Composting associated with planting pits [بوركينا فاسو]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Moussa Bonzi
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Zai avec apport de compost (french)
technologies_959 - بوركينا فاسو
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
De Pury Jean Pascal Etienne
Centre Ecologique Albert Schweitzer (CEAS)
سويسرا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ouedraogo Elisée
Centre Ecologique Albert Schweitzer (CEAS)
سويسرا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Centre Ecologique Albert Schweitzer (CEAS) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
INERA Institut de l'environnement et de recherches agricoles (INERA Institut de l'environnement et de recherches agricoles) - بوركينا فاسو1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Zabré women’s agroecological programme [بوركينا فاسو]
A demand-driven initiative, by a women’s association, aimed at the promotion of composting through training and extension, using project staff and local facilitators.
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Compost production, and its application in planting pits (zai) by farmers on fields near their homes.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
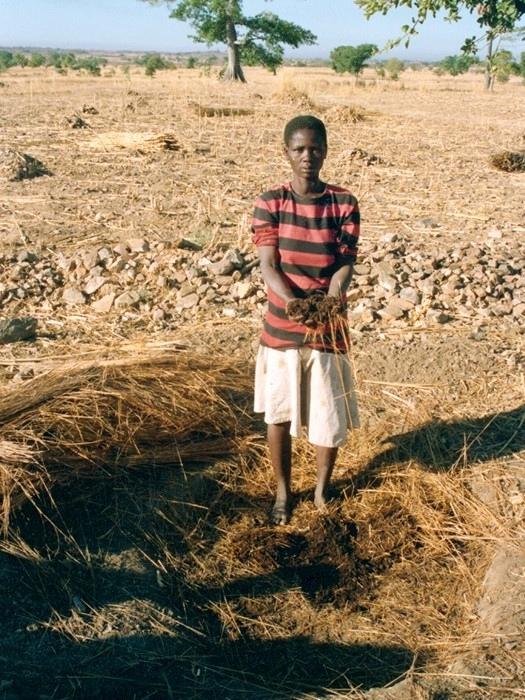
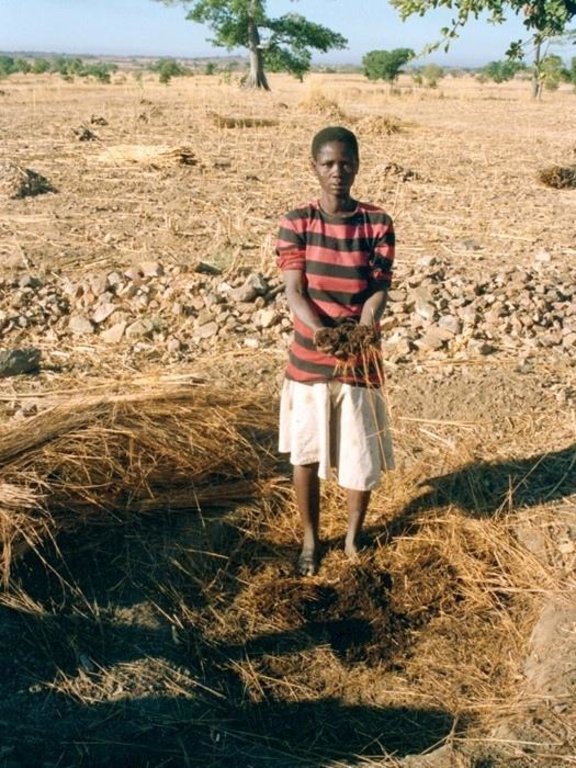
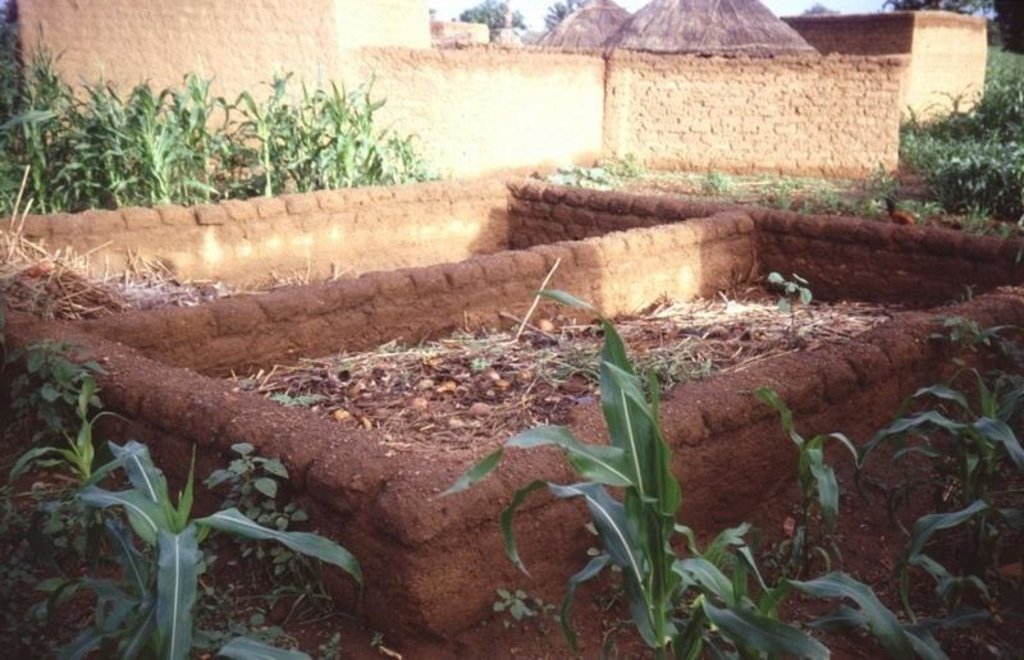
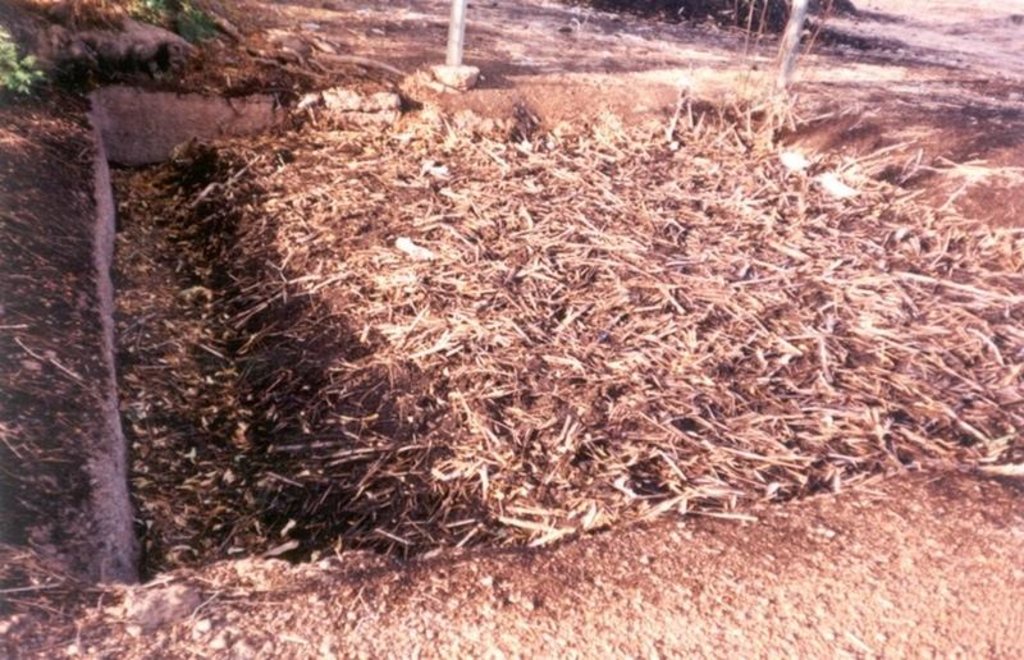
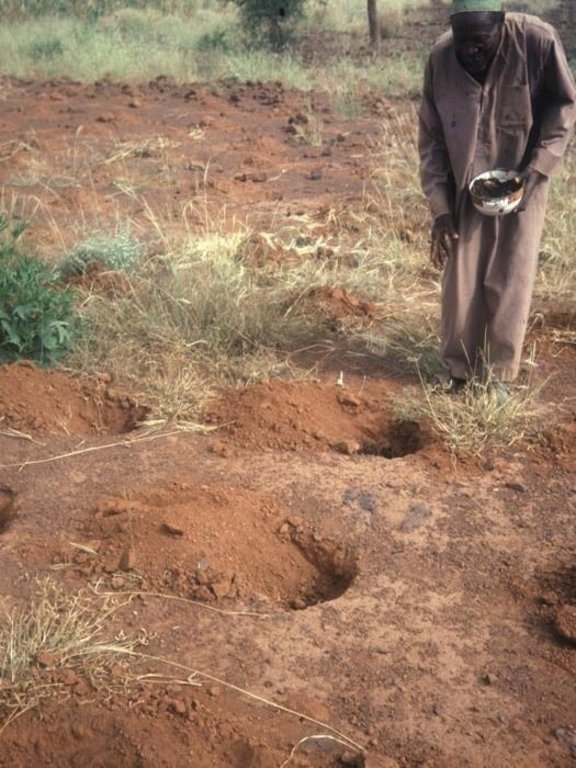
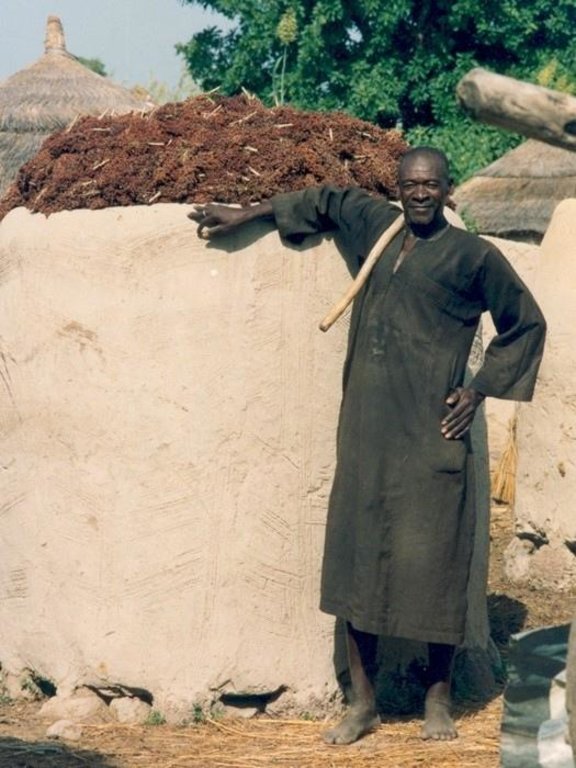
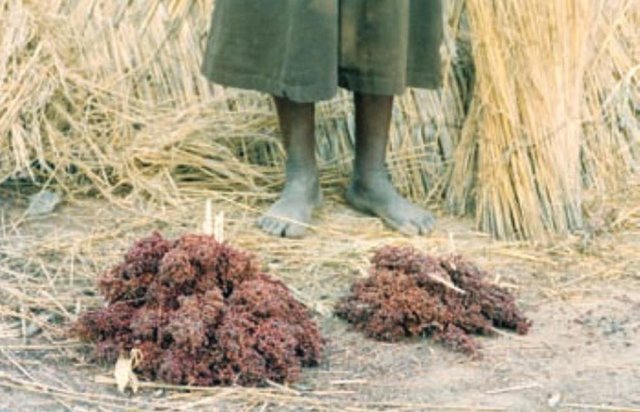
Compost is produced in shallow pits, approximately 20 cm deep and 1.5 m by 3 m wide. During November and December layers of chopped crop residues, animal dung and ash are heaped, as they become available, up to 1.5 m high and watered. The pile is covered with straw and left to heat up and decompose. After around 15-20 days the compost is turned over into a second pile and watered again. This is repeated up to three times - as long as water is available. Compost heaps are usually located close to the homestead. Alternatively, compost can be produced in pits which are up to one metre deep. Organic material is filled to ground level. The pit captures rain water, which makes this method of composting
a valuable option in dry areas.
The compost is either applied immediately to irrigated gardens, or kept in a dry shaded place for the next sorghum seeding. In the latter case one handful of compost is mixed with loose soil in each planting pit (zai). These pits are dug 60 cm by 60 cm apart. Three to four grains of sorghum are planted in each pit. Compost in the pits both conserves water and supplies nutrients. This enables the sorghum plants to establish better, grow faster and reach maturity before the rains finish. As compost is applied locally to the crop, not only is the positive effect maximised, but also the weeds between the pits do not benefit. The water retaining capacity of the compost (absorbing several times its own weight) makes the difference. This is much more important than the additional nutrients, which only become available in subsequent years, and do not anyway completely replace all the nutrients extracted by the crops.
The planting pits also help by harvesting runoff water from the microcatchments between them. Boulgou experiences erratic and variable rainfall with frequent droughts. The poor soils are often crusted and have a low water-retention capacity. Due to a high and increasing population, the land has become exhausted, and fallow periods are no longer sufficient as a consequence. Fertility and yields have declined. Sorghum without compost is more vulnerable to drought and crop failure.
During the dry season, after harvest, fields are grazed by cattle of the nomadic pastoral Peuhl, who also herd the agriculturalists’ livestock. Interestingly, the Peuhl have started to systematically collect the manure for sale, since the increased demand (for composting) has led to doubling of the price. Composting has been applied in Boulgou Province of Burkina Faso since 1988.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بوركينا فاسو
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Boulgou Province, Burkina Faso
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 200 km2.
Map
×2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- المحاصيل الزيتية - الفول السوداني
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب - الذرة الرفيعة
- الخضروات - الخضروات الورقية (السلطات، الملفوف، السبانخ، وغيرها)
- الخضروات - الخضروات الجذرية (الجزر والبصل والشمندر وغيرها)
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- البازلاء
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم

أراضي الرعي
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- البغال والحمير
- zebu cattle

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Population increase has led to cultivation of all the available arable land, thus shortening or eliminating fallow periods.
Organic matter in the soil is reduced, the water holding capacity of the soil has diminished and consequently yields have fallen. This has been compounded by the droughts of the 1970s and 1980s. Thirty years ago farmers harvested 800 kg/ha each year, but by the 1980s yields had fallen to merely 400 kg/ha on average.
Main products/ services: Sorghum and zebu cattle (after harvest)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
- حصاد المياه
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (causes agricoles: Suppression des jachères; surpâturage), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Secheresse du sol due à la destruction de l'humus plus qu'aumanque de pluie.), Expansion démographique, manque de connaissances (Comment acquerir ces connaissances)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), manque de moyens financiers (comment en produire avec des connaissances)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
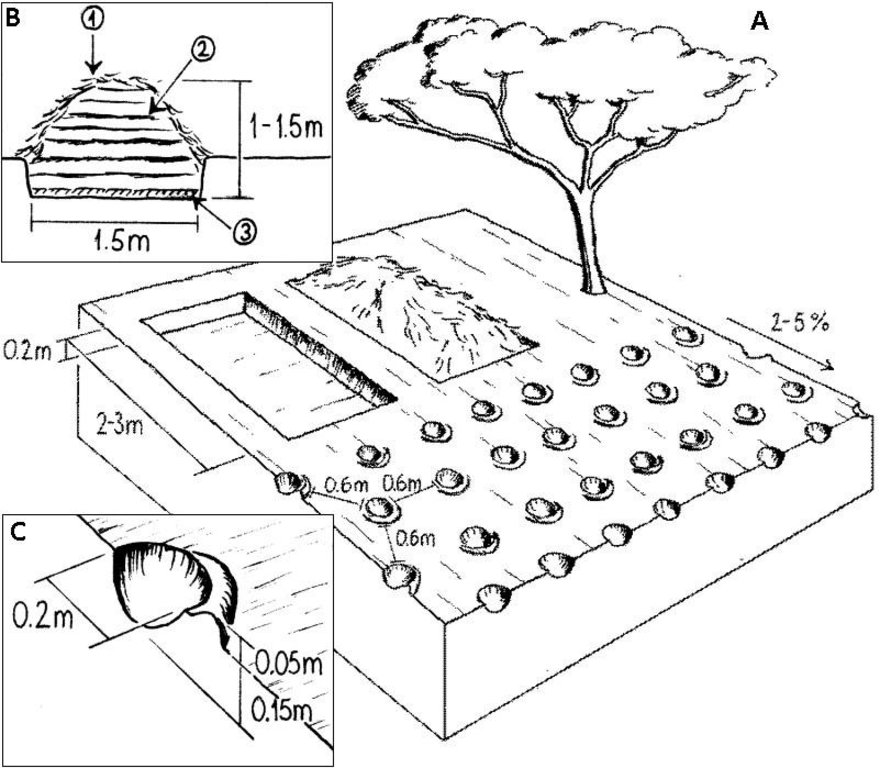
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
A: Overview of compost making and zai planting pits within a field. Tree shade helps to conserve moisture in the compost pits.
B: Cross section of compost pit: protective straw (1); successive layers of compost (2), clay layer at the bottom (3).
C: Detailed view of zai planting pit.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility, improvement of soil structure
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost
Quantity/ density: 7-10 t/ha
Remarks: applied in planting pits
المؤلف:
Mats Gurtner
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transport compost to the fields: | April / annual |
| 2. | Deepen planting pits (zai) (to original dimensions of 15 cm deep, 20 cm diameter, and 60 cm apart) and apply a handful of compost mixed with earth, just before planting sorghum | After the first rains / annual |
التعليقات:
Editors’ comments: Soil fertility decline is a major problem for much of Africa, and composting provides an opportunity for local mitigation of this. There are many ways of making compost, and this case is a good example of ‘aerobic heap compost’ from Burkina Faso. Here, the compost is concentrated in planting pits, which additionally harvest water.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Clay | 1 | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 12,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 12,0 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig two compost pits (3 m by 1.5 m and 20 cm deep). Cover the bottom of each pit with 3 cm clay layer. | beginning of the dry season (November). / initial establishment |
| 2. | Put 20 cm layer of chopped crop residues (cereal straw) into thecompost pit (water with one bucket). Add 5 cm layer of animal manure. Add 1 cm layer of ash. Repeat steps 1–3 until the compost pile is 1.0–1.5 m high. | November / annual |
| 3. | Cover pile with straw to reduce evaporation, and leave to decompose. | November / annual / up to 3 times (as long as water is available) |
| 4. | Turn compost after 15 days into the 2nd pit, then after another 15 days back into the 1st pit. Water the pile after each turning with 3 buckets of water. | / up to 3 times (as long as water is available) |
| 5. | Store ready compost in dry shady place. | January / annual |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Wheelbarrow renting | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | None | None | 1,0 | |||
| معدات | None | None | 1,0 | |||
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Wet straw | ha | ||||
| مواد البناء | ash | ha | ||||
| غير ذلك | Compost transportation | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 30,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 30,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, knife, digging stick, bucket
Costs relate to production and application of one ton of compost per hectare - which a farmer can make in one year and is the product of one full compost pit. The compost is directly applied to each planting pit: since the pits all in all
constitute only around 10-15% of the field surface, compost is effectively applied at a concentration of 7-10 t/ha. This rate is equal to actual rates applied in small irrigated gardens (<0.1 ha). If compost is produced in deep pits, production is cheaper because there is less work involved.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Duration of establishment: 1 week
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture: Fine / heavy (elevations) and coarse/light (depressions)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (and decreasing further)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1) and mixed (ranked 2, in good years)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
By several times in dry years, compared to no compost use
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Integration of agriculturalists and pastoralists
Input constraints
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water for compost making
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Soil fertility
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
5000
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Strong trend towards growing spontaneous adoption. Almost everybody wants to imitate neighbors - but not everyone had received adequate training. Demand grew because of the expanded membership of the association. Some pastoralists use it in their gardens.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
All land users, even the poorest, can learn to make and apply compost. No jealousy amongst land users, which is a prerequisite for ist spread/acceptance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep going with training and extension. |
|
Possibility of doubling cereal yields in normal years: any surplus production can be sold How can they be sustained / enhanced? Produce enough good compost/manure. |
| Ensures yields in dry years, giving security against drought and hunger. |
|
Gives high income in dry years due to production increase and double prices on the market for the surplus How can they be sustained / enhanced? However the government is attempting to stabilise prices, so this benefit might not endure. |
| Requires only locally available resources, and knowledge about compost application is ‘owned’ by the farmers: nobody can take it away from them. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The modest quantity of compost applied is not enough to replace the nutrients extracted by the crops in the long term | Small amounts of nitrogen and phosphorous fertiliser need to be added and crop rotation practiced. |
| The short/medium term local benefits are not associated with a positive overall, long-term ecological impact because there is a net transfer of organic matter (manure) to the fields from the surroundings | Improve management of the vegetation outside the cropland, avoiding overgrazing etc to increase manure production. |
| Needs considerable water and thus also extra labour | Pit composting helps to reduce water requirement in drier areas and at the same time reduces labour input. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Ouedraogo E . Influence d’un amendement de compost sur sol ferrugineux tropicaux en milieu paysan. Impact sur laproduction de sorgho à Zabré en 1992. Mémoire de diplôme.. 1992.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
CEAS Neuchâtel, Switzerland
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zougmore R, Bonzi M, et Zida Z . Etalonnagedes unités locales de mesures pour le compostage en fosse de type unique étanche durable. Fiche technique de quantification des matériaux decompostage, 4pp. 2000.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zougmore R, Bonzi M, et Zida Z . Etalonnagedes unités locales de mesures pour le compostage en fosse de type unique étanche durable. Fiche technique de quantification des matériaux decompostage, 4pp. 2000.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zougmore R, Bonzi M, et Zida Z . Etalonnagedes unités locales de mesures pour le compostage en fosse de type unique étanche durable. Fiche technique de quantification des matériaux decompostage, 4pp. 2000.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zougmore R, Bonzi M, et Zida Z . Etalonnagedes unités locales de mesures pour le compostage en fosse de type unique étanche durable. Fiche technique de quantification des matériaux decompostage, 4pp. 2000.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zougmore R, Bonzi M, et Zida Z . Etalonnagedes unités locales de mesures pour le compostage en fosse de type unique étanche durable. Fiche technique de quantification des matériaux decompostage, 4pp. 2000.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Zabré women’s agroecological programme [بوركينا فاسو]
A demand-driven initiative, by a women’s association, aimed at the promotion of composting through training and extension, using project staff and local facilitators.
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية