Afforestation for firewood production [أفغانستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Bettina Wolfgramm
- المحررون: MIAJAN MAROOFI, Hekmatullah Sharifzai, Roziya Kirgizbekova, Aslam Qadamov, Aqila Haidery
- المُراجع: William Critchley
Bunyodi jangal baroi tavlidi chubi sukht
technologies_668 - أفغانستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
Sari Joy Village, Rustaq District
أفغانستان
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Researcher:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
27/10/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
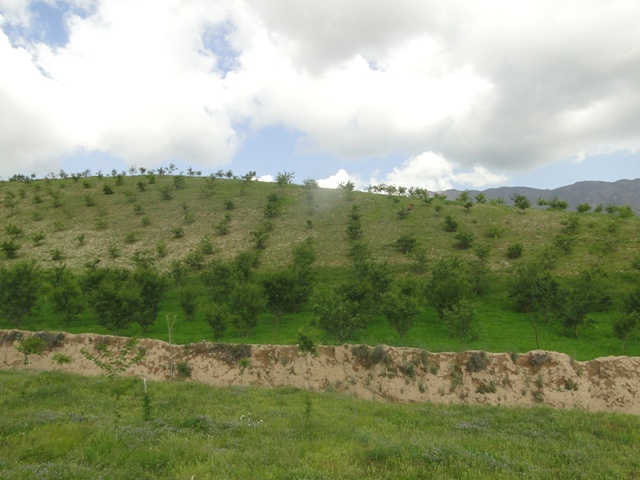
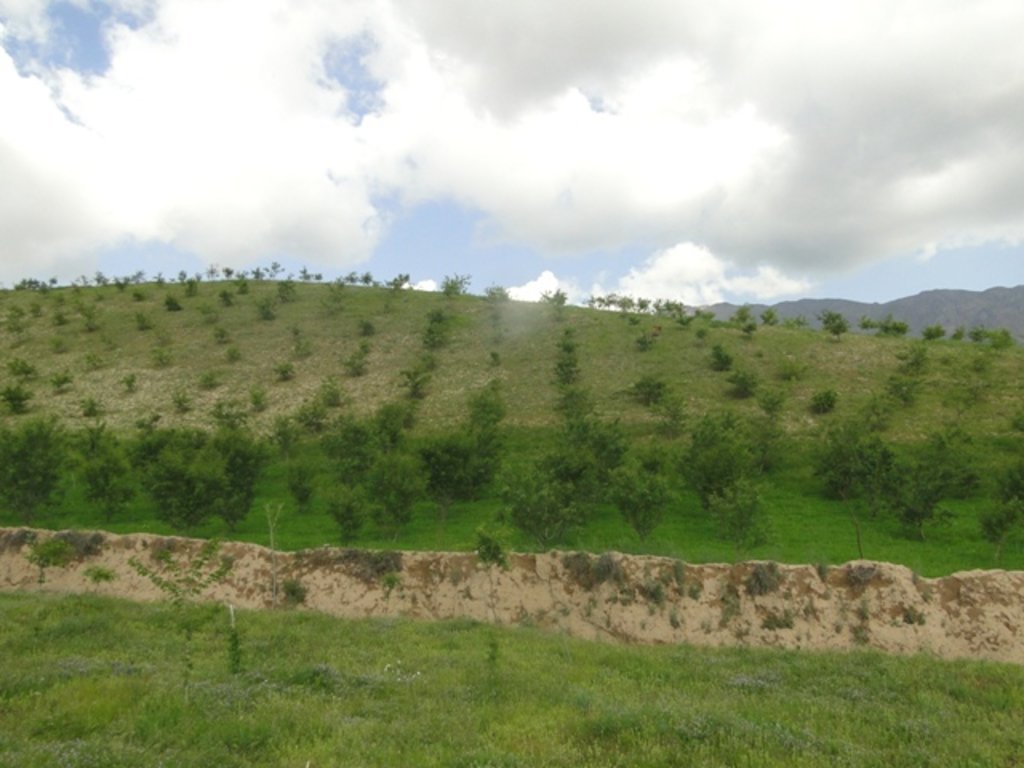
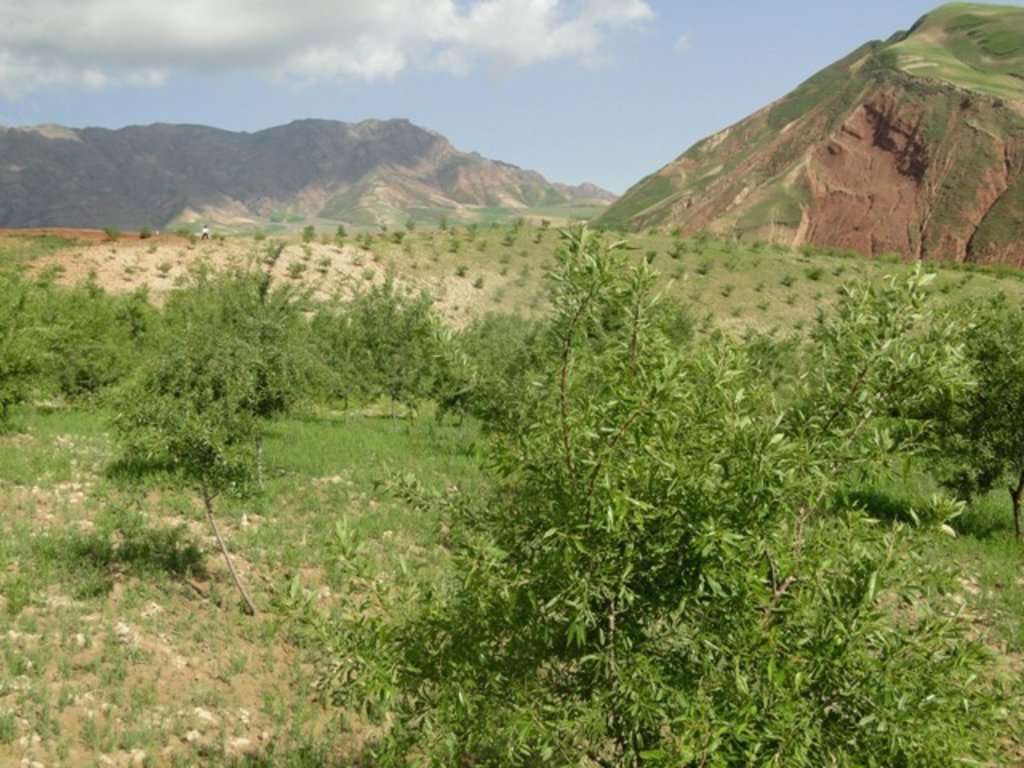
Non-fruit and fruit trees are planted on heavily degraded forest land to protect the land from erosion and further degradation and provide fuelwood for the local community.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Project supported implementation of afforestation has taken place in the villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 and 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter, and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580 mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use, and includes low levels of vegetation cover, severe water erosion of topsoil, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting the socio-economic well-being of local communities, as well as contributing to the risk of being adversely affected by drought - and landslides and flash foods triggered by heavy rainfall. The data used for the documentation of the technology are based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zones of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months. The three villages are home to ethnic Qarluq communities. Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions
Despite the low forest cover in Rustaq, Afghanistan, local communities strongly rely on fuelwood and animal dung for cooking and heating throughout the whole year. Forests are mainly found on community land with open access to all, and there are no protection measures in place. The high demand on fuelwood for household needs places strong pressure on the remaining patches of forests and bushes, which are currently threatened by eradication. Such high demand in the area is likely to remain as there are no other alternative energy sources. The mass destruction of local forests is one of the main causes of intensive erosion, aridification, loss of topsoil and formation of gullies. Low forest cover increases vulnerability to severe rainfall and risks of landslides.
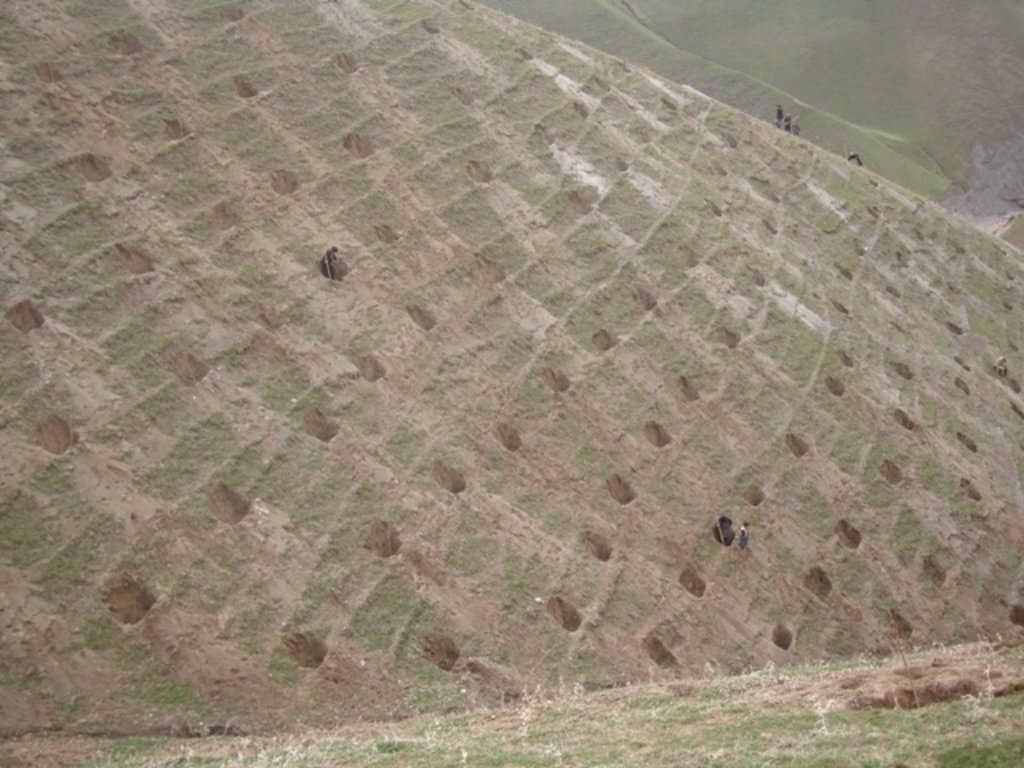
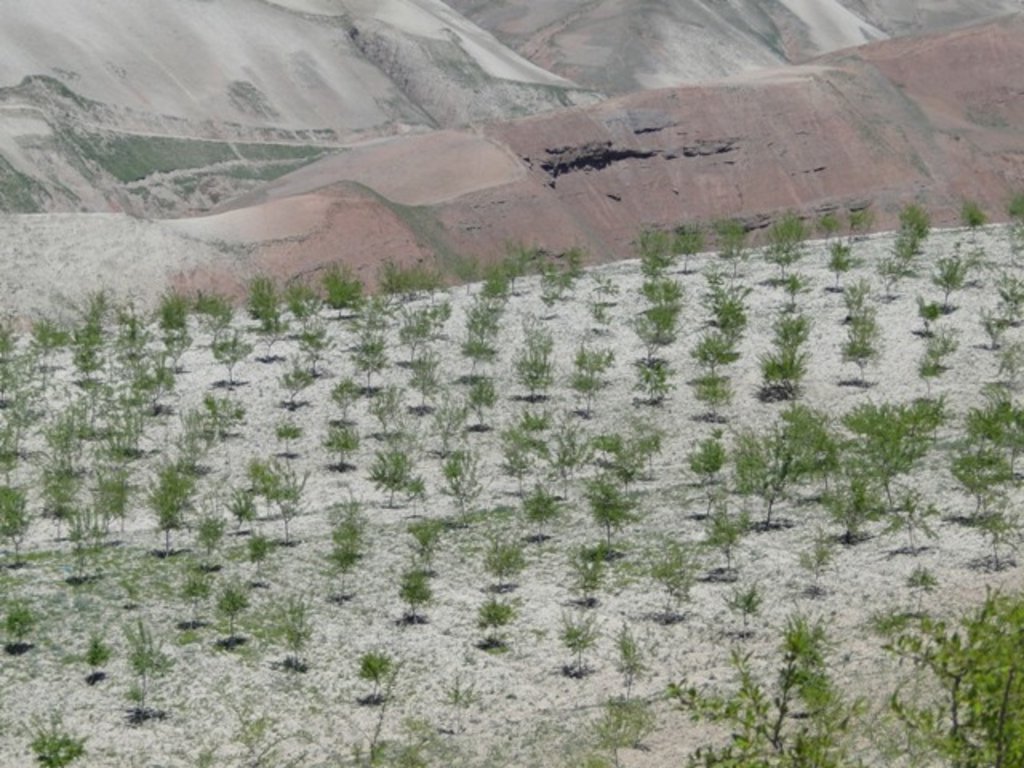
Afforestation measures in the three villages were initiated to halt the land degradation and provide sustainable firewood. The reforestation sites are largely on community land with a small share on private land. The area is characterized by hilly (16-30%) and steep (31-60%) slopes. Planting and maintaining forest in such conditions requires close support in the appropriate design of forest plots, and relevant maintenance recommendations, which can then ensure the survival of the plantation. A plot of 0.2 ha is divided into 4 m x 3 m sections. Each tree is placed in a pit of 50 cm x 30 cm with rich soil around the roots. Once the tree is planted, it is watered and covered with lime. Russian willow, acacia, mulberry and almond are the most common tree species used for afforestation purposes.
Most of the newly established forest sites are located at walking distance of the nearby villages: this is important to help provide protection of the plot from animal intrusion and ensure proper maintenance of the trees. The forest plot is watered for three years in a row. The Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC) pays 0.60 US cents per tree per year to sustain the survival of the plantation within the first year. The funding for the irrigation is provided by the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT). LIPT supported the afforestation activities through the provision of technical and financial support. The tree seedlings were supplied by the project, and financial incentives were provided to engage the community in tree-planting.
The plantations are still very young: however, the land users express support for the new forest in their villages, and have observed localized stabilization of the soil and improvement in vegetation cover. There are high expectations of the new forest, which promises access to sustainable fuelwood and non-forest products, such as almonds and mulberry. The grass and tree leaves from the forest plots are already used for animal fodder.
Women and children under 15 years old are expected to be the direct beneficiaries of the new forest. They will no longer spend long hours to collect and deliver fuelwood, bushes and dung. A small portion of women reported involvement in forest establishment activities, while the majority are taking part in protecting the forests from livestock.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أفغانستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai
التعليقات:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM impementers from Sari Joy (5 plots), Jawaz Khana, (4 plots), and Dashti Mirzai (3 plots) as compiled during focus group discussions. Additionally insights were gained through interviews in all three villages on farmers experiences and observations of afforestation plots, with both SLM implementers (20) and observers (10).
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الحرجي
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Acacia, Russian willow, mulberry. almond, grass and leaves for fodder
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Some of the forest land has been heavily degraded and was used as grazing land for an extensive period. Most of the land is forest land.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
During the first three years the forest requires irrigation due to aridity. The first year of irrigation is supported by the project, and the rest of the irrigation measures are implemented by the local community with the support of the NRMC.
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
23.6 ha
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
Aslam Qadamov; Roziya Kirgizbekova
التاريخ:
03/04/2017
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The establishment activities begin with selecting the area for reforestation. Most of the reforestation sites are on slopes above 6% steepness . A plot of 0.2 ha is divided into 4 m x 3 m sections. Planting pits of 50 cm x 30 cm are prepared for planting the trees. Each tree is placed in a pit and good soil is added to the roots. Most popular species used for reforestation are: Russian willow, acacia and mulberry. The newly planted tree is watered and the trunk is covered with a lime and water solution for protection and better growth.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 ha
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
67,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Design of the forest plot | إدارية | Winter |
| 2. | Digging pits 50 cmx 30 cm for tree plantation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | End of winter |
| 3. | Planting tree seedlings 3m x 4m | نباتية | Spring/Rainy season |
| 4. | Watering the tree after planting | نباتية | Spring |
| 5. | Covering the tree with lime | تدابير أخرى | Spring |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Design of the forest | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | |
| العمالة | Digging pits/holes for the trees | person-day | 22,0 | 5,3 | 116,6 | |
| العمالة | Planting tree seedlings and watering | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | |
| العمالة | Fertilizer and lime application | person-day | 8,0 | 5,3 | 42,4 | |
| معدات | Meter | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| معدات | Shovel | piece | 2,0 | 3,8 | 7,6 | |
| معدات | Pickaxe | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| معدات | Rope | meter | 500,0 | 0,07 | 35,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Accacia seedlings | piece | 275,0 | 0,45 | 123,75 | |
| المواد النباتية | Russian willow seedlings | piece | 275,0 | 0,45 | 123,75 | |
| المواد النباتية | Mulberry seedlings | piece | 275,0 | 0,45 | 123,75 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | DAP | kg | 250,0 | 0,9 | 225,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Lime | kg | 25,0 | 1,5 | 37,5 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 998,85 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland
التعليقات:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protecting the trees from livestock | إدارية | Spring/Summer |
| 2. | Pest and disease control | نباتية | Spring |
| 3. | Irrigation | زراعية | Summer/First three years |
| 4. | Replanting dead trees | نباتية | Spring |
| 5. | Pruning | زراعية | Spring |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Pest and disease control | person day | 7,5 | 5,3 | 39,75 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Replanting dead trees | person day | 7,5 | 5,3 | 39,75 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Irrigating the trees | person day | 10,0 | 5,3 | 53,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Pruning | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 159,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
564,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 564 mm, with minimum in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximum in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Derived from the publicly available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Local land users refer to the soil type where reforestation is implemented as:
Dark soil is characterized as: moderately deep; topsoil texture medium, below surface texture medium; and medium topsoil organic matter.
Light soil is characterized as: moderately deep; texture medium; medium, low organic matter.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water varies in the three study villages. Sari Joy and Dashti Mirzai have good surface water availability, which is also food for drinking. Jawaz Khana has poor water both in quality and availability. Water has to be fetched from a distant stream.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
The land users in the area where the Technology is applied belong to the Uzbek ethnic minority group Qarluq. Although the men are generally the main land users, women and children also take active part in the related work. The functions of men and women are clearly distinguished within the Afghan society. At the same time within the family this division of work and functions also results in men and women working hand-in-hand. An improvement of the family’s livelihood situation is expected to positively affect all family members. While it is recognized that the involvement of women is key in order to secure basic human rights for everyone, to achieve good governance, sustainable development, and to efficiently contribute to poverty reduction (SDC 2004), it is also clear that a context sensitive approach is of high importance.
Women in rural Afghanistan are involved in many production and income generating activities that contribute to the overall household income, however very few women own resources such as land and livestock, and their income generating options are fewer in comparison to that of men.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for water. The payment is made either in kind or in cash to Mirob - the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج حيواني
إنتاج الخشب
إنتاج الغابات غير الخشبية
تنوع المنتج
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land users learned new methods of planting trees based on the local conditions.
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
The established forest is expected to become a reliable source for firewood, which will decrease the burden of women and children under 15 years, who spend long hours to collect firewood.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
فقدان التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
تعليقات بشأن تقييم الأثر:
Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits for their Technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all SLM implementers are reflected here.
Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدة جدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly, well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrixes compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: During the FGD with SLM implementers, a multi-criteria matrix was elaborated, and different SLM practices were rated. In the framework of this exercise, SLM implementers were asked to jointly discuss and rate short term (1-3 years) and long-term (10 years) returns. As the SLM technology was only implemented 1-2 years ago, it is too early to compare benefits to maintenance costs. Farmers have little experience so far on the actual benefits of the SLM technology. The ratings are mostly based on expected benefits and not on actual benefits.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
23.6 ha have been afforested with LIPT support
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
Based on the Land User Protocol: Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%".
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The tree plantations protect the soil from erosion. The land is less vulnerable to heavy rainfall, which washes off the topsoil |
| There are very high expectations about production of firewood. Availability of firewood in local forest will make it much easier to access firewood for cooking and heating by local households. |
| Apart from firewood and wood production, other non-timber products are provided by the afforestation plots, such as fodder for livestock from grass (alfalfa, sainfoin) and tree leaves during autumn. Also some plots are planted with almond and mulberry, which can be collected for own use or for selling. |
| Local people value the recreational benefit of the forest, which make their villages greener and provide green spaces for the local people. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The afforestation measures in the village including establishing the forest and protecting it, mobilizing the community around a common goal, and this has a positive impact on the village as a whole. |
| The planted trees and grass under the trees improve the vegetation cover and increase soil quality, which is then less prone to erosion |
| Improved varieties of fruit and non-fruit tree species used for afforestation help to diversify the tree species in the village and make the soil less resistant to dry spells |
| The expected combined benefits of wood and non-wood products, especially when the harvesting period starts, may have positive impact on households' income and food security. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The establishment costs for afforestation measures are very high | |
| The young trees are vulnerability to droughts | |
| During maintenance some plots require irrigation | |
| Afforestation plots, which are established on former grazing land, reduces the grazing land in the village and deprives animals from grazing land |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Community provides weak or no protection of the afforestation site, which results in low tree survival | |
| Weak funding sources for irrigation of the afforestation plots, particularly during the first three years when the trees are young, might compromise the new plantations | |
| Afforestation is established mostly on community land, where unclear land tenure rights persist, which may cause conflict in the community over forest vs grazing land |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
No field visits were conducted
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by the CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 15 land users who have implemented afforestation, participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 30 persons interested in afforestation implementation, of which 20 persons are from households that already have implemented afforestation.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Close collaboration took place during the compilation of this material with the technical staff of the LIPT project in Rustaq.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Information provided in the reports of the LIPT project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Guidelines for Focus Groups Discussions
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Methods section of the Rustaq NRM study
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية