Disaster risk reduction and sustainable land-use by integrated rehabilitation of flashflood/debris flow affected site [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Stefan Michel
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Umed Vahobov
Снижение риска стихийных бедствий и устойчивое землепользование через интегрированное восстановление местности разрушенного селевым потоком
approaches_4320 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Muhidinov Nodir
nodir.sfl@gmail.com
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Tajikistan
SLM specialist:
Negmatov Negmatjon
negmatdzhon.negmatov@giz.de
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Strengthening of Livelihoods through Climate Change Adaptation in Kyrgyzstan and TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
GIZ Tajikistan (GIZ Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies

Applying drip irrigation for efficient irrigation water use … [Tajikistan]
Drip irrigation substantially saves water compared to conventional furrow irrigation. Here the technology is applied for different perennial and annual crops and with use of different sources of water.
- Compiler: Stefan Michel

Cultivation of local juniper species for rehabilitation of … [Tajikistan]
The local species of juniper trees (Juniperus seravschanica, Juniperus turkestanica and Juniperus semiglobosa) are rarely rejuvenating under conditions of intensive grazing and are difficult to propagate in nurseries. The technology describes the propagation of these important trees from locally collected seeds and their cultivation.
- Compiler: Stefan Michel
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
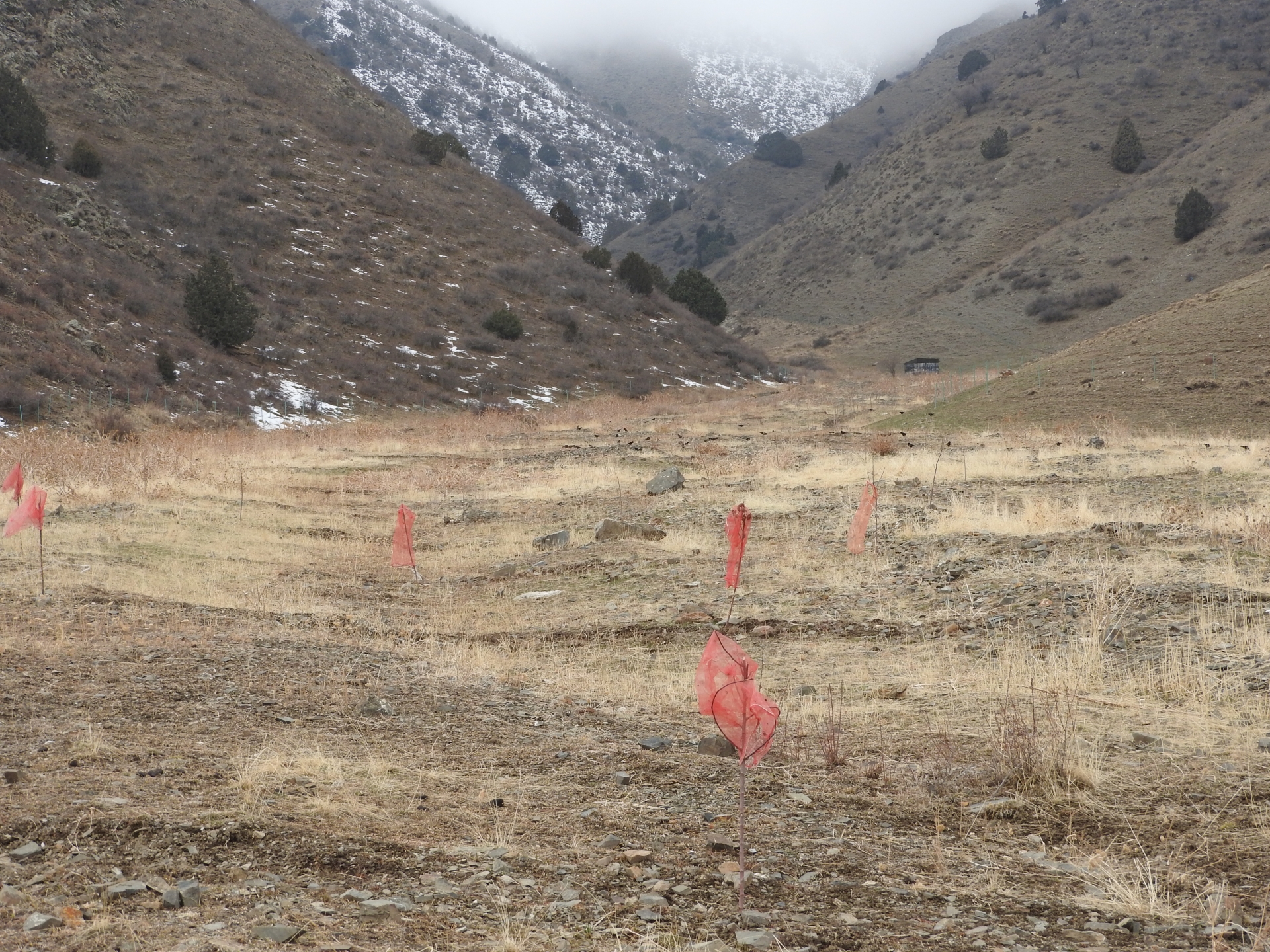
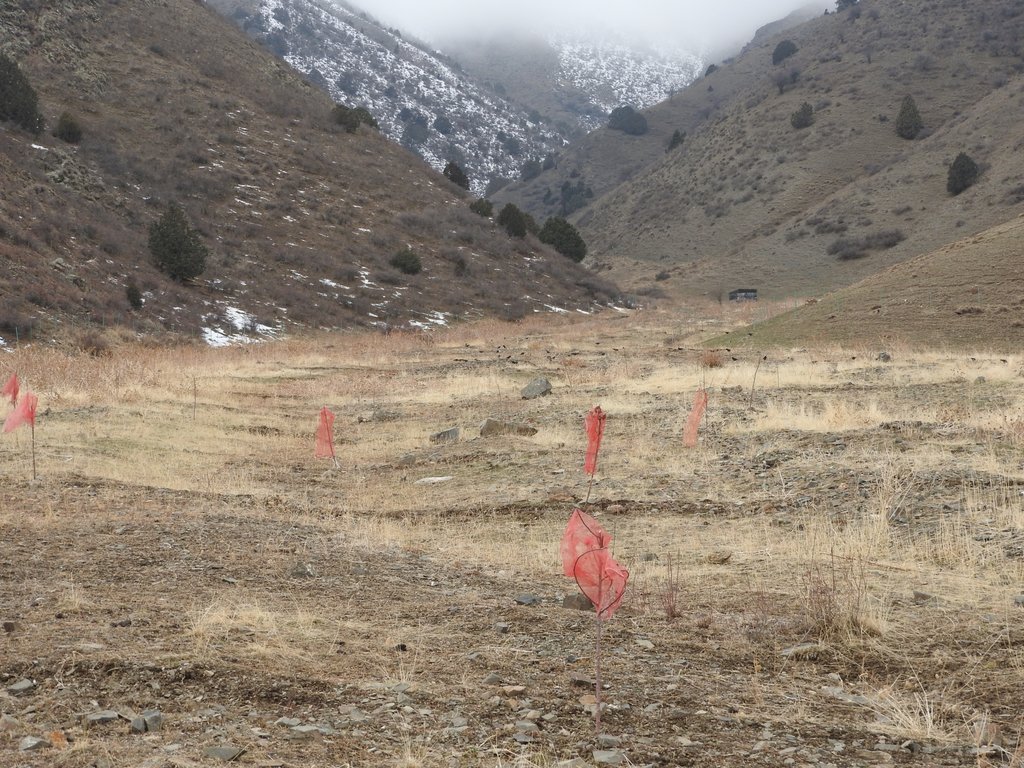
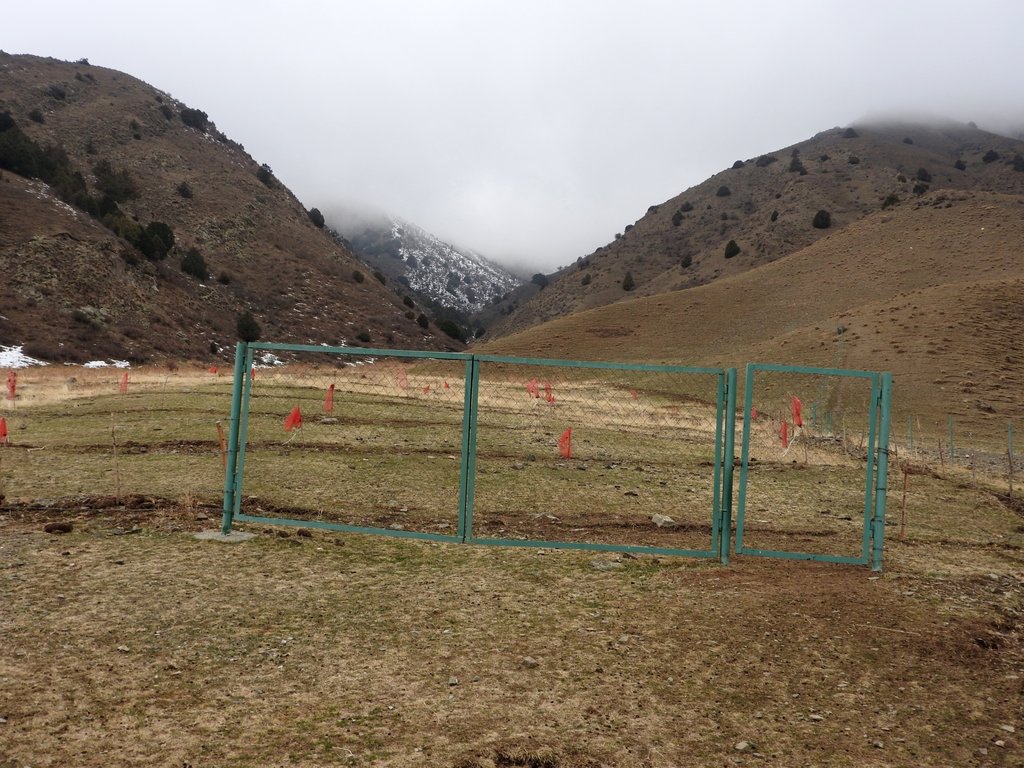
A site affected by a debris flow was rehabilitated by joint communal work and integrated preventive measures addressing the upper catchment as well as the valley and the debris conus were implemented in collaboration of community, individual farmers, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Local people in many parts of Tajikistan, among these the project region at the northern main slope of the Turkestan range, report about formerly unknown flashfloods and debris flows, even in areas where such events are not remembered. Also relief, soil and vegetation often confirm that such sites for long times had not been transformed by these forces. The occurrence of flashfloods and debris flows in formerly not affected areas, unusual seasons or an increase in frequency and destructiveness of such events can be attributed to land degradation in upper catchment areas in combination with climate change impact.
The degradation of the vegetation in upper catchments has contributed to reduced infiltration of water and high and fast surface runoff. Important elements of this degradation are overgrazing and deforestation. Overgrazing and out of season grazing cause the reduction of the protective plant cover and the multiple trails of livestock with compressed soil reduce infiltration and increase the surface runoff. Deforestation is typically related to intensive livestock grazing, in particular by goats, as intensive browsing prevents the regeneration of shrub and tree vegetation. In upper catchments affected by these processes during heavy rainfall and snow melt large amounts of water concentrate in small valleys and take with them large amounts of soil and gravel. The deforestation in valleys contributes to the intensity of such flashfloods and debris flows.
The frequency and intensity of these events is increasingly exacerbated by the impact of climate change. The already visible trends and predictions show higher levels of aridity, higher temperatures during the vegetation season, reduced overall precipitation in catchment areas – all affecting the retention potential of upper catchment areas – and more irregular rainfall patterns, reduced snow packs and accelerated snow melt as well as the loss of glaciers as buffers of water flow. These factors all contribute to a higher frequency and intensity of flashflood and debris flows and their occurrence in previously not or less affected areas.
Near the village Shamoli in Shakhriston district, as in many other locations, such a debris flow made a road impassable and has destroyed pasture lands and five hectares of arable lands belonging to several farmers with another 10 ha being at risk in case such events occur again. Local people assisted by the Committee of Emergency Situations opened and cleaned the road. The developed in collaboration with experts an integrated approach for rehabilitating the affected lands and reducing the disaster risk. The approach included the following elements:
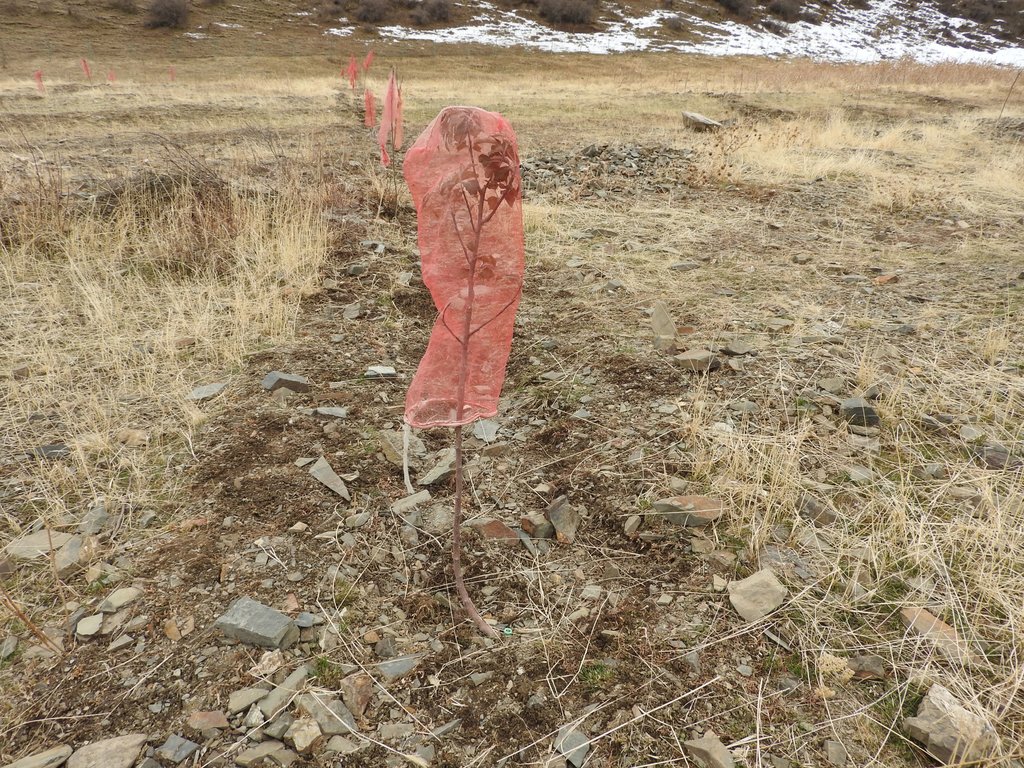
•Blocking of gullies with planting of willows for reducing sediment load in case of future flashfloods;
•Agreement with the forestry enterprise about general regulation of grazing and tree planting (specifics to be decided by the forestry enterprise);
•Joint communal work (hashar) for cleaning affected arable lands from debris;
•Fencing of 4 ha lands in the valley leased by one farmer from the forestry enterprise for rehabilitation of protective vegetation and sustainable land use (orchard and hay making);
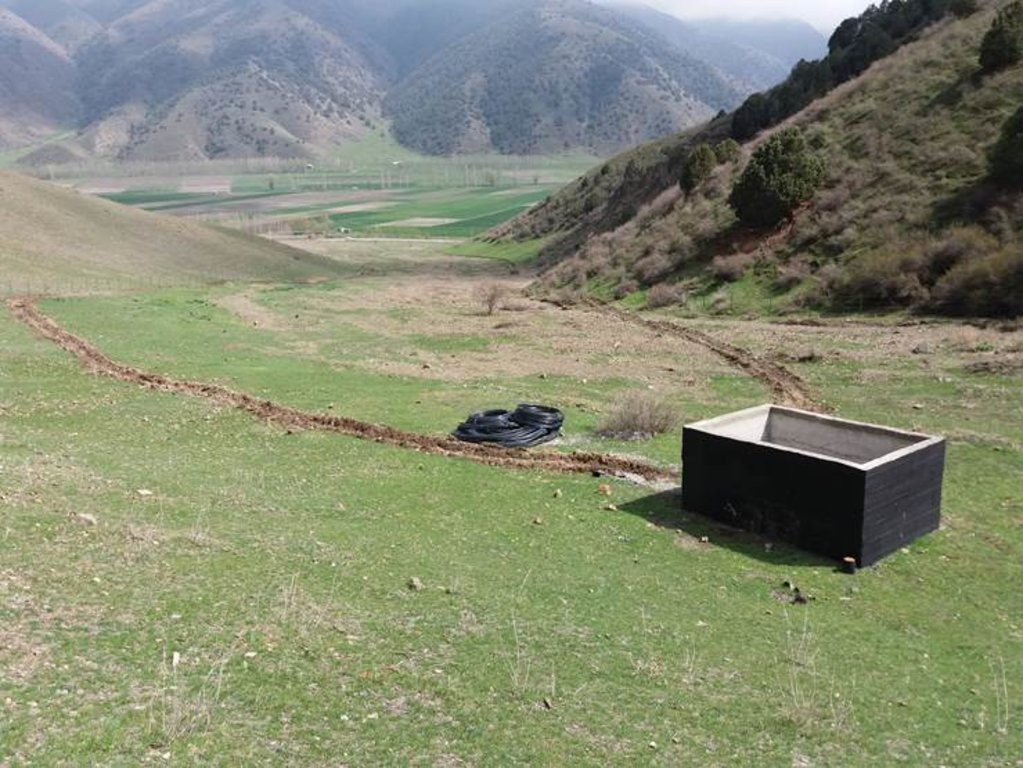
•Construction of reservoir for water collection from spring and use for drip irrigation of trees planted at the debris conus in the opening of the valley.
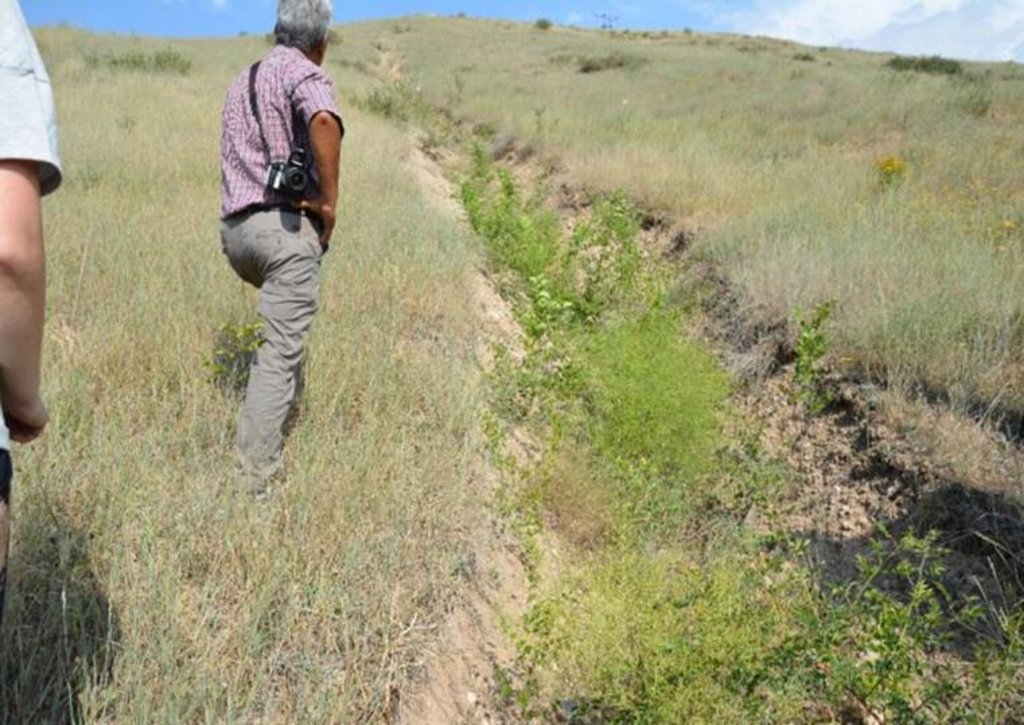
The approach brought together the Committee of Emergency Situations, the administrative communities, affected local people and the forestry enterprise. Assisted by experts provided by the project, the situation was jointly analyzed; risks identified and the integrated intervention planned. The project assisted with technical planning, construction supervision, purchase and transportation of construction materials. The community contributed about 30% of the overall costs, mainly in form of voluntary communal work, the so called hashar. One farmer leased the most critical area at the opening of the valley and took the responsibility for the maintenance of the area in exchange for the opportunity to use hay and fruits from the planted trees.
The approach is generally replicable. But in most such sites the upper catchment areas belong to different communities, often to different districts and substantial parts are located in neighboring Kyrgyzstan. Therefore addressing the degradation of these areas and a reduction of disaster risk through integrated watershed management in the entire catchments will require more collaboration across administrative boundaries and even national borders.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Sughd region
Further specification of location:
Shahriston district; Shahriston sub-district, Shamoli site
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2017
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date when the Approach was initiated:
less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Type of Approach
- project/ programme based
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
Rehabilitation of land affected by debris flow and reduction of risk of future events.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
For complex measures the financial assistance by the project was needed.
institutional setting
- enabling
Communal work for addressing issues affecting the entire community or individual members.
collaboration/ coordination of actors
- enabling
Collaboration between community members, community leadership, Committee for Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
Understanding of SLM issues insufficient, involvement of external experts needed.
workload, availability of manpower
- enabling
Communal work for addressing issues affecting the entire community or individual members.
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
Individual farmers and local community
Discussion of rehabilitation and prevention measures;
Implementation of works;
Maintencance of site with protection plantation.
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
Experts provided by GIZ
Advise on disaster risk reduction, blocking of gullies, planting of trees, drip irrigation.
- local government
Community administration, Committee of Emergency Situations, forestry enterprise
Identification of risk sites;
Design, planning and supervision of interventions;
Lease of intervention site;
Regulation of grazing and tree planting in upper catchment.
- international organization
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Overall project implementation;
Technical planning and oversight;
Procurement of construction materials via competitive bidding process
If several stakeholders were involved, indicate lead agency:
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Local community members, asking community leadership and GIZ staff for assistance to address impact of debris flow |
| planning | interactive | Involvement of community members in planning |
| implementation | Local community members carrying out works through traditional voluntary community work ("hashar"). | |
| monitoring/ evaluation | Local farmer maintaining the planted area controls condition of irrigation system and trees. | |
| maintenance | Local farmer maintaining the planted area. |
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- all relevant actors, as part of a participatory approach
Specify on what basis decisions were made:
- evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
- personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
No
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Describe/ comments:
Not of specific relevance for this approach.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, a little
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Describe institution, roles and responsibilities, members, etc.
Existing community institutions have been strengthened through joint successful implementation of the works and the need for further collaboration.
Specify type of support:
- financial
- capacity building/ training
- equipment
Give further details:
Fencing, materials of irrigation system, technical advice.
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
If yes, is this documentation intended to be used for monitoring and evaluation?
No
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
No
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- 2,000-10,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Government of Germany, implemented via Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). The approach has been implemented in the frame of a much larger program and the specific budget for the SLM component of the Approach cannot be determined.
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify type(s) of support, conditions, and provider(s):
Technical planning and supervision, procurement of materials and transportation funded by GIZ.
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- none
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- voluntary
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
5.5 Other incentives or instruments
Were other incentives or instruments used to promote implementation of SLM Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify:
The farmer managing the site in the valley, where trees have been planted, can use the fruits and the hay produced from the site. This is the key incentive for him to carry out all maintenance.
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach empower local land users, improve stakeholder participation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Mobilization for joint work to address problems affecting all farmers/community members
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Integration of different technologies to rehabilitate lands and reduce future disaster risk.
Did the Approach improve coordination and cost-effective implementation of SLM?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Collaboration between land users, community leadership, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
Did the Approach mobilize/ improve access to financial resources for SLM implementation?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Mobilization of financial resources from GIZ.
Did the Approach improve knowledge and capacities of land users to implement SLM?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Knowledge of and skills to implement several technologies for land rehabilitation, sustainable land use and disaster risk reduction.
Did the Approach build/ strengthen institutions, collaboration between stakeholders?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Collaboration between land users, community leadership, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
Did the Approach improve issues of land tenure/ user rights that hindered implementation of SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Lease of critical site to motivated farmer by forestry enterprise.
Did the Approach lead to improved food security/ improved nutrition?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Rehabilitation of affected farmlands and reduced disaster risk.
Did the Approach improve the capacity of the land users to adapt to climate changes/ extremes and mitigate climate related disasters?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Reduced risk of disasters, which increase due to climate change.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- increased production
Fruits and hay from rehabilitated critical site.
- reduced risk of disasters
Reduced risk of disasters, which increase due to climate change and threaten productive lands and property.
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- yes
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Rehabilitated lands and reduced risk. |
| Use of products from critical site, which was planted with fruit trees. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Same as land users' view. |
| Mobilization of collaboration and joint communal work. |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| High costs of fencing | External funding. |
| High costs of irrigation system | External funding. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| High costs of fencing |
External funding; Cheaper temporary electric fencing; Approaches without fencing, based on agreement in the community to prevent livestock damage through herding. |
| High costs of irrigation system |
External funding; Planting of drought resistant trees. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Applying drip irrigation for efficient irrigation water use … [Tajikistan]
Drip irrigation substantially saves water compared to conventional furrow irrigation. Here the technology is applied for different perennial and annual crops and with use of different sources of water.
- Compiler: Stefan Michel

Cultivation of local juniper species for rehabilitation of … [Tajikistan]
The local species of juniper trees (Juniperus seravschanica, Juniperus turkestanica and Juniperus semiglobosa) are rarely rejuvenating under conditions of intensive grazing and are difficult to propagate in nurseries. The technology describes the propagation of these important trees from locally collected seeds and their cultivation.
- Compiler: Stefan Michel
Modules
No modules