Assisted natural regeneration [Нигер]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Dieter Nill
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Régénération naturelle assistée (French)
technologies_1626 - Нигер
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
Герман
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive
Нигер
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ГерманТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Misereor - Герман1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
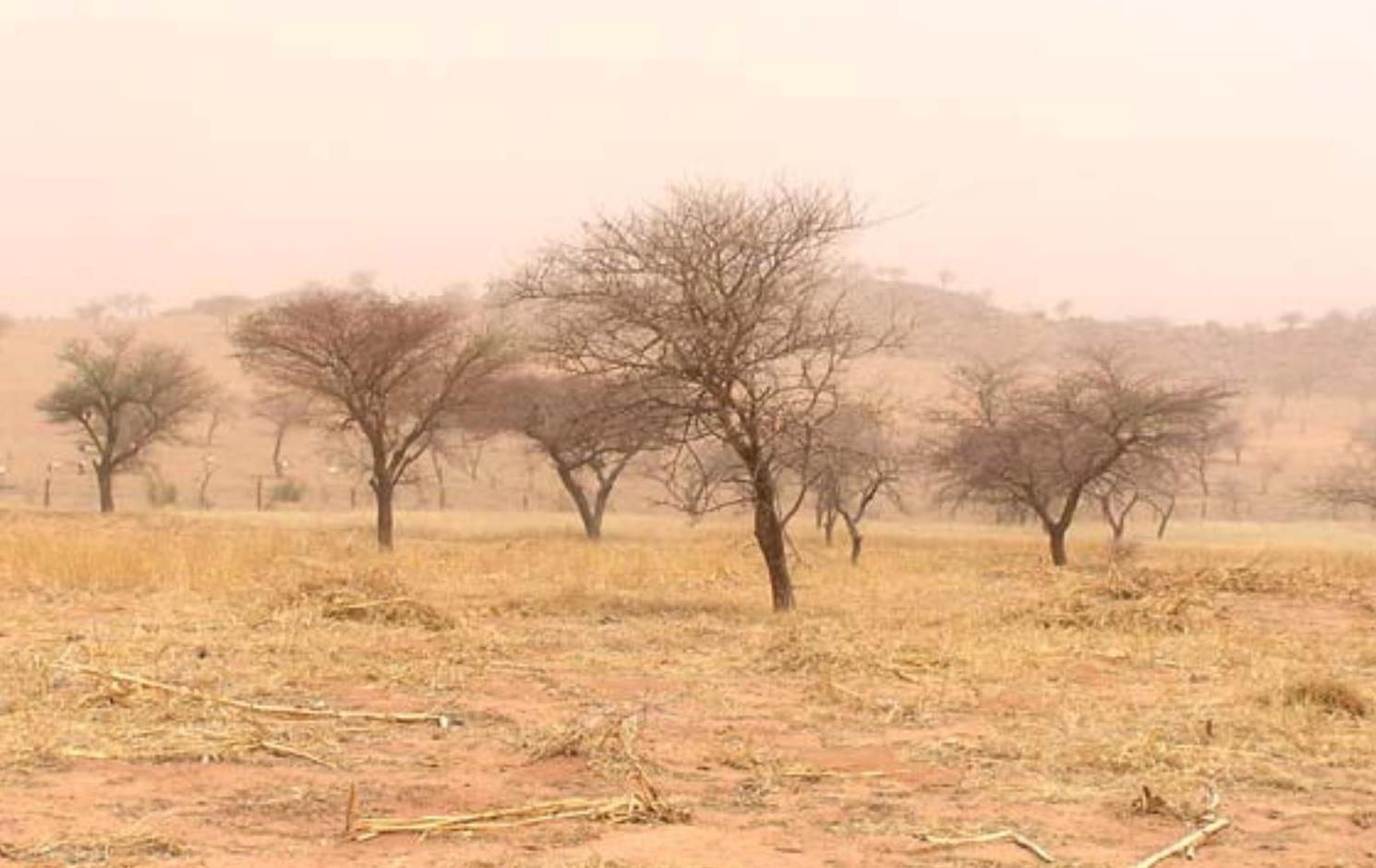
Assisted natural regeneration (ANR) is an agroforestry technique, which consists in protecting and preserving tree seedlings growing naturally on cropland or forest/rangeland.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
It involves selecting which natural tree seedlings to leave and placing a stake next to them to identify them. The recommended density on cropland is between 60 and 80 trees per hectare. ANR is carried out mainly on individual plots where monitoring and upkeep are easier.
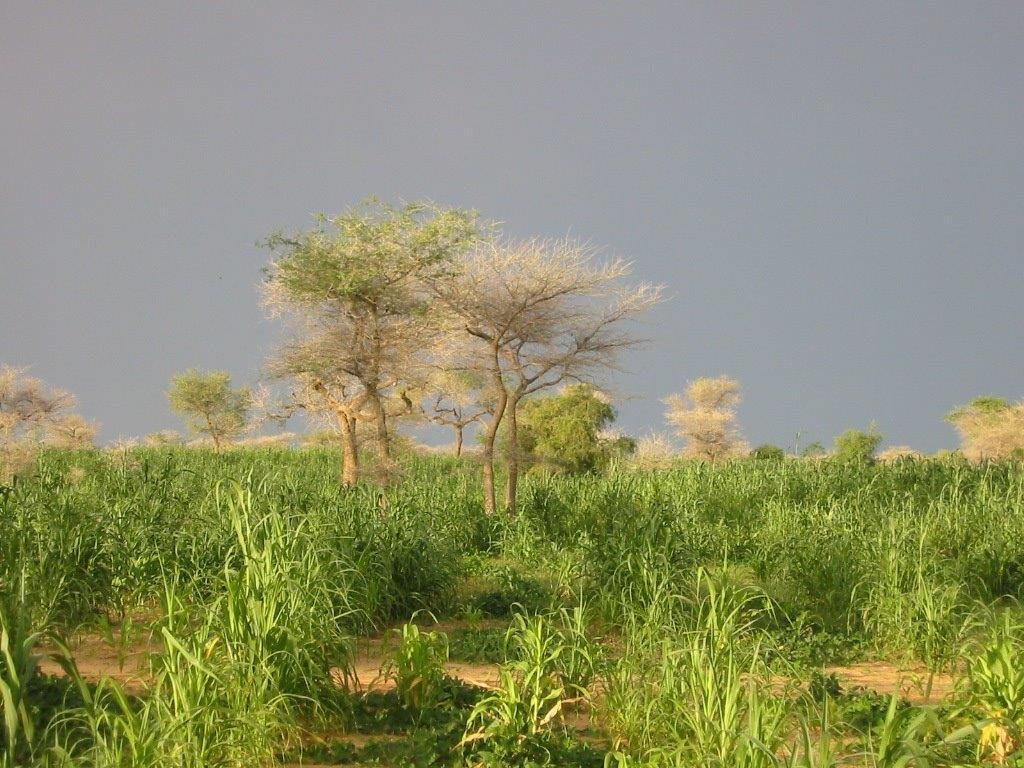
Purpose of the Technology: Tree roots and fallen leaves help to stabilise the soil and thereby reduce water erosion. Some tree species have a fertilising effect on the soil. Legume species (for example, Faidherbia albida) enrich the soil with nitrogen. Other species circulate nutrients from the subsoil into the topsoil thanks to leaf fall. The shade provided by trees lowers soil temperature and reduces the evapotranspiration and thus water stress of plants. They also act as a windbreak and provide protection against wind erosion.
The environmental effect of ANR depends to a large extent on tree density. The reintegration of trees and shrubs into any ecosystem has positive ecological effects and improves and protects the soil. The vegetation provides shelter and forage for animals and contributes to biodiversity. Trees have positive effects on crop yields, when they do not compete with the crops for water. They also provide products and byproducts, such as wood, fruits, leaves, forage, ingredients for medicinal products, etc. Faidherbia albida, for example, has no leaves in the rainy season, which is beneficial for crops. In the dry season, it is green and provides sheltered places for animals to rest. Leaves that fall from this type of tree fertilise the soil. The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In order to implement this technique, there must be a very clear legal framework governing land tenure.
In order to ensure the success of this measure, it is important to protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years. The young trees are pruned regularly to stimulate growth, so that they quickly achieve the height required to make them safe from browsing animals. The choice of tree species depends on the intentions of the farmers (browse for animals, sale of fruits or byproducts such as shea butter, dawa-dawa, medicinal products, etc.). The technique requires no investment, apart from the work involved, and can be implemented by any land owner.
Natural / human environment: The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Нигер
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Niger
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 1,000-10,000 км2
Тайлбар:
Assisted Regeneration has been applied in farmers' fields in combination with stone bunds and planting holes (tassa).
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by German Development Cooperation (GIZ/KfW): PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- биологийн төрөл зүйлийг хамгаалах / сайжруулах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- ХАА-ой-бэлчээрийн цогц систем

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- тосны ургамал - газрын самар
- үр тариа - шар будаа
- үр тариа - жирийн сорго
- буурцагт ургамал - вандуй
Мод, бут тариалах - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- манго, давжаа манго, гуав
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Нүүдлийн мал аж ахуй
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
- Сайжруулсан бэлчээр

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
- (Таримал) байгалийн ой/мод бүхий газар
(Сэргээсэн)байгалийн ой/тармаг ойд: Менежментийн төрлийг тодорхойлно уу:
- Сонгомол огтлол
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Түлшний мод
- Жимс, самар
- Ойн бусад дагалт бүтээгдэхүүн
- Бэлчээрийн талбай/Хариулгатай бэлчээрлэлт
Тайлбар:
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crop: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow pea and mangoes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water and wind erosion, fertility decline
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): increasing pressure on land, mostly small farmers, traditional land rights, fields are individually managed, grazing land are commons
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Тийм (Технологи хэрэгжүүлэхээс өмнөх үеийн газар ашиглалтын талаархи асуулгыг бөглөнө үү)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Тайлбар:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Байгалийн ба сайжруулсан ойн менежмент
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А1: Ургамал/ хөрсөн бүрхэвч

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
Тайлбар:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрс салхиар эвдрэх
- Et: Хөрсний гадаргын зөөгдөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of crop rotation, clearing of trees in fields), droughts (severe droughts of the 70ies and 80ies), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population), governance / institutional (no clear landuse regulation on common lands)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Not applicable
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 60-80
Trees/ shrubs species: e.g. Faidherbia albida
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selecting which natural tree seedlings to leave: the choice of tree species depends on the intentions of the farmers (browse for animals, sale of fruits or byproducts such as shea butter, dawa-dawa, medicinal products, etc.). |
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years | |
| 2. | The young trees are pruned regularly |
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Labour: 5 man-days per ha.
• Cost of awareness raising, training and dissemination.
• Shears for pruning.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Landforms: Foot slopes and valley floors
Altitudinal zone: 200 m a.s.l.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil texture (topsoil): Fine to medium (sandy to clayey loams)
Soil fertility is very low - medium
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: > 10 m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- нэн ядуу
- ядуу
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence (mainly for small agropastoralists) and surplus is sold on market (medium agropastoralists). Commercial markets: Some vegetable growing and pastoralists.
Level of mechanization: Ox and donkey used for animal traction
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
Land ownership: Also individual, not titled
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
малын бүтээмж
модлогийн бүтээмж
бүтээмж буурах эрсдэл
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
livelihood and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season. The trees help to improve soil fertility and protect against erosion
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
гадаргын урсац
ууршилт
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
ашигт төрөл зүйл
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
competition with crops for water
stray animals often wipe out ANR efforts
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
The naturally growing trees are maintained during field preparation, some of the side branches may be pruned on the bigger trees, sometimes the Young trees are protected with some thorny branches. No other maintenance needed.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Farmers only received information and training. No external material support needed.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Tree roots and fallen leaves help to stabilise the soil and thereby reduce water erosion. Some tree species have a fertilising effect on the soil. |
| The shade provided by trees lowers soil temperature and reduces the evapotranspiration and thus water stress of plants. They also act as a windbreak and provide protection against wind erosion. |
|
ANR contributes to sustainable farming. It is one of the most widely accepted of the land improvement techniques promoted by development projects. The vegetation provides shelter and forage for animals and contributes to biodiversity. Trees have positive effects on crop yields. They also provide products and byproducts, such as wood, fruits, leaves, forage, ingredients for medicinal products. The wood, leaves, pods and fruits provided by trees in crop fields help the owners to meet their family’s needs during the lean season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In order to implement this technique, there must be a very clear legal framework governing land tenure. It is important to protect the tree seedlings and saplings from browsing animals during the first few years. |
| It does not require a high level of organisation to implement it and it is not costly. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| During the dry season stray animals often wipe out ANR efforts made by farmers on their land. | |
| In some places, anyone can collect fruits, leaves and pods from trees, and this discourages farmers from investing in ANR. | |
| In some places, only the owner of the land is allowed to establish trees on cropland. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна