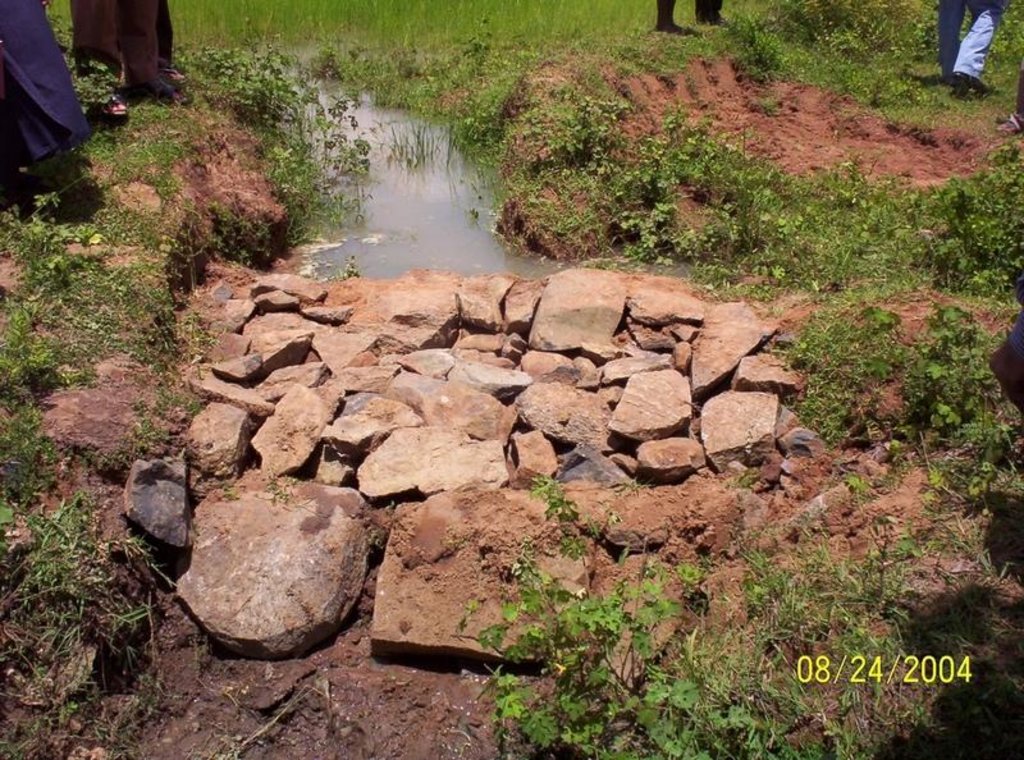
Dugout Sunken Pond with Catchment Treatment [India]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
Bandha/ Pokhari (Oriya)
technologies_1475 - India
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Patnaik Kishore Chandra
India
SLM specialist:
Pradhan Gandhi
India
SLM specialist:
Tripathy Dasarathi
MALKANGIRI (ORISSA) INDIA
India
SLM specialist:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
Semiliguda, Koraput, Orissa, India
India
SLM specialist:
Mohanty K.C
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society
Malkangiri Orissa India
India
SLM specialist:
Mishra BIJAYALAXMI
IDCWDP
Koraput
India
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute - IndiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society - IndiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
IDCWDP (IDCWDP) - India1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
20/08/2004
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches
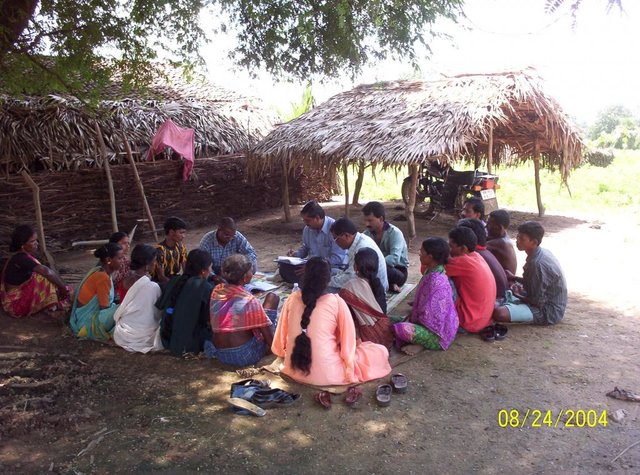

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [India]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compiler: Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
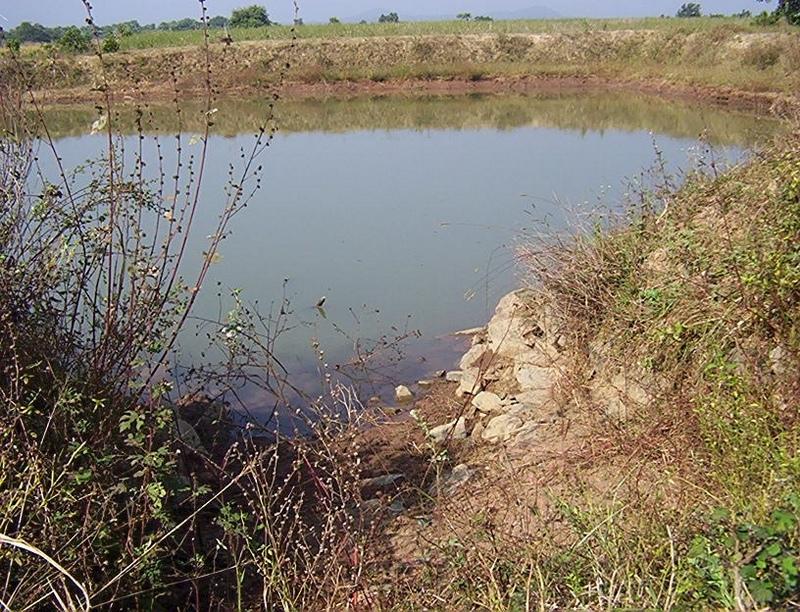
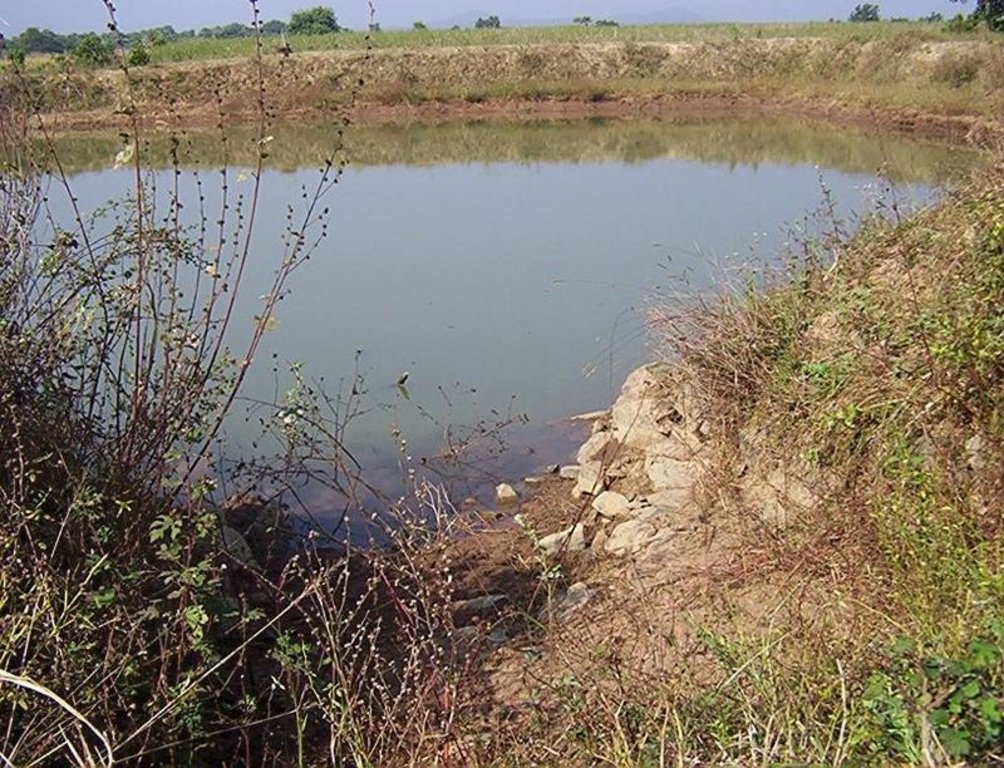
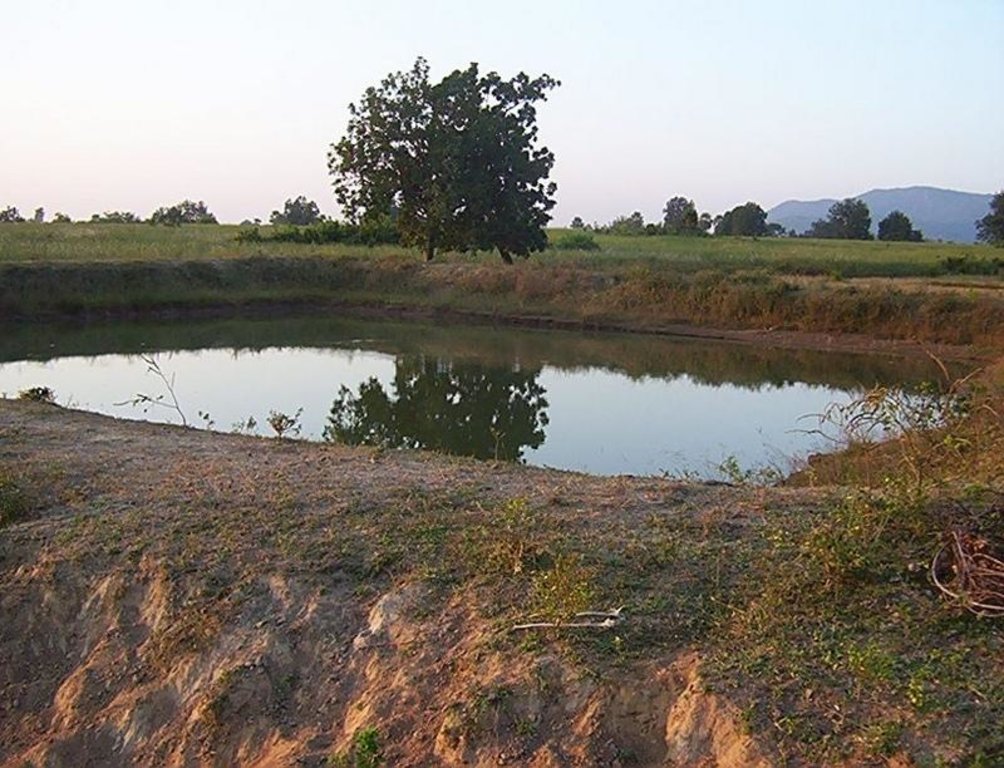
Dugout sunken pond with catchment treatment.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
(1) Total size of the project area = 4.75 Ha.
(2) Different structures taken up in the project area are
(i) Brushwood check dam- 6 Nos.
(ii) Drop structure- 8 Nos.
(iii) Dugout sunken pond - 1 No.
(3) All the above structures were positioned to ridge to valley treatment
(Ref.QT-6/2.1.2/a)
Purpose of the Technology: 1) Storage of runoff for cattle and human use.
2) Construction of structures to check soil erosion and sand casting.
3) Pisciculture.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment :-
1) SWC specialist selected sites for dugout sunken pond, layout the design.
2) SWC specialist also selected sites for drop structures, brushwood check
dams in gullied portion of project area with reference to vertical interval
of slope gradient and space between structures.
3) The execution of work were done by concerned villagers on payment basis.
4) During execution, 20% of the total cost of the dugout sunken pond was
contributed by the villagers in shape of labour.
5) Training on technical know how imparted to the villagrs during execution
of pond, bund, drop structure and brush wood check dam.
Maintenance:-
1) The dugout sunken pond requires (a) Desiltation once in two years (b)
Repair of earthern bund around inlet and outlet every year.
2) The drop structure & brushwood check dams requires little maintenance when
ever requires.
3) One management group has formed in the same village & funds has been
raised by doing pisciculture in the pond.
4) The management group is taking major reponsibility for its maintenance.
Natural / human environment: (1) Drainage line stablilized (2) Adjuscant area cultivated (3) Users group
formed and pisciculture taken up for the Ist time in the village.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
India
Region/ State/ Province:
Orissa
Further specification of location:
Orissa/ Malkangiri
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
National Watershed Development Project for Rainfed Area (NWDPRA)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Major food crop: Paddy

Grazing land
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion):
1) A fellow, undulating, gullied piece of land.
2) Acute sand casting at the down stream cropland.
3) About 40% of the project area were practicing local paddy which suffers from erratic rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): A piece of land which depends upon the mercy of the Rain God for annual production.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Nov
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
- beekeeping, aquaculture, poultry, rabbit farming, silkworm farming, etc.
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0475 km2.
A fellow, understanding, gullied piece ofland selected for the technology which suffers from sand casting and uncertainity of rain.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Erosion problem), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Common social practices
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Aerial view of dugout sunken pond
Location: Siadimal, Korkonda. Malkangiri/Orissa/ India
Date: 15.3.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, water harvesting / increase water supply, Control of sand casting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.45
Vegetative measure: In earthern bund slope
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Compact
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.7
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Vertivera and local grass slods
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/brushwood check dam
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.6
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/ drop structure
Vertical interval between structures (m): 9
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.05
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 5.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Dam/Pan/Dugout sunken pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Structural measure: Bund/Trapizoidal
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.85
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.50+8.9/2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 157
Construction material (earth): Soil excavated from pond is used to built bund around pond.
Construction material (stone): Inlet and outlet of pond and drop structure are made up of stone
Construction material (wood): Brush wood check dams are made up of wooden poles and bush wood.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 3%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:41
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Rupee
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
45.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
0.89
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection grass sods and vertivera slips | Vegetative | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Transporting grass sods on established banks | Vegetative | beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Watering | Vegetative | When dry in Ist. Season |
| 4. | Dugout sunken pond-Surveying | Structural | Summer season |
| 5. | Dugout sunken pond- soil excavated from pondage area used in trapizodical bund around leaving inlet & outlet portion. | Structural | Summer season |
| 6. | Dugout sunken pond- Collection and transporting stone to inlet & outlet site | Structural | Summer season |
| 7. | Dugout sunken pond- construction of inlet & outlet with stone | Structural | Summer season |
| 8. | Dugout sunken pond- collection of local grass sods & vertiver slops | Structural | Onset of rain |
| 9. | Dugout sunken pond- turfing the bund slopes and planting of vertiver slips in rows at up stream and down steam side of inlet and outlet | Structural | On set of rain |
| 10. | Brushwood check dam- surveying | Structural | Summer season |
| 11. | Brushwood check dam- collection of wooden poles and brush wood | Structural | Summer season |
| 12. | Brushwood check dam- collection of picked up stones | Structural | Summer season |
| 13. | Brushwood check dam- fixing of wooden pole, weiving with brush wood, filling up the gaps with picked up stones | Structural | Summer season |
| 14. | Brushwood check dam- collection of vertiver slips and planting in upstream and downstream of each structure | Structural | On set of rain |
| 15. | Drop structure- surveying | Structural | Summer season |
| 16. | Drop structure- collection & transportation of stones to work spot | Structural | Summer season |
| 17. | Drop structure- construction of drop structure with stones | Structural | Summer season |
| 18. | Drop structure- collection of vertiver slips and planting at up stream and down stream of structure | Structural | On set of rain |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 225.0 | 225.0 | 14.0 |
| Equipment | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 49.0 | 49.0 | |
| Equipment | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| Other | Royalty charges for stones | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
| Other | Fishery and feed | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | |
| Other | Field bunding | ha | 1.0 | 73.0 | 73.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Water way | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 372.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting vertiver slips & grass sods for gap filling | Vegetative | Onset of rain /annual |
| 2. | Collection of grass sods and gap fillling to bund layers | Structural | On set of rain/Annualy |
| 3. | Desiltation | Structural | Before on set of rain/Biannualy |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Field bunding | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Water way | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 21.0 | |||||
Comments:
The above calculation is based on the total establishment/ recurring cost both born by the project and land users is devided by the total project area i.e 4.75 ha. To get average hect. cost.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Availability of stone affects the cost from implementing SWC
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1760.00
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
South Eastern Ghat Agro Climatic Zone
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (423 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (2-7% slope)
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Land users from SWC technology area proctise contour plough, line sowing and using HYV paddy have increased their income significantly.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour and aniaml traction (bullock plough, both ranked 1)
Market orientation of production system: Pisciculture (Selling at village level)
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
Fish add to their income
production area
Comments/ specify:
Closure of land by pondage area
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
Comments/ specify:
Pisciculture support to live stock, dirnking water for cattle
Socio-cultural impacts
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Management group formed and strengthened due to continurous income from pisciculture.
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Training conducted
Linkage with other institutions
Comments/ specify:
Due to different activities in the pond linkage to other institution has increased like Horticulture, Fishery etc.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
90
Quantity after SLM:
40
excess water drainage
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Due to water storage
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
87
Quantity after SLM:
45
Other ecological impacts
Biodiversity
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
Soil moisture regime
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If the community find the technology is low cost to teke up and gets eye catching benefits, then the treand of adoption is good.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Water problem for human and cattle solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of pond needed |
|
Damage of crops reduced by construction of series of structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? More field bunding, vegetative cover should be imparted. |
|
Users group brings villagers closure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manageent group to be reorganised annuly |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Water scarcity of the area partly solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular desilting shound be done. |
|
Heavy sand casting and soil loss controled How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetative cover required for catchement area |
|
Crop production increased in the project area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Should be replicated by the people. |
|
Pisciculture added extra income to the villagers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Hybrid fingerlings to be adopted |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Sand casting could not be checked fully | By full vegetative cover and more structural measures it can be checked. |
| Sediment deposit in down stream area decreased | The loss can be over come by increasing crop yield. |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
Available from where? Costs?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
Available from where? Costs?
-do-
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [India]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Compiler: Srikanta Kumar Parida
Modules
No modules