Conservation tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) [Словен]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Matjaz Glavan
- Редактор: –
- Хянагч: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ohranitvena obdelava tal z vdelavo mulčenih rastlinskih ostankov
technologies_5494 - Словен
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
Газар ашиглагч :
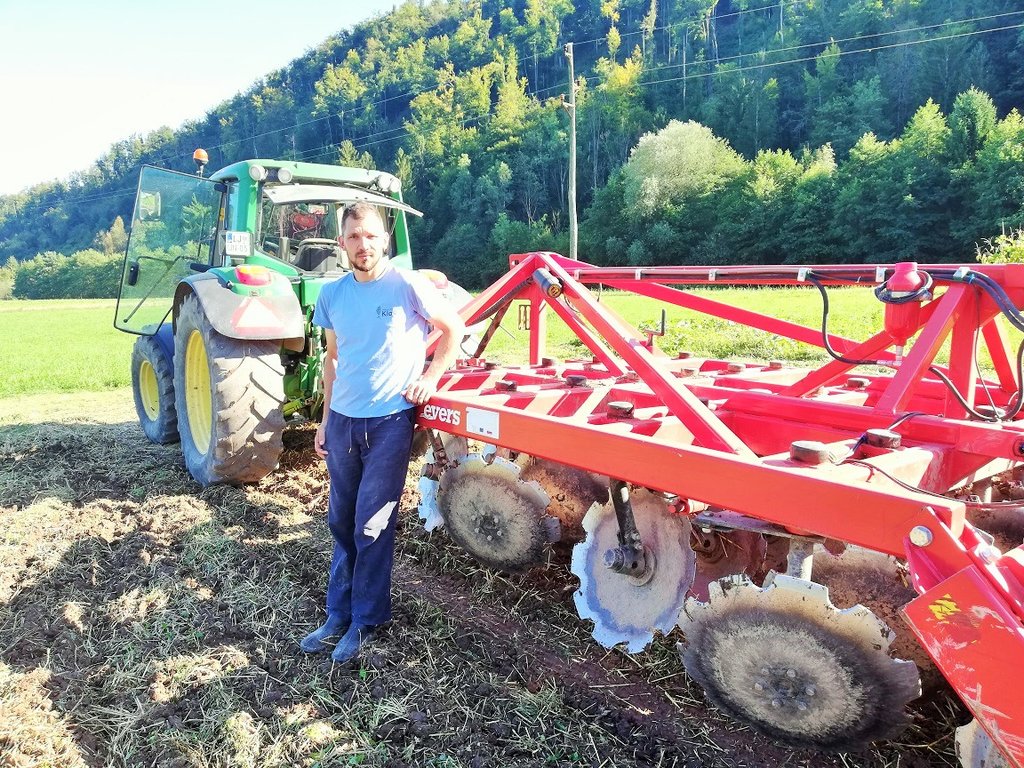
Mrzlikar Anton
Family farm
Словен
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Department for Agronomy, University of Ljubljana - Словен1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Conservation tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) of harvested crop or a green manure that are part of the rotation). Crop residues are partially incorporated/mixed in topsoil layer (down to 10 cm) using a disc harrow, chisel plough, sweeps, field cultivators, that leave more than 30% of the soil surface covered with crop residue. Technology contributes to less soil disturbance, increase of soil organic matter, better soil structure and better water holding capacity of soils.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
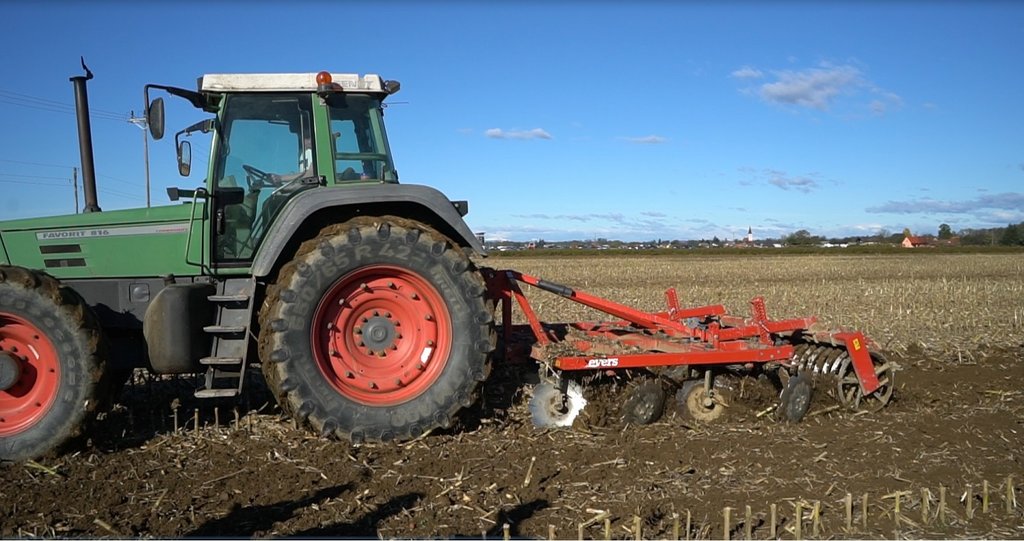
1. The technology of conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) is applied in flatlands around the Municipality of Vrhnika with an average altitude of 290 m.a.s.l. Average annual precipitation is 1400 mm. The area is characterized with often stormy precipitation events and occasional summer droughts. A farmer applies this technology on various soil types from silty loam to silty clay Gleysol to organic Histosol soils (peat). Soils in the area are generally moderately deep to deep with medium soil organic matter (Gleysol) of 3-7% or with a high share of organic matter (Histosol) of >20% (Ljubljana moors). The area has good availability of surface water and groundwater of good drinking quality. Gleysol areas are drained (drainage systems) to prevent floods to enable cultivation. Histosol areas are drained (open-channel drainage systems) to enable arable crop production. However, due to high groundwater and many surface water sources, certain areas are regularly flooded during flood events mostly in late autumn, winter and spring. Salinity is not a problem due to high precipitation and leaching. Farmer practices rotational agriculture. Less than 5% of income coming from off-farm activities. The examined farm household has an average wealth and is fully mechanized/motorized. the farm has good access to services and infrastructure. The examined farm is medium in scale with land partly owned by the land user and partly leased from other private owners.The general biodiversity of the area is medium on Gleysols to high on Histosol where nature protection Landscape Park of Ljubljansko Barje (The Ljubljana Moors Landscape Park) is located.
Part of the farmers land parcels is located inside boundaries of Krajinski park Ljubljansko barje /Ljubljana Moor Landscape park. Park takes a lot of actions to secure peat soils. This almost 16,000 hectares large lowland marshy plain is marked by an interminable mosaic of grasslands, broadleaf woodlands, fields, ditches and hedges.
The farmer decided to abandon conventional ploughing technology and to start with conservational tillage technology when he noticed that the organic layer of peat soils in these areas started to become thinner. Farmer introduced this technology to preserve peat soils of Ljubljana Moors on his parcels in 2015. With ploughing, peat was mixed and decomposing - mineralise. In 18th-century peat layers of up to 2m depth were exploited for the same use as firewood. Only shallow layers of peat soil (up to 1 m) are still covering agricultural areas. As peat is a source of fertility farmers are seeking ways of preserving it. Farmer Anton Mrzlikar took a lead and started with conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till).
Video https://vimeo.com/97415985 presents the effects of conservational tillage with incorporated mulched plant residues (mulch-till) on soil stability. This is a simulation of abundant summer rain and its impact on the tilled soils in terms of water infiltration capacity and erodibility. The result of this simulation is presented very clearly. It shows the difference between long-term conventional versus conservation tillage (mulch-till). Conventional tillage ploughs the top 25-28 cm of the soil at least once or twice a year. The soil is inverted, its structure breaks down and the surface is left bare. The first raindrops break the structural aggregates causing soil surface siltation and blockage of the soil pores. Thus vertical water flow is blocked and redirected as surface runoff, causing distinct erosion. If fertilizers and pesticides are used, the water flow will transport them, along with the soil particles, to surface waters where they cause pollution or surface ponding on the fields. This leads to an uneven distribution of substances across the field surface.
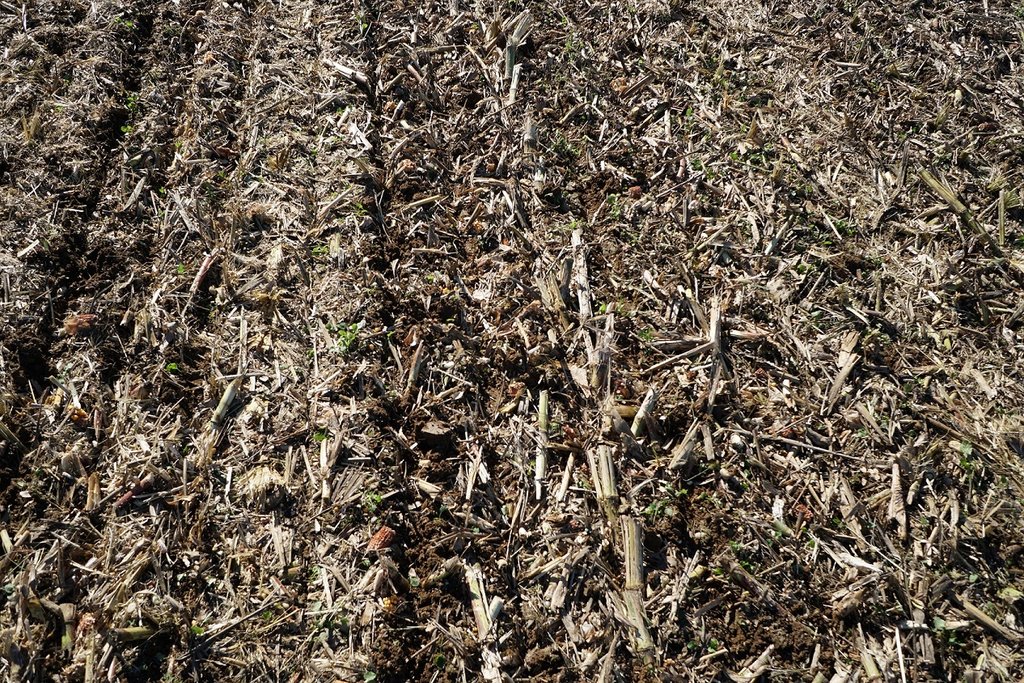
In conservation tillage (mulch-till), a shallow, 10 cm layer of topsoil is mixed with organic residues which are thus retained near and on the surface. In this way, soil structure is reinforced with good soil water infiltration and absorption. Despite heavy rainfall, the soils do not show any signs of erosion. There is no surface flow. Water drains into the soil vertical flow where it is available to the plants.
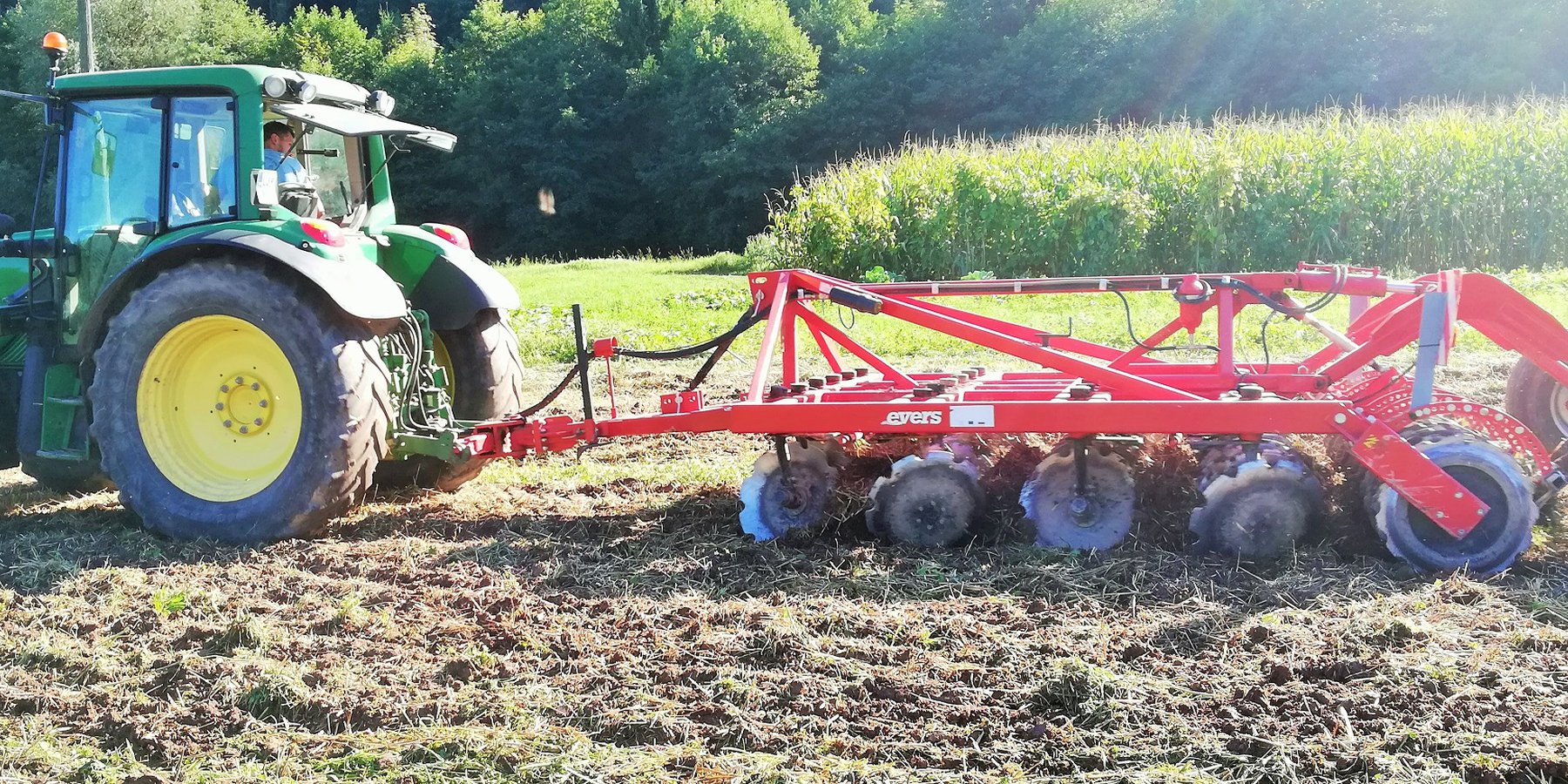
2. The farmer usees of 4-row-disk harrow tillage machinery (vario-disc) on arable fields for all crop types. When cultivating fields he crosses fields 1 - 2 times (depends on soil moisture). Every few years he uses chisels to break and shatters (aerate) the soils (depends on crop type - cereals and drought years). After main/first crop he seeds various cover crops (if fodder is needed they harvested it otherwise is used for green manure). He uses manure 30-40 t/ha. He applies typical dairy cow farm rotation (cereals/maize/soya/grass-clover mix). Cover crops are classified as rapes, cereals, oats, grass-clover, grass.
3. The main function is an increase of organic matter, retain water, increase soil biodiversity, stabilise soil structure in the soils and reduce water erosion, as well as reduce energy consumption and costs. This leads to better (1) productivity due to nutrients slow-release, (2) better water holding capacity and (3) decreased soil compaction threat. The technology was introduced to prevent decomposition of organic matter on Ljubljana moor peat soils.
4. Major inputs needed to establish is to change machinery and to gain new knowledge and experiences. They had to buy 4-row disc harrows, chisels plough and new seeders (maize). Seeding machines for cereals and oilseed rape are hired from other farmers. It is important that soils are covered all year round. Soils must be dry when cultivated.
5. The benefits are (1) increase in soil organic matter, (2) increase soil water holding capacity, (3) to maintain soil productivity, (4) increase in yields quantity and quality, (5) reduce energy consumption, (6) reduce workload - 3-4 times less time used for cultivation, (7) reduce costs.
6. Land users like (1) reduced workload and energy consumption, (2) positive impact on soil fertility and stability, (3) preserves organic matter - decrease peat soils decomposition, (4) as soils need to be covered all the time they produce more feed for cows, (5) smooths surface fields, (6) with disc harrow is easy to till soils even when residues are present on fields, (7) less soil compaction
Land users dislike: (1) investment cost for new machinery are high, (2) time to change in doing things and practice, (3) on clay soils (Gleysol) surface ponding is occurring, (4) soils need to be drier for tilling in comparison to ploughing.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.4 Технологийн дүрс бичлэг
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
This is a simulation of abundant summer rain and its impact on the tilled soils in terms of water infiltration capacity and erodibility. The result of this simulation is presented very clearly. It shows the difference between long-term conventional versus conservation soil tillage.
Conventional tillage ploughs the top 25-28 cm of the soil at least once or twice a year. The soil is inverted, its structure breaks down and the surface is left bare. The first raindrops break the structural aggregates causing soil surface siltation and blockage of the soil pores. Thus vertical water flow is blocked and redirected as surface runoff, causing distinct erosion. If fertilizers and pesticides are used, the water flow will transport them, along with the soil particles, to surface waters where they cause pollution or surface ponding on the fields. This leads to an uneven distribution of substances across the field surface.
In conservation tillage (mulch-till), a shallow, 10 cm layer of topsoil is mixed with organic residues which are thus retained near and on the surface. In this way, soil structure is reinforced with good soil water infiltration and absorption. Despite heavy rainfall, the soils do not show any signs of erosion. There is no surface flow. Water drains into the soil vertical flow where it is available to the plants.
Он, сар, өдөр:
04/12/2017
Байршил :
Ljubljana, Biotechnical Faculty, University of LJubljana
Зураглаачийн нэр :
Rok Mihelič, Marko Zupan, Matjaž Glavan - Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
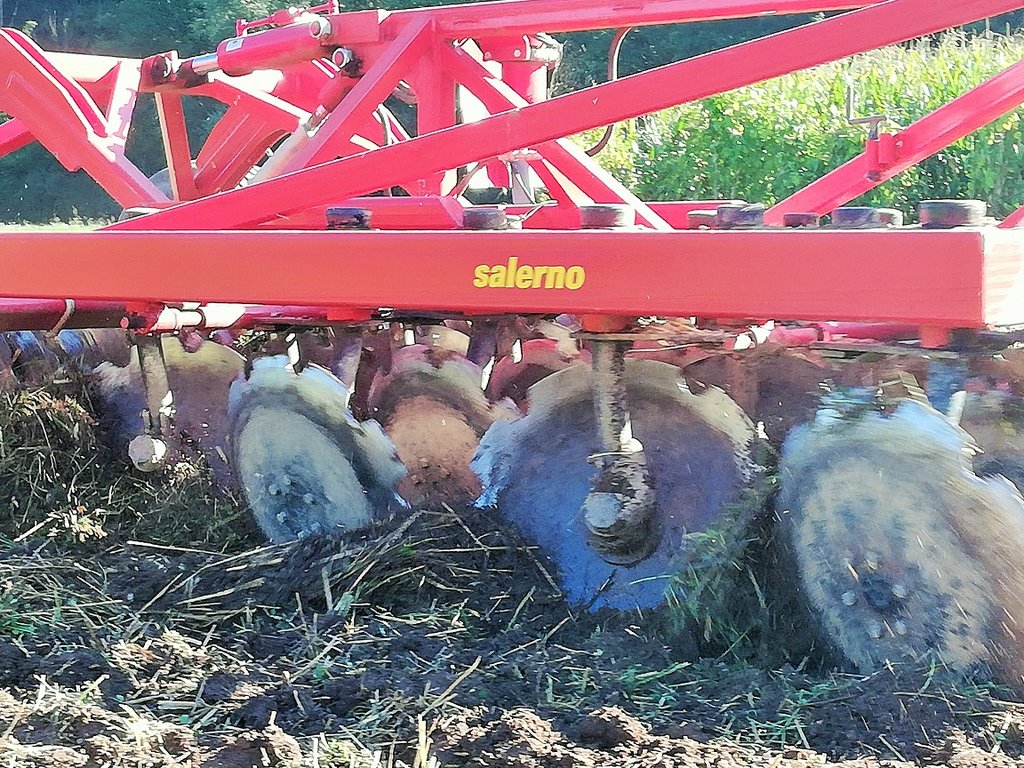
Presenting 4-row disch harrow in action.
Он, сар, өдөр:
12/04/2017
Байршил :
Slovenia
Зураглаачийн нэр :
Rok Mihelič, Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
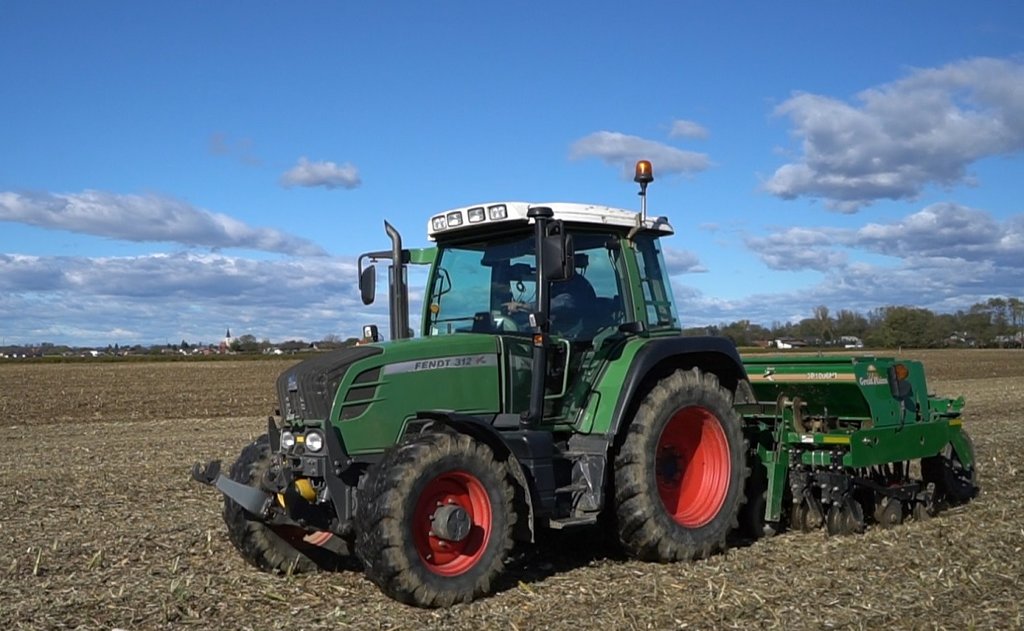
Presening seeder (cereals/oilseed rape) in action and condition of soil surface after tillage and seeding.
Он, сар, өдөр:
12/04/2017
Байршил :
Slovenia
Зураглаачийн нэр :
Rok Mihelič, Agronomy Department, Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Словен
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Central Slovenia
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Podlipa, Vrhnika. This specific farmer applies this technology on Ljubljansko barje, othewise is applied all over Slovenia
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай байнгын хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
Part of his land parcels is located inside boundaries of Krajinski park Ljubljansko barje /Ljubljana Moor Landscape park. Park takes a lot of actions to secure peat soils. This almost 16,000 hectares large marshy plain is marked by an interminable mosaic of grasslands, broadleaf woodlands, fields, ditches and hedges.
http://www.ljubljanskobarje.si/?lang=en
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2015
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Farmer introduced this technology to preserve peat soils of Ljubljana Moors on his parcels in 2015. With ploughing, peat was mixed and decomposing - mineralise. In 18th-century peat layers of up to 2m depth were exploited for the same use as firewood. Only shallow layers of peat soil (up to 1 m) are still covering agricultural areas. As peat is a source of fertility farmers are seeking ways of preserving it. Farmer Anton Mrzlikar took a lead and started with mulch-till.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ эрс тэс байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
- Үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн газар
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- cereals - maize - legumes - grass-clover mix
Тариалалтын тогтолцоо:
Эрдэнэ шиш эсвэл тэжээлийн ургамал/бэлчээр ээлжилсэн
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Үгүй
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
cereals/maize/soy/grass-clover mix, additionally cover crops after main crop (soil must be covered all year round
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 хариулт руу шилжинэ үү)
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Хамгийн бага хөрсний эвдрэл
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
- А3: Хөрсний гадаргыг сайжруулах
А3: Хөрс боловсруулах тогтолцоог ялгана уу:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

Хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших
- Ps: Органик хөрсний хомсдол
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
Тайлбар:
It is impossible to prevent degradation in the form of peat soil mineralisation in agricultural soils.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Хэмжээ ба нэгж талбайг тодорхойл:
30 ha
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
EUR
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
0.9
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
50 EUR
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of fields: Leveling depressions, reconstruction of drainage channels, using chisels to loose, break and aerate soil in deeper layers | two year before implemenation, dry soil. |
| 2. | Purchase of 4-row disc harrow | 1st year |
| 3. | Purchase of seeder for maize | 1st year |
| 4. | Purchase of seeder for cover crops | 1st year |
| 5. | Hire seeder for cereals (wheat, barley) | 1st year |
| 6. | Home made chisel plow for loosening the soil | 2nd year |
| 7. | Purchase of spraying machine | 3rd year |
| 8. | Purchase of GPS navigation system | 3rd year |
Тайлбар:
The agricultural technology activities are listed in chronological order. Rotation cycle takes 3 years
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | chisel plow material (home made) | EUR/piece | 1.0 | 6500.0 | 6500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | seeder fo cover crops | EUR/piece | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 50.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | seeder for maize | EUR/piece | 1.0 | 7500.0 | 7500.0 | 50.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | 4-row disk harrow | EUR/piece | 1.0 | 23000.0 | 23000.0 | 50.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | sprayer | EUR/piece | 1.0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 25.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | GPS navigation | EUR/piece | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | hire seeder for cereals | EUR/ha | 15.0 | 50.0 | 750.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 42762.5 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 47513.89 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагчаас нийт өртөгийн 100%хүрэхгүй зардал гарсан бол хэн үлдсэн хөрөнгө оруулалтыг хийснийг тодорхойл.
50% - Agency for agricultural payments (EU funds); 25% - sharred among farmers
Тайлбар:
Cost for hiring seeder is calculated for 15ha as cereals cover 15ha of arable land.
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of 4-disc harrow | 6 time per year, before or after use of equipment |
| 2. | Maintenance of Spayer | before use nozzels check, after use cleaning |
| 3. | Maintenance of seeder for maize | before and after use |
| 4. | Maintenance of seeder for cover crops | before and after use |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintenance of 4-disc harrow | hour | 6.0 | 6.25 | 37.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintenance of Spayer | hour | 6.0 | 6.25 | 37.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintenance of seeder for maize | hour | 4.0 | 6.25 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintenance of seeder for cover crops | hour | 1.0 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Lubricant cartridge for4-disc harrow | cartridge | 18.0 | 5.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Nozzels for Spayer | nozzel | 20.0 | 4.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Lubricant cartridge for seeder for maize | cartridge | 4.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Lubricant cartridge for seeder for cover crops | cartridge | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 301.25 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 334.72 | |||||
Тайлбар:
There is a big difference between conventional and conservation tillage in time spend cultivating fields.
Farmer estimates reduction in workload (no ploughing) for 3-4 times in comparison to the conventional ploughing system.
Farmer points out an increase in green mass yield (clover, grass) due to cover crops which can be used as feed for livestock or green manure. He said that the most important part of this conservational system (mulch-till) is to prevent weeds to germinate, and that's why soil needs to be covered at all times.
He also states that top and subsoil layers are loose.
He states that he still uses the same amount of plant protection products.
The use of herbicides and fertilisers is at the same range as before the shift in practice, but he expects improvements in the future when he will further enhance knowledge on crop types, rotation and cover crops.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
The starting cost - The type of machinery is needed that has to be robust and heavy to much-till and seed into the soil.
The machinery must be in use to return a profit. Working hours are reduced now (no ploughing). Machine operators with more competences can reduce costs.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Чийглэг
Heavy summer thunderstorms and showers. Local precipitation.
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- шаардлагагүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Их (>3 %)
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Organic matter on Gleysol is around 6% and on Histosol (peatland) more than 30%. Bellow the peatland is clay (called "polžarica", or "snail clay")
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Сайн
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ус
Усны давсжилт асуудал болдог уу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үер усанд автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
Тохиолдлын
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
On Ljubljana moor, seasonal floods are occurring regularly due to the high water table.
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Их
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
This true especially for the Ljubljana moor.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- Хүүхэд
- Дунд нас
- Ахимаг нас
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Дунд-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
83 ha of agricultural land and 7 ha of forest
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Хувь хүн, цол эргэм бүхий
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- Хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
Газар ашиглалтын эрх уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилдаг уу?
Тийм
Тайлбар:
2/3 of land is hired from The Farmland and Forest Fund of the Republic of Slovenia
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
үр тарианы чанар
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
It increased due to the fact that soil has to be covered at all times (grass, clover, cover crops) to retain soil moisture and prevent soil erosion and to provide an optimal living condition for soil life (fauna, flora). Previously the land was left bare after harvesting cereals until autumn or even spring.
тэжээлийн чанар
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to more fodder, the farmer managed to increase the number of livestock (dairy cows).
үйлдвэрлэл зогсох эрсдэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to the fact that soils are not ploughed anymore, a farmer has in wet years (more precipitation in a short period of time, especially in the springtime) problems on organic marshland and clay gley soils being fully saturated. This causes a reduction in the germination of seeds and weaker growth of plants due to hypoxia.
олон янз бүтээгдэхүүн
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More different types of cover crops in production. Some are used as nitrogen fixators or for loosening the soils with deep rots.
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The land management simplified due to fewer machines needed and less time need for land cultivation and soil preparation.
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н хөрөнгө оруулалтын зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less petrol nedeed for land cultivation.
тариалангийн газрын орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More livestock means more income.
хөдөлмөр хүчний хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Workload decreased due to abandoning of ploughing.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The farmer observed positive impacts and seeks for more knowledge on this topic to improve its practice.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
ууршилт
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
хөрс нягтрах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах С
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамал бүрхэвч
газрын дээрхи / доорхи С
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
гангийн нөлөө
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Difficult to quantify. An increase in soil organic matter has an impact on CO2 sequestration.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | Сайн | |
| Улирлын температур | Зун | Өсөлт | Сайн |
| Жилийн дундаж хур тундас | Сайн | ||
| Улирлын хур тундас | Хавар | Өсөлт | Дунд зэрэг |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Дулааны долгион | Сайн |
| Ган гачиг | Сайн |
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Тайлбар:
Benefits are on short term slightly negative due to investment costs, but in the long term they are positive - they pay off.
Maintenance benefits are positive for short as well as on long-term returns as less machinery and less land management activities is needed.
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
Only one farmer in the area that uses this technology. On the map you can observe his fields. In the last year many of his collegues observed advantages of this technology and hires his machinery as agriculture service of tillage. In majority of times before cover crops seeding.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Хувьсан өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд Технологид сүүлд ямар нэг шинэчлэл хийгдсэн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Reduction of workload (no ploughing, less time spent on the field) |
|
Change in farmers mindset is longlasting; they are forced to gain new knowledge on technology impact on soil condition With more knowledge and better handling of technology, the cost of maintenance and time spent in the field can reduce significantly. |
|
Increase in green mass yield (clover, grass) - it can be used as feed for livestock or green manure. Soil covered all year round + residues impact increase in soil organic matter, soil water content, biological activity, soil structure, less soil compaction. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Cost and time reductions are substantial - 3-4 times less in comparsio to conventional - ploughing. |
|
Farmers became aware of the importance of conservation soil management and its impact on soil properties and finally on the process of production-chain (soil-feed-milk). With proper shaping of knowledge (advising, education) - Conservational tillage has the potential to develop into the direction of organic farming. |
| Soil structure and fertility improve |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| On heavy soils (Glaysoils) surface ponding can occur if the farmer is not experienced with using technology. | Observe weather regularly and follow meteorological forecasts. Try to avoid wet periods. |
| Weed may be a problem in the warmer part of the year, mainly after cereals are harvested. | They use herbicide and adapt or improve crop types in rotation. |
| Peatland on Ljubljana moor. There are small parcels and soil in springtime is wet prohibiting to cultivate at any time (high water table). | Observe weather regularly and follow meteorological forecasts. They have to observe soil water content conditions periodically at peatland parcels. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Farmers still need to use herbicides as weeds are a problem especially in the early stage of crop growing (narrow-leaf) and in the last stage when crops go into senescence and light gets to the ground (broad-leaf). |
As this is a conventional type of farm, they use herbicides. However, with the promotion of organic agriculture, the expansion of vegetable production, and innovations in GPS and sensors technology hoeing/weeding machines/equipment is getting popular. This problem is even more problematic in light/alluvial soils. |
| Surface ponding on heavy soils is a problem in case of longlasting rain periods in spring, which are due to climate change more often in the described area. |
It is crucial to use chisel plow in this soils to break soil layers deeper and provide drainage potential of this soils. In light alluvial soils, this problem is not observed. |
| When a farmer in under Slovenian agricultural conditions decides to change from conventional to conservation tillage, it has to change all machinery. | Farmers need to get as much as possible information on technology. Farmers have to make a business plan. EU funds can help with subsidy payments for investments on the farm (approx. 50-60%). |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
1 farmer
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
1 farmer
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
1 specialist
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
10/05/2019
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
OHRANITVENA OBDELAVA TAL –STANJE V SLOVENIJI
URL:
http://www.digitalna-knjiznica.bf.uni-lj.si/du1_ograjsek_simon.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Izzivi uvajanja konzervirajoče (ohranitvene) obdelave tal
URL:
http://www.kmetzav-mb.si/Lombergar_18/Lomb_5_2_18.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
NOVE TEHNOLOGIJE IN SODOBNI TRENDI OBDELOVANJA TAL
URL:
http://www.kgzs-ms.si/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/STAJNKO_NOVE-TEHNOLOGIJE.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Ohranitvena obdelava : primerjava lastnosti mehansko obdelanih in neobdelanih prsti
URL:
https://www.dlib.si/details/URN:NBN:SI:DOC-LTCNTC4J
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
SZOORT - Slovensko združenje za ohranitveno obdelavo in rodovitnost tal
URL:
http://www.szoort.si/
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Ohranitveni način obdelave tal
URL:
https://www.program-podezelja.si/sl/247-eup/izmenjevalnik-idej/seznam-izzivov/759-ohranitveni-obdelave-tal
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна