WINDBREAKS [الفيليبين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1421 - الفيليبين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
retired governement official:
Mananghaya Florencio
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rondal Jose
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Elliptical Road, Diliman, Quezon City 1100, PHILIPPINES
الفيليبين
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - الفيليبين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
19/01/2006
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Planting of herbaceous plants or trees along property boundaries to serve as windbreaks and as sources of fodder and fuel
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
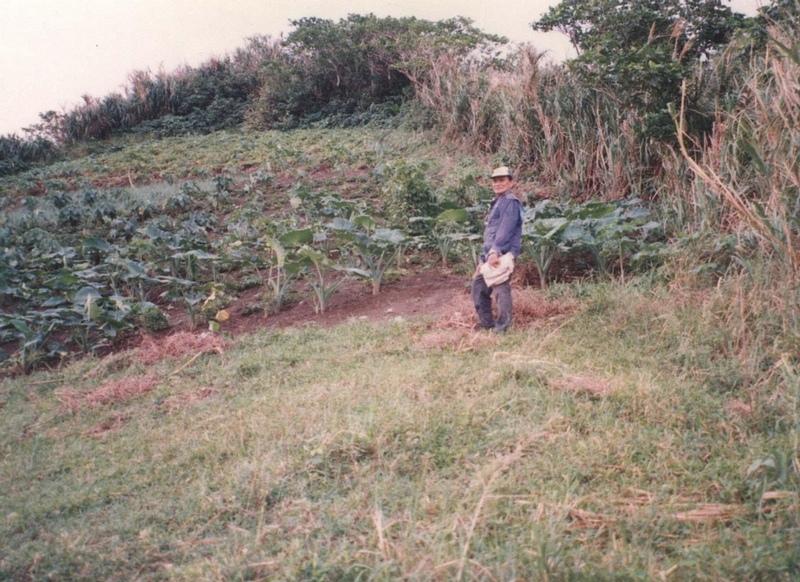
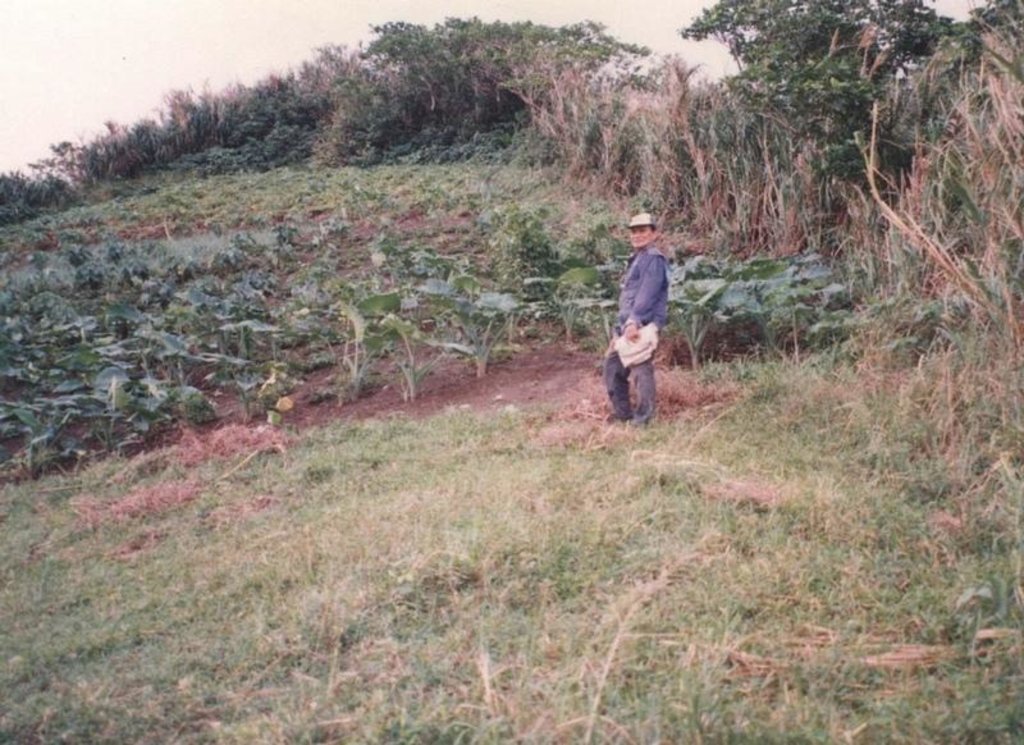
The main characteristic of the technology is the planting of herbaceous crops, grasses or trees along property boundaries. The grasses and herbs are occassionally cut and served as fodder or fuel. The trees are allowed to grow up to maturity which will then be felled for timber (construction) or for boat making. With time, especially when trees are used for boudary planting, individual fields look like boxes from the air. The choice of plants between two adjacent farms is agreed upon by the two landowner.
Purpose of the Technology: The boundary planting serves as windbreak to protect agricultural crops from wind damage. Other uses are fodder and fuelwood. The planting especially when done along the contours also trapped eroded soil from the upper portions of the field.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Planting is done once. The herbs and grasses are regularly cut to serve as animal feed. Trees are allowed to grow to maturity. Dead branches are gathered to be used as fuel.
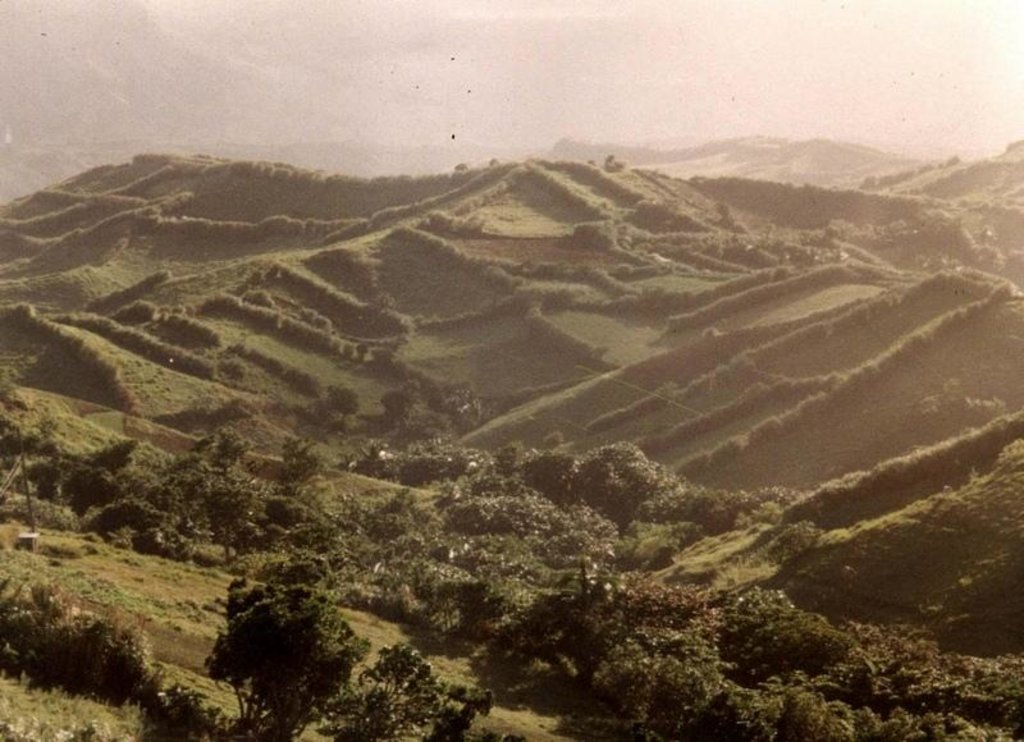
Natural / human environment: The area where the technology is applied is frequently visited by typhoons. The climate is maritime and even at times when there are no typhoons, wind speed is still strong enough to cause damage to crops. Susceptibility to wind damage is further agravated by the nature of the terrain which is mostly hilly.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الفيليبين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Batanes, Philippines
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Batanes
Map
×3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Major cash crop: None indicated; major food crop: corn, garlic; other crops; rootcrops
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crop damage due to frequent typhoons and strong winds.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low crop yield due to wind damage, poor crop quality and lack of market.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Corn, garlic or root crops are grown in separate fields. Corn is planted in December; garlic in September and rootcrops in July.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- مصد الريح/حزام حماية
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3, 5, 0.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Mahogany, native shrubs
Perennial crops species: Coconut
Grass species: Napier
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
4.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedling/planting | نباتية | beginning of rainy season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of dead branches (trees) | نباتية | /twice a year |
| 2. | Cutting (grass) | نباتية | /every two months |
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Perimeter length (m) of area to be treated/planted.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
rainy season lasts for 5 to 6 months
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zones: 0-100m a.s.l. (hills range from 70 to 270 meters altitude)
Landforms: hill slopes (slopes are gentle and gradual )
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium: (1 to 2 years fallow period improves soil fertility)
Topsoil organic matter: 1-3% (Average O.M. content is 2 .0 percent)
Soil drainage is good to medium: (Medium only in depressions)
Soil water sotrage is medium: (soil is deep)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
10% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
5% of the land users are average wealthy and own 8% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Fishing
Level of mechanization: animal traction: Plowing, harrowing, furrowing
Market orientation: Market is practically non-existent
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average farm size is 1,200 sq.m.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
fodder source --> medium 20-50%
جودة العلف
إنتاج الخشب
منطقة الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
conservation / erosion knowledge medium (20-50%)
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
socio cultural conflicts - little (5-20%) - conflicts between two adjacent farms possible
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
increase in soil fertility
التعليقات/ حدد:
medium 20-50%
biodiversity enhancement
التعليقات/ حدد:
medium 20-50%
Fuelwood source
التعليقات/ حدد:
high 50-100% - dead branches, twigs
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Almost all the agricultural areas have adopted the technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Low maintenance cost How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent removal of unnecessary foliage |
|
Protect crops from wind damage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of canopy and foliage |
|
Improves soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use vegetative parts as mulch. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage adoption for other land users |
|
Provides other benefits such as fodder and fuelwood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent cutting in the case of reeds/grasses to stimulate new growth. |
|
Provides residue for organic matter build-up How can they be sustained / enhanced? Frequent cutting and spreading of vegetative parts |
|
Trap for eroded soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? Close-spacing of trees and grass |
|
Good for eco-tourism How can they be sustained / enhanced? Aggressive promotion and marketing |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Competition with crops for space | Use narrower strips for hedgerows |
| Shading effect of trees | Planting of "taro" in shaded area. Frequent cutting of branches |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Loss of space for crops | Use narrower strips for windbreaks |
| Possible sanctuary for pests | Practice integrated pest management |
| Shading effect in the case of tree windbreaks | Use of shade tolerant crops. Trees should be pruned regularly. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية