Rehabilitation of degraded communal grazing land [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Nicole Guedel
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kshetigrasta samudayik charan bhumi ko punaruththan (Nepali)
technologies_1492 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/11/2004
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Rehabilitation measures, including eyebrow pits and live fencing, were implemented on degraded communal grazing land to
reestablish a protective vegetative cover
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
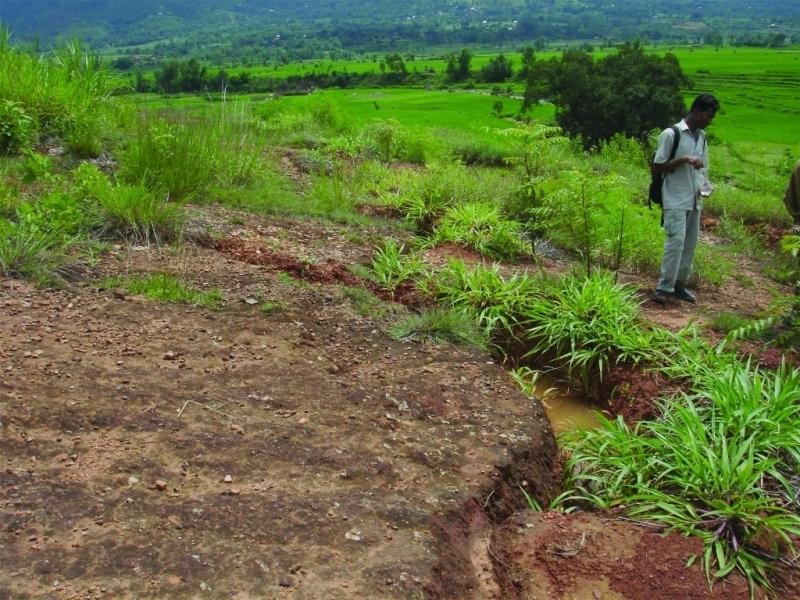
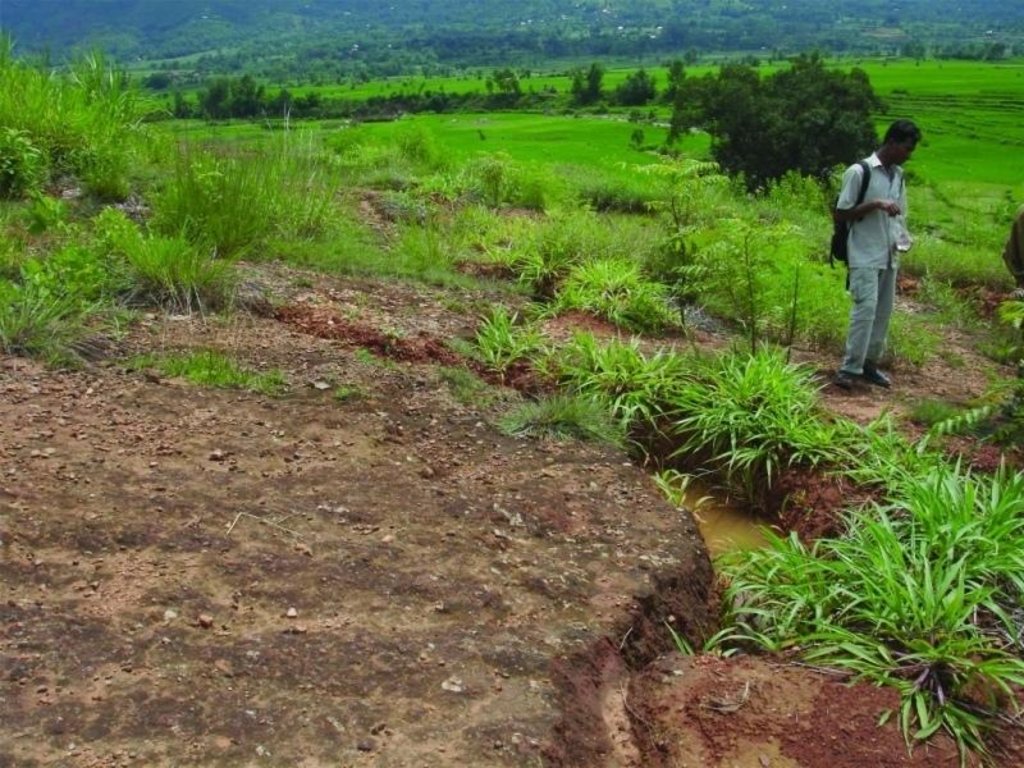
An area of heavily degraded grazing land was rehabilitated by establishing eyebrow pits to control and harvest runoff, planting trees and grasses, and fencing the site to control grazing. The main purpose was to re-establish vegetative cover on the almost bare, overgrazed site. The site is community land of the 40 households (240 people) of Dhotra village in the Jhikhu Khola watershed. These people are very dependent on this area due to the lack of alternative grazing sites. The rehabilitation site is surrounded by irrigated cropland downstream, grazing land, and degraded sal (Shorea robusta) dominated forest. Rainfed forward-sloping terraces immediately adjoin the site.
About 130 eyebrow pits were dug, together with catch drainage trenches. Several species of grass and fodder were planted along the ridges of the eyebrows and drainage trenches. Contour hedgerows were established between the eyebrow pits and trenches, and trees were planted just below the pits. The maintenance is quite easy: the vegetation needs to be cut back from time to time and the pits cleaned before the pre-monsoon period. The remaining bare areas should be revisited each year and replanted.
The area has a distinct dry season from November to May and a wet monsoon period from June to October. Annual rainfall is around 1200 mm. The site has red soils that are highly weathered and, if not properly managed, are very susceptible to erosion.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيبال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kavre Palanchok/ Dhotra village, Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The hedgerow technology came from the Philliphines, modified from the SALT (Sloping agriculture land technology) technology. The eye brow pit technology was implemented by the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management in Nepal and was adapted from them. Villagers approached the People and Resource Dynamics Project (PARDYP) for advice. PARDYP assisted, based on experiences made before with rehabilitation experiments under similar conditions. Mainly developed according to theoretical and site specific knowledge.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- مربى ماشية محدد
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem is the small per capita landholding size for cropping. These holdings are mostly rainfed, have a low soil fertility status and acidity problems, and are susceptible to erosion. Intense rainfall at the beginning of the rainy season causes considerable soil loss (rill and gully erosion).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Overgrazing leading to lack of vegetation.
Ranching: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 3
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- تحويل المياه والصرف
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.019 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر

التدابير الإدارية
- M5: التحكم في/تغيير تركيبة الأنواع
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, in blocks
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (insufficient forage supply from the private land.), education, access to knowledge and support services (identification of appropriate SWC technologies and appropriate collaborators)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (for daily household needs ( litter , firewood, timber), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (excessive rainfall during pre-monsoon and monsoon), poverty / wealth (to buy planting materials and for logistics), labour availability (for community level social work)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
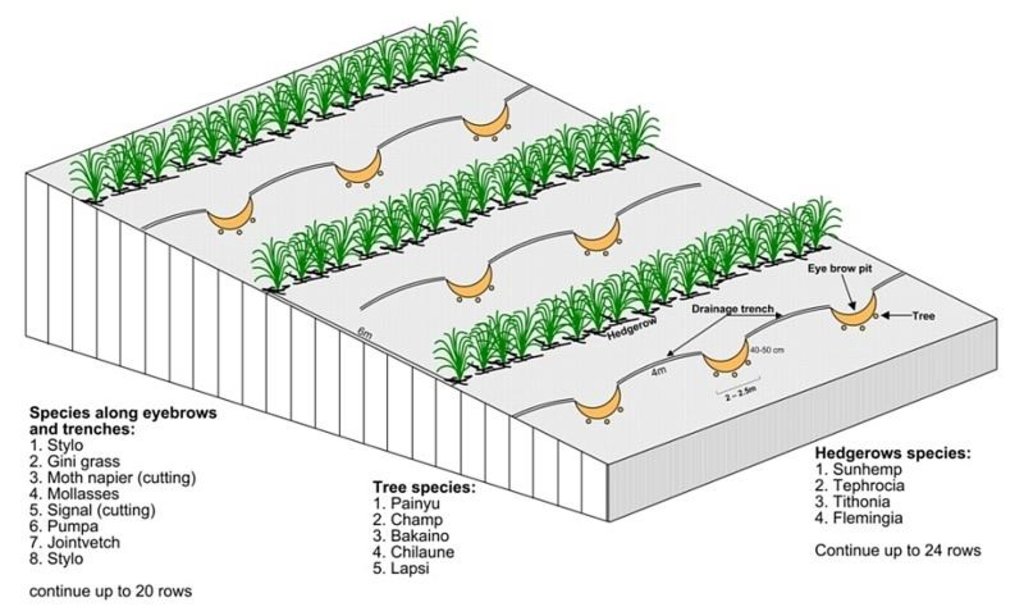
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical drawing of layout of vegetative and structural measures.
Location: "Dhotra" village, near Dhulikhel. Kabhre Palanchok district
Date: July 2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase in organic matter
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 m
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 120
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4 m
Trees/ shrubs species: Prunus cerasoides, Michelia champaca, Melia azedarach, Schima wallichii,Cherospondias axillaries
Grass species: Stylosanthes guianensis, Panicum maximum, Pennisetum purpureum, Melinis minutiflora, Brachiaria decu
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2.00%
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 5-10 m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-2 m
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5-4 m
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Spacing between structures (m): 6 m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40-50 cm
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1-1.5m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2-2.5 m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-30
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5 m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-2 m
Structural measure: diversion ditch / cut-off drain
Spacing between structures (m): 6 m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0-30 cm
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10-30 cm
Construction material (earth): soil resulting from the digging activities were used to construct eyebrow shaped bunds.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: closing for change of management / intensity level - grazing as well as "symbolic" fencing by small living fence to delineate SWC area.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of tree seedlings and cuttings and sowing of grass seeds. | نباتية | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 2. | Drawing layout of eyebrow terraces, drainage ditches, hedgerows on the bare land | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 3. | Digging holes for eyebrow pits, drainage ditches | بنيوية أو هيكلية | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 4. | Making sure that all livestock is stall- fed | إدارية | All the time |
| 5. | Establishing small live fences with grasses and shrub cuttings | إدارية | before onset of monsoon (June) |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Eyebrow terraces and vegetative measure | Persons/day | 52,0 | 2,0 | 104,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 23,0 | 23,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Transportation | ha | 1,0 | 41,0 | 41,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Lunch, tea for farmers | ha | 1,0 | 47,0 | 47,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 233,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cutting vegetation | نباتية | 3 times /year |
| 2. | planting vegetation in any gaps | نباتية | before monsun /annual |
| 3. | Cleaning of sediment-filled pits | بنيوية أو هيكلية | oncea year, before onset of monsoon |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, spade,sickle, hoe, spade
All costs and amounts were roughly estimated by the technicians and authors in 2004.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 900 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Also very steep
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average is variable
Soil texture: red soils with high clay content
Soil fertility was very low before implementation of rehabilitation activities
Topsoil organic matter was low before implementation of rehabilitation activities
Soil drainage / infiltration was poor before implementation of rehabilitation activities
Soil water storage capacity was very low before implementation of rehabilitation activities
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Water quality (untreated): More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
95% of the land users are average wealthy.
3% of the land users are poor.
2% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Only limited grazing area for whole village
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased carrying capacity of land; about $17 was collected from selling grass seeds and grass
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
collected money used for social work
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
At the beginning a few people opposed the activities
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
about 80 percent bare land covered by the various grasses
فقدان التربة
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
into irrigation canal downstream
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The high establishment costs of the technology means that the shortterm benefit for the community only matches the costs involved. In the long-term the environmental benefit of rehabilitated land is high and
economically it is positive.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
40 households in an area of 0.019 sq km
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
40 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No initiative could be seen in the area , but inerst is there.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
The technology already started generating income from the degraded land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In the long run, by selling grass and grass seed, funds can be generated. |
|
The technology is effective against land degradation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More tree and fruit species should be added and grass species multiplied to cover the remaining bare land |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
The technology package is easy to apply as it does not need much knowledge and is cost effective. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure and grasses is required |
|
Improvement can be seen fast and easily; the vegetation cover increased and the loss of top soil decreased. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Nakarmi, G. (2000) Soil Erosion Dynamics in the Middle Mountains of Nepal, a report submitted to PARDYP, ICIMOD, Kathmandu.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICIMOD
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Schreier, H.; Brown, S.; Shah, P. B.; Shrestha, B.; Merz, J. (2002) Jhikhu Khola Watershed – Nepal, CD ROM. Vancouver: Institute for Resources and Environment, University of British Columbia.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICIMOD
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Shrestha, B. (2004) Progress Report PARDYP-Nepal. Paper presented at the PARDYP – Access Mid Year Meeting, 19-22 July 2004, ICIMOD, Kathmandu.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية