Automatic Pumping System (Ram Pump) Using Natural Stream Flow for Domestic and Agricultural Purposes [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Be Gechkim
- Editors: Navin Chea, SOBEN KIM, Sophea Tim
- Reviewers: Nimul CHUN, Ursula Gaemperli
Water pumping engine run by water flow (Ram Pump)
technologies_2136 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
Acting Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries ,Preaek Prasab:
land user:
Hour Pros
(+855) 97 69 14 569
Facebook: Kraties' chicken farm (In Khmer) / Mixed Green Community (in Khmer)
Farmer
Saob Krom Village, Saob commune, Preaek Prasab district, Kratie province
Cambodia
Commune Extension Worker at Saob commune office:
Sopheak Song
(+855) 97 94 23 388
N/A
Office of Saob commune, Preaek Prasab District, Kratie Province
Saob Leu Village, Saob commune, Preaek Prasab district, Kratie province
Cambodia
Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Sambo :
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
12/04/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
This equipment use without motor or machine just needs water flow speed and can use for many years without much maintenance.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
This equipment is able to automatically pump water without the use of fuel, requires little maintenance and can transfer water for domestic and agricultural uses including livestock raising and the cultivation of crops.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
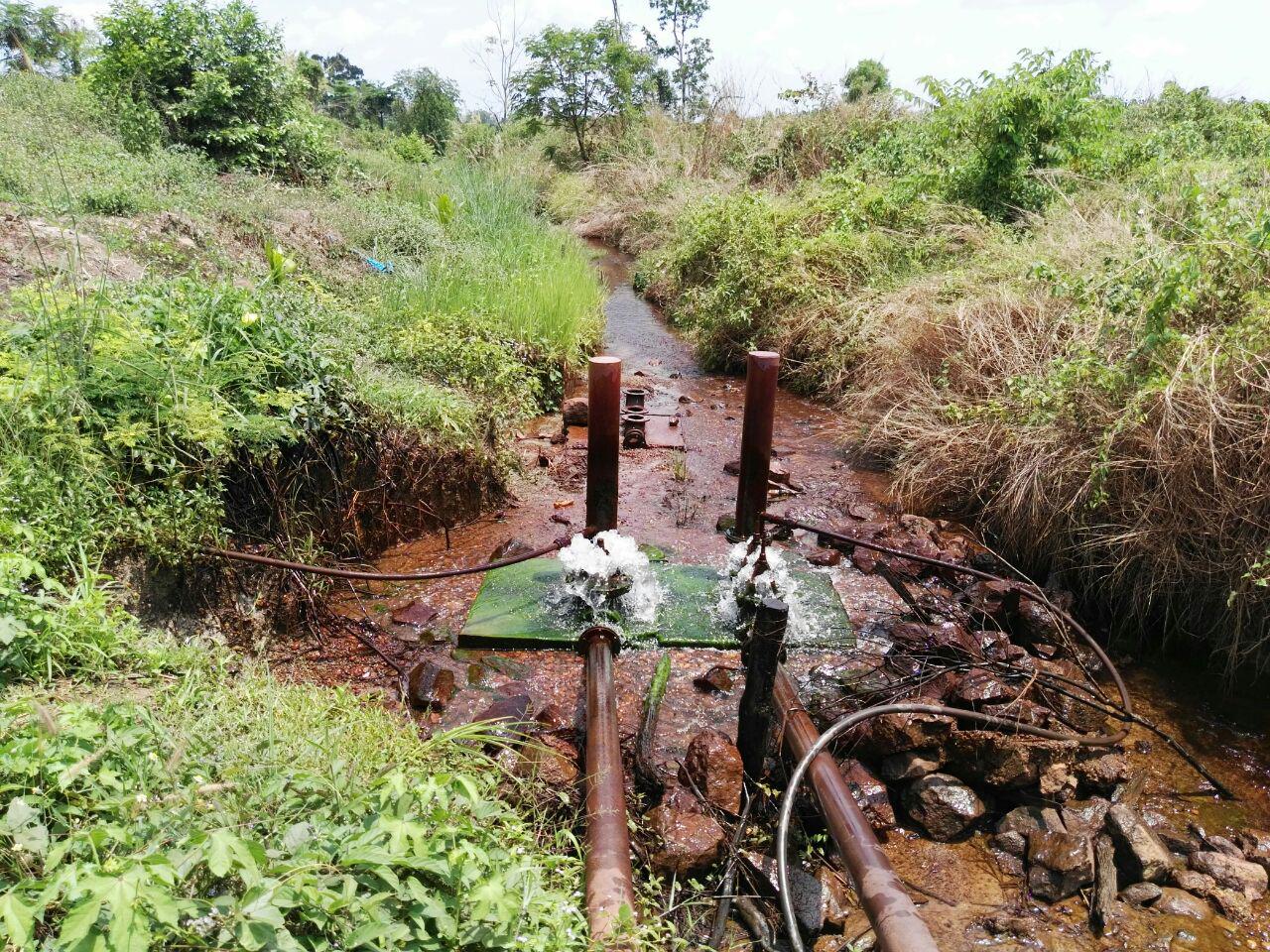
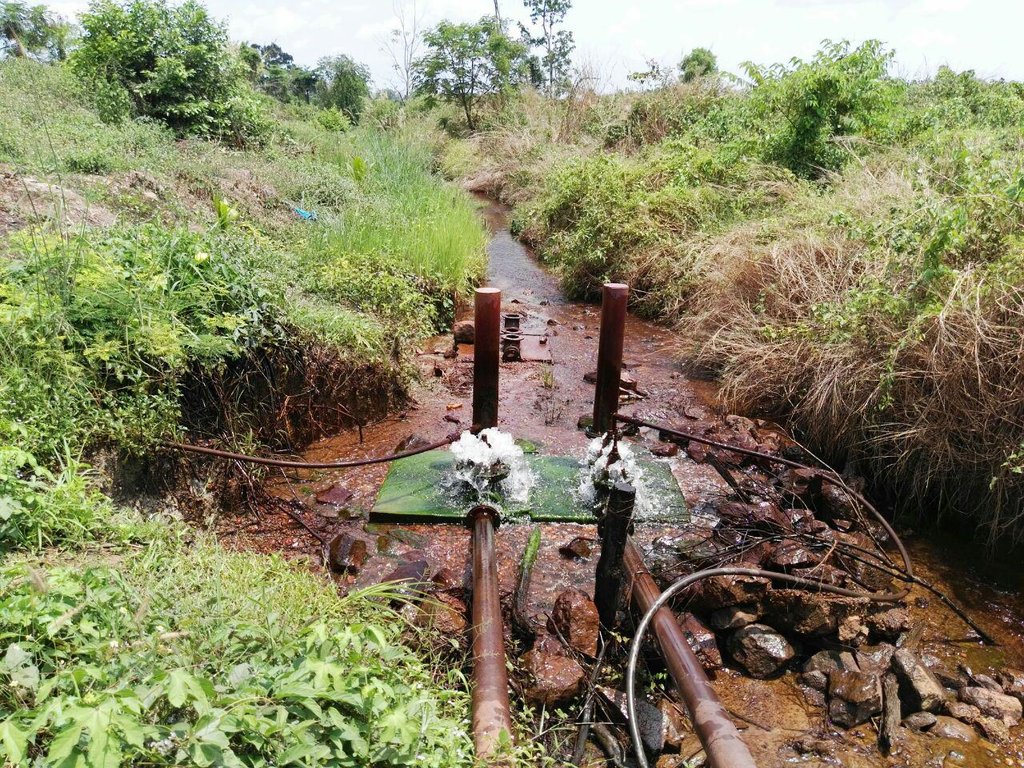
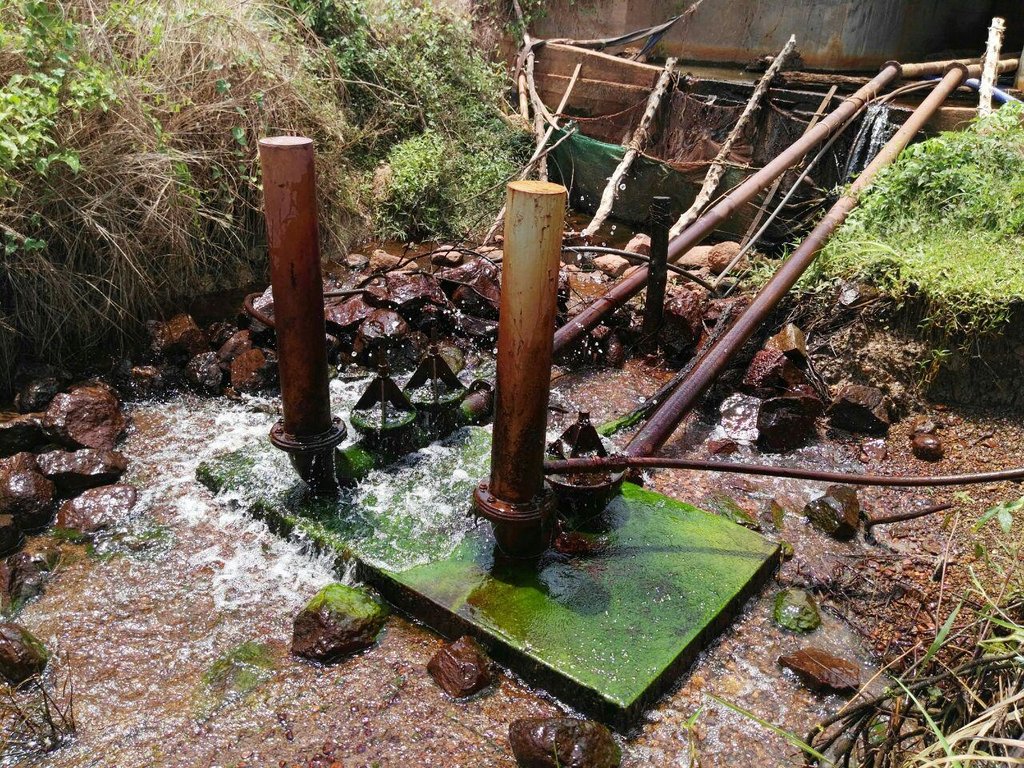
A ram pump which uses a natural stream flow is an equipment that pumps water, which is used for long time ago in Europe and some parts of Asia. However, it has been lost, but then because of the requirement, which its processing depends only on water flow and it will work as long as the water flow is available and no need much care that cause this technology is reintroduced (ACF, 2009). As such, this pumping equipment does not need a machine or fossil fuel and requires less labor. According to the above advantages, Mr. Hour Pros, a farmer in Saob Krom village, Saob commune, Preaek Prasab district, Kratie province, is the first person who did the installation. Even though, the cost of installation is relatively high at USD 1,500 depending on the types of materials from which it is manufactured (he selected the high quality of the iron pipe connections), this pumping equipment is quite durable and can be used for up to 20-30 years, he said. Furthermore, it has no adverse impacts on the environment since there are no greenhouse gas emissions.
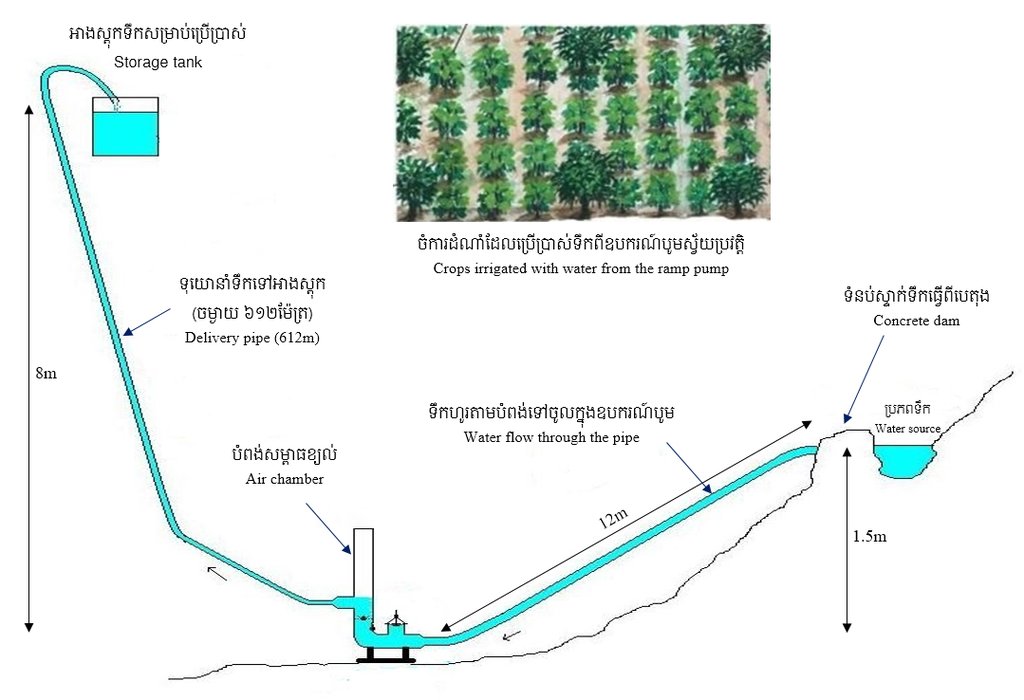
This ram pump was installed at Sre Ngeat dam, where there is a natural stream flowing throughout the whole year. As a part of the installation of the ram pump the farmer constructed a concrete dam across the stream with a water gate that can be opened. Additionally, a concrete base had to be built 1.5 meters lower than the water level in the dam in order to house the ram pump equipment. A 12-meter steel pipe which is 144 mm in diameter runs straight from the dam’s water gate directly to the pumping equipment. From the pumping equipment, there is a 30 mm hose (the size of this outlet must be smaller than that of the inlet) that transfers the pumped water to the location where it is needed. This pump is operated by the air pressure that is created by the water flowing from the dam to the pipe of pump and uses the air pressure to pushes water through the small pipe to bring water to the place where it is utilized, which is around 600 meters away at an elevation of around 8 meters compared to the pumping equipment. This ram pump has a pumping capacity of around 1.5 cubic meters per hour and can operate for 24-hours a day, with the ability to pump up to a height of 20 meters.
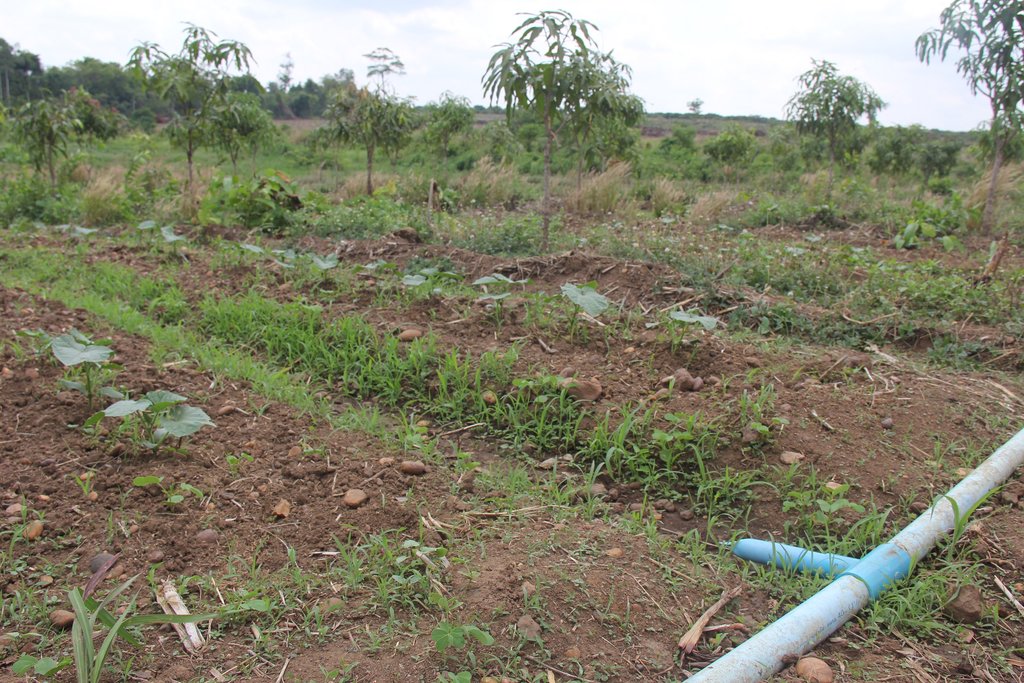
The water that is supplied by the ram pump is stored in two big water tanks (each one with a capacity of 4.7 m3), which can then be used for household consumption, the raising of about 100 chickens, and for the open valve irrigation of 5 ha of agricultural land. Another advantage of this pump system is that it does not affect the water quantity or pollute the downstream flow due to the fact that this system only took about 20-30 % of the water from the dam; 70-80% of the water was able to flow downstream, and so this allocation of the water supply did not cause any dispute between upstream and downstream users.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
N/A
Name of videographer:
N/A
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
Saob Krom Village, Saob commune, Preaek Prasab district, Kratie province
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2015
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- during experiments/ research
- Research on the Internet
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Farmers created the equipment by their own by learning more through YouTube.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Waterways, waterbodies, wetlands
- Ponds, dams
Main products/ services:
Sre Ngeat dam can provide water all year round both in dry and rainy seasons.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Needs supported from automatic pump only when having no rain.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Mango trees and vegetable cultivation such as long bean, cucumber, lettuce, water morning glory
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- water diversion and drainage
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
This equipment was installed on the Sre Ngeat dam in Saob Krom village, Kratie province.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
This equipment can provide enough water for cultivation along sloping areas to reduce soil erosion and a part of soil fertility restoration.
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
This pumping system is located on a natural stream flow of 1.5 meters height in comparison with the ground of placing the equipment. A 12 meter steel pipe which is 144 mm in diameter runs straight from the dam’s water gate directly to the pumping equipment. The outlet hose is 30 mm in diameter. The distance from the pump to the area where the water is being used is around 600 meters, and it lies at an elevation of 8 meters compared to the pumping point. The water is pumped up at 1.5 cubic meters per hour and can be pushed up to a height of 20 meters.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Automatic Pumping Device
Specify volume, length, etc. (if relevant):
Setup space: 1 square meter
other/ national currency (specify):
Riel
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20000 Riel
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy materials | Other measures | Dry season |
| 2. | Equipment preparation | Structural | Dry season |
| 3. | Equipment installation | Structural | Dry season |
| 4. | Preparation of irrigation system for vegetable | Structural | Dry season |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Total of establishment that done by themselves and materials | Total | 1.0 | 6000000.0 | 6000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 6000000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
N/A
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Access water for using everyday | Other measures | Everyday |
| 2. | Change valve | Structural | Every each years |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Change valve | set | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 100000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
For repairing, it costs around 25 USD a year for changing of the valve.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Construction materials and hose that is needed because of far distance between the ram pump and water use places.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1138.20
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
The average annual rainfall in 2015 is 1138.2 mm, in 2014 is 1696.5 mm, in 2013 is 1661.8 mm.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Department of Meteorology, Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology (2015)
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
Medium-scale because he has only 30 hectares and other have until 50 hectares.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Comments:
Water resource for technology installation is the open access place but the water from technology is for only the own person.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Crop production increased because there is enough water for irrigation leading to increased crop production.
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
Can be managed because of enough water from the river is easily available now and it does not require a lot of labor.
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
Comments/ specify:
Ram pump can provide enough water all the time with less labor.
irrigation water availability
Comments/ specify:
More water can be extracted automatically.
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
The using of equipment is help to reduce labor, time, cost of reparation, and no needs much maintenance. This technology also reduced fuel consumption for pumping water because ram pump is powered by the water flow.
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Increase in revenue because it does not cost much to pump water. In addition more crops can be grown now.
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
Because enough water for irrigate is available now more different crops are grown now.
economic disparities
Comments/ specify:
With this technology extra income can be generated and furthermore the costs of irrigation were reduced.
workload
Comments/ specify:
The workload decreased due to the automatically working ram pump.
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Regarding the water pump technology the farmer improved his knowledge constantly by doing. And actually he got enough experience to act as facilitator for other farmers. This means he shares his knowledge with neighbors which drives them to use this technology too.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
Comments/ specify:
The quantity of water is not reduced or increased as the ram pump accesses only 20 to 30% of water flow and it does not cuts off water flow.
excess water drainage
Comments/ specify:
Ram pump can be used to extract water regularly without labor.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
Other farmers and neighbors still get water from the dam because the system has accessed to water only 20 to 30%.
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
Without using any machines that it does not emit greenhouse gases.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
The farmer gets many benefits because before had to expense a lot for the labour to pump the water from well and also he had to spend money for fuel which is not anymore necessary now.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Even it costs much at the beginning it still gain a better profit compared to the use of pumping by machine with gasoline for regular water access. |
| Does not involve the use of too much labor because it is able to pump water by itself. |
| Water for irrigation is available at all times and during all seasons. |
| An increase in income through the improved crop cultivation deploying the water supplied by the ram pump. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| A reduction of impacts on the environment because no fuel is being used in the pumping process. |
| A ram pump can operate for many years and does not cost a lot to maintain. |
| A reduction in the amount of labor and time to obtain water for consumption. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The equipment is expensive to install. | Save money in order to purchase one. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| - |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
A place
- interviews with land users
A person
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
3 people
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
ACF (2009). Hydraulic Ram Pump Systems. From
Available from where? Costs?
https://www.pseau.org/outils/ouvrages/acf_gravity_fed_system_in_rural_areas_6_hydraulic_ram_pump_systems_2009.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Judy of the Woods. Homemade Hydraulic Ram Pump. Retrieved on May 20 2017 from
URL:
http://www.judyofthewoods.net/diy/ram_pump.html
Title/ description:
Hydraulic ram pump 8 inches in Cambodia. Retrieved on May 20 2017 from
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5MiLas_FCfQ
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules