Assisted natural regeneration [النيجر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Dieter Nill
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Régénération naturelle assistée (French)
technologies_1626 - النيجر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
ألمانيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive
النيجر
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Misereor - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
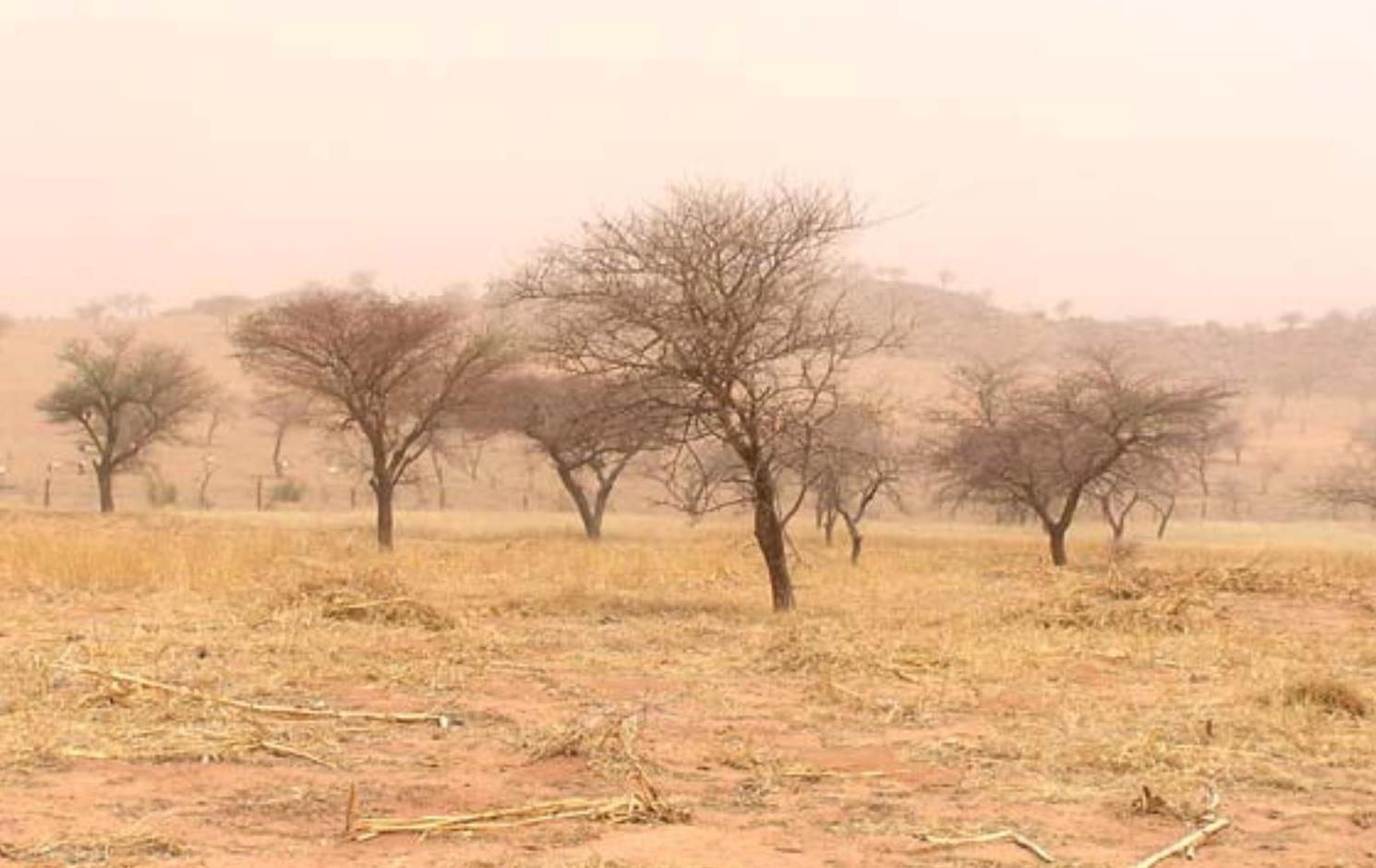
Assisted natural regeneration (ANR) is an agroforestry technique, which consists in protecting and preserving tree seedlings growing naturally on cropland or forest/rangeland.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
It involves selecting which natural tree seedlings to leave and placing a stake next to them to identify them. The recommended density on cropland is between 60 and 80 trees per hectare. ANR is carried out mainly on individual plots where monitoring and upkeep are easier.
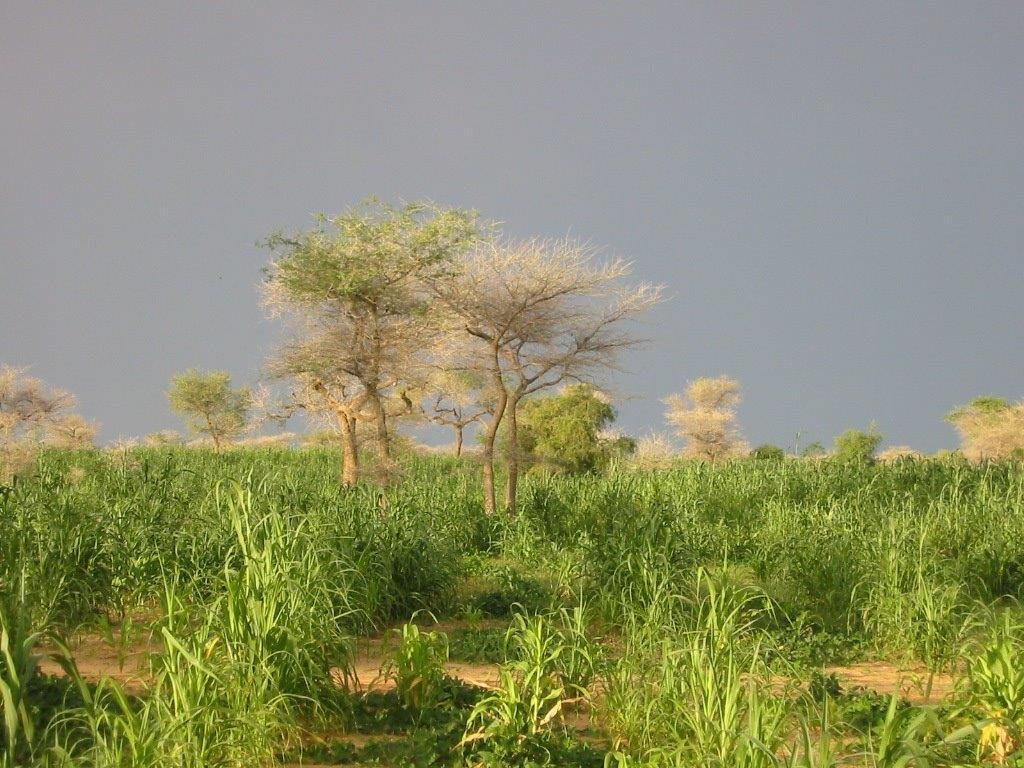
Purpose of the Technology: Tree roots and fallen leaves help to stabilise the soil and thereby reduce water erosion. Some tree species have a fertilising effect on the soil. Legume species (for example, Faidherbia albida) enrich the soil with nitrogen. Other species circulate nutrients from the subsoil into the topsoil thanks to leaf fall. The shade provided by trees lowers soil temperature and reduces the evapotranspiration and thus water stress of plants. They also act as a windbreak and provide protection against wind erosion.
The environmental effect of ANR depends to a large extent on tree density. The reintegration of trees and shrubs into any ecosystem has positive ecological effects and improves and protects the soil. The vegetation provides shelter and forage for animals and contributes to biodiversity. Trees have positive effects on crop yields, when they do not compete with the crops for water. They also provide products and byproducts, such as wood, fruits, leaves, forage, ingredients for medicinal products, etc. Faidherbia albida, for example, has no leaves in the rainy season, which is beneficial for crops. In the dry season, it is green and provides sheltered places for animals to rest. Leaves that fall from this type of tree fertilise the soil. The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In order to implement this technique, there must be a very clear legal framework governing land tenure.
In order to ensure the success of this measure, it is important to protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years. The young trees are pruned regularly to stimulate growth, so that they quickly achieve the height required to make them safe from browsing animals. The choice of tree species depends on the intentions of the farmers (browse for animals, sale of fruits or byproducts such as shea butter, dawa-dawa, medicinal products, etc.). The technique requires no investment, apart from the work involved, and can be implemented by any land owner.
Natural / human environment: The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيجر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Niger
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10,000-1,000 كم2
التعليقات:
Assisted Regeneration has been applied in farmers' fields in combination with stone bunds and planting holes (tassa).
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by German Development Cooperation (GIZ/KfW): PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- المحاصيل الزيتية - الفول السوداني
- الحبوب - الدخن
- الحبوب - الذرة الرفيعة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- البازلاء
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- المانجو، المانغوستين، الجوافة
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الرعي المرتحل
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
- مراعي محسنة

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)
التعليقات:
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crop: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow pea and mangoes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water and wind erosion, fertility decline
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): increasing pressure on land, mostly small farmers, traditional land rights, fields are individually managed, grazing land are commons
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
- الحراجة الزراعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of crop rotation, clearing of trees in fields), droughts (severe droughts of the 70ies and 80ies), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population), governance / institutional (no clear landuse regulation on common lands)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Not applicable
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 60-80
Trees/ shrubs species: e.g. Faidherbia albida
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selecting which natural tree seedlings to leave: the choice of tree species depends on the intentions of the farmers (browse for animals, sale of fruits or byproducts such as shea butter, dawa-dawa, medicinal products, etc.). |
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years | |
| 2. | The young trees are pruned regularly |
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour: 5 man-days per ha.
• Cost of awareness raising, training and dissemination.
• Shears for pruning.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Foot slopes and valley floors
Altitudinal zone: 200 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture (topsoil): Fine to medium (sandy to clayey loams)
Soil fertility is very low - medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: > 10 m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence (mainly for small agropastoralists) and surplus is sold on market (medium agropastoralists). Commercial markets: Some vegetable growing and pastoralists.
Level of mechanization: Ox and donkey used for animal traction
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
التعليقات:
traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
Land ownership: Also individual, not titled
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج حيواني
إنتاج الخشب
خطر فشل الإنتاج
تنوع المنتج
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season. The trees help to improve soil fertility and protect against erosion
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
الأنواع المفيدة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
competition with crops for water
stray animals often wipe out ANR efforts
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The naturally growing trees are maintained during field preparation, some of the side branches may be pruned on the bigger trees, sometimes the Young trees are protected with some thorny branches. No other maintenance needed.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Farmers only received information and training. No external material support needed.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Tree roots and fallen leaves help to stabilise the soil and thereby reduce water erosion. Some tree species have a fertilising effect on the soil. |
| The shade provided by trees lowers soil temperature and reduces the evapotranspiration and thus water stress of plants. They also act as a windbreak and provide protection against wind erosion. |
|
ANR contributes to sustainable farming. It is one of the most widely accepted of the land improvement techniques promoted by development projects. The vegetation provides shelter and forage for animals and contributes to biodiversity. Trees have positive effects on crop yields. They also provide products and byproducts, such as wood, fruits, leaves, forage, ingredients for medicinal products. The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In order to implement this technique, there must be a very clear legal framework governing land tenure. It is important to protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years. |
| It does not require a high level of organisation to implement it and it is not costly. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| During the dry season stray animals often wipe out ANR efforts made by farmers on their land. | |
| In some places, anyone can collect fruits, leaves and pods from trees, and this discourages farmers from investing in ANR. | |
| In some places, only the owner of the land is allowed to establish trees on cropland. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط