Post-fire Natural Mulching [البرتغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Sergio Prats Alegre Prats
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
No intervention, needle carpet, caruma (Portuguese)
technologies_1298 - البرتغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Keizer Jan Jacob
Centre for Environmental and Marine Studies (CESAM) - Department of Environment and Planning-University of Aveiro
البرتغال
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - البرتغالاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) - البرتغال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
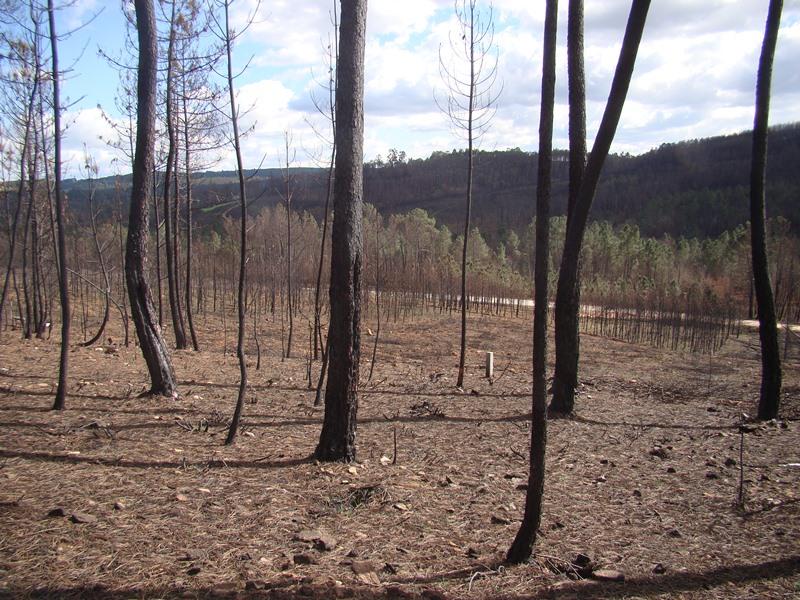
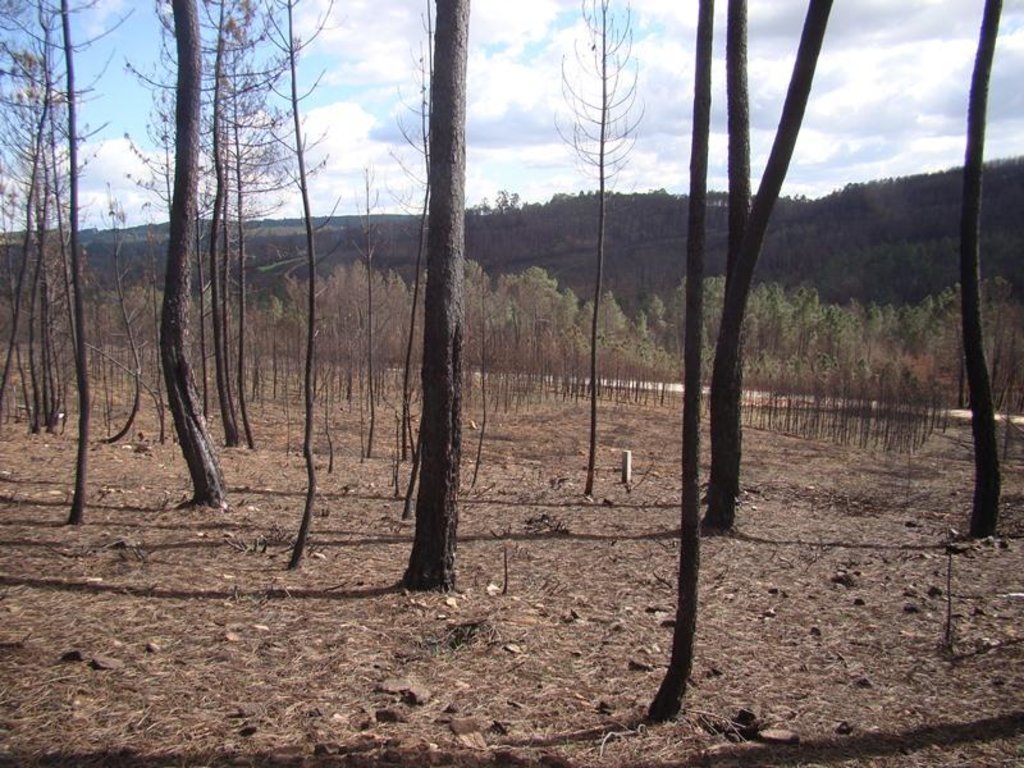
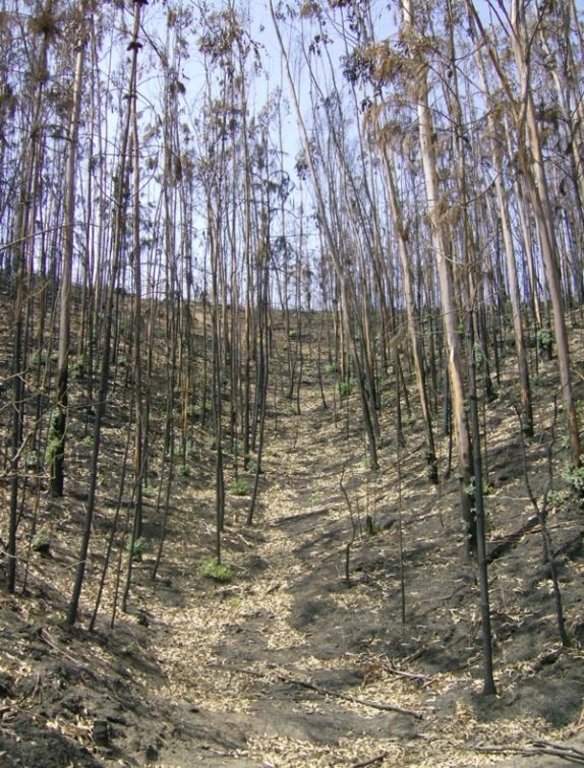
In certain situations, the leaves from the burnt trees created a natural carpet that protect the soil from being eroded.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In the 2007 summer a wildfire affected the locality of Pessegueiro do Vouga, municipality of Sever do Vouga, north-central Portugal. The area was afforested with eucalypt and pine plantations. The research team of the University of Aveiro checked that in some burnt areas the crown damage was very small, despite the litter and underground vegetation were totally consumed by fire. The pine site presented a markedly lower fire severity, with the canopies only partially consumed by the fire, so it allow to study the effect of fire severity on soil erosion by comparison with adjacent slopes burned a high severity.
Purpose of the Technology: In a wildfire that affected a pine plantation in central Portugal in 2007, the research team of the University of Aveiro set up an experiment in order to test the effect of forest residue mulching as a soil erosion mitigation treatment. However, the low fire severity resulted in an elevated litter cover prior any technique was applied. The objective is to determine were “no action” in post-fire management will still result in low soil erosion values.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The high litter cover will decrease post-fire soil erosion by reducing raindrop impact over the ashes and the bare soil, and decrease the runoff amount by increasing water surface storage, decrease of runoff velocity, and increase infiltration. As the needle litter cover was natural, no action was needed. After a simple assessment of the remaining ground cover in the burnt area, the "no intervention" option should be selected if the soil is covered by litter, leaves or needles. The benefits of this are not only the mitigation of soil erosion (and associated soil fertility losses) immediately after forest fires, but also the long-term conservation of the soil resources without additional costs.
Natural / human environment: The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-)natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. Since the 1980´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, aided by a general warming and drying trend but driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
البرتغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Portugal, Aveiro
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Sever do Vouga, Pessegueiro de Vouga
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.0E-5 m2.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
نوع الشجرة:
- أنواع الصنوبر (الصنوبر)
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Strong increases in runoff and erosion should be a main land management concern following wildfires, as they constitute a serious threat to land-use sustainability and downstream aquatic habitats and human infrastructures. The forest owners and managers need to establish target areas to apply cost-effective post-fire soil erosion mitigation treatments, included the “no action” option.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of wood resources and productivity.
Plantation forestry: Pines logged every 30 years, after fire natural regeneration if possible, but mainly after fire there is a change to eucalypt plantations
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
Number of growing seasons per year: 3
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: September to May
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
التعليقات:
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Land use change has been associated to increasing fire frequency in the region), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Pine plantations are prone to fire), population pressure (Since the 80´s land use had change to increase afforestation with flammable species (i.e. pine and eucalypts))
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
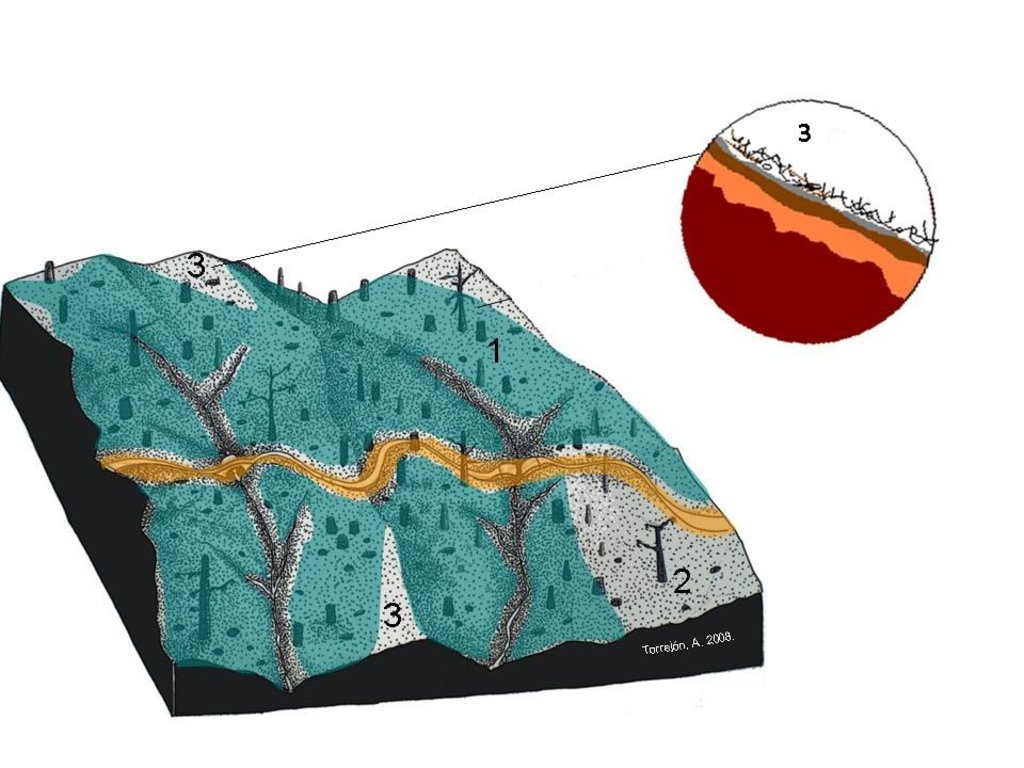
Natural mulch is often present in areas burnt at low severity or only partially burnt (3). This areas as well as planar areas (2) must be areas for no mitigation treatment or “no action” after forest fires.
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: natural needle carpet
Remarks: Up to 50% litter cover
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Natural cover |
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
No cost are envisaged for this technology. Visual assessment of the soil cover can be susceptible for costs, for example consulting, but we think it is not eligible.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Topsoil organic matter is high (forest soil)
Soil fertilits is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium - poor (fire reduce soil infiltration capacity. Also, soil water repellency is present).
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Forest plantation
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, commercial/ market
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- شركة
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some reduced wood production can be associated to the technique by carrying out selective felling.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Public awareness of the technology is very limited. It is necessary to show it to landowners and stakeholders and increase dissemination.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
As natural mulching has no cost, any benefit is always very positive
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The land users are not aware about the advantages of natural mulching, but in fact they apply it when they have not economic resources.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some times logging after fire reduces the natural mulching capacity to prevent post-fire erosion
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| No cost |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
It is a technology with no associated cost and with low failure possibilities and a strong soil erosion control. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Inform land owners and forest managers to avoid post-fire logging in areas with natural mulching and therefore avoid the decrease in the technology effeciency. Some times logging after fire reduces the natural mulching capacity to prevent post-fire erosion. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| No possible to harvest the logs during the first period after the fire | Assume the cost of selective felling |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Some people argue that can increase fire risk | Fire risk will not be probably increase as the surrounded areas were frequently also burned |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Prats SA, MacDonald LH, Monteiro M, Ferreira AJD, Coelho COA, KeizerJJ. 2012. Effectiveness of forest residue mulching in reducing post-firerunoff and erosion in a pine and a eucalypt plantation in north-centralPortugal. Geoderma 191: 115–124.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Shakesby RA, Boakes JD, Coelho COA, Bento-Gonçalves JA, Walsh RPD.1996. Limiting the soil degradational impacts of wildfire in pine and eucalyptusforests in Portugal. Applied Geography 16: 337–355.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
RECARE project: Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe trhough Land Care. http://www.recare-project.eu/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية