Intercropping of orange trees with mungbean in mountainous areas [كمبوديا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Navin Chea
- المحررون: Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- المراجعون: Nimul CHUN, SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
Intercropping
technologies_3146 - كمبوديا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Chea Sarith
Land User
كمبوديا
Acting Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh:
Doung Phanny
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh.
كمبوديا
Chief Office of Agricultural Extension at Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat:
Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Bakan:
Agronomic Official at District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng:
Seng Kompheak
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng
كمبوديا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - كمبوديا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
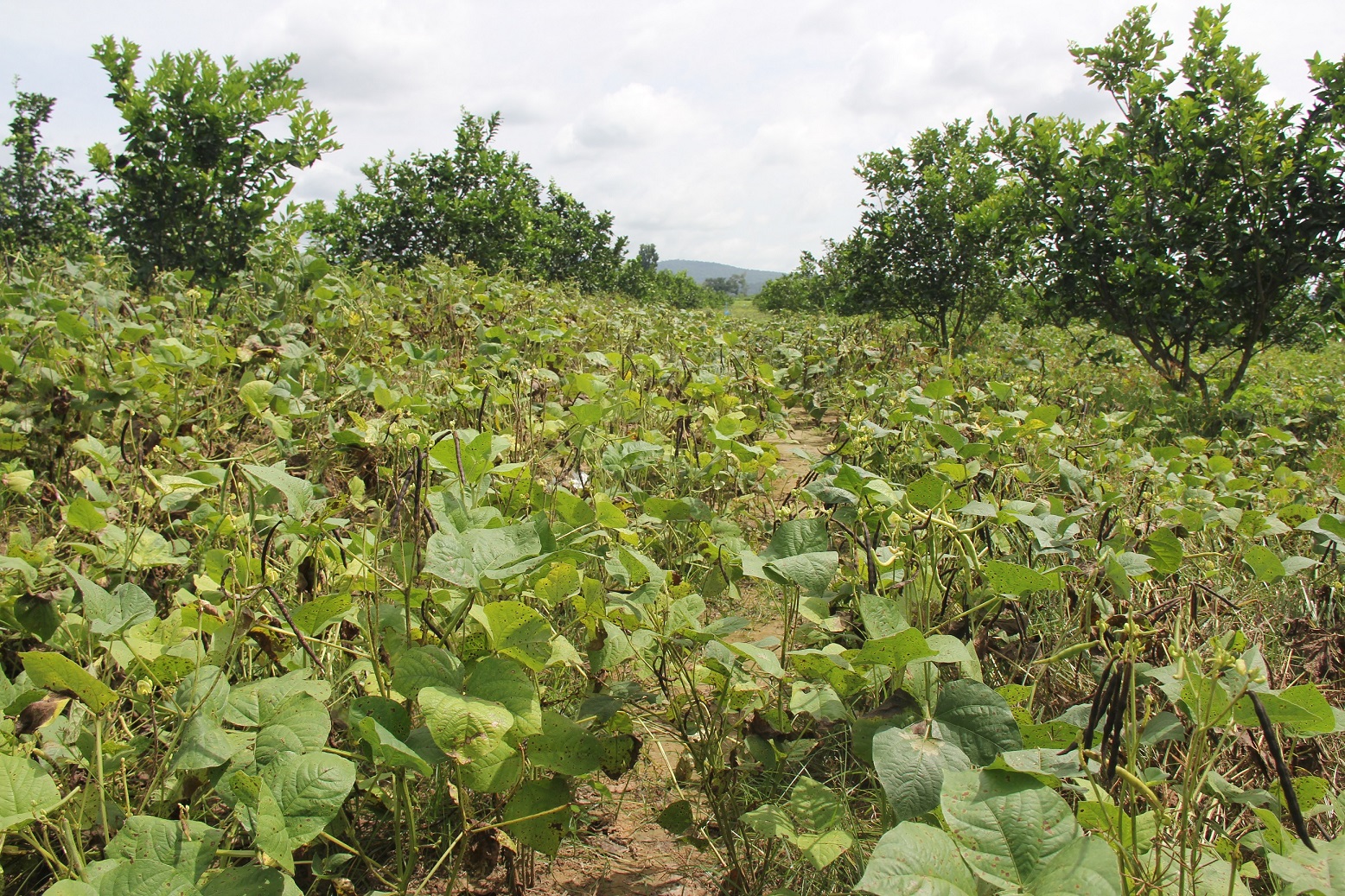
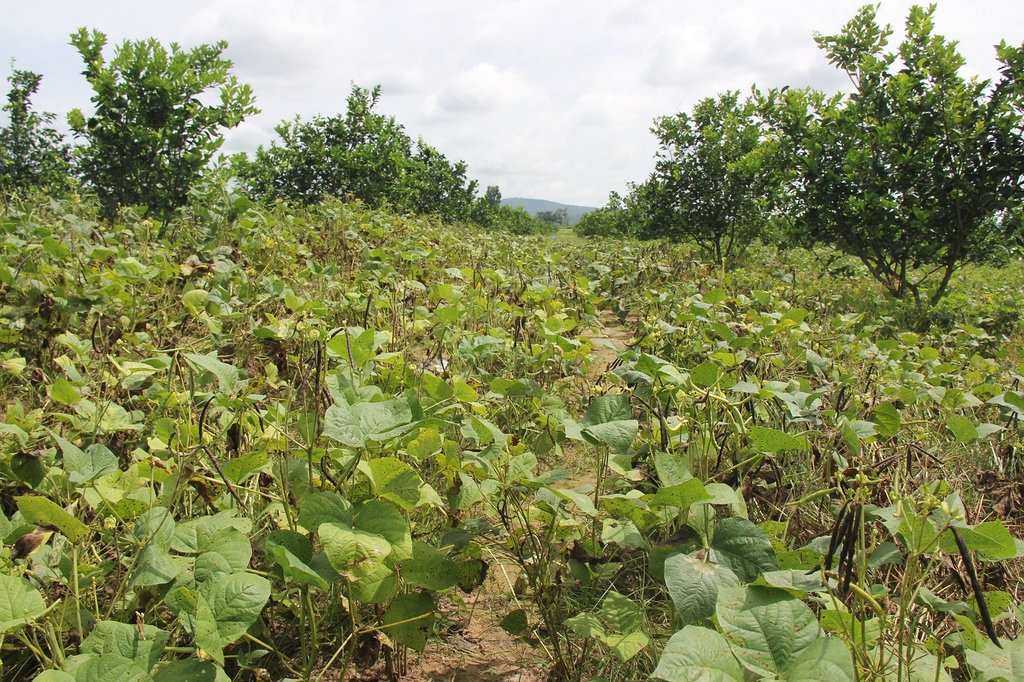
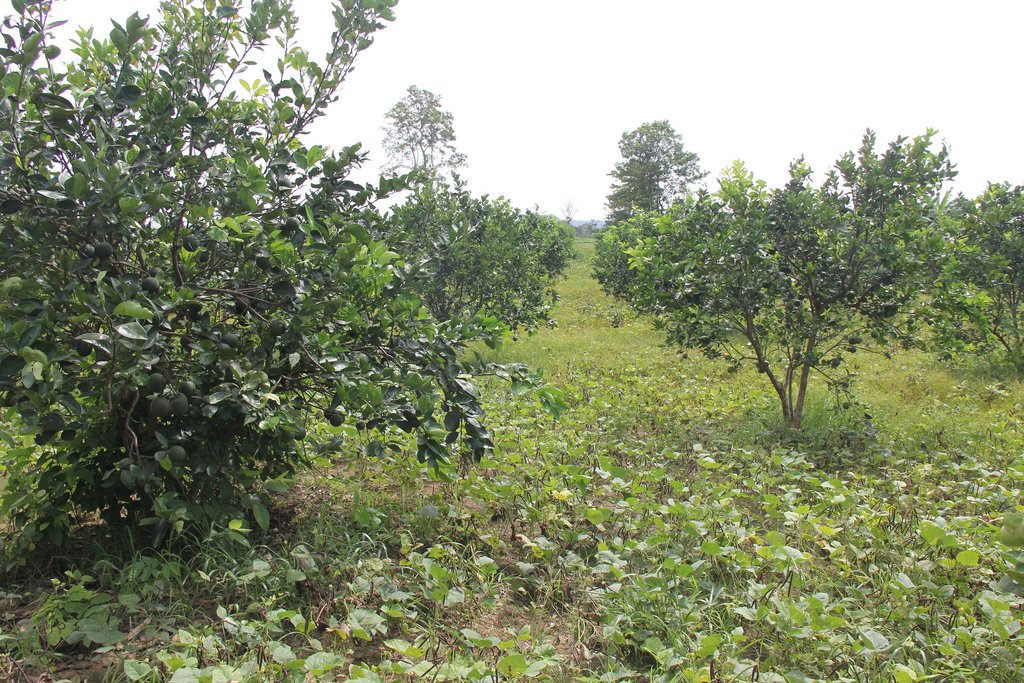
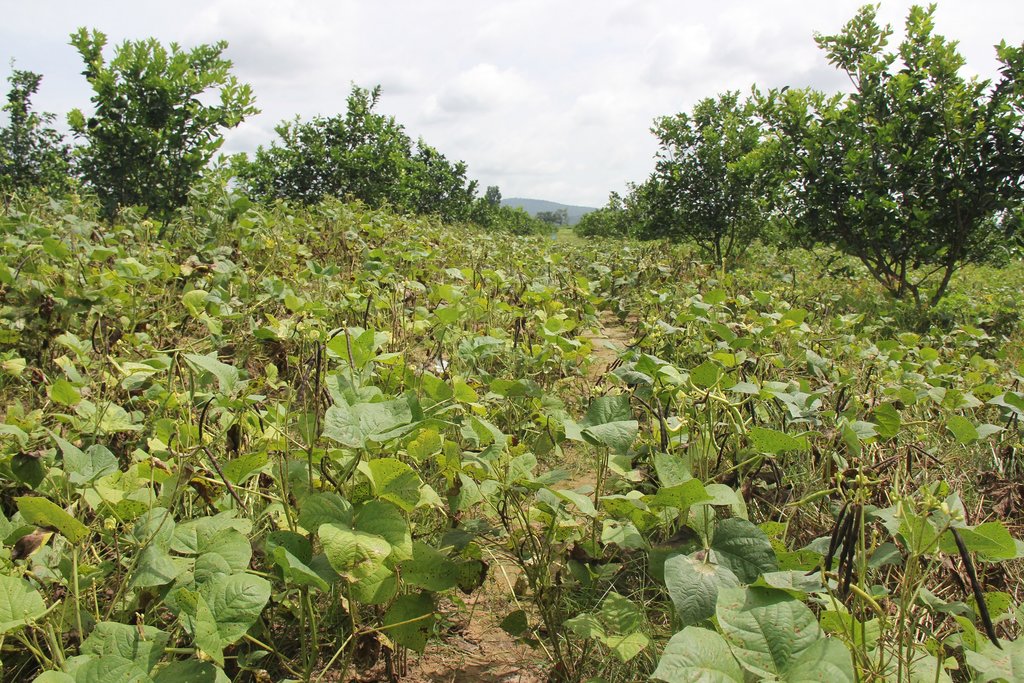
Intercropping of mungbean between orange trees improves soil fertility and generates income before the orange trees bear fruit.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Agroforestry is a farming practice that can involve growing of a mixture of woody perennials like trees, shrubs, palms, bamboos, etc. with crops and/or animals, on the same land-management units. Agroforestry systems play an important role in ecological and economical interactions between the different land use components (Lundgren and Raintree, 1982). It represents an interface between agriculture and forestry, and encompasses mixed land-use practices. Agroforestry systems are composed of three attributes:
1. Productivity (improved tree products, yields of associated crops, reduction of cropping system inputs, and increased labor use efficiency);
2. Sustainability (beneficial effects of woody perennials);
3. Adoptability (MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP, 2016).
In Cambodia, mungbean grows throughout the whole year almost, depending on the moisture factor. Mungbean is short maturity crop which can be grown both in sloping upland and in lowland areas. In upland areas farmers usually plant their second crop in August and harvest it in October. Mungbean is a crop that can be grown on many soil types, but grows best on alluvial, sandy, and volcanic soils which well drained containing high levels of nutrients (incl. N, P, K, Ca, Mg) and organic matter (MAFF, 2005). Mungbean crop duration depends on the variety, with short-term, medium-term and long-term being harvested between 60-65 days, 65-75 days, and 75-80 days, respectively.
Mungbean residues can make an active contribution to improvement of soil quality through nitrogen fixation and subsequent incorporation of this nitrogen into the soil after root and nodule degeneration by Rhizobium bacteria. The incorporation of the organic root material also improves the soil structure (MAFF, 2005, Chadha, 2010, IRRI-CIMMYT Alliance, 2009). The taproot of the mungbean can penetrate the soil to a depth of 50-60 centimeters. Sometimes, some land users grow mungbean as a green manure crop specifically to improve soil quality (Tauch Ung, 2010).
Mr. Chea Sarith is one example of land user who practices intercropping of orange trees with mungbean since 2013. The main purpose is to improve soil fertility, to prevent soil erosion, and to generate income before the orange trees provide fruit. In addition, it eases the weed control. After the harvest the farmer leaves the plant residues on the soil to provide organic matter. With the objective not to harm the roots of the orange trees, he avoids tilling the soil. In general, mungbean grows twice a season depending on the rainfall distribution and soil moisture.
The average yield of direct seeded mungbean as an intercrop between orange trees is about 1,200 kg/ha (harvested 3 times per crop). If mungbean is grown as a single crop the yield is usually ranges from 1,300 to 1,400 kg/ha. The market price for mungbean grain is usually about 4,500 to 5,000 Riel/kg.
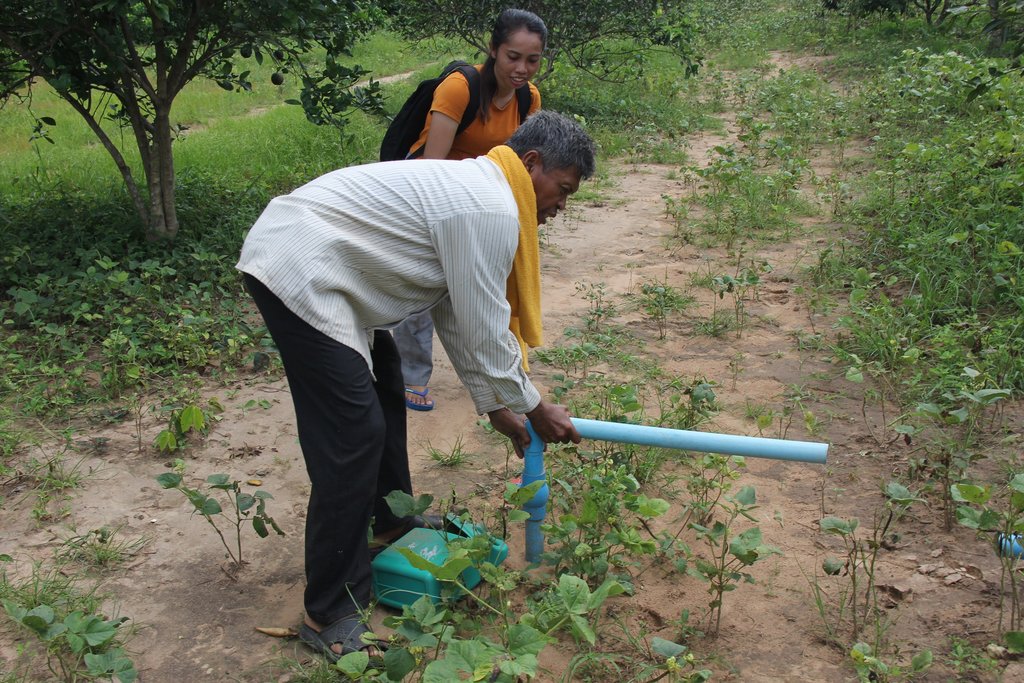
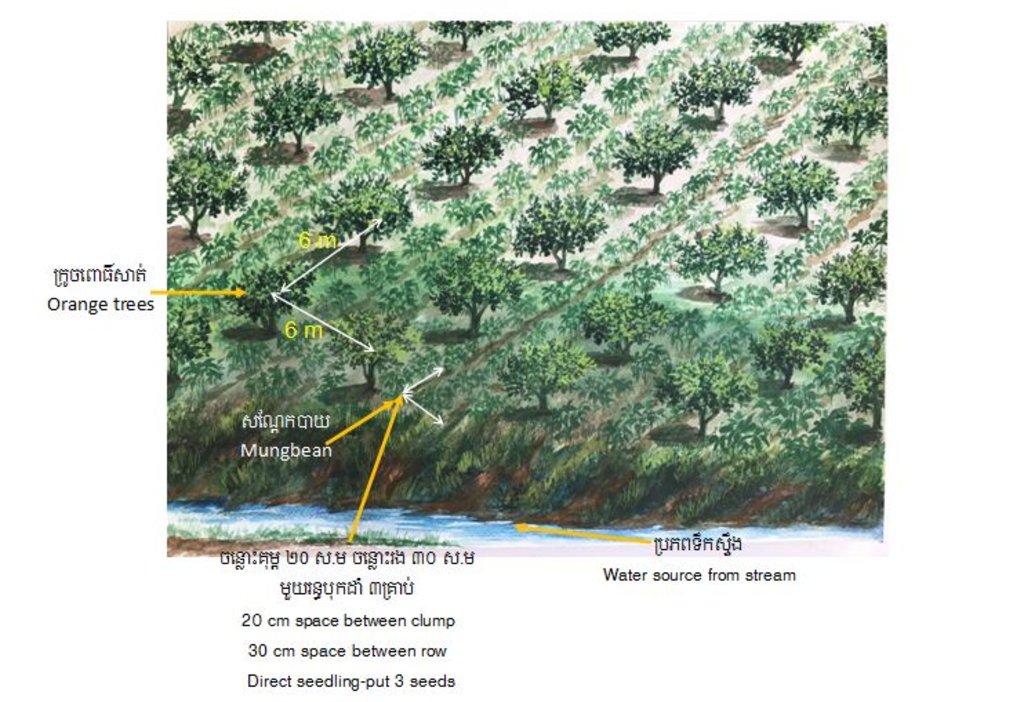
Before planting orange trees the soil requires two turns of ploughing. After first ploughing the soil should dry during 1-2 months, before it can be ploughed again by a wheel harrow. Orange trees then are planted in rows into pits of 1 m x 1 m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between the trees, as well as between the rows is usually 6 meters. Before planting, the orange tree seedlings (bought from outside) are usually kept at the farm site for 15 to 20 days, which to allow them to adapt to the conditions of the growing environment. The farmer installed a water pipe in the underground to irrigate the fruit orchard. The nearby stream serves as water source. After the tree plantation, mungbean is sown by direct seeding on the remaining bare soil. This is done by putting 3 to 4 seeds into the seed holes (3 to 4 cm sowing depth at a plant spacing of 20 cm and a row spacing of 30 cm. After harvest the residues of the mungbean plants are squashed by machine and left to rot on the soil surface until is the next mungbean cycle starts by direct seeding.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كمبوديا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Phnum Kravanh of Cambodia.
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2013
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Through farmers experience, investigation on cropping and natural fertilizer application.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الموالح (الحمضيات)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Orange trees belong to the long lifespan crop which provide fruit at the age of 4 years. The lifespan of getting fruits is approximately 20 years. Then in general, the farmer cuts the trees down and grow it again. However, it depends on the yield it provides. Mungbean can be harvested within two months and half and can be harvested 3 times per crop cycle.
التعليقات:
Orange and mungbean.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
التعليقات:
Degraded forest, soil from termite mound.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
There is a stream near the farm for supply the water for orange trees.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة

التدابير البنيوية
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
The former degraded forest soil was rehabilitated by the rotten residues of the mungbean, the deep penetration of its taproots, and by the nitrogen fixation through the symbiotic association of nitrogen fixing bacteria in the nodular roots of the mungbean. Thus, the soil structure and the soil fertility were improved little by little.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
The area of implementing this technology is 4 hectares with 1096 orange trees. The pit of planting orange trees is 1m x 1m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between trees and between rows is usually 6 meters to get enough sunlight. The mungbean is planted by direct seedling by inserting 3 to 4 seeds per hole (the hole is 3-4 cm in depth). The spacing between the holes is 20 cm and the row spacing is 30 cm. The farmer of this farm also installed an irrigation system by setting up a pipe under the ground.
المؤلف:
Mr. Khoun Sophal
التاريخ:
05/07/2017
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
4 hectares
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
KHR (Riel)
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4000,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
20000
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear degraded forest | January |
| 2. | Clear the termite mound to flatten the area | Dry season |
| 3. | Drying the soil by sunlight | Dry season |
| 4. | Buy orange trees and adapt them to the condition of the area | Dry season |
| 5. | Planting orange trees | August |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Clear the degraded forest soil | Person-day | 80,0 | 2000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Collect the residue of forest and then burn | Person-day | 60,0 | 20000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Clear 40 termite mounds in 4 hectares | Person-day | 48,0 | 20000,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Hire labor to carry the soil of termite mound to put in the hole of orange tree for planting | Person-day | 180,0 | 20000,0 | 3600000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Grass cutting marchine | piece | 2,0 | 1200000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Two wheel tractor | piece | 1,0 | 12000000,0 | 12000000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Orange seedlings | seedling | 1026,0 | 6000,0 | 6156000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Pumping machine | piece | 1,0 | 1200000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Irrigation system such as big tube, small tube etc | set | 1,0 | 8000000,0 | 8000000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Planting orange trees | Person-day | 51,0 | 20000,0 | 1020000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Pesticide sprayer machine | piece | 3,0 | 600000,0 | 1800000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Spraying pesticide hand pump sprayer | piece | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 38776000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 9694,0 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering during dry season in the first year of planting orange trees | Two times per day during dry season |
| 2. | Spraying pesticides when there is present of insects on orange trees | Spray once time per season |
| 3. | Pruning some branches of orange trees | When the orange trees 2 years (One year cut some branches once time) |
| 4. | Apply organic fertilizer for the orange trees | When the orange trees are 4 years |
| 5. | Spray against weeds | Spray once time per half month. |
| 6. | Spray pesticides on mungbean plants | When mungbean flowering |
| 7. | Direct seeding of mungbean | August |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Watering the orange trees | Person-day | 11,0 | 20000,0 | 220000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Pruning some branches of orange trees | Person-day | 100,0 | 20000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Hire labor to spray pesticides | Person-day | 8,0 | 20000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Hire labor to harvest mungbean when mature | Person-day | 120,0 | 20000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Mungbean seed (1 hectare need 25 kg of mungbean) seeds) | hectare | 4,0 | 312500,0 | 1250000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Pesticides for orange trees | bottle | 4,0 | 40000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Chemicals for improving of stem of mungbean | package | 60,0 | 1500,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Pesticide to kill worms on mungbean | bottle | 2,0 | 40000,0 | 80000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Direct seeding of mungbean | Person-day | 56,0 | 20000,0 | 1120000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 7480000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1870,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
The maintenance costs then depend on the age of orange trees. The cost calculation of maintenance of orange trees is for year period, but the the recurrent costs for mungbean cultivation is calculated only for one crop cycle (two months and half).
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The establishment of an orange tree orachard requires a lot of money.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1225,70
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
In 2015 the annual rainfall is 1225.7 mm, in 2014 is 1128.1 and in 2013 is 1316 mm.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Ministry of water resources and meteorology, 2015
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
On Phnum Kravanh mountain area.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
PH=6
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
The total crop land is 15 hectares.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
There is free access of water stream nearby. He never has water usage conflict.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The soil fertility was improved, so that the crop production increased steadily. In addition, the farmer now doesn't grow only orange trees, but he also grows mungbean.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The residues of mungbean contain many nutrients, which is suitable for getting good crop quality.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the farmer plants more than one crop on the plot now, it reduces the production failure. This means that farmer get income from mungbeans before the orange trees provide fruits. The better weed control also reduces insects, which could be harmful to the crop.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
There are mungbean and orange trees, now.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced chemical fertilizers on orange trees and mungbean, because after harvesting mungbean residues are kept on the soil which is very good green manure for soil.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The farm income increases considerably due the intercropping system, as both mungbean and orange trees provide yield. In addition, mungbeans provide yield two times per year. Last but not least , mungbean play a key role as green manure which reduces the input of chemical fertilizers and therefore cost.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The mungbean and orange tree cultivation does not consume much of labor force because he doesn't have to spend a lot of time for weeding (as instead of weed mungbeans cover the soil now). On the other hand, the farmer mentioned that the orange plantation is time consuming at the beginning, when the orange trees has to be planted. As well the mungbean need more time at the moment when the plot has to be prepared for first direct seedling. But the technology as a whole entails not a lot of maintenance workload as he uses machinery such as pesticide sprayer machine and mungbean squash machine to facilitate the labor.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The diversification of the crops (oranges and mungbean) has considerably raised the income and therefore strongly prevent food insecurity situations.
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The reduction of chemical fertilizer and pesticides provides safer products that improves the health situation. In addition, mungbean and orange fruit deliver many nutrition benefits to human health.
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
He has joined the orange trees community to sell the orange fruits. Many researches are convinced of his success and the tastiness of his oranges; as for example researchers from the District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh, Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat etc.”
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
By doing the farmer learned that degraded soil can be rehabilitated by the mean of mungbean residues acting as green manure. And from the moment the soil is rehabilitated he can see that this green manure prevents soil degradation at high degree.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Mungbean and orange trees keep the soil moisture, prevent the evaporation to the atmosphere.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Orange trees and mainly the mungbean intercrop cover the soil almost entirely all year around.
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The residue of mungbean reduce soil compact by improving the soil structure through providing organic matter to the soil. The increased amount of soil organisms make the sol less compact.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
The residues of mungbean left on the soil after harvesting are transformed to organic matter by the process of decay and therefore contribute essentially to increased soil organic matter.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Orange trees and mungbeans are the vegetation cover to avoid bare land, so the sunlight will not come directly to the the soil.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is more than one crop (orange trees and mungbean).
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Now, the soil is somewhat richer in termites, ants, earthworms, crickets ect.
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Orange trees and mungbean cultivation promote soil organisms in the habitat.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | زيادة | باعتدال |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | فصل جاف | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | زيادة | باعتدال |
التعليقات:
Change in rainfall. If there is too much rain, the soil will be saturated and the root will be spoiled what reduces the yield of mungbean.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
When the orange trees grow bigger, it will provide very high income.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Get income from the mungbean before orange trees provide fruit as a potential source of income. |
| The residues from the mungbean plants help to improve soil fertility. |
| The potential market of orange tree fruits is good, with traders buying directly from producers at the farm. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Residues of mungbean improve soil fertility, reduce soil degradation and help rehabilitate the degraded land. |
| In the initial 3 to 4 years of growth of orange trees it is important to grow short term crops like mungbean to provide an income source. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Orange trees require a lot of water. | Grow near a water source such as a stream or river, or dig ponds to hold water. Land users need to consider a potential water source. |
| When the soils become saturated due to excessive rain, the mungbean plant roots can degenerate and result in low grain yields and low grain price (due to poor grain quality). | There is little that farmers can do to improve the performance of the mung bean crop in conditions of soil moisture saturation. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| As the orange trees grow bigger there is reduced opportunity for intercropping with mungbean. | Grow intercrops that do not require much sunlight, such as ginger or galanga |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
One place
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
one person.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
4 persons
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
04/07/2017
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Chadha, M. L. (2010). Short Duration Mungbean : A New Success in South Asia.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
N/A
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP. (2016). Forest Restoration and Rehabilitation “ Enhancing Climate Change Resilience of Rural Communities Living in Protected Areas in Cambodia .”
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Ministry of Environment(MoE). Free of charge.
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
MAFF. (2005). Mung bean.
عنوان الرابط URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.maff.gov.kh/agri-tech/56-ដំណាំឧស្សាហកម្ម/ការដាំដុះសណ្តែក/1519-ដំណាំសណ្តែកបាយ.html
العنوان/الوصف:
Tauch Ung. (2010). Overiew of mung bean.
عنوان الرابط URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwhP4tVirBPsOTM3OWFiMzktZTdmNi00NjMyLTg1NjktMzFhYzhmMzUyMjVl/view?hl=en
العنوان/الوصف:
IRRI‐CIMMYT Alliance. (2009).The importance of legumes in cereal cropping systems.
عنوان الرابط URL:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/images/pdfs/the_importance_of_legumes_in_cereal_cropping_systems.pdf
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية