Conservation tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) [سلوفينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Matjaz Glavan
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ohranitvena obdelava tal z vdelavo mulčenih rastlinskih ostankov
technologies_5494 - سلوفينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
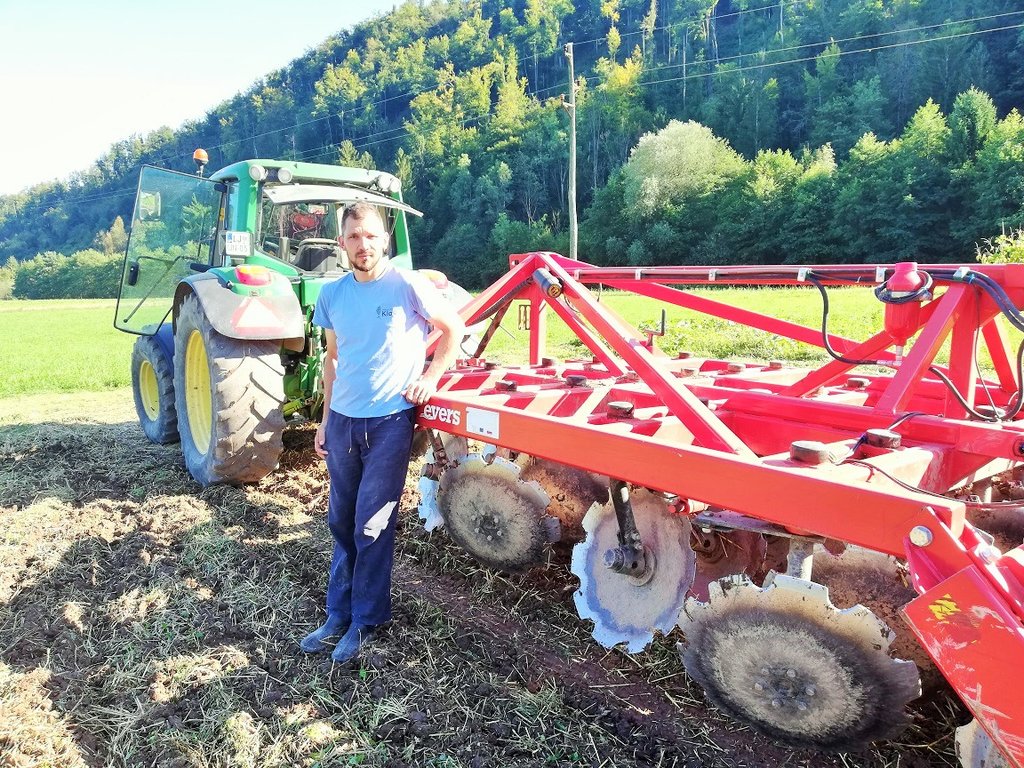
Mrzlikar Anton
Family farm
سلوفينيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Department for Agronomy, University of Ljubljana - سلوفينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
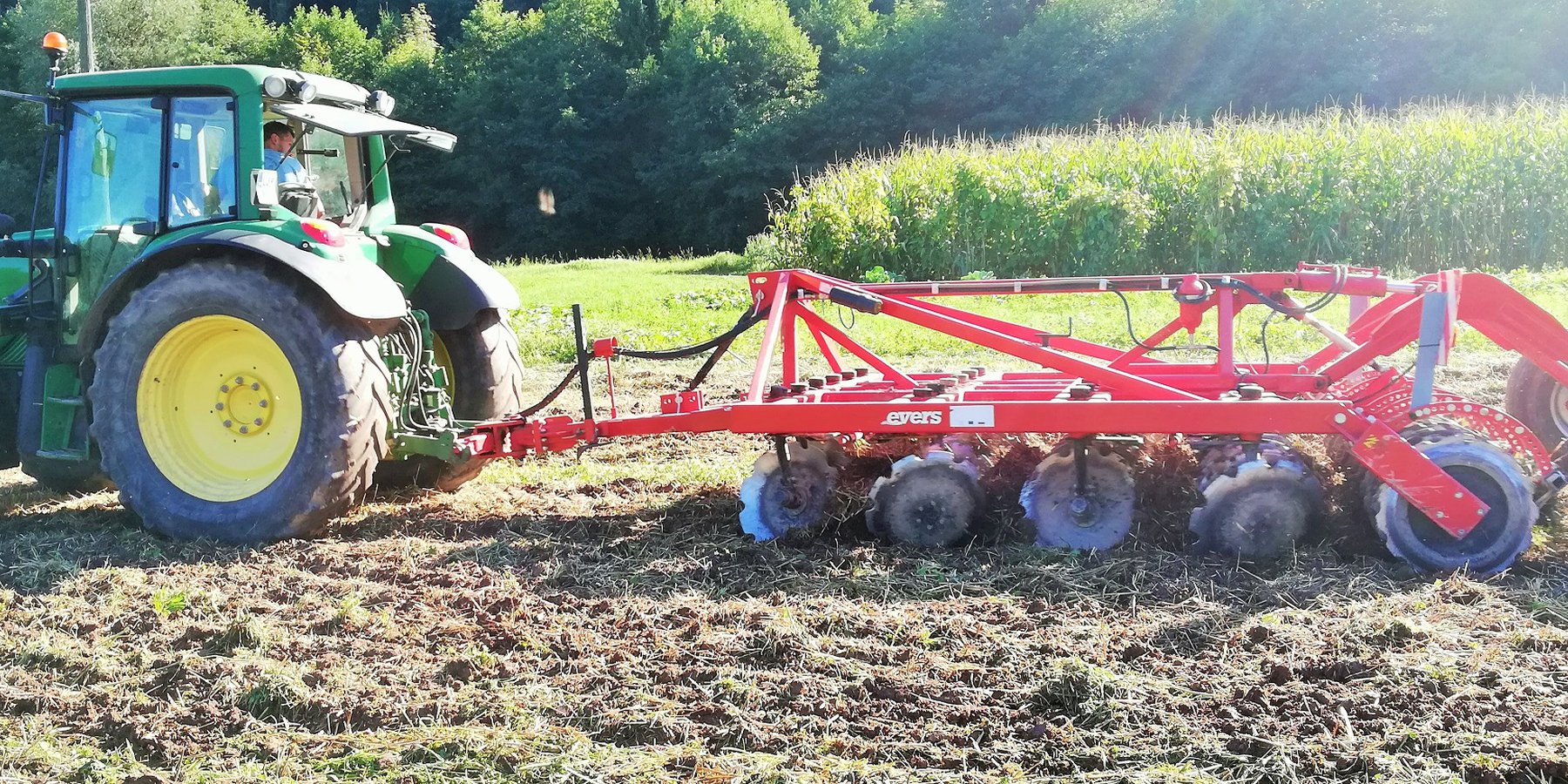
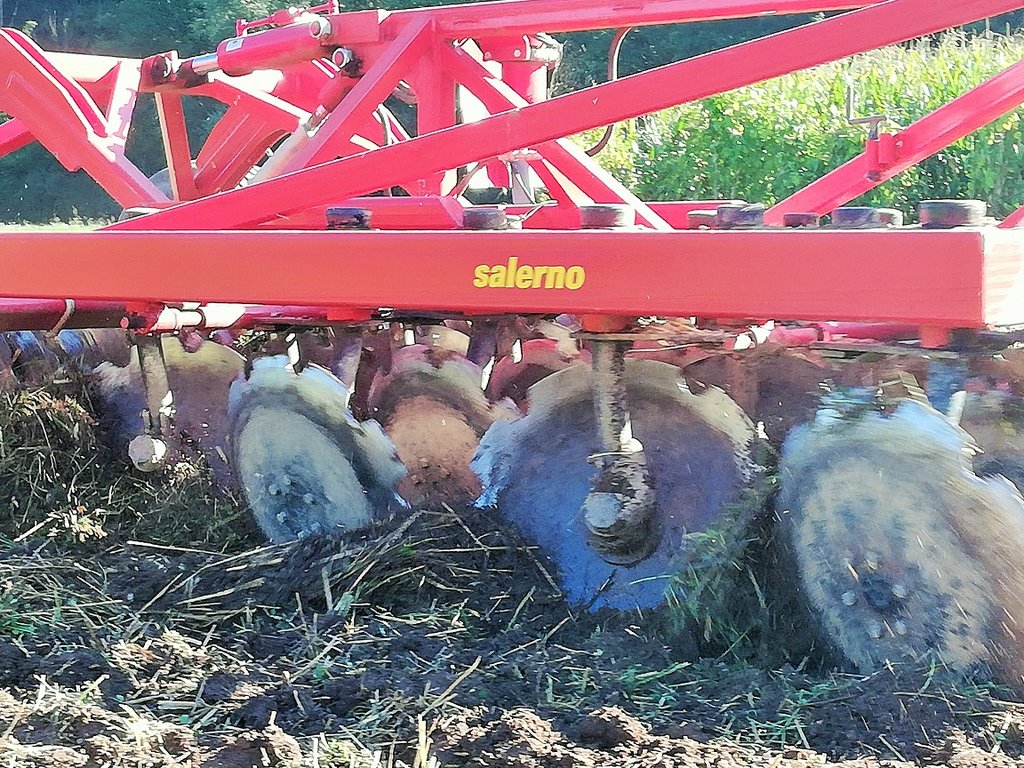
Conservation tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) of harvested crop or a green manure that are part of the rotation). Crop residues are partially incorporated/mixed in topsoil layer (down to 10 cm) using a disc harrow, chisel plough, sweeps, field cultivators, that leave more than 30% of the soil surface covered with crop residue. Technology contributes to less soil disturbance, increase of soil organic matter, better soil structure and better water holding capacity of soils.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
1. The technology of conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) is applied in flatlands around the Municipality of Vrhnika with an average altitude of 290 m.a.s.l. Average annual precipitation is 1400 mm. The area is characterized with often stormy precipitation events and occasional summer droughts. A farmer applies this technology on various soil types from silty loam to silty clay Gleysol to organic Histosol soils (peat). Soils in the area are generally moderately deep to deep with medium soil organic matter (Gleysol) of 3-7% or with a high share of organic matter (Histosol) of >20% (Ljubljana moors). The area has good availability of surface water and groundwater of good drinking quality. Gleysol areas are drained (drainage systems) to prevent floods to enable cultivation. Histosol areas are drained (open-channel drainage systems) to enable arable crop production. However, due to high groundwater and many surface water sources, certain areas are regularly flooded during flood events mostly in late autumn, winter and spring. Salinity is not a problem due to high precipitation and leaching. Farmer practices rotational agriculture. Less than 5% of income coming from off-farm activities. The examined farm household has an average wealth and is fully mechanized/motorized. the farm has good access to services and infrastructure. The examined farm is medium in scale with land partly owned by the land user and partly leased from other private owners.The general biodiversity of the area is medium on Gleysols to high on Histosol where nature protection Landscape Park of Ljubljansko Barje (The Ljubljana Moors Landscape Park) is located.
Part of the farmers land parcels is located inside boundaries of Krajinski park Ljubljansko barje /Ljubljana Moor Landscape park. Park takes a lot of actions to secure peat soils. This almost 16,000 hectares large lowland marshy plain is marked by an interminable mosaic of grasslands, broadleaf woodlands, fields, ditches and hedges.
The farmer decided to abandon conventional ploughing technology and to start with conservational tillage technology when he noticed that the organic layer of peat soils in these areas started to become thinner. Farmer introduced this technology to preserve peat soils of Ljubljana Moors on his parcels in 2015. With ploughing, peat was mixed and decomposing - mineralise. In 18th-century peat layers of up to 2m depth were exploited for the same use as firewood. Only shallow layers of peat soil (up to 1 m) are still covering agricultural areas. As peat is a source of fertility farmers are seeking ways of preserving it. Farmer Anton Mrzlikar took a lead and started with conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till).
Video https://vimeo.com/97415985 presents the effects of conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) on soil stability. This is a simulation of abundant summer rain and its impact on the tilled soils in terms of water infiltration capacity and erodibility. The result of this simulation is presented very clearly. It shows the difference between long-term conventional versus conservation tillage (mulch-till). Conventional tillage ploughs the top 25-28 cm of the soil at least once or twice a year. The soil is inverted, its structure breaks down and the surface is left bare. The first raindrops break the structural aggregates causing soil surface siltation and blockage of the soil pores. Thus vertical water flow is blocked and redirected as surface runoff, causing distinct erosion. If fertilizers and pesticides are used, the water flow will transport them, along with the soil particles, to surface waters where they cause pollution or surface ponding on the fields. This leads to an uneven distribution of substances across the field surface.
In conservation tillage (mulch-till), a shallow, 10 cm layer of topsoil is mixed with organic residues which are thus retained near and on the surface. In this way, soil structure is reinforced with good soil water infiltration and absorption. Despite heavy rainfall, the soils do not show any signs of erosion. There is no surface flow. Water drains into the soil vertical flow where it is available to the plants.
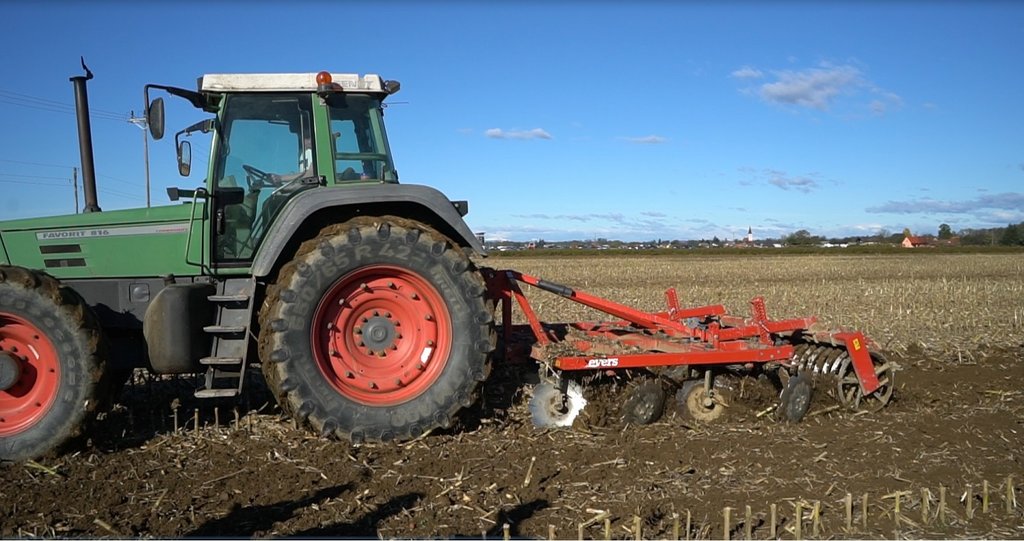
2. The farmer usees of 4-row-disk harrow tillage machinery (vario-disc) on arable fields for all crop types. When cultivating fields he crosses fields 1 - 2 times (depends on soil moisture). Every few years he uses chisels to break and shatters (aerate) the soils (depends on crop type - cereals and drought years). After main/first crop he seeds various cover crops (if fodder is needed they harvested it otherwise is used for green manure). He uses manure 30-40 t/ha. He applies typical dairy cow farm rotation (cereals/maize/soya/grass-clover mix). Cover crops are classified as rapes, cereals, oats, grass-clover, grass.
3. The main function is an increase of organic matter, retain water, increase soil biodiversity, stabilise soil structure in the soils and reduce water erosion, as well as reduce energy consumption and costs. This leads to better (1) productivity due to nutrients slow-release, (2) better water holding capacity and (3) decreased soil compaction threat. The technology was introduced to prevent decomposition of organic matter on Ljubljana moor peat soils.
4. Major inputs needed to establish is to change machinery and to gain new knowledge and experiences. They had to buy 4-row disc harrows, chisels plough and new seeders (maize). Seeding machines for cereals and oilseed rape are hired from other farmers. It is important that soils are covered all year round. Soils must be dry when cultivated.
5. The benefits are (1) increase in soil organic matter, (2) increase soil water holding capacity, (3) to maintain soil productivity, (4) increase in yields quantity and quality, (5) reduce energy consumption, (6) reduce workload - 3-4 times less time used for cultivation, (7) reduce costs.
6. Land users like (1) reduced workload and energy consumption, (2) positive impact on soil fertility and stability, (3) preserves organic matter - decrease peat soils decomposition, (4) as soils need to be covered all the time they produce more feed for cows, (5) smooths surface fields, (6) with disc harrow is easy to till soils even when residues are present on fields, (7) less soil compaction
Land users dislike: (1) investment cost for new machinery are high, (2) time to change in doing things and practice, (3) on clay soils (Gleysol) surface ponding is occurring, (4) soils need to be drier for tilling in comparison to ploughing.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
This is a simulation of abundant summer rain and its impact on the tilled soils in terms of water infiltration capacity and erodibility. The result of this simulation is presented very clearly. It shows the difference between long-term conventional versus conservation soil tillage.
Conventional tillage ploughs the top 25-28 cm of the soil at least once or twice a year. The soil is inverted, its structure breaks down and the surface is left bare. The first raindrops break the structural aggregates causing soil surface siltation and blockage of the soil pores. Thus vertical water flow is blocked and redirected as surface runoff, causing distinct erosion. If fertilizers and pesticides are used, the water flow will transport them, along with the soil particles, to surface waters where they cause pollution or surface ponding on the fields. This leads to an uneven distribution of substances across the field surface.
In conservation tillage (mulch-till), a shallow, 10 cm layer of topsoil is mixed with organic residues which are thus retained near and on the surface. In this way, soil structure is reinforced with good soil water infiltration and absorption. Despite heavy rainfall, the soils do not show any signs of erosion. There is no surface flow. Water drains into the soil vertical flow where it is available to the plants.
التاريخ:
04/12/2017
الموقع:
Ljubljana, Biotechnical Faculty, University of LJubljana
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Rok Mihelič, Marko Zupan, Matjaž Glavan - Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Presenting 4-row disch harrow in action.
التاريخ:
12/04/2017
الموقع:
Slovenia
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Rok Mihelič, Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Presening seeder (cereals/oilseed rape) in action and condition of soil surface after tillage and seeding.
التاريخ:
12/04/2017
الموقع:
Slovenia
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Rok Mihelič, Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
سلوفينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Central Slovenia
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Podlipa, Vrhnika. This specific farmer applies this technology on Ljubljansko barje, othewise is applied all over Slovenia
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Part of his land parcels is located inside boundaries of Krajinski park Ljubljansko barje /Ljubljana Moor Landscape park. Park takes a lot of actions to secure peat soils. This almost 16,000 hectares large marshy plain is marked by an interminable mosaic of grasslands, broadleaf woodlands, fields, ditches and hedges.
http://www.ljubljanskobarje.si/?lang=en
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2015
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Farmer introduced this technology to preserve peat soils of Ljubljana Moors on his parcels in 2015. With ploughing, peat was mixed and decomposing - mineralise. In 18th-century peat layers of up to 2m depth were exploited for the same use as firewood. Only shallow layers of peat soil (up to 1 m) are still covering agricultural areas. As peat is a source of fertility farmers are seeking ways of preserving it. Farmer Anton Mrzlikar took a lead and started with mulch-till.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- cereals - maize - legumes - grass-clover mix
نظام زراعة سنوي:
الذرة أو دورة مماثلة مع القش / زراعة المراعي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
cereals/maize/soy/grass-clover mix, additionally cover crops after main crop (soil must be covered all year round
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
A3: التمييز بين أنظمة الحراثة:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Ps): هبوط التربة العضوية، استقرار التربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
It is impossible to prevent degradation in the form of peat soil mineralisation in agricultural soils.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
30 ha
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EUR
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,9
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
50 EUR
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of fields: Leveling depressions, reconstruction of drainage channels, using chisels to loose, break and aerate soil in deeper layers | two year before implemenation, dry soil. |
| 2. | Purchase of 4-row disc harrow | 1st year |
| 3. | Purchase of seeder for maize | 1st year |
| 4. | Purchase of seeder for cover crops | 1st year |
| 5. | Hire seeder for cereals (wheat, barley) | 1st year |
| 6. | Home made chisel plow for loosening the soil | 2nd year |
| 7. | Purchase of spraying machine | 3rd year |
| 8. | Purchase of GPS navigation system | 3rd year |
التعليقات:
The agricultural technology activities are listed in chronological order. Rotation cycle takes 3 years
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | chisel plow material (home made) | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 6500,0 | 6500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | seeder fo cover crops | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 50,0 |
| معدات | seeder for maize | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 7500,0 | 7500,0 | 50,0 |
| معدات | 4-row disk harrow | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 23000,0 | 23000,0 | 50,0 |
| معدات | sprayer | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 25,0 |
| معدات | GPS navigation | EUR/piece | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | hire seeder for cereals | EUR/ha | 15,0 | 50,0 | 750,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 42762,5 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 47513,89 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
50% - Agency for agricultural payments (EU funds); 25% - sharred among farmers
التعليقات:
Cost for hiring seeder is calculated for 15ha as cereals cover 15ha of arable land.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of 4-disc harrow | 6 time per year, before or after use of equipment |
| 2. | Maintenance of Spayer | before use nozzels check, after use cleaning |
| 3. | Maintenance of seeder for maize | before and after use |
| 4. | Maintenance of seeder for cover crops | before and after use |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Maintenance of 4-disc harrow | hour | 6,0 | 6,25 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Maintenance of Spayer | hour | 6,0 | 6,25 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Maintenance of seeder for maize | hour | 4,0 | 6,25 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Maintenance of seeder for cover crops | hour | 1,0 | 6,25 | 6,25 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Lubricant cartridge for4-disc harrow | cartridge | 18,0 | 5,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Nozzels for Spayer | nozzel | 20,0 | 4,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Lubricant cartridge for seeder for maize | cartridge | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Lubricant cartridge for seeder for cover crops | cartridge | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 301,25 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 334,72 | |||||
التعليقات:
There is a big difference between conventional and conservation tillage in time spend cultivating fields.
Farmer estimates reduction in workload (no ploughing) for 3-4 times in comparison to the conventional ploughing system.
Farmer points out an increase in green mass yield (clover, grass) due to cover crops which can be used as feed for livestock or green manure. He said that the most important part of this conservational system (mulch-till) is to prevent weeds to germinate, and that's why soil needs to be covered at all times.
He also states that top and subsoil layers are loose.
He states that he still uses the same amount of plant protection products.
The use of herbicides and fertilisers is at the same range as before the shift in practice, but he expects improvements in the future when he will further enhance knowledge on crop types, rotation and cover crops.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The starting cost - The type of machinery is needed that has to be robust and heavy to much-till and seed into the soil.
The machinery must be in use to return a profit. Working hours are reduced now (no ploughing). Machine operators with more competences can reduce costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Heavy summer thunderstorms and showers. Local precipitation.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Organic matter on Gleysol is around 6% and on Histosol (peatland) more than 30%. Bellow the peatland is clay (called "polžarica", or "snail clay")
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
On Ljubljana moor, seasonal floods are occurring regularly due to the high water table.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- مرتفع
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
This true especially for the Ljubljana moor.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- أطفال
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
83 ha of agricultural land and 7 ha of forest
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
2/3 of land is hired from The Farmland and Forest Fund of the Republic of Slovenia
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
جودة المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
It increased due to the fact that soil has to be covered at all times (grass, clover, cover crops) to retain soil moisture and prevent soil erosion and to provide an optimal living condition for soil life (fauna, flora). Previously the land was left bare after harvesting cereals until autumn or even spring.
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to more fodder, the farmer managed to increase the number of livestock (dairy cows).
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the fact that soils are not ploughed anymore, a farmer has in wet years (more precipitation in a short period of time, especially in the springtime) problems on organic marshland and clay gley soils being fully saturated. This causes a reduction in the germination of seeds and weaker growth of plants due to hypoxia.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
More different types of cover crops in production. Some are used as nitrogen fixators or for loosening the soils with deep rots.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The land management simplified due to fewer machines needed and less time need for land cultivation and soil preparation.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less petrol nedeed for land cultivation.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
More livestock means more income.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Workload decreased due to abandoning of ploughing.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The farmer observed positive impacts and seeks for more knowledge on this topic to improve its practice.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Difficult to quantify. An increase in soil organic matter has an impact on CO2 sequestration.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | جيدا | ||
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الربيع | زيادة | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | جيدا |
| جفاف | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Benefits are on short term slightly negative due to investment costs, but in the long term they are positive - they pay off.
Maintenance benefits are positive for short as well as on long-term returns as less machinery and less land management activities is needed.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
Only one farmer in the area that uses this technology. On the map you can observe his fields. In the last year many of his collegues observed advantages of this technology and hires his machinery as agriculture service of tillage. In majority of times before cover crops seeding.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Reduction of workload (no ploughing, less time spent on the field) |
|
Change in farmers mindset is longlasting; they are forced to gain new knowledge on technology impact on soil condition With more knowledge and better handling of technology, the cost of maintenance and time spent in the field can reduce significantly. |
|
Increase in green mass yield (clover, grass) - it can be used as feed for livestock or green manure. Soil covered all year round + residues impact increase in soil organic matter, soil water content, biological activity, soil structure, less soil compaction. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Cost and time reductions are substantial - 3-4 times less in comparsio to conventional - ploughing. |
|
Farmers became aware of the importance of conservation soil management and its impact on soil properties and finally on the process of production-chain (soil-feed-milk). With proper shaping of knowledge (advising, education) - Conservational tillage has the potential to develop into the direction of organic farming. |
| Soil structure and fertility improve |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| On heavy soils (Glaysoils) surface ponding can occur if the farmer is not experienced with using technology. | Observe weather regularly and follow meteorological forecasts. Try to avoid wet periods. |
| Weed may be a problem in the warmer part of the year, mainly after cereals are harvested. | They use herbicide and adapt or improve crop types in rotation. |
| Peatland on Ljubljana moor. There are small parcels and soil in springtime is wet prohibiting to cultivate at any time (high water table). | Observe weather regularly and follow meteorological forecasts. They have to observe soil water content conditions periodically at peatland parcels. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Farmers still need to use herbicides as weeds are a problem especially in the early stage of crop growing (narrow-leaf) and in the last stage when crops go into senescence and light gets to the ground (broad-leaf). |
As this is a conventional type of farm, they use herbicides. However, with the promotion of organic agriculture, the expansion of vegetable production, and innovations in GPS and sensors technology hoeing/weeding machines/equipment is getting popular. This problem is even more problematic in light/alluvial soils. |
| Surface ponding on heavy soils is a problem in case of longlasting rain periods in spring, which are due to climate change more often in the described area. |
It is crucial to use chisel plow in this soils to break soil layers deeper and provide drainage potential of this soils. In light alluvial soils, this problem is not observed. |
| When a farmer in under Slovenian agricultural conditions decides to change from conventional to conservation tillage, it has to change all machinery. | Farmers need to get as much as possible information on technology. Farmers have to make a business plan. EU funds can help with subsidy payments for investments on the farm (approx. 50-60%). |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
1 farmer
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
1 farmer
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
1 specialist
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
10/05/2019
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
OHRANITVENA OBDELAVA TAL –STANJE V SLOVENIJI
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.digitalna-knjiznica.bf.uni-lj.si/du1_ograjsek_simon.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Izzivi uvajanja konzervirajoče (ohranitvene) obdelave tal
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.kmetzav-mb.si/Lombergar_18/Lomb_5_2_18.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
NOVE TEHNOLOGIJE IN SODOBNI TRENDI OBDELOVANJA TAL
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.kgzs-ms.si/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/STAJNKO_NOVE-TEHNOLOGIJE.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Ohranitvena obdelava : primerjava lastnosti mehansko obdelanih in neobdelanih prsti
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.dlib.si/details/URN:NBN:SI:DOC-LTCNTC4J
العنوان/الوصف:
SZOORT - Slovensko združenje za ohranitveno obdelavo in rodovitnost tal
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.szoort.si/
العنوان/الوصف:
Ohranitveni način obdelave tal
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.program-podezelja.si/sl/247-eup/izmenjevalnik-idej/seznam-izzivov/759-ohranitveni-obdelave-tal
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية