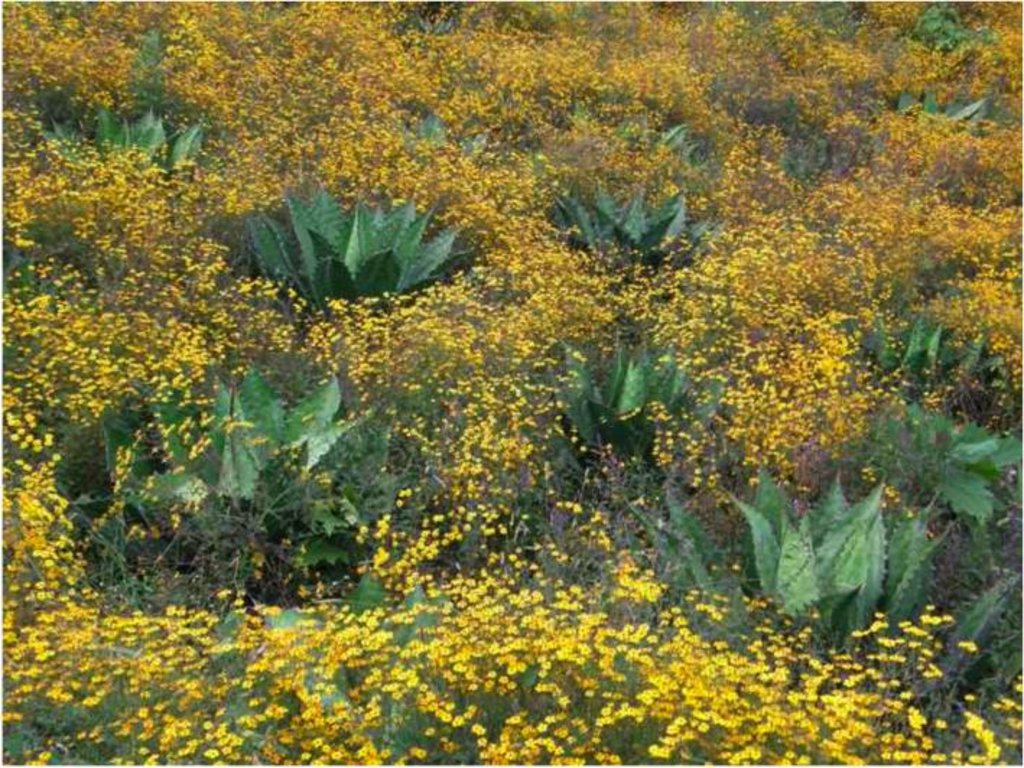
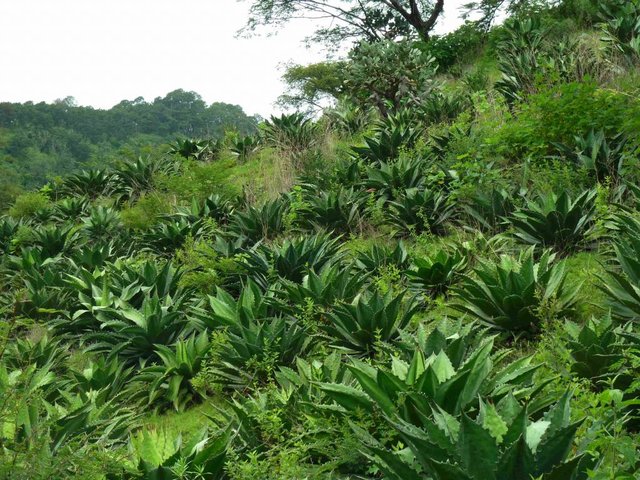
Land reclamation by agave forestry with native species [المكسيك]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Prat
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Recuperación de tierras degradadas por agaveforestería con especies locales de agaves, arboles y herbaceas (Spanish)
technologies_1114 - المكسيك
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Martínez Palacios Alejandro
Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias y Forestales, Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo
المكسيك
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ríos Patrón Eduardo
Delegación de SEMARNAT en Michoacán, Unidad de Planeación y Política Ambiental
المكسيك
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias y Forestales (IIAF) - المكسيكاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Institut de recherche pour le développement IRD (Institut de recherche pour le développement IRD) - فرنسااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
SECRETARÍA DE MEDIO AMBIENTE Y RECURSOS NATURALES (SECRETARÍA DE MEDIO AMBIENTE Y RECURSOS NATURALES) - المكسيكاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo (UMSNH) - المكسيك1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Participative actions for economic benefits of agave forestry [المكسيك]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce Mezcal) associated with trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Prat

Land reclamation by agave forestry with native species [المكسيك]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce mezcal) associated wotj trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Prat
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Agave forestry land reclamation system with native agaves, trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participatory action for a sustainable production of mezcal and other products in order to generate high incomes for farmers.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
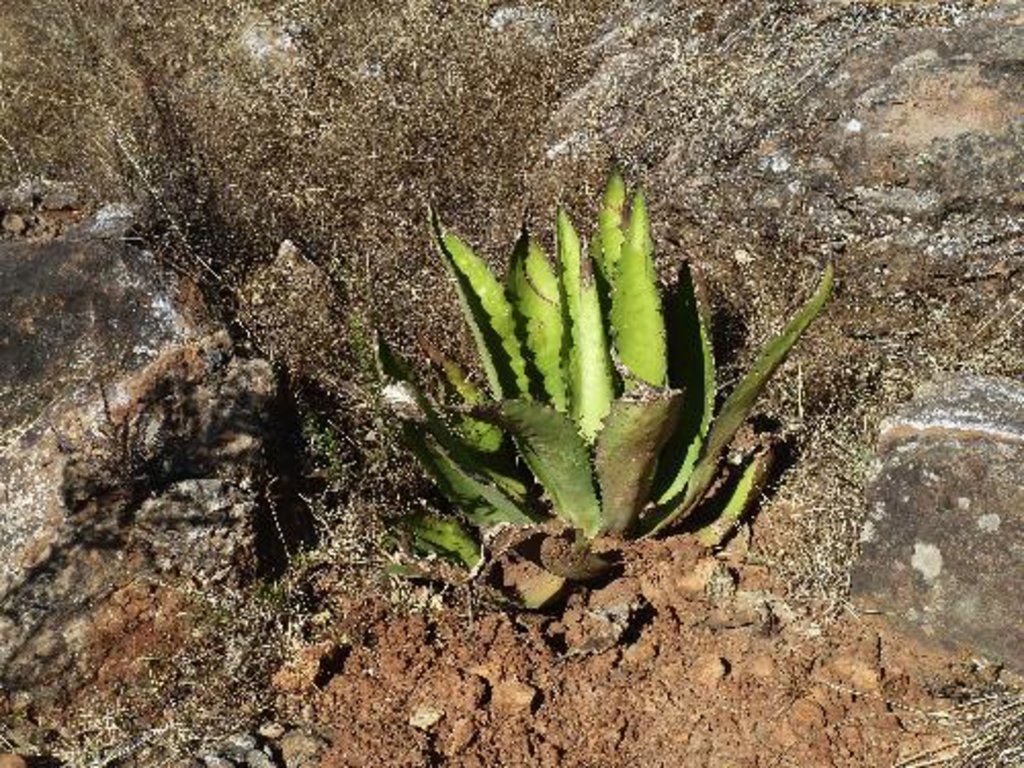
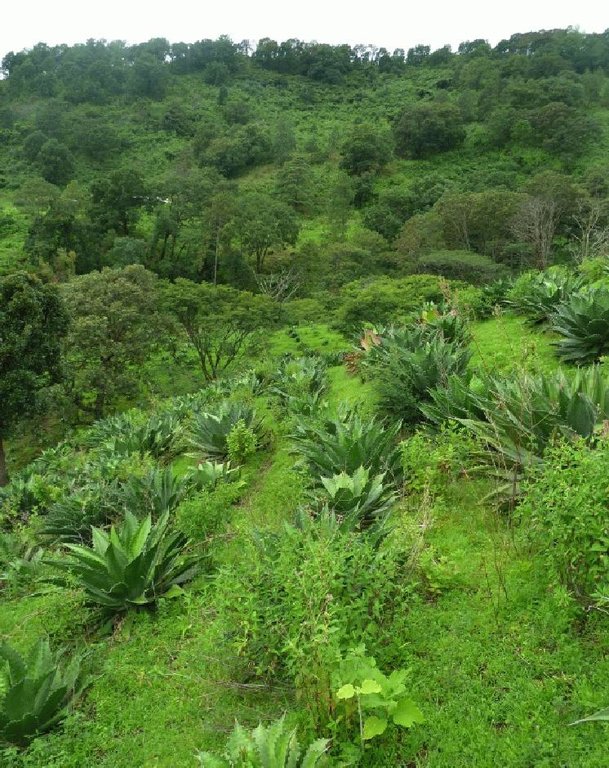
Rehabilitation of degraded land is achieved using native agave (Agave inaequidens), trees and/or fruit trees, shrubs and grasses to create, over the medium-term (7-10 years), sustainable production of a traditional alcoholic drink (mezcal) made from agave and/or cosmetic and medicinal products, and/or fibres and/or fodder for cattle and/or wood. Between the agave plants, native vegetation is managed or planted for use as food, fodder and/or medicinal products. Depending on the slope and the level of land degradation, continuous planted rows of agave provide a ’green’ barrier that controls soil erosion and runoff.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose is to achieve sustainable land rehabilitation while generating a high income for the farmer. This allows reducing the amount of livestock and overgrazing, which is the main cause of soil erosion in this region. The production of mezcal gives local farmers high incomes. Trees, shrubs and grasses for medicinal uses, food, and fodder are complements of agave production and are processed mainly by women, while agave harvesting is a male activity. As it is very attractive financially, farmers stay in the communities instead of emigrating to cities or abroad. Biodiversity is preserved and increased using native plants (agaves, trees, shrubs, grasses). These plant associations are effective at controlling plant pests and diseases. Turning eroded into productive soil sequesters carbon and increases water availability as a result of the new soil cover.
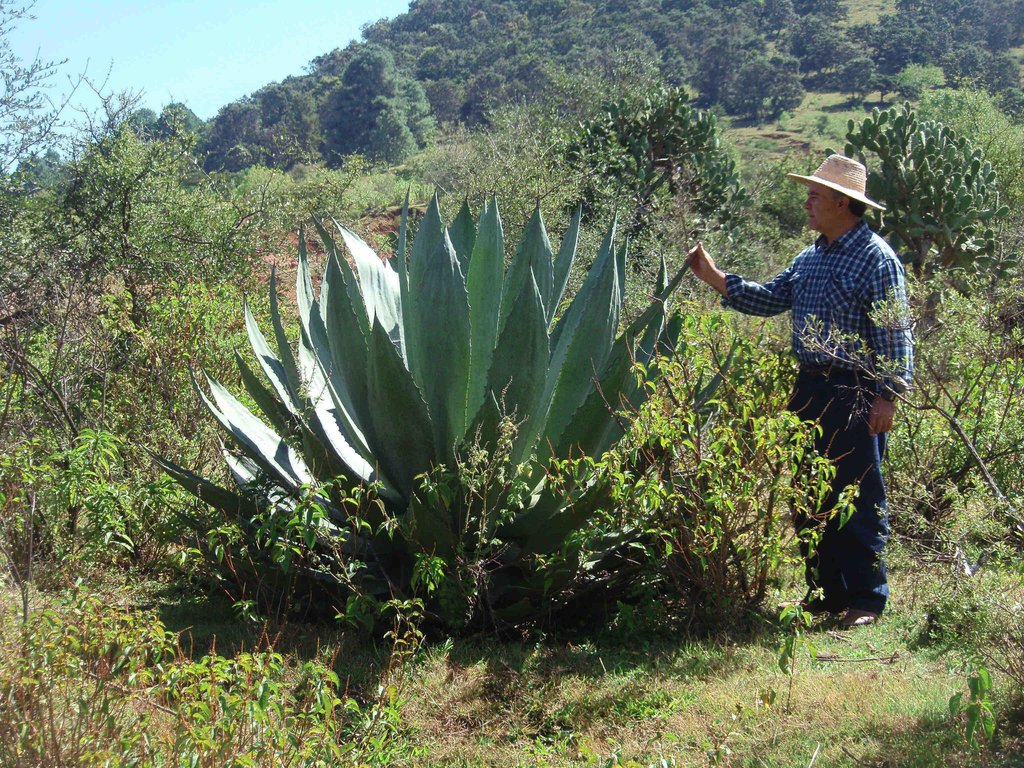
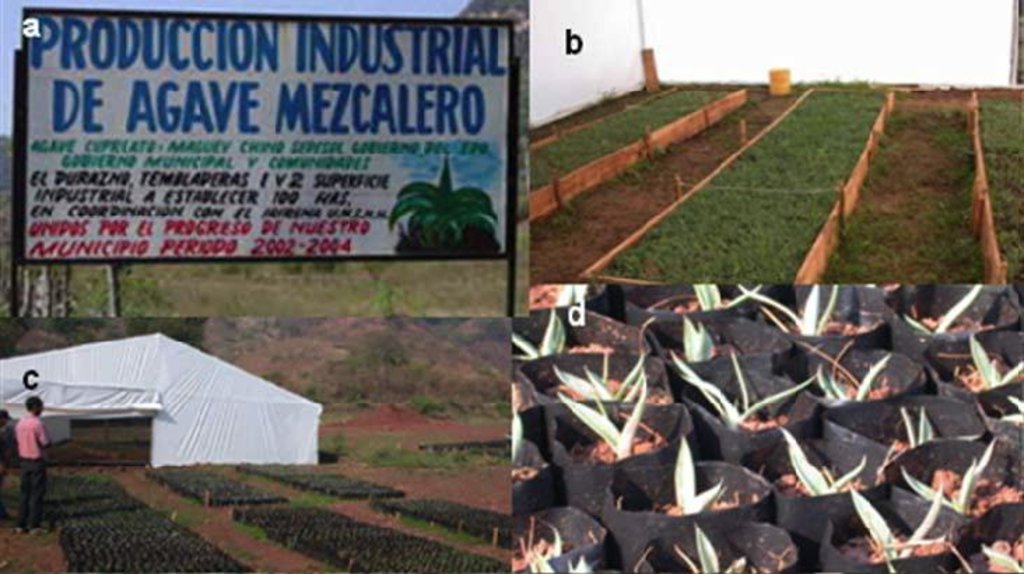
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Unlike most agave, Agave inaequidens reproduces from seed, which requires harvesting the seeds from native plants in the fields. One plant generates 80,000 seeds with a 90% success rate of germination, which is enough to cover 25 ha of agave forestry plantations set up to control soil erosion. After harvesting seeds from native agaves, trees and shrubs, seedlings and small plants are raised in a greenhouse and nursery managed by the owners and tenants of the land in the first year. At the beginning of the rainy season, these are planted in plots protected from cattle grazing for at least the first two years after planting. The harvesting activity for trees, shrubs and grasses is done annually, but for the agaves only once every 7 to 12 years depending on the degree of soil degradation. Some months before harvesting, the flower from the stem has to be cut. The leaves are then cut and left in the plot while the 50 kg heart of the agave (“piña”) is removed. Mezcal is produced from the heart and requires an average of three weeks and at least two men to process 25 agave plants (1.5 tonnes), which produces about 300 litres of mezcal.
Natural / human environment: Poverty levels in the area are medium to high and the income from agriculture accounts for only 10 to 20% of the total family budget. People, therefore, do not have time to install soil erosion protection systems in the fields. Cattle graze freely everywhere and the number of animals is increasing annually, which also increases soil erosion. Locals know how to produce mezcal, but they prefer to buy it from other people who take wild plants from their lands to process them. The proximity of the site to the Michoacán of Ocampo state capital and the recognition of the designation of origin for mezcal by the authorities will enhance its value for future production.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
المكسيك
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Mexico/Michoacán state
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Morelia municipality
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
630 km2 is the area of the Cointzio watershed. Untill now (2010), 10 ha have been managed with this technics and from 2011, 50 ha/year will be done (at least)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
10 years ago, at Titzio, close to Cointzio basin, A. Martinez developped the culture of a wild native agave (Agave Cupreata) for alcohol production which was done traditionnaly for local consumming. We are following this project and objectives, but we are improving it for land remediation and soil erosion control too with a new species of native Agave (A. inaequidens)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الصبار / السيزال
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 190; Longest growing period from month to month: June to November

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Mainly overgrazing due to uncontrolled grazing by cattle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water due to the storms and improper land use.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)

أراضي الرعي
- Extensive grazing
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- تحسين أصناف النباتات/سلالات الحيوانات
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك

التدابير الإدارية
- M3: التخطيط وفقا للبيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
التعليقات:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, breaking compacted topsoil, contour ridging, breaking compacted subsoil
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pu): فقدان الوظيفة الإنتاجية الحيوية بسبب أنشطة أخرى

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: soil management (System of one year culture/one year fallow with cattle), overgrazing (THE real cause of soil erosion here), poverty / wealth (Cattle is used as a "bank on 4 feet")
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Untill 30 years ago, some wood was used for carbon used for cooking), population pressure
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
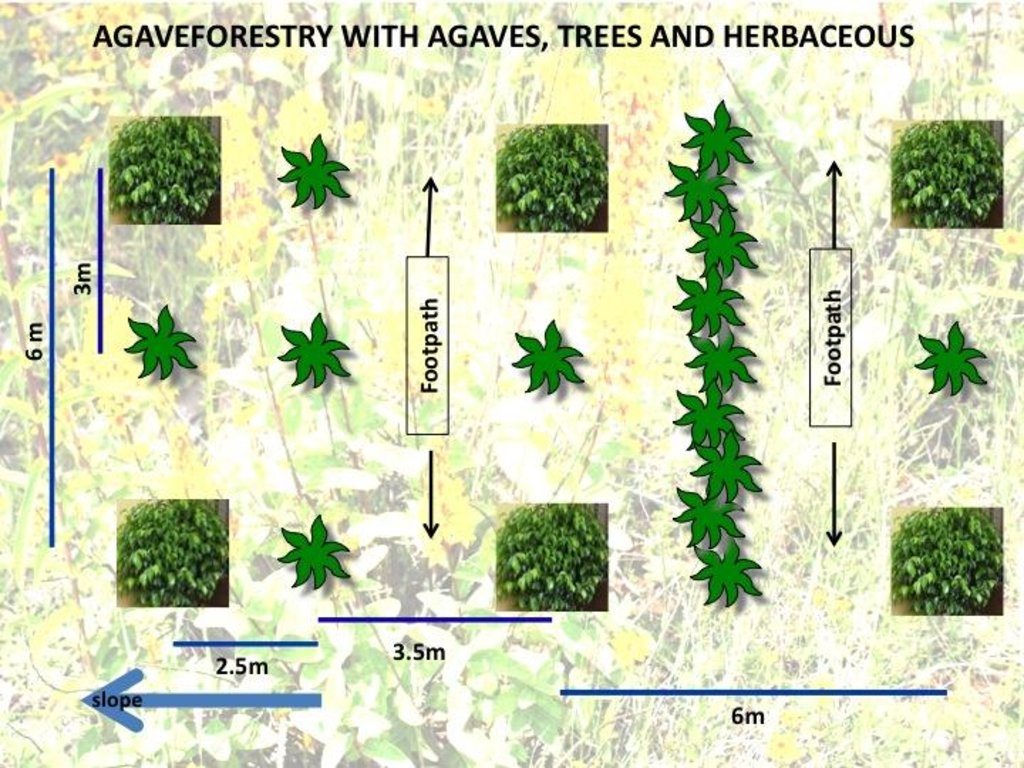
Agave production is based on planting them with trees along the contour. Herbs are maintained / planted or sown between the plants. Depending on the slope, one or more dense lines of agaves (1 plant every 25 cm) is planted for control of soil erosion and runoff, including a lateral gradient to the gully which will evacuate the excessive runoff. Footpaths are planned for the maintenance of the plantation
Location: Michoacán. Mexico
Date: 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (low for reproduction, plantation and cultivation and middle for alcohol production)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (low for reproduction, plantation and cultivation and middle for alcohol production)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Native trees+herbaceous
Agronomic measure: Herbaceous
Material/ species: Native herbaceous
Agronomic measure: Leafs from trees
Material/ species: Native trees
Quantity/ density: 270
Remarks: Trees per ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Contour ridging
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: Agave inaequidens+native trees+herbaceous
Quantity/ density: 830/270
Remarks: Agaves/Trees per ha
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 1200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0,25
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Perennial crops species: Agave inaequidens (mature between 7 to 14 years)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 30%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Natives plants are used, planted according to the slopes and the rest of vegetation still existing
المؤلف:
Alejandro Martinez, apalacios56@gmail.com
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
100 ha
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
mexican pesos
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
13,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
160
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection and collect Agave and tree seeds | 1 week |
| 2. | Building of greenhouses incl. soil and organic matter | 1 month |
| 3. | Fencing of greenhouses with barbed wire, poles and nails (0.5 ha | |
| 4. | Seeding & maintaining in greenhouses | 3 monthes |
| 5. | Installation of a nursery for agaves and trees and transplantation of seedlings in plastic bags | 2 weeks |
| 6. | Plant care and maintaining in nursery (9 months) | 9 monthes |
| 7. | Transportation of plants in plastic bags | |
| 8. | Plantation of plants (agaves and trees) |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Building of greenhouses | persons/day | 21,0 | 523,8095 | 11000,0 | |
| العمالة | Seeding & maintaining in greenhouses | persons/3 months | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | |
| العمالة | Installation of a nursery for agaves and trees | persons/day | 14,0 | 1071,4285 | 15000,0 | |
| العمالة | Plant care and maintaining in nursery | persons/9months | 2,0 | 15000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Selection and collect Agave and tree seeds | plants | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Materials for plant care | months | 9,0 | 2777,7777777 | 25000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Materials for greenhouse | trees | 60000,0 | 0,056666666 | 3400,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Materials for greenhouse | agave | 200000,0 | 0,035 | 7000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Materials for fences | m | 1500,0 | 2,4 | 3600,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Materials for nurserys | trees | 60000,0 | 1,5 | 90000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Materials for nurserys | agaves | 200000,0 | 0,2 | 40000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 235500,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 18115,38 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning around plants to give them space the first 3 years (For 1 person 10 days) | 1 time/year |
| 2. | Cutting the scape before the harvest (For 1 person 15 days) | 1 time in agave life (between 7-14 years) |
| 3. | Weeding around plants to give them space during the first 3 years (10 person days) | 1 time/year |
| 4. | Cutting the stalk before the harvest (15 person days) | 1 Agavelife time (7 to 14 years old) |
| 5. | Replanting of agaves after 7 to 14 years (restarting of a new cycle of production, see establishment activities) |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Weeding around plants | persons/day | 10,0 | 160,0 | 1600,0 | 10,0 |
| العمالة | Cutting the stalk before the harvest | persons/day | 15,0 | 150,0 | 2250,0 | 10,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 3850,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 296,15 | |||||
التعليقات:
Calculations are for the plantation of 200,000 plants (agaves and trees) which correspond to the numbers of plants for 100 ha in the agave forestry example presented here. The main portion of these plants is planted by the community on the own land; the rest is given or sold to other communities or private people. The lifetime of the greenhouse, nursery and fencing installations are around 10 years.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most important factors determining the costs are: 1) the materials to build a greenhouse and the personal to take care of young plants; 2) the difficulties to make holes in the indurated soils, which takes time and efforts; and 3) the distance between the nursery and the field requires time and efforts (truck carrying the plants).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainy season from june to october
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: Also steep, very steep and moderate
Altitudinal zone (2000-2500 m a.s.l.) : The Agave inaequidens grows is this conditions but other spieces of Agaves grow in other agroclimatic conditions
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: For Agaves and herbaceous no problems, for trees much more difficult
Soil texture (topsoil): For Agaves, trees and herbaceous no problems
Soil fertility is very low - medium: For Agaves, trees and herbaceous no problems
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - poor: For Agaves and herbaceous no problems, but some difficulties for some tree species
Soil water storage capacity is very low - medium: For Agaves and herbaceous no problems, but some difficulties for some tree species
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: Also > 50 m and for Agaves, trees and herbaceous no problems
Availability of surface water: Also poor/ none and for Agaves and herbaceous no problems, but some difficulties for some tree species
Water quality (untreated): Also unusable
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Use of native species
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men for hard works: digging holes during the plantation and carrying plants during the harvest
Women and men, do the rest of the activities
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Relative level of wealth: average, poor, very poor
34% of the land users are average wealthy.
33% of the land users are poor.
33% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: off farm incomes represent between 80 to 90% of the annual incomes! This money is obtain through an "external" job, business, trade, or by money send by family from the USA
Market orientation of production system: 90% commercial but some plants (fruit trees, some herbaceus) can be consummed.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for seed collect, greenhouse, digging holes, plantation, cleaning and harvesting and in some case, tractor can pass to make sub soiling for the plantation of Agave lines to control soil erosion.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Also 15-50 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
- ejido
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
- ejido
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
- ejido
التعليقات:
"ejido" is the community organisation in Mexico: land belongs to the state but it is managed by the community. Some areas can be used by everybody; others are assigned to the land user families.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduction number of animals but improvement of meat production
إنتاج الخشب
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Directly by plants , indirectly with the money earned, it is possible to buy medecinal products.
If producers sell their alcohol production abroad, no problems, if not problems!
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Huge beneficts can create great conflicts!
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
impact on the community due to the huge beneficts
التعليقات/ حدد:
It can be positive as well as negative (may induce corruption, violence)
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The production of alcohol beverage (certified Mescal) from agaves, and/or in medicinal products, will generate very high Incomes for stakeholders. Life will change drastically. This allows the farmer's sons to stay in the community and work in the fields.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
biodiversity
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
That is why, state institutions fund the installations of this system meanwhile the production did not start. After that, benefits generated will be enough to motivate people to increase by themselves, the surface to remediate, without economical helps.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
50 households covering 10 percent of the stated area
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The program just start in 2010, so it is too early to reduce the experience at few hectares!
As the land users belongs to the same comunity ("ejido"), formally, all the inhabitants are involved in some way by this experience
Comments on spontaneous adoption: As the program just started in 2010, it is impossible to have an exact overview of the results now (end of 2011). As the land users belong to the same community ("ejido"), formally, all the inhabitants are involved in some way
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It is too early to identify an adoption trend.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Remediation of degraded land turning it to a sustainable production generating very high incomes in the medium term How can they be sustained / enhanced? life will change drastically and not necessarily for the better. Transparency and communication regarding benefits and land use are necessary. |
|
Project done in a participative way where different kind of stakeholders are involved: administrations, politics, scientists and people. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain workshops dynamic between stakeholders, present results to other authorities and forum |
|
Low-cost project but need to be funded and supported with technical and institutional advice to initiate the first cycle of the project. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Farmers can start to produce their mezcal from the wild agaves to sell them to wholesalers and use this money to pay for the project. |
|
As a result of the economical benefits, young people will stay in the communities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Involve the young to guarantee the future: develop the marketing, the diversification of the products, the quality of production, etc. |
|
It will hopefully reduce the number of cattle, which are the main cause of soil erosion, as farmers lose interest in cattle raising. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Authorities need to monitor this and inform the farmers about the ecological impact of too much free cattle grazing. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Obligation to find external funds to pay the first steps of the system (greenhouse, planting, etc.) due to the lack of incomes amongst farmers. | Involve all stakeholders in the project |
| Be sure that alcohol production will not be consummed in excess in the community | Control of the volume of the production, and the sufficiently high selling price should avoid "losing" the production at local scale |
| Risk that the benefits will be captured by few people | Transparency and stakeholder communication in accounting for the benefits |
| Marketing and selling the products | Authorities help the farmers to contact sellers. The formation of communities of producers, leading to products conforming to regulations that maintain good quality and provide certification. |
| Owing to the high incomes, life will change drastically and not necessarily for the better. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Colunga-García Marín P., D. Zizumbo-Villareal, J.T. Martínez. 2007. Tradiciones en el aprovechamiento de los agaves mexicanos: una aportación a la protección legal y conservación de su diversidad biológica y cultural. In: En lo Ancestral hay Futuro: del Tequila, los Mezcales y otros Agaves. P. Colunga-GarcíaMarín, L. Eguiarte, A. Larqué, D. Zizumbo-Villarreal (eds). CICY-CONACYT-CONABIO-SEMARNAT-INE. México D.F., pp. 85-112.
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
DESIRE project Mexico partner (IRD 22)
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.desire-project.eu/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Participative actions for economic benefits of agave forestry [المكسيك]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce Mezcal) associated with trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Prat

Land reclamation by agave forestry with native species [المكسيك]
Land reclamation with local agave (to produce mezcal) associated wotj trees, shrubs and grasses planted through participative actions for economic benefit.
- جامع المعلومات: Christian Prat
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية