Buhaya agroforestry system [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Godfrey Baraba
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Ekibanja (Kihaya)
technologies_1177 - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Government :
Government :
Mashauri Babylus
Bukoba DC
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
Government :
Rutatatinisibwa Dominick
Bukoba DC
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
Government :
Rwezaula Raphael
Bukoba DC
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kaihura Fidelis
K-TAMP
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
مستخدم الأرض:
Shaaban Habibu
Kyema village farmer
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Indigenous knowledge transfer [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
- جامع المعلومات: Godfrey Baraba
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
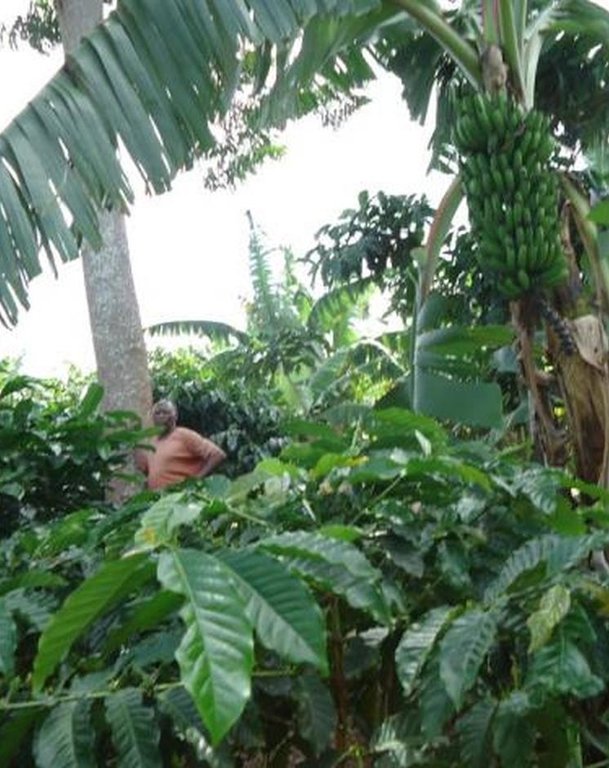
Traditional agroforestry system comprising mixture of banana, coffee, fruit trees, biannual crops, annual crops and timber trees which together optimize the use of soil, moisture and space.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
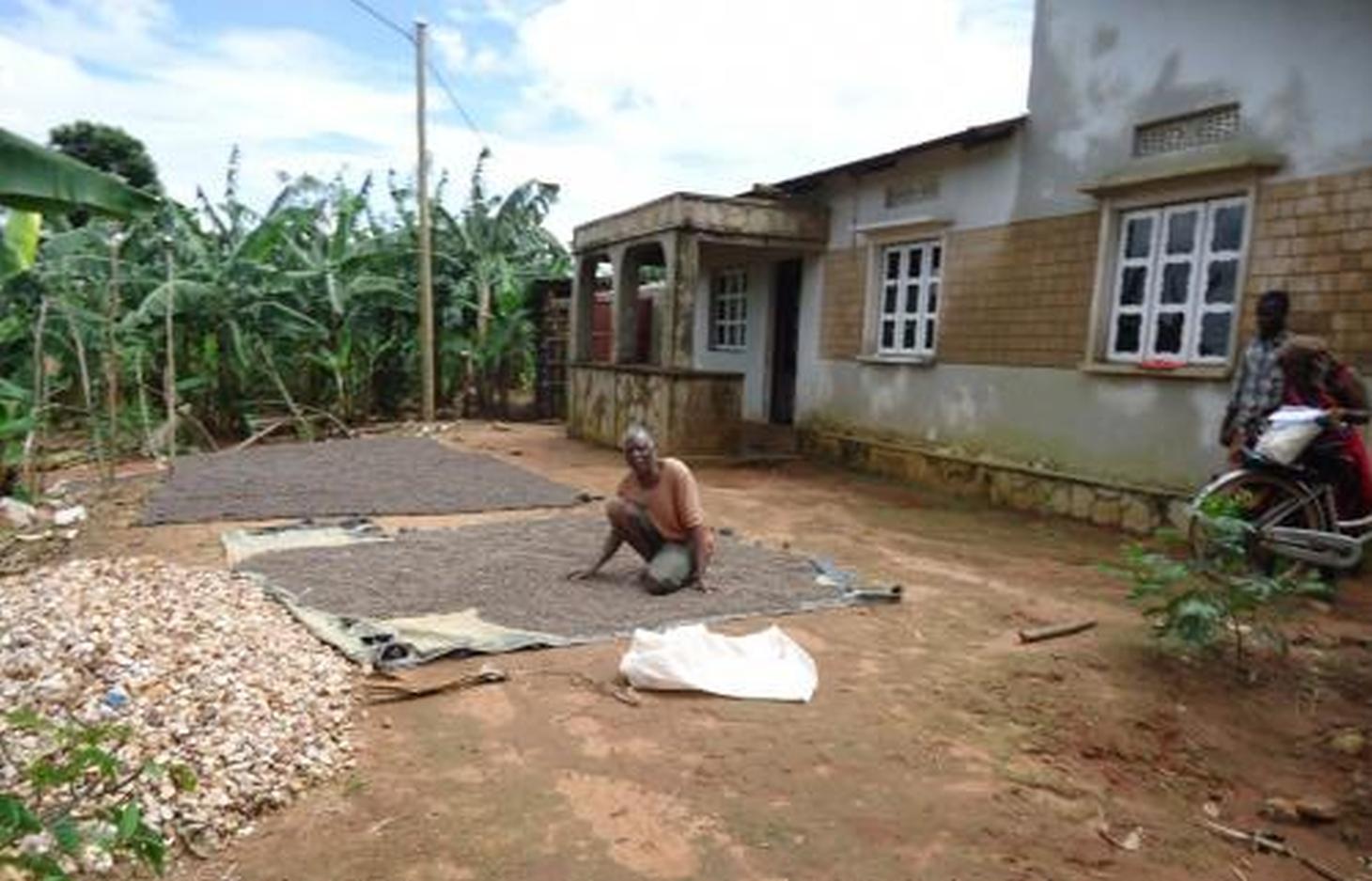
الوصف:
Buhaya agro forest system is a mix of annual and perennial crops together with trees and shrubs are densely planted on a restricted area usually 0.5 -2ha per household to increase crop yield, wood production and conserve soil and water. Buhaya agro forest system is applied on individual owned land specific at home steady. In this technology a plot of 1ha comprises of :
1.Perennial crops (coffee, banana, ) on average (10,000/36 coffee plants can be planted in one hector randomly in the alternating manner with banana, 10,000/25 banana stools) can be planted in 1ha randomly in the alternating manner with coffee.
2.Annual and biannual crops (eg. Maize, beans, cassava, sweet potatoes, yams etc) are planted in the between spaces. Maize and beans are planted twice in the short (Masika) and long rains (Vuli) where tubers are planted at any time throughout the year.
3.Trees and shrubs (eg. Makkhamia spps, Maesopsis and migorora). Trees are planted along the boundaries spaced at an average of 15m to act as wind break and timber production. Shrubs are planted at closed distance in between trees to act as live fence.
Buhaya agro forest system was practiced since early 1900. Application of farmyard manures and crop residue mulch are the supportive measures. The land owners keep small livestock/ few cattle under zero grazing to obtain manure for soil fertility improvem
Purpose of the Technology: The purposes for applying the technology is to control soil erosion and nutrient improvement.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of Buhaya agro forest system is done on a virgin land starting in the dry season July to September and it normally takes 2-5years by doing the following activities.
1.To prepare the land by cutting, removing/burning shrubs and grasses followed by land tillage. This is the difficult job and sometimes it can force the farmer to plant annual crops before planting perennial crops due to inadequate preparation time.
2.To dig holes of different size according to what crop is meant for in the alternating manner. This activity is done after harvesting annual crops in shot rainfalls (March to June).
3.To plant banana in July and August followed by coffee in September to November and March to May next year.
4.To plant trees along the boundaries followed by planting shrubs between the trees spacing to create a live fence.
5.To plant cassava, yams, pawpaw, avocados and mangoes. These are planted randomly and in a few quantity.
The maintenance of Buhaya agro forest system is the simple but tidies job requires all the year to be working in the garden. The required activities are
1.To weed the field as preparation for planting seasonal crops( i.e maize and beans) twice per year in dry seasons.
2.To remove unwanted banana suckers (desuckering) and harvested banana stems in order to maintain a required number of plants( mother, daughter and grand daughter) per stool. This requires a lot of time for assessing the plant health as well as spacing.
3.To plant and harvest maize and beans twice per year.
4.To prune coffee trees, harvest coffee cherry, dry, and market them once per year.
5.To replace harvested cassava and yams as required.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tanzania
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Bukoba District (Kyema village)
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
It is said that in 1939 after second world war there was a hunger in Bukoba which forced people to plant banana instead of the traditional cropping of sorghum and millet. During the British colonial people were forced to cultivate coffee; as well health services introduced by Christian missionaries increased the population growth which revealed pressure on land and forced to opt agro forest.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - البطاطا الحلوة، واليام، والقلقاس/الكوكويام، وغيرها
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- البن، في مزارع مفتوحة
- فواكه أخرى
- Makkhamia spps, Maesopsis and Migorora
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September to December; Second longest growing period in days: 65; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

أراضي الرعي
نوع الحيوان:
- الماشية - للعمل وليس لإنتاج الألبان
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem was soil erosion and excessive nutrient mining
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Limited suitable land for cropping in the area
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (cultivation along the slopes versus across the slopes.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Routeenly harvests without fertilization implies permanent removal of nutriets.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (average rainfall 1,200mm on slopes), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sandstone parent material), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate extension services)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (Limited household income to invest in sustainable land management), labour availability (Labour force dominated by the elderly)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Overview of the Buhaya agroforestry system. Average of 5m spacing between banana plants then alternate with coffee after two stools. Cassava and yams scattered at the space after 6 to 10 stools. beans and maize are planted in the left space to make sure all soil surface is covered. Long trees (Maesopsis spps) spaced at 10m.
Location: Kyema village. Bukoba/Kagera/Tanzania
Date: 22 MAY 2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The importance of diversification for income stabilization.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Trees can improve income generating and assure food security in the sense of food accessibility.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Makhamia spp, Maesopsis eminii are planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mangifera indica, Carica papaya, Persia americana are planted
Perennial crops species: Musa spp are planted
Change of land use type: Change from cropland (Annual and biannual crop production eg. millet, sorghum and beans) to Aggro forest.
المؤلف:
Godfrey Baraba, BOX 491, BUKOBA
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.60
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | July to August |
| 2. | Digging holes | Jan & Jul |
| 3. | Planting banana and coffee | Jul to Sep |
| 4. | Planting trees and shrubs | Feb & Sep |
| 5. | Planting biannual crops | March, Apr, Oct, Nov &Dec |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Land preparation | persons/day/ha | 333,3 | 1,25 | 416,63 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Digging holes | persons/day/ha | 81,63 | 1,25 | 102,04 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting banana and coffee | persons/day/ha | 33,33 | 1,25 | 41,66 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting trees, shrubs and biannual crops | persons/day/ha | 158,6 | 1,25 | 198,25 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Axes | pieces/ha | 5,55 | 3,128 | 17,36 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machete | pieces/ha | 5,55 | 1,877 | 10,42 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hand hoes | pieces/ha | 5,55 | 3,128 | 17,36 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Spades | pieces/ha | 2,7 | 3,148 | 8,5 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Banana suckers | pieces/ha | 571,0 | 0,1875 | 107,06 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Coffee seedlings | pieces/ha | 357,0 | 0,3125 | 111,56 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Mysopsis | pieces/ha | 33,0 | 0,125 | 4,13 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Migorora | pieces/ha | 80,0 | 0,125 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Avocado | pieces/ha | 11,0 | 3,167 | 34,84 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Mangoes | pieces/ha | 5,0 | 3,125 | 15,63 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Cassava | pieces/ha | 47,0 | 0,0317 | 1,49 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Yams | pieces/ha | 26,0 | 0,031 | 0,81 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1097,74 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1097,74 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Feb & Sep |
| 2. | Desuckering | Jul to Sept |
| 3. | Planting annual crops | March to Jul & Sep to Dec |
| 4. | Punning, harvesting and drying coffee | May to October |
| 5. | Cassava and yams harvesting. | Jan to Dec |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Weeding | persons/day/ha | 200,0 | 1,25 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Desuckering | persons/day/ha | 57,0 | 1,25 | 71,25 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting annual crops | persons/day/ha | 50,0 | 1,25 | 62,5 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Prunning, harvesting and drying coffee | persons/day/ha | 285,5 | 1,25 | 356,88 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | pieces/ha | 10,0 | 2,5 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | pieces/ha | 26,0 | 0,031 | 0,81 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Cassava | pieces/ha | 48,0 | 0,0317 | 1,52 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Beans | pieces/ha | 20,0 | 1,25 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Cassava and yams harvesting | persons/day/ha | 2,3 | 1,25 | 2,88 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 795,84 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 795,84 | |||||
التعليقات:
The above cost was calculated as 1manday equivalent to 8 working hours with the following performances; ploughing 30m2, weeding 400m2, land clearing 10m2, de suckering 30 stools, Harvesting and pruning 3 coffee trees.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is labour. This is because the technology is labour intensive, while labour force is inadequate.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Bimodal, length of dry period 180dys
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: 12.8%
Altitudinal zone: 1194m.a.s.l. taken by GPS
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water: Permanent water stream in plenty
Water quality (untreated): Tap water not found in the whole village
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Butterflies, earthworm and ants readily available
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men usually plays part in field establishment while women engaged in maintenance. Children participates in maintenance as well.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The one who did not apply the technology depends on more than 85% of his income from off farm activities.
Market orientation of production system: Coffee is 100% for commecial the rest are for home consumption.
Level of mechanization: Land cultivation only at establishement, then weeding is done by bare hands and planting bu small hand hoes (vihosho)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
No larger arable land found unoccupied in the areas.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
Water sources are mainly permanent streams found in different land ownership, but water uses are free.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
16kg
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
35kg
إنتاج الخشب
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
All crops are weeded at once
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Individual had excess food for sale
الوضع الصحي
الفرص الثقافية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Individual exposuers to expatriet and trading partners
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
No wind break events reported in the area
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
This technology supports high quality and quantity coffee and other crops production and as a results improves farmers income.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
use of new adapted varieties.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
387 households covering 75 percent of the stated area
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
387 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Almost 75% of the area is under agroforestry practices.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technique has been in place for centuries
The average farm size is 1 acre per households and all 607 households implemented this technology. Other technologies are practiced in different area within the village. Therefore the SLM technology area is approximately 15% of the total catchment area.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Diversification of production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improved farmers knowledge and skills in agroforestry systems management |
|
Reliable income from multiple crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge in farming as a business |
|
Technology is traditional and widely accepted How can they be sustained / enhanced? Strengthen linkages to sources of improved technologies |
|
Reduced workload How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Complimentarity of produced diverse crops How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
The technology is not complicated in terms of input requirements and application How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improved farmer linkage to sources of improved materials e.g. research |
|
Inputs are locally and readily available How can they be sustained / enhanced? Facilitation of farmer own produced improved inputs |
|
Maintenance costs decreases with increasing production period How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Markets are readily available How can they be sustained / enhanced? Feeder road maintenance should be given higher priority |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High competition of nutrients among different species | Improved farmers knowledge and skills in agroforestry systems management |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Some tree species host pests | Improve farmers knowledge on tree pests prevention and cleaning |
| Limits farm mechanization | Improved farmers knowledge and skills on improved maintenance without mechanization |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/partners-contacts/tanzania/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Indigenous knowledge transfer [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
- جامع المعلومات: Godfrey Baraba
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية