Kanda [أفغانستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Aqila Haidery
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Kanda
technologies_1659 - أفغانستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Sediqi Ali Ahmad
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation
أفغانستان
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Sthapit Keshar
Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation
أفغانستان
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Arbab Ziauddin
Sourakhak Watershed Committee, Kahmard
أفغانستان
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
30/12/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
A traditional underground water tank carved out of rocks to collect rainfall and snow water and reduce evaporation losses.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
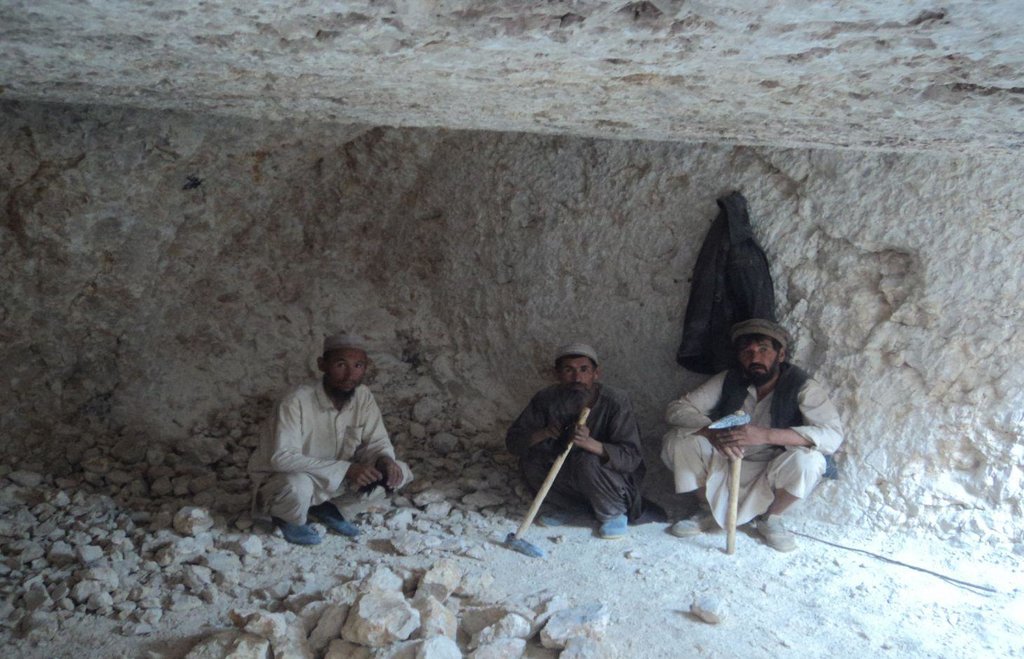
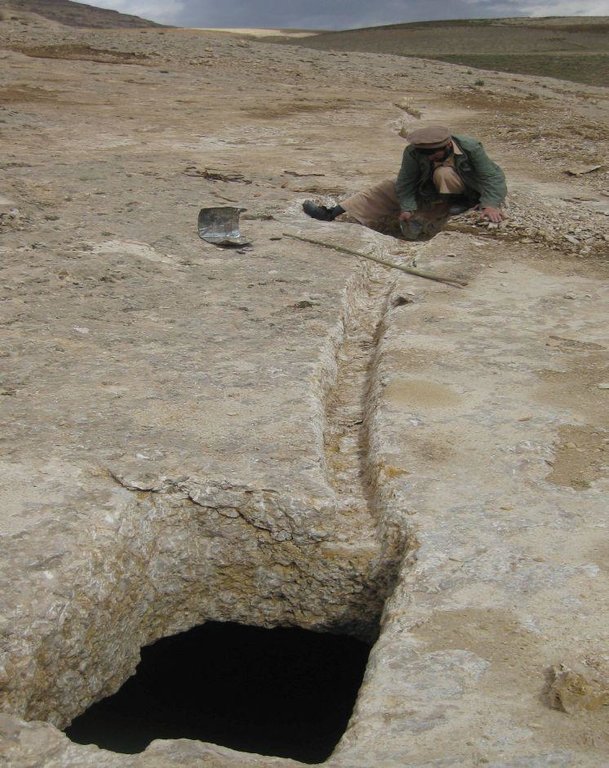
Kanda is an indigenous technology for collecting rain and snow melt. The technology comprises an underground tank carved out of rock (limestone), channels to convey the runoff into the underground tank or kanda and a rocky catchment from where runoff is collected. Kanda technology is applied in Afghanistan in many places, particularly in areas which experience scarcity of water for human beings, livestock and irrigation.
Purpose of the Technology: Due to high evaporation rates and low precipitation, harvesting runoff in open tanks is not an efficient way of water harvesting. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation is implementing community based watershed management projects in Kahmard district of Bamyan province (Afghanistan) since 2008 with financial support from the International Swiss Re Award for sustainable watershed management (2009) and the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). One of the activities for sustainable watershed management is plantation of fruit and non-fruit trees in the selected watersheds (upland areas) which were used for grazing and extraction of vegetation for domestic use. Due to water scarcity in the upland areas, irrigation of the planted saplings becomes very difficult and water has to be transported on donkey from far locations. To overcome this constraint, Kanda was identified as the most potent technology for harvesting runoff and snow melt.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For constructing Kandas, Kanda makers from Dara-e Suf district in Samangan province had to employed as there are no experts in Kahmard. Based on feasibility studies, eight kandas have been constructed including 4 kandas in Sourakhak wa-tershed and 4 in Baqa Kushta watershed. The size of each kanda is 6 m length, 6 m in width and 3 m in height. To convey the runoff into the tank, 10-20 m long graded channels were carved out of the rocks. The establishment cost of one Kan-da was approximately US$ 7163. Kanda making requires special skills, especially when it is carved out of rocks. A kanda maker has sound understanding of the area’s geology, and this wisdom is gained through learning by doing and ances-tors.. In Kahmard, 2-3 experts worked for 4-5 months for one Kanda.
Natural / human environment: In 2012, due to sufficient rains, 2 Kandas which did not have leakage problems in Sourakhak watershed got full with runoff water, which was then used for irrigating 6500 saplings seven times during the year. Kahmard district has a semi-arid cli-mate. Some years are dry with rainfall of about 190 mm. Considering this context, it becomes very necessary to tap rainwater, especially in the rainfed uplands, and use it for irrigating saplings or for livestock.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أفغانستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bamyan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kahmard
2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Kanda technology is an age old water harvesting traditional technology.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- access to water
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- مراعي محسنة
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Sheeps, goats
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Scarcity of water in the upland makes plantation activities and livestock productivity difficult. Carrying water from far places for irrigating plants is an expensive activity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Degraded upland watershed resulting severe flash flood.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection, protection against natural hazards
Other forest products and services: flash flood
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 90; Longest growing period from month to month: March-July
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.005 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك
التعليقات:
Specification of other structural measures: Under ground cistern
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Bush collection for fire wood), overgrazing (By sheep and goets), droughts (Natural climate phenomenon), land tenure (Common land without good management), poverty / wealth, governance / institutional (Lack of organizationals for organization for supporting management of common resources.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Rainfed agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Change in climate patterns), population pressure (Fast increasing population which depands on natural resources for livelihoods), war and conflicts (Leading to uncontrolled cutting down of trees and shrubes)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
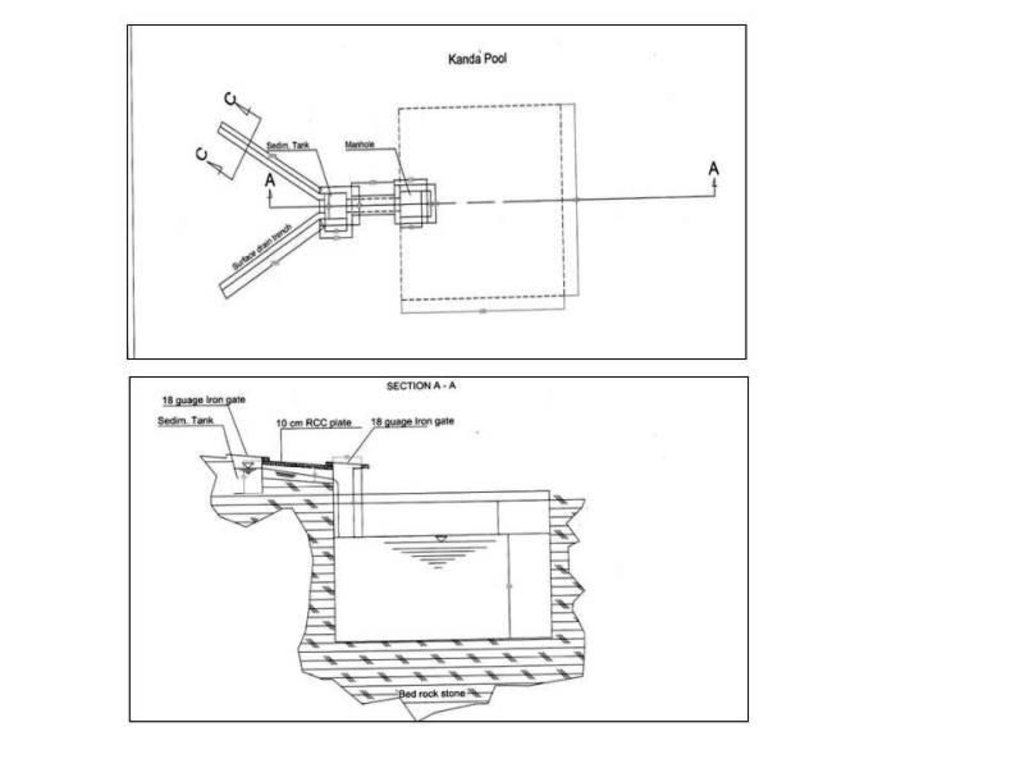
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical drawing of a Kanda constructed at Baqa Kushta watershed in Kahmard district (Bamyan province).
Size of one Kanda tank:
Length:6m
Width :6m
Height:3m
108 cu.m water can be stored in one Kanda.
Location: Baqa Koshta watershed. Kahmard
Date: 24/03/2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, Reduction in evaporation and seepage losses
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Structural measure: cistern(from rock)
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Construction material (other): Constructed from rock
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | kanda | 1,0 | 5640,0 | 5640,0 | 15,0 |
| معدات | Equipement | kanda | 1,0 | 458,0 | 458,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Materials | kanda | 1,0 | 1065,0 | 1065,0 | 8,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 7163,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once/year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Cleaning of the canals and Kanda | persons/day/kanda | 2,0 | 5,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 10,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
The kanda is for water collection which runoff and snow melt. The usage of water for sapling irrigation because there is upland and no water resources.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Because there is fully of rocks.
Soil texture: Mostly rocky
Topsoil organic matter: Because there is erosion
Soil fertility is low (Loss by wind and water erosion)
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor because there is fully of rock
Soil water storage capacity because of rocky catchment
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Because there is to much workload
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
40% of the land users are average wealthy.
50% of the land users are poor.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
خطر فشل الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
نوعية مياه الشرب
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
expense for construction
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased availability of water for small scale irrigation such as trees, sapling and livestock and increase successful afforestation in dry land areas which in the longer term will lead to increased income, fuel wood and timber for land user and greener watersheds
aesthetic value due to greener watershed
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to water harvesting
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
sediments due to excavation of rocks
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
Contributes to flash flood risk reduction by supporting regreening effort
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
This technology is very positive and useful for land users and collected the water for irrigation and livestock.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: It is an indigenous technology applied in many other districts of Afghanistan in Dara-e Suf and Ruy-i Doab districts of Samangan province by several families either collectively or privately without external support. In Dare-e Suf are not constructed inside of rocks but in soil.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
The technology supports plantation activities in sites which are far from perennial water sources How can they be sustained / enhanced? The collected water should be used efficiently during irrigation by combining with conservation measures like mulching, drip or pitcher irrigation |
|
As the kanda catchment is rocky, infiltration losses are minimized and most of the surface runoff is harvested How can they be sustained / enhanced? The channel must be constructed properly so that all runoff is trapped and conveyed to the Kanda. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
An indigenous multipurpose technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? Kanda size can be improved if the catchment area and precipitation amount are considered. This also depends on availability of long-term rainfall data. |
|
Requires minimum maintenance when constructed properly How can they be sustained / enhanced? Kanda, conveyance canals, sediment pits and catchment areas should be cleaned. If any leakages occur in the tank, they should be sealed. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Due to a lack of geological and hydro-meteorological information, it is not possible to prepare precise and cost-effective kanda proposals | Make best use of traditional wisdom, install hydro-met stations if possible and make adjustments based on regular monitoring. |
| If the kanda and sediment trap tanks are not cleaned regularly and the kanda opening is not covered, sedimentation can be problem leading to reduced Kanda capacity and also animals could fall | Cleaning and maintenance works must be carried out by the local people every year before spring rains. The openings must be covered. |
| Due to availability of water, there can be grazing pressure near the Kanda | Watershed committee members and guards should ensure that the site is protected from over grazing. Construct Kandas outside the selected watershed for livestock purposes. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Establishment cost is high if the catchment is rocky | Needs external support during the establishment phase |
| Lack of kanda makers in some districts like Kahmard | Get kanda makers from other districts and build capacities of interested local people. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
عنوان الرابط URL:
www.wocat.net(Online Technology Database)
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية