ROAD CONSTRUCTION AND MANAGEMENT [Nepal]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
SADAK NIRMAN TATHA BEBASTHAPAN
approaches_2522 - Nepal
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
SLM specialist:
Sintah Ganga Raj
VDC, chamrangbesi
Nepal
SLM specialist:
Shrestha Deepika
Jwagal.Kupondol
Nepal
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Kathmandu University (KU) - NepalName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Sarada Batase Village Development Committee (Sarada Batase VDC) - Nepal1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
02/11/2012
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
It is a particular land conservation project to construct and manage road for the sustainable use of land.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Aims / objectives: The main Objective if road construction is:
Mainly for the transportation so that it will make local people easy to travel.
Local people will be economically benefited.
For the development of the village.
To improve the living standard of local people.
.
Methods: Local people first decided the direction from where the road passes through. Then they collected funds and used dozer to dig and local people broke the stone. There was a voluntary participation of local people on road construction and gave huge contribution in road construction process.
Stages of implementation: First of all they were given knowledge about both the importance as well as consequences that they would be facing during the process of road construction.Keeping the consequences aside they decided to give some contribution in road construction to improve their life-style , they started gathering money and they voluntarily worked like passing stone ,breaking them and used dozer for main purpose. Funds for road construction was also provided by VDC
Role of stakeholders: 40% of the investment were done by the local people rest by the government.
Other important information: EIA was not done for construction of road.
Lack of engineer involvement for road construction.
Unmanaged road.
Lack of technology.
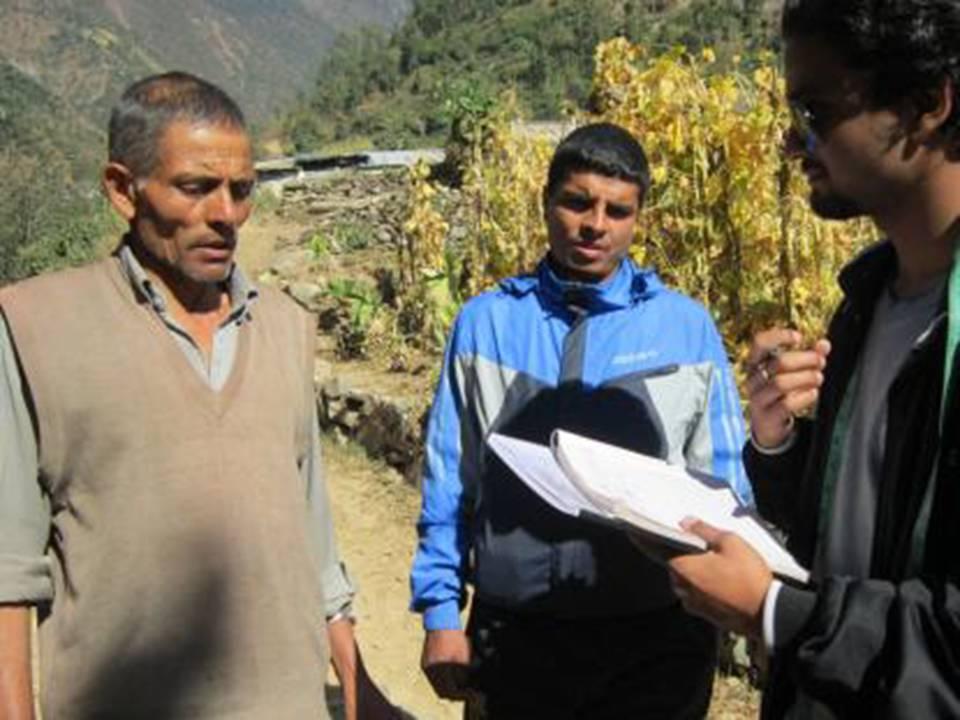
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Nepal
Further specification of location:
kavre
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2009
Year of termination (if Approach is no longer applied):
2009
2.7 Type of Approach
- recent local initiative/ innovative
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Transportation)
The main objective was to know about the road construction, how it was made, what were the budget, problems and treatment.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main problem in road construction was dust particle while the construction was carrying on due to which there was a health problem.
Lack of technical knowledge.
Some conflict among the villagers about their land use during road construction.
Some natural calamities like soil erosion.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
Financial problem as villagers had no large amount of money to invest
Treatment through the SLM Approach: They together collected money and some financial help from VDC's were given so that they can invest it during the road construction.
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- enabling
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The road in the village has passed through different land owners so it has helped greatly.
- hindering
Conflicts among villagers for land use during road construction.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Solve it through several meetings.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
Due to less economical interest less technology were hired.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Dozer, elevators and loaders were hired for the construction.
workload, availability of manpower
- hindering
people workload was increased due to less technology use.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: All the villagers worked together.
other
- hindering
health problem due to dust particles.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: people used mask and glasses to avoid dust.
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
Invested money and helped in construction. Collected money and worked together. Not much differences as they both contributed in road construction. Women were less in number as compared to men as they had to work in their houses. Some of them were busy with house works. People whose land were used for construction were not paid well. They had a great problem dealing with it because the land which was used in road construction was only the source for them to earn money.
- local government
Supported in the aid.
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
Supported in the aid.
- government and VDC
Funded for road construction.
If several stakeholders were involved, indicate lead agency:
All the villagers were involved in road construction and gave huge contribution in constructing the raod
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | funding was done by both government and local people . |
| planning | interactive | construction planning was done by villagers. |
| implementation | self-mobilization | Local people initiated and implemented the work |
| monitoring/ evaluation | none | |
| Research | none |
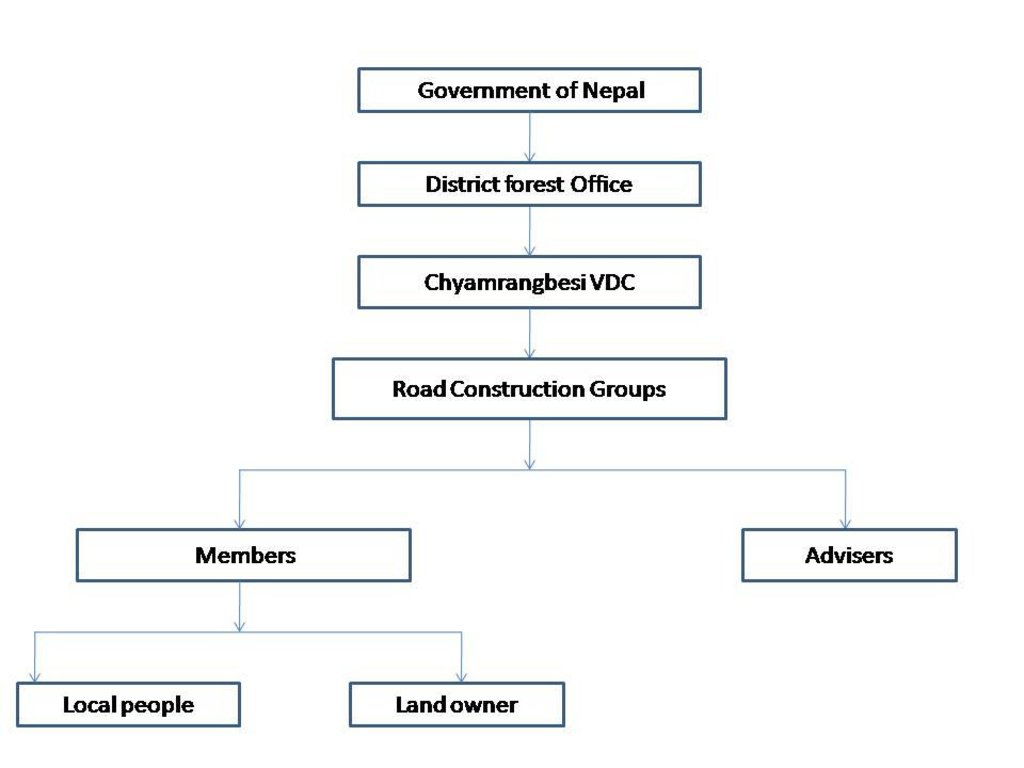
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
Description:
It is a sequential chart showing different participants that played an important role in the road construction.
Author:
Deepika Shrestha (Jwagal,Kupondol)
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- land users alone (self-initiative)
Explain:
In order to develop their village,for transportation purpose so that they could travel from one place to another easily, for business purpose they made decision on the choice of SLM Technology
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). Local People asked for the financial help with government.Government provided some help but that was not enough so villagers among themselves collected money for the construction of the road
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Describe/ comments:
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Lack of interest.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, moderately
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- equipment
Give further details:
some advices were given before construction.
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
Comments:
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by government, land users through observations; indicators: financial support for road construction.
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators
road construction aspects were regular monitored by government, land users through observations; indicators
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The width of road, slope angle and curve distance.
There were several changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Road width, slope angle and curve width.
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Yes
Specify topics:
- economics / marketing
- ecology
- technology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
local peoples and VDC.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- 100,000-1,000,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (funded for road construction.): 50.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (Supported in the aid.): 10.0%; local community / land user(s) (collected money.): 40.0%
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| machinery | fully financed | |
| tools | fully financed | |
- infrastructure
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| roads | partly financed | |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- voluntary
Comments:
Villagers voluntary worked for road construction for development for their village.
Machinery and tools were fully financed but due to lack of technicians, machine were not used properly.
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Because while road construction all the trees were cut down due to which habitat of birds and animals were destroyed and natural calamities like soil erosion occurred and water pollution,noise pollution ,air pollution etc were also the problem faced during road construction.
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
They have established shops, hotels and different vegetables can be sent to urban areas like kathmandu easily.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. While extending the road,more land is required due to which dispute between the land owner may rise.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
With road construction , transportation facility has become easy, also progress in business and living standard.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Their have improved economic status and also living standard by growing crops in their land and transporting it to urban areas like Kathmandu ,by establishing shops hotels etc.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- increased production
transportation facilities
- increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
growing and selling the products
- reduced workload
transportation facilities due to which their workload dereased.
- affiliation to movement/ project/ group/ networks
some project may come and work for their village.
- environmental consciousness
pollution like air pollution,water pollution were reduced,sound health,healthy and fresh environment
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
road construction helps to improve their living and economical standard.
- for business purpose
they grow vegetables and send to city.
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- no
If no or uncertain, specify and comment:
Lack of financial support for road construction,technicians,machines ,tools etc
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| They can sell their products and earn money. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: planting trees on the side of the road which will make soil hard and prevent from landslides, soil erosion which damages the road.) |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| sick person can be taken to hospital easily. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Wall line structure can be made so it prevent from landslides and soil erosion.) |
| Transportation facility will be available. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Road must be maintained from time to time.) |
| Import and Export of different local product. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Production of local product should be increased.) |
| People can travel to village easily. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: road should be pitched and should be extended. ) |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Dust particle may cause harm. | Road must be pitched. |
| If road is extended then land user must sacrifice some portion of their land. | Land users should be paid well for their land. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Road is gravelled and dusty. | Road must be pitched . |
| Road is dangerous and rough so maximum chance of accident. | Stone block must be constructed to prevent accident. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules