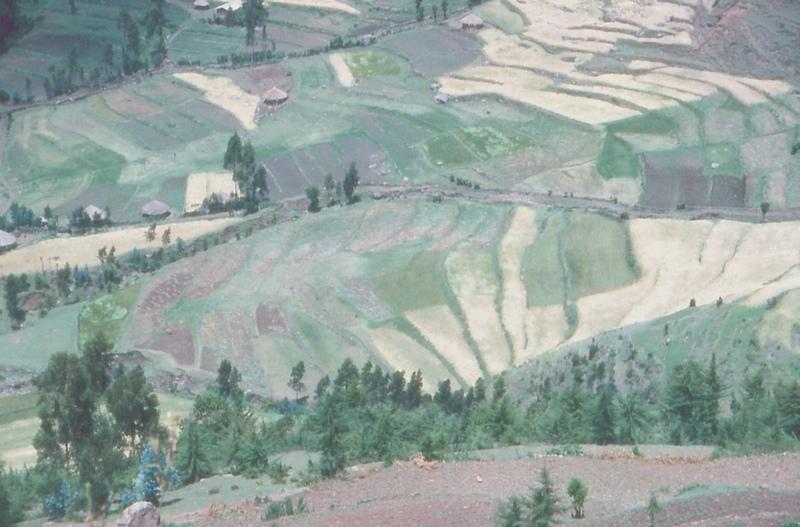
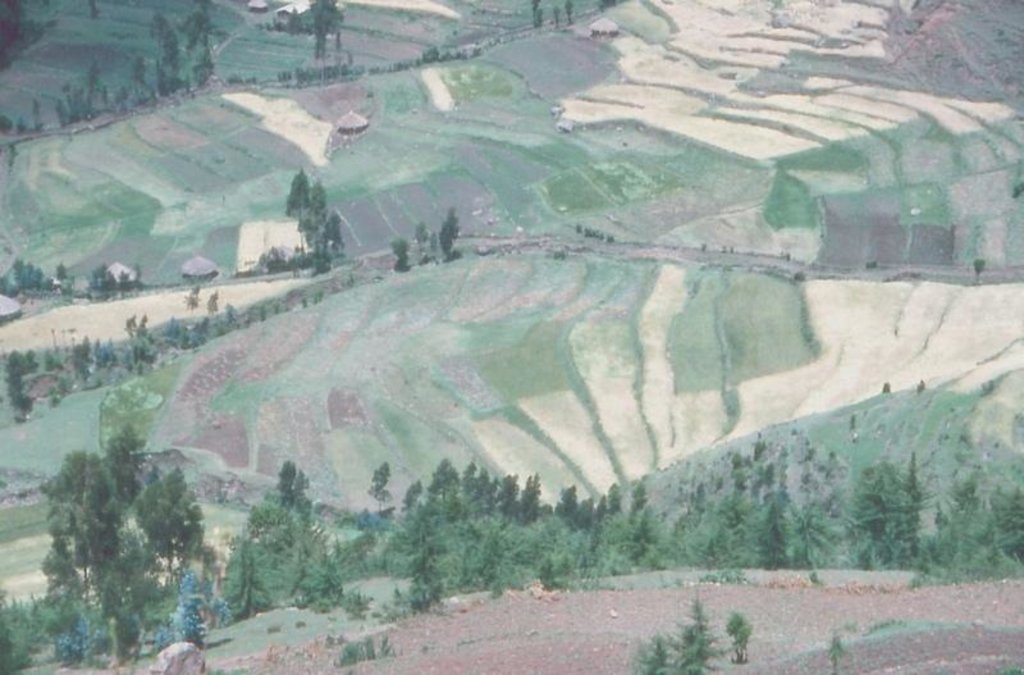
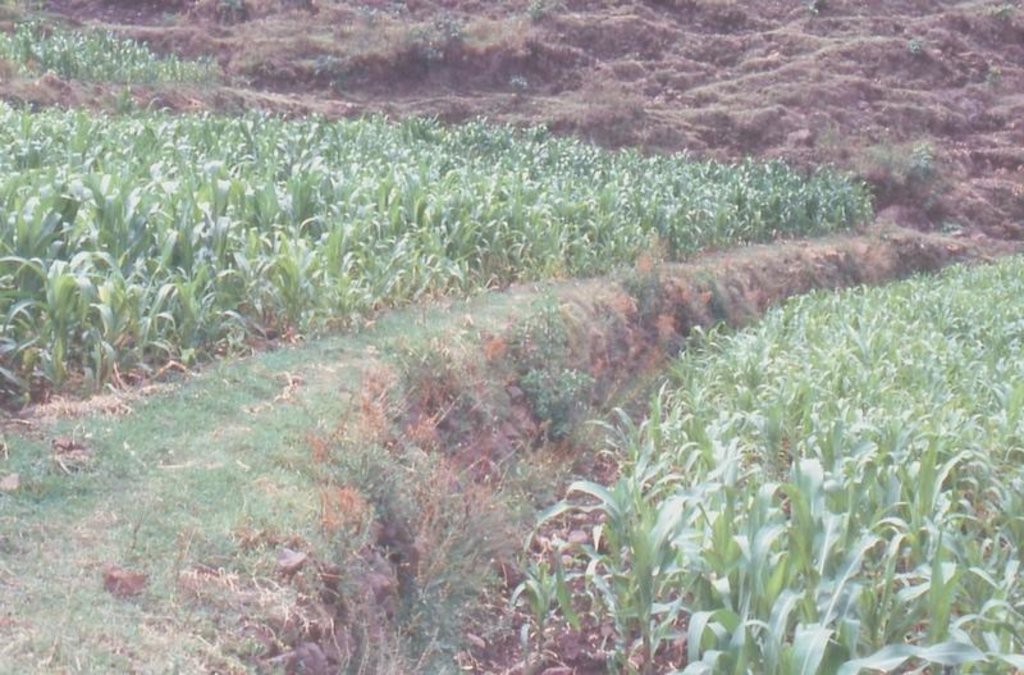
level bund with double stone walls [Ethiopia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Sabina Erny
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
cab
technologies_1061 - Ethiopia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Department of Geography, University of Basel (Department of Geography, University of Basel) - Switzerland1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
05/09/2003
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches
food-for-work programm [Ethiopia]
food-for-work programm with distribution of grains and oil
- Compiler: Sabina Erny
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
level bund with double stone walls with soil and grass to stabilize the structure
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Two level rows of stones are piled up and the space between them is filled up with soil. Grass is growing on it so it can stabilize the bund. The soil can accumulate behind the bund. The land and the bunds slowly develop into terraces. It is combined with contour ploughing.
Purpose of the Technology: control runoff and soil erosion
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: through food-for-work program. Maintenance is up to the farmers, some maintain it regularly, throughout the year, others don't.
Natural / human environment: on gentle and steep slopes
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Ethiopia
Region/ State/ Province:
South Wello
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
it was implemented by the government
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping

Grazing land
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): erosion, decline of soil fertility and yield decline other major SWC specialist: shortage of grazing land and of forage
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): erosion, runoff, drought, climate
Grazingland comments: area closure: only during July-October some areas are closed, otherwise no area closure any more. Make hay for the cattle to feed them in the dry season.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: barley/wheat/emmer wheat - beans or teff - maize - barley/wheat/emmer wheat - beans or teff - maize
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Nov Second longest growing period in days: 150 Second longest growing period from month to month: Feb - Jun
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- cross-slope measure
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S2: Bunds, banks
Comments:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour tillage
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wo: offsite degradation effects
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
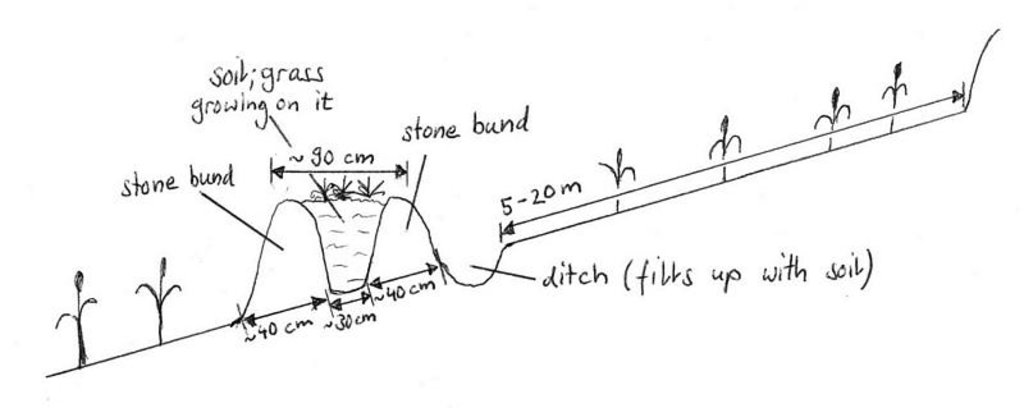
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Drawing showing a level bund with double stone walls, Maybar, Ethiopia
Location: Maybar. Wello
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Contour tillage
Remarks: because of the design of the terraces
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 10.00%
Construction material (earth): earth from the ditch just behind the structure on the upper side
Construction material (stone): normal, big stones from the field
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
birr
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.8
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
0.50
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | it has grown itself on the bund | Vegetative | |
| 2. | measurement of fields, to know where to build the bunds | Structural | |
| 3. | constructing the stonewalls | Structural | December - January |
| 4. | filling the bunds in between with soils from the ditch behind the structure, on the upper side | Structural | December - January, sometimes in November and June |
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | contour ploughing | Agronomic | dry season and rainseason / several times |
| 2. | none, cattle are grazing on it | Vegetative | |
| 3. | observation | Structural | December-January/every year after harvesting |
| 4. | rebuilding the structure | Structural | December-January/every 1-3 years |
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
the slope: the steeper, the more bunds are needed; labour is a problem if there is no food-for-work any more
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1067.00
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
Moist dega
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked1, mainly steep hills), footslopes and ridges (both ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2, more than 80% of the land has a slope degree from over 13%) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (about 40% of the area) and moderately deep (both ranked 1), shallow and deep (both ranked 2)
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (of the major soil type)
Soil fertility: Medium
Topsoil organic matter: High (ranked 1, in the major soil type) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2, somtimes there is waterlogging)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
10% of the land users are rich and own 38% of the land (only rough estimates).
58% of the land users are average wealthy and own 36% of the land (only rough estimates).
32% of the land users are poor and own 26% of the land (only rough estimates).
Off-farm income specification: farmers employ others for ploughing, so they can go to the market
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, ploughing with oxen) and manual work (ranked 2, hacking)
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
200
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: some farmers are building level bund with double stone wallss without any incentives
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Biological soil conservation techniques for Maybar area, Ethiopia. Kassaye Goshu. 1997.
Available from where? Costs?
CDE, Bern
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Classification of the Environment Conditions. H.-J. Krüger. 2003.
Available from where? Costs?
CDE, Bern
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Area of Maybar, Wello, Ethiopia: Long-term Monitoring of the Agricultural Environment 1981-1994
Available from where? Costs?
CDE, Bern
Title, author, year, ISBN:
The Use, Maintenance and Development of Soil and Water Conservation Measures by Small-Scale Farming Householfs in Different Agro-Climatic Zones of Northern Shewa and Southern Wello, Ethiopia.Yohannes Gebre Michael. 1999.
Available from where? Costs?
CDE, Bern
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

food-for-work programm [Ethiopia]
food-for-work programm with distribution of grains and oil
- Compiler: Sabina Erny
Modules
No modules