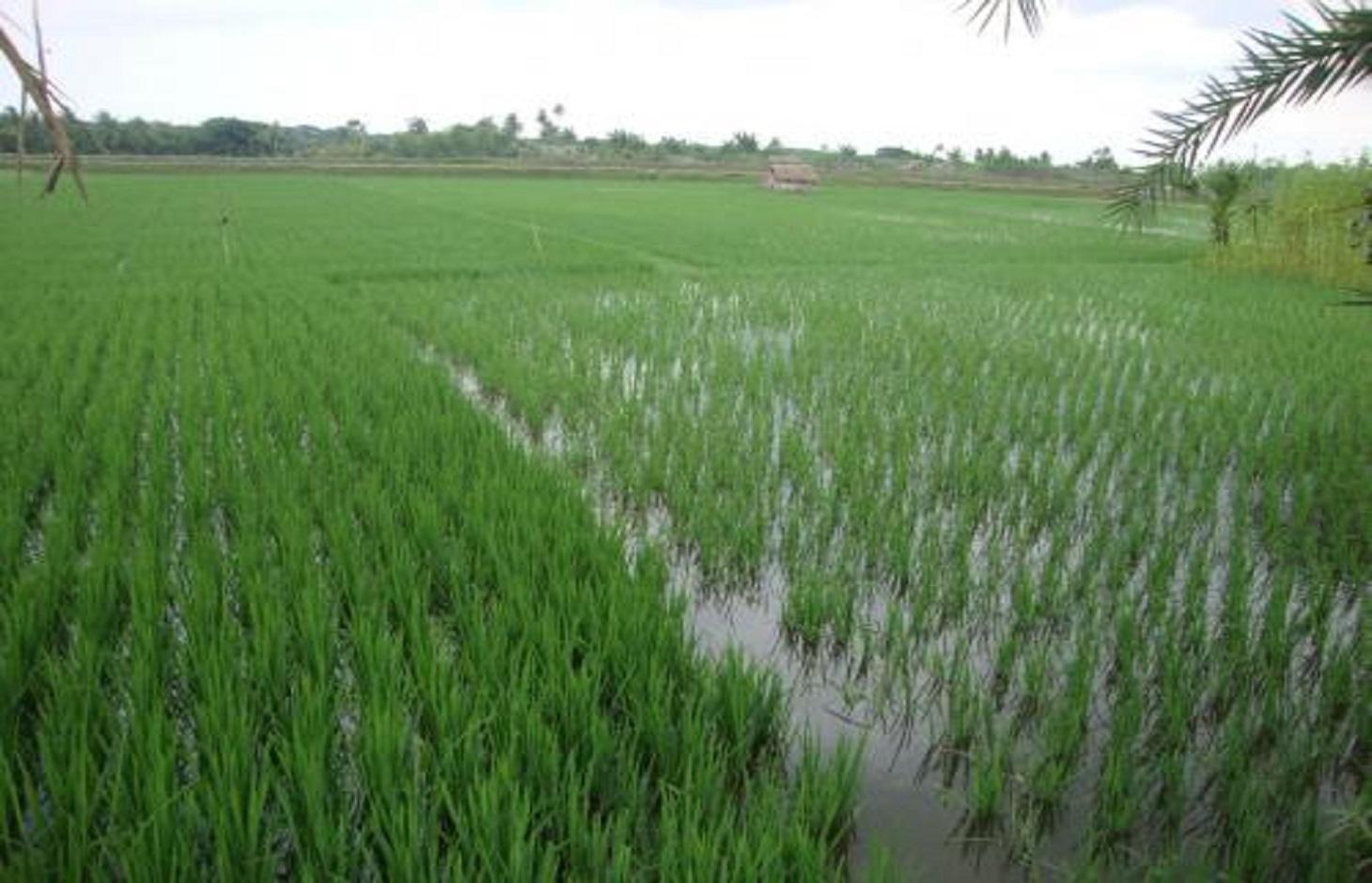
Gher (shrimp cultivation) boundary usage for multiple cropping.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
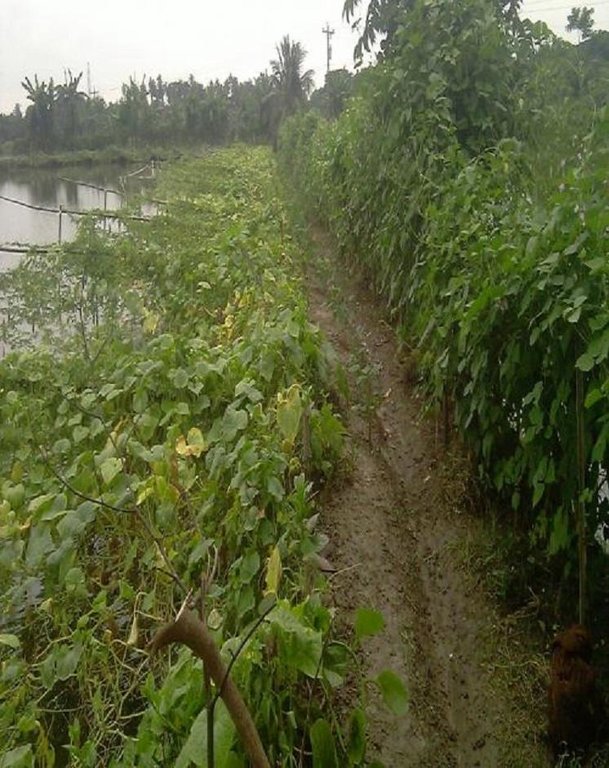
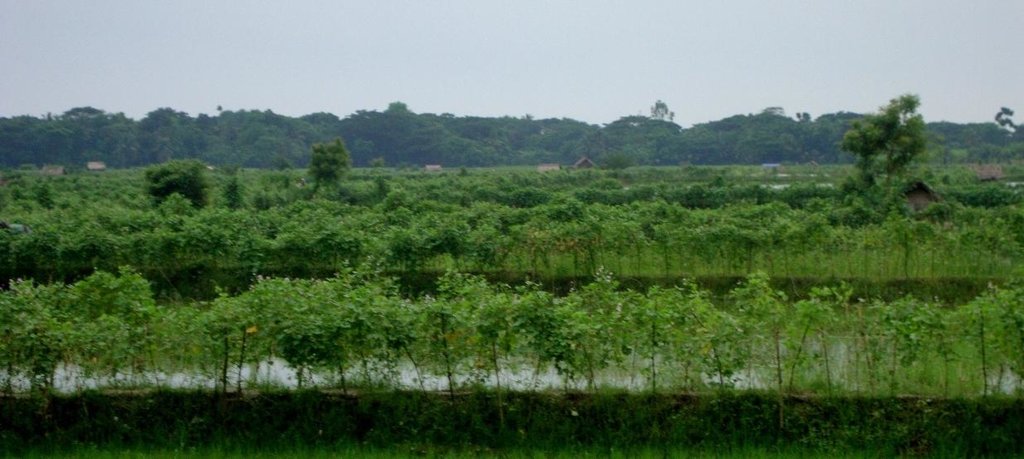
Gher is a local word used for shrimp cultivation plot. The boundaries of these ghers are nowadays raised and maintained to grow vegetables, fruits and also some tree species. In this case the boundary of the plot is raised at least 3 feet with grest width 1 feet plus depending on the height of the boundary (Bund/dyke). Within the gher the land is used for both sweet water prawn (Golda) or saline water prawn (Bagda) with other different types of fishes (locally called Sada Mach) if suitable depending on the salinity of water. Some of the gher lands are used for transplanted Aman with shrimp/fishes.
Farmers dug a ditch along the boundary or in any corner of the field or at the center of the plot to preserve water and fishes during the dry season. In some of the cases the farmers used shallow tube well water to sustain the fishes. In non-to slightly saline areas they used it even for boro (winter rice).
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is a boundary which is used for various types of crops, including year round vegetables and land for rice and fishes including shrimps.
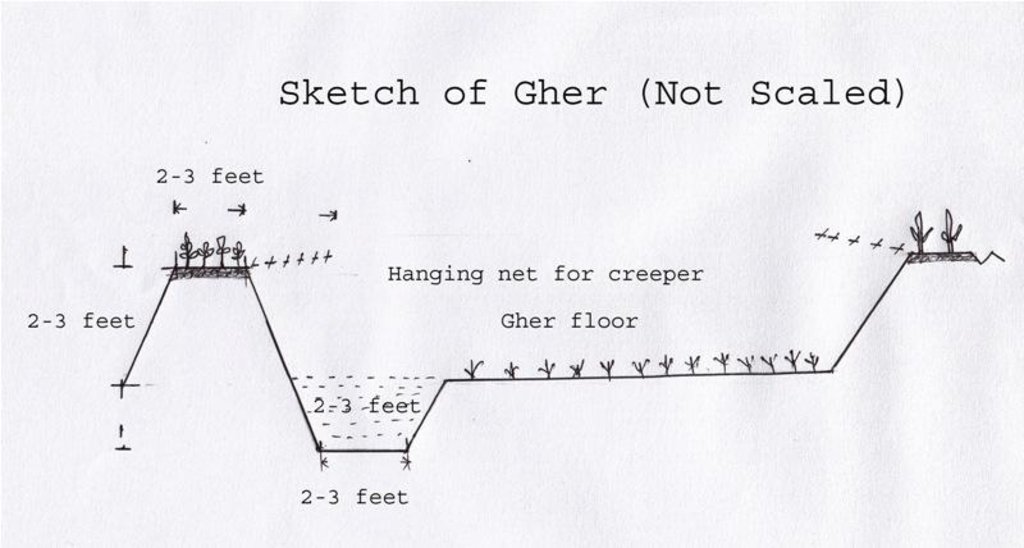
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The boundary is constructed above flood level (2-3 feet), the width is approx. 2-3 feet, the ditches are 2-3 feet deep along the boundary or at the corner or at the center.
To grow vegetables farmers used nylon nets for creeping supported by the bamboo or Dhaincha or strings.
Top soils kept on top of the bunds to avoid relatively less fertile soil on the bunds.
Main inputs are seeds of vegetables, nets, bamboo, strings, fingerlings of fish etc.
Natural / human environment: The salinity of the soils from the bunds is washed away by rainwater, which facilitates vegetable production: Rain water desolves salt and moves to the bottom of the bund, and soil becomes non-saline or slightly saline where vegetable could be grown.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بنغلاديش
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bangladesh Southern region
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Khulna
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- Cropland and aquaculture
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water salinity during dry season; tidal surge; cyclones
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water salinity; tidal surge; sidre (name of a cyclone)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mo: Other
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Gher use is very much variable. The main issue of using land is to adapt soil and water salinity. Some ghers are used for only shrimp, some are mixed with other fishes, some are mixed with transplanted Aman. But the boundary/bunds are used for year round vegetables, Banana, fruits (Kul, Guava, Mango) etc.
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Mixed: Mo: Other
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 160; Longest growing period from month to month: July to Sept
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تربية النحل، واستزراع الأسماك، والدواجن، وتربية الأرانب، وتربية دودة القز، الخ.
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Gher (Shrimp cultivation) boundary used for multiple crops; vegetables, fruits, tree etc in southern coastal region of Bangladesh.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير البنيوية
- الحواجز والضفاف

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Salinization: salination of top soil is due to saline ground water coming in shallow depth), Salinization (The area under this issue is in coastal zone. Conflict of land use is prominent. The lands became saline as other stakeholders keep saline water for other uses (salt production, shrimp))
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The gher boundary is raised approximately 2-3 feet with a crest of 2-3 feet. A ditch also dug to store water and fish during dry season.
Location: Dumuria. Khulna
Date: 03-09-13
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It is only land manipulation.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Previously farmer did not put the top soil on the top of the bunds. That impedes crop production on bunds.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, Decrease of soil salinity, Increase of options for growing more crops
Agronomic measure: Top soil kept on top
Structural measure: Bunds
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-50
Construction material (earth): Bunds are raised by piling earth
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Bunds are used for year round cropping
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Taka
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
79,0
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Nov-Dec |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | ha | 10,0 | 65,0 | 650,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 2,0 | 300,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Watch and ward | ha | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Seeds, nets etc | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1605,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | زراعية | July/Nov |
| 2. | Cultural practices | زراعية | Aug-Oct/Dec-March |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 20,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Piling earth to construct gher bunds
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Availability of labour
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Most of the rainfall experienced in rainy season
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Coastal plain, narrow ridge with broad flat basin
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low - low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women casually worked during harvesting vegetables
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
70% of the land users are poor.
Level of mechanization: Power triller on hire.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
15-50 ha: Mainly owner of lands of this area
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مؤجر
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Desalinized soil of the bund
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
الفرص الثقافية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cash from vegetables
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conflicts to use water resource
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Growing and marketing of year round vegetables help the farmer to get cash money throughout the year. That improves their livelihood and access to health care, education etc.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Ghers are ponded and no water can be drained
التربة
الملوحة
التعليقات/ حدد:
+ Soil salinity reduced as washed by rainwater -> found in soils of Gher bunds
- Due to ground water abstraction -> found in coastal regions, increasing trend
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
Salinity is washed out from the bund by rainwater. Consequently year round vegetable can be grown on bunds of the gher besides fish in the main land or transplanted rice (depending on the salinity of soil and water and choice of farmers).
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
Long term benefit is yet to be observed
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Leased land users are not capable to adopt the technology.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Growing more crops will benefit the farmer with more return. As of now marketing of the goods are facilitated by local small entrepreneurs. Most of them have poor linkage with broader markets. How can they be sustained / enhanced? These entrepreneurs could be appropriately linked with bigger one at regional levels (Upazila/ Districts). At the same time road net works are to be alleviated to facilitate access of transport to carry farmers good with all securities. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Land could be used as farmers are managing themselves How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain production and produce such as vegetables and fishes deserve uninterrupted marketing linkage essential. |
|
Changes in land management by the farmer to grow multiple crops indeed scale up their economy than before. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain the farming system good variety and quality seeds supply will enhance the scenario. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Water management of the areas became critical, specially sweet water | Good water management system is to be introduced through local and regional planning. |
| Conflicts of land uses are prominent. | Social awareness and concept of land zoning seems to be essentials at all levels. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Due to construction or rearrangement of field bunds (Dykes) almost all drainages ways blocked. Consequently the whole area became water logged. This situation will definitely aggravate soil quality, environment and ultimate ecosystem | Community approach to manage the landscape will be effective. In this regard local administration and community leaders can play a vital role. |
| Soils of Gher boundaries (Dykes) are subject to erosion when exposed to rain water. | Good cover crops and management are necessary to protect soils from erosion. At same time farmers may be trained on this issue. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية