Sweet Potato Ridge [Ethiopia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Daniel Danano
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1068 - Ethiopia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Italy1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
05/12/2008
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Earth embankment formed by digging a channel and pile the soil to form a ridge on which potato is planted.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Sweet potato ridge are constructed from the soil dug out of the furrow. Farmers make the furrow and ridge by dengora and a hoe. In some cases oxen scoop are used to move the soil and form the embankment. Sweet potato is planted by cuttings. It is often planted during the end of the main rainy season. There are different methods employed in making ridge and furrows. The furrows are meant to collect rain water and the cuttings of sweet potato planted on the ridge. The plant benefits from the soil water stored by the farrows. It has deep roots that go deep insearch of soil water. Water could also move up by capillary movement. Forming the ridges and basin is quite labours. The ridges are frequently made new and in some cases the former ridges and furrows are maintained. The technology suits to sub-humid and semi arid agro-ecological zones having sandy loam soils.
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Ethiopia
2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Originated locally from long term experiences and improvments
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Major food crop annual cropping: Sorghum, sweet potato
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: Chat
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil mositure stress, erosion and over population.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Shortage of rains, lack of finance for purchasing improved seeds and fertilizers.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Sorghum-Sweet Potato-Maize-Legumes
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 21 0Longest growing period from month to month: May - Nov
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- water diversion and drainage
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 km2
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing, poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
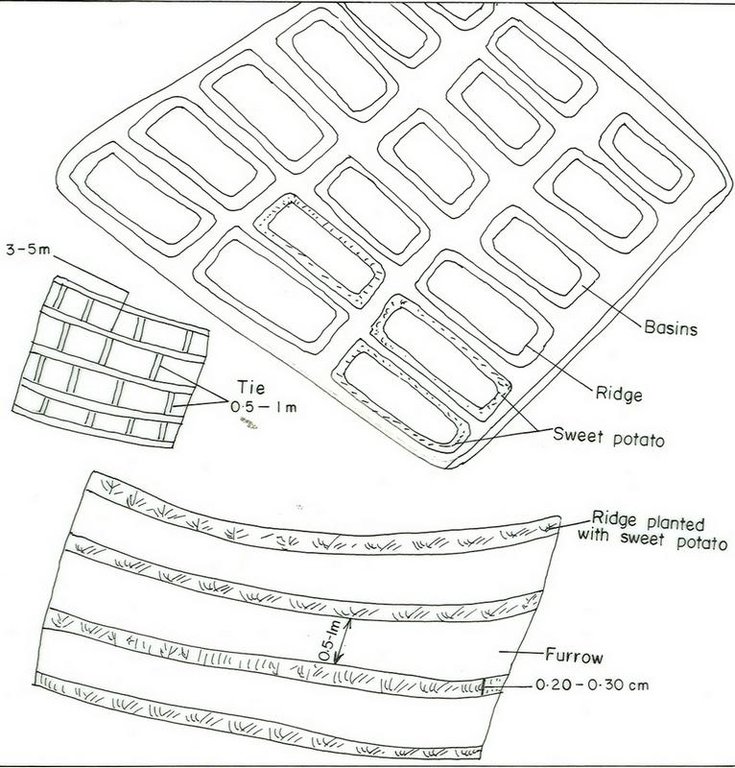
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Oromia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope length, increase in soil fertility
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Sweet potato
Quantity/ density: 20000-2500
Remarks: along the contour
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize, sorghum, chat
Remarks: row and broadcast
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Sorghum, chat
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Sorghum, chat, maize
Green manure
Material/ species: Sweet potato
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 1500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Trees/ shrubs species: some accacia trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, mango
Perennial crops species: chat
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 1.5-2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2-0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5-1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-70
Structural measure: Ridge and furrows
Spacing between structures (m): 2-3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.51
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-70
Construction material (earth): Soil dug is embanked to form the ridge
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 3%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Birr
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.6
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
0.81
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seed bed preparation | Vegetative | dry season |
| 2. | Pitting | Vegetative | after rain |
| 3. | Manuring | Vegetative | all season |
| 4. | Planting | Vegetative | during rains |
| 5. | Cultivation | Vegetative | during rains |
| 6. | Excavation (furrow formation) | Structural | dry period |
| 7. | Embankment (ridge forming) | Structural | |
| 8. | Planting sweet potato | Structural | rainy season |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 73.0 | 73.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 183.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | Agronomic | dry season / each cropping season |
| 2. | Harrowing | Agronomic | dry season / each cropping season |
| 3. | Contour ridging | Agronomic | dry season / each cropping season |
| 4. | Planting | Agronomic | rainy season / each cropping season |
| 5. | Cultivation | Agronomic | rainy season / 2-3 |
| 6. | Reconstructing basins, ridges and tie | Vegetative | dry eason / |
| 7. | Applying more manure | Vegetative | all season / |
| 8. | Repair of ridges and furrows | Structural | before planting/1 |
| 9. | Placing of fertile soil on the ridges | Structural | before planting/2 |
| 10. | Applying manure during cultivation | Structural | after planting/1 |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Total labour expended to till the land, pulverize it, harrow and making of the ridges. The cost further include the monetary estimate of manuring the land and purchasing of the sweet potato cuttings, assuming these are purchased from market.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Soil dryness and texture-light soils are very simple for opration and the least cost is incurred. Loam soils are good soils with moderate cost of investment.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l. (ranked 1), 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (ranked 2) and 2001-2500 m a.s.l. (ranked 3)
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Also gentle (ranked 2) and moderate (ranked 3)
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil depth on average: Also Deep and shallow (both ranked 2)
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- commercial/ market
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
25% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (sweet potato is mostly planted on level and gentle slopes and hence land preparation is made largely by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, most part consumed at home) and mixed (ranked 2, small portion of the sweet potato is sold at market)
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
Due to population pressure land shortage is a critical problem humpering production and productivity
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
sweet potato leaves are used for fodder
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
sweet potato leaves are used for fodder
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
50
Quantity after SLM:
0
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
Other ecological impacts
Soil fertility
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
downstream siltation
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
85% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: more farmers are practicing the technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Improve production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of high yielding varieties and fertilizers |
|
Reduces risk of crop failure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage more crop type |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Efficiently controls soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? The ridges retard surface flow and the furrow provide space for rain water storage |
| Allows maximum storage of rain water |
|
Improves water storage capacity of soils How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sweet potato improves the soil structure by initiating microbial activities |
|
Reduces evapotranspiration rate of soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sweet potato provide dense ground cover and hence reduce evapotranspiration losses |
|
Improves soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sweet potato is naturally a soil fertility enhancing crop. |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules