Water run-off control plan on cultivated land [جنوب أفريقيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Carin Pretorius
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
Watercourses and contours
technologies_956 - جنوب أفريقيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/06/1999
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Artificially built watercourses with contour banks with a specific gradient
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
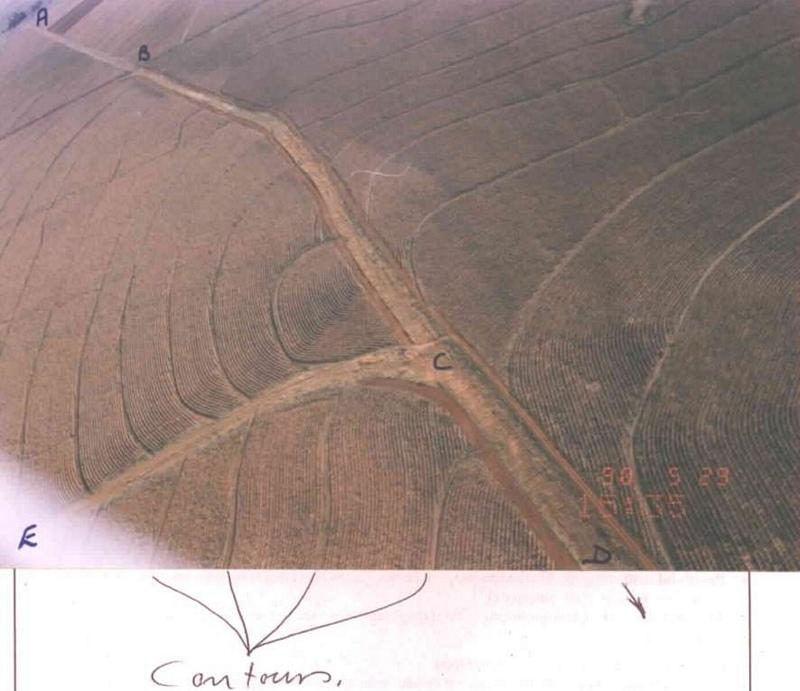
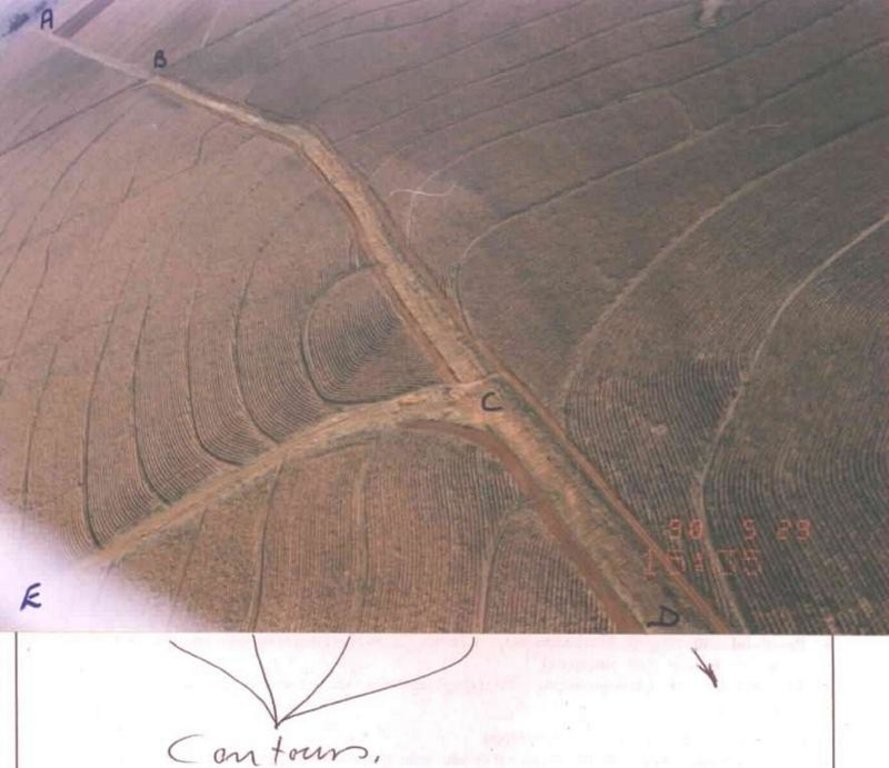
Watercourse: According to the topography, one or two watercourses are needed to drain any excess run-off water during high rainfall intensities. A watercourse is built directly downhill. A perennial grass adapted to the specific environment is established in the watercourses. Maintenance requires that the grass must be fertilised according to the climate of the area. Regular (once or twice a year) cutting of the grass is very important to maintain a good grass cover, through which soil erosion in the watercourse can be prevented.
Contour banks: These are built with a gradient to spill the excess water into the watercourse. The purpose of contour banks is to shorten the slope so as to reduce the speed of the water and prevent soil erosion. The maintenance requires keeping the canal in good shape and maintaining the height of the banks.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
جنوب أفريقيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
North West Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Lichtenburg
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The contour part came mainly form the USA.
The watercourse part was developed in South Africa.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cultivating lands without the necessary soil conservation works to prevent soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cultivating the lands preventing soil erosion through plant directions
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 m2.
Although the total extent of the farm is 584 ha, only 250 ha plus 50 ha adjacent land was addressed through this technology.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Cultivating land on a step slope without proper conservation practices.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - How to solve the problem)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Topography; concentrating water in valleys causing soil erosion (steep slopes).), Poor conservation ethic
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
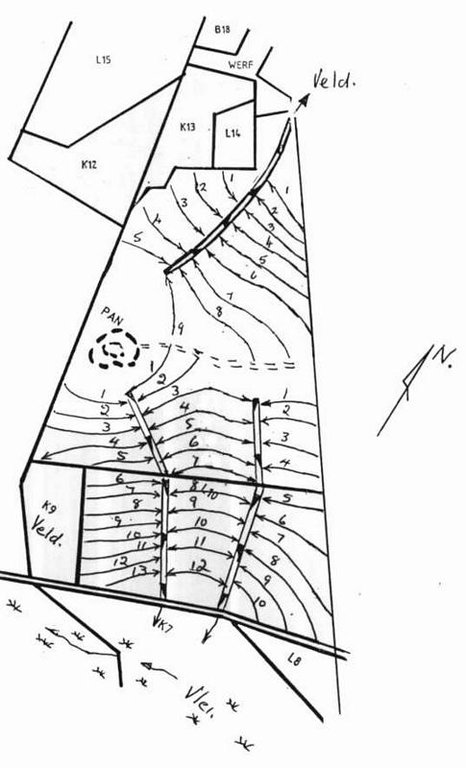
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Water run-off control plan
Location: Lichtenburg. North West
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, Maintain soil fertility as less fertilizer are lost by water run-off
Vegetative measure: watercourses
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): seeds 6-8kg/ha
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops, G : grass
Grass species: Digitaria Smuts, Eragrostis curvula, Cynodom dactylon
Structural measure: bunds/banks: contour
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3-1.75
Spacing between structures (m): 72-33
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Construction material (earth): Construction contour banks with soil form the ditches
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.3%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
rand
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
6.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Established grass in the watercourses | نباتية | After construction according to design specifications |
| 2. | Surveying | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 3. | Construction of contours | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Any time depending on soil moisture |
| 4. | Construction of watercourse | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Before growing season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building contours and watercourses | زراعية | Any time / Before planting of crops |
| 2. | Building contours and watercourses | زراعية | Depending on soil moisture / |
| 3. | Maintenance | زراعية | Before planting of crops / Annually |
| 4. | Cultivation between contours | زراعية | Depending on the crop / Annually |
| 5. | Maintaining a good grass cover | نباتية | Rainy season /Once or more times a year depending on the grass |
| 6. | Fertilisation of the grass in the watercourse | نباتية | Rainy season /Once or twice in the rainy season |
| 7. | Watercourse, cutting the grass | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Beginning of rainy season/Annual |
| 8. | Contours repairing flood damage | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season/After heavy rains |
| 9. | Contour opening ditches | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Before planting of cops/Annual |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor & plough or a grader
Contours per kilometre. NB currant tariff for subsidy. Watercourse construction per volume soil moved and grass establishing per ha above the current tariff for subsidy from April 1998
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Soil moisture and clay contents
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 100% of the land.
90% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land (If management is good).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers are dedicated to make a living out of farming, although there are some farmers with an off-farm income such as transport.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
منطقة الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
25
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
4
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: So little, almost none. The lack in technicians from government promoting this technology and to deliver technical services are the main reasons expect for the poor conservation ethic of the farmers.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good regular maintenance |
| Building up a good layer of topsoil |
| Effective run-off control of excess rainwater |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Effective erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
|
Improve water infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Increase crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good cultivation practices and maintenance of contours |
|
Prevent off-site siltation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Hampers cultivation | Adapt change in cultivation practises |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Cannot think of any |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية