Orchard of mangoes and oranges for food and income security [Uganda]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- Editors: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Richard Otto Kawawa, Sunday Balla Amale, Bernard Fungo
- Reviewers: John Stephen Tenywa, Nicole Harari, Renate Fleiner, Donia Mühlematter
Poto Muyema akuba
technologies_2819 - Uganda
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Akello Scovia
Amuru District Farmers froup
Pakuma village, Palwong parish, Pabbo sub-county Amuru district
Uganda
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Switzerland1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
26/05/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Species of Mangoes and Oranges planted for income and food security.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
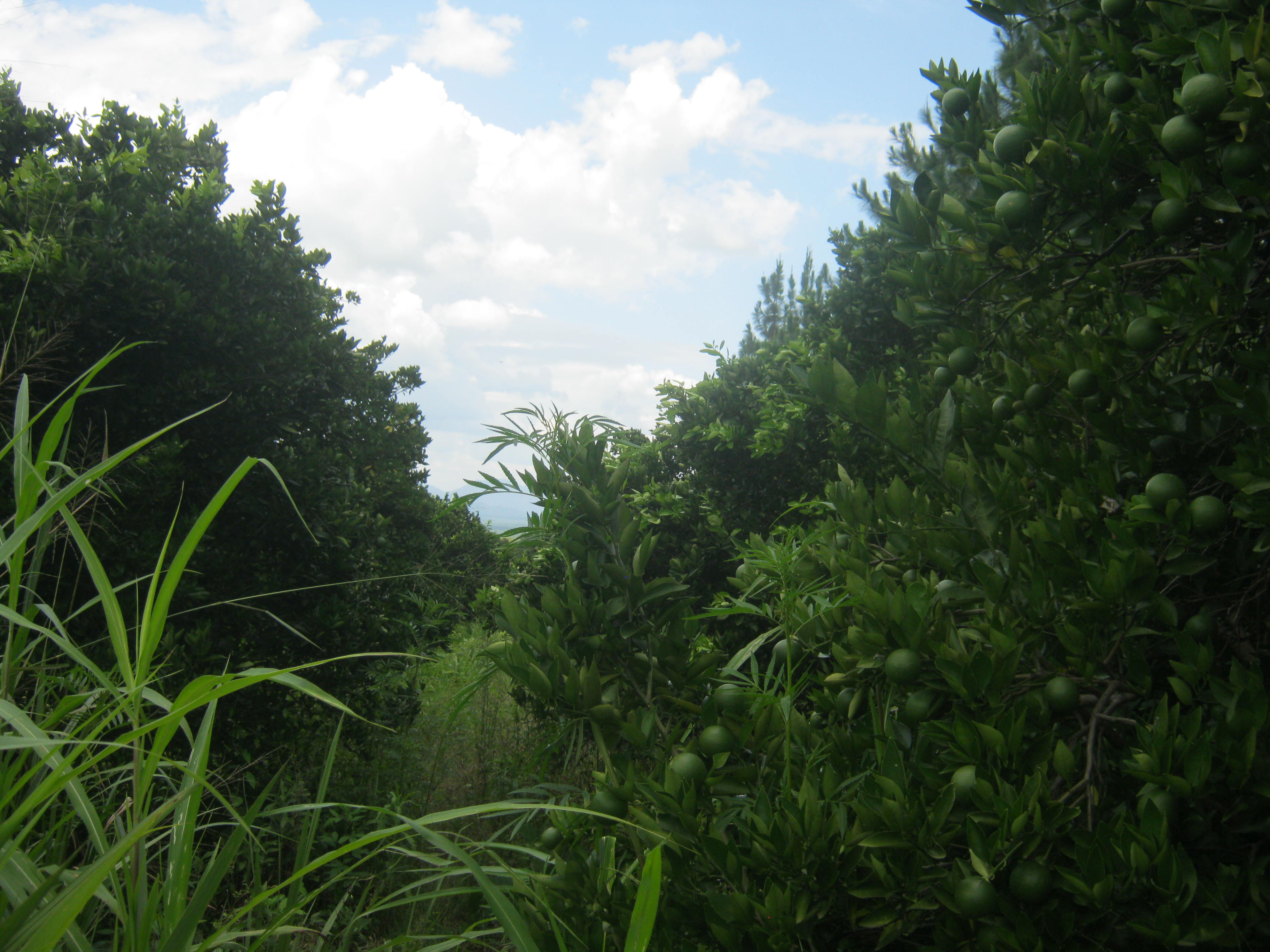
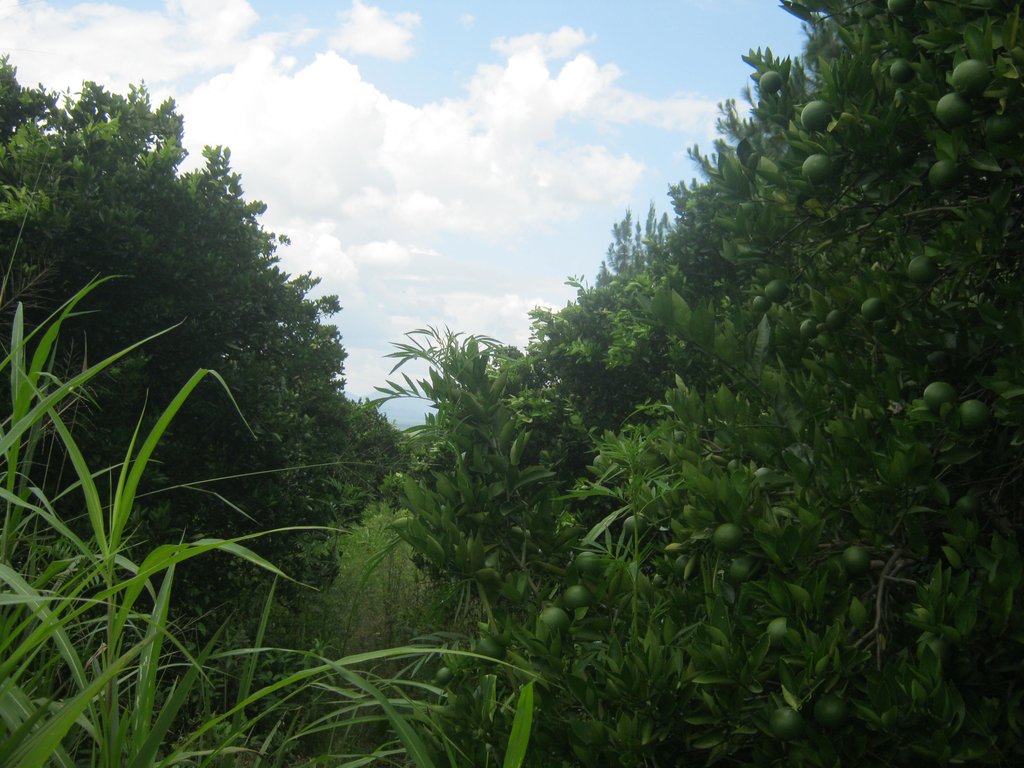
Growing mangoes and oranges is becoming a common practice among farmers in Northern Uganda for food security and increased household income. As seasons become shorter and erratic, failure of traditional crops like beans and maize is increasing. Mangoes and oranges are more adapted to sub-humid conditions and can endure longer dry spells yet yield well. Thus, farmers are taking on improved varieties of mangoes and oranges developed by the National Agricultural Research System. The mango and orange seedlings are planted with only spot weeding to maintain the grass cover for soil moisture. The activities involved in establishing the orchards include (1) linking up with the extension worker for information on what varieties and how to plant on which type of soils (2) site selection (3) buying seedlings (4) planting and (4) watering if planted during the dry season with the following input requirements seedlings, hired labour of at least 2-3 people paid on monthly basis and watering can. At the time of planting the land user digs a hole up to a depth of about 0.5 metres using a fork so that the roots are allowed to grow out easily and plant the fruit trees spaced at 10 metres x 10 metres allowing the grass to grow without removing or cutting. If planting is done in the dry season and the ground is too dry the farmer applies water once a week slowly using a bucket so that it has time to sink in the soil. If the land user plants during the wet season, watering is not necessary. This practice is liked because yields are high due to leaves litter as well as the demand for fruits in addition to being easily fertilised using organic fertilizer locally obtained and treated . In the long run, the high costs incurred at the time of establishment in buying seedlings and paying labour. The presence of fruits from the orchard provides both food and income to the household, which should be other crops such as maize and sim fail due to drought. What is not liked about this technology is that the grass grown in the garden is liked by livestock during the dry season. Herdsmen searching for pasture drive their animals into the gardens, resulting into constant conflicts between livestock owners and the land user. The grass also poses a risk of fire during the dry season. Additional efforts to put in place a community bylaw on controlled grazing would reduce conflicts and free range grazing of animals contrarily to fencing which may be an additional benefit to sustainably managing land by the land user.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
Video Showing tree Orchard for soil fertility improvement.
Date:
26/05/2017
Location:
Pakuma viallge , Palong parish, Pabbo sub-county Amuru District
Name of videographer:
Issa Aiga
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Uganda
Region/ State/ Province:
Amuru District, Northern Region,Uganda
Comments:
Map showing technology site in Northern Uganda.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2012
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Supported by Norther Uganda Social Action Fund.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
Main products/ services:
Maize inteplanted with mangoes and oranges.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
2 times within a year.
Livestock density (if relevant):
2 cows kept at neighbours farm.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
- A3: Soil surface treatment
- A4: Subsurface treatment
- A5: Seed management, improved varieties

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

management measures
- M5: Control/ change of species composition
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
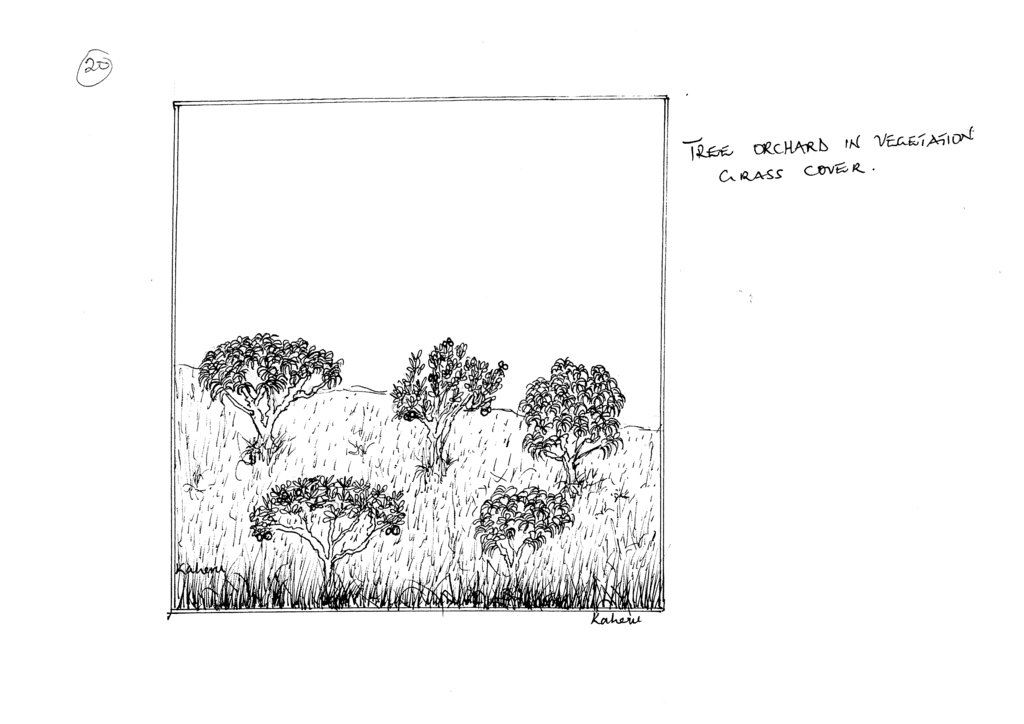
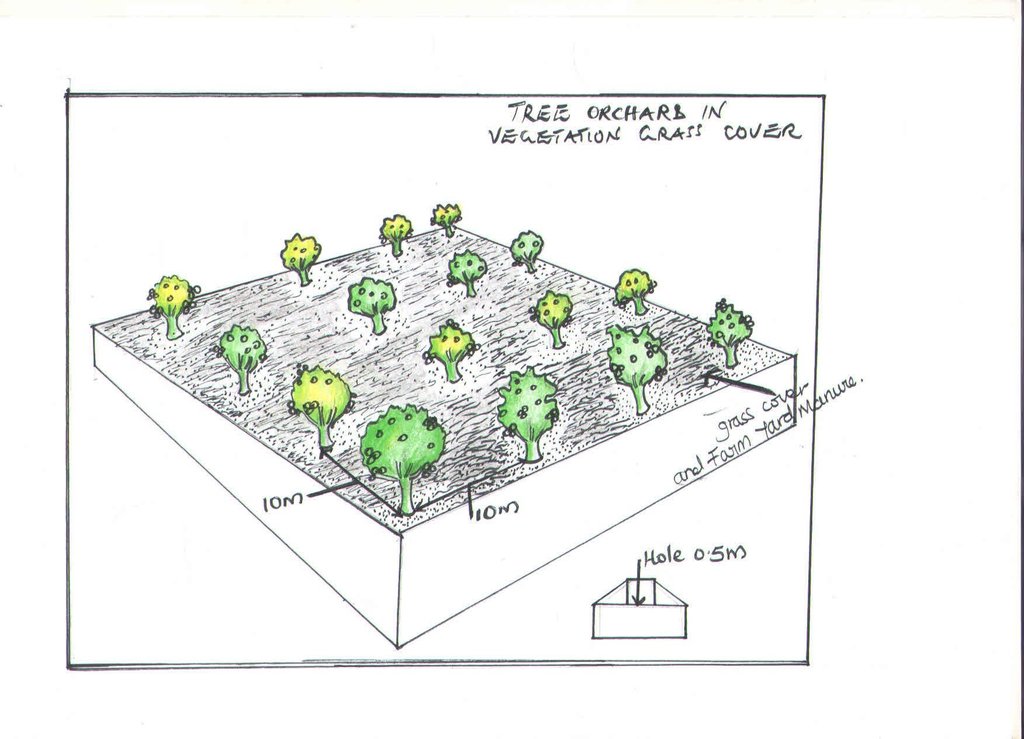
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
The technology is established on 0.5 acres of land gentle sloped with the hole dug up to a depth about 0.5 metres using a fork so that the roots are allowed to grow out easily and plant the fruit trees spaced at 10 metres x 10 metres allowing the grass to grow without removing or cutting. If planting is done in the dry season and the ground is too dry the farmer applies water once a week slowly using a bucket so that it has time to sink in the soil.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
0.5 acres
other/ national currency (specify):
UGX
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
3400.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5000 per person per day but in most cases charge more than this depending on the season (sunny or rainy season)- sunny more money is charged.
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Look for land | Agronomic | Before estaslishment |
| 2. | Look for seedlings and tools to use | Management | Once before establishment |
| 3. | Look for labour | Management | Before establishment |
| 4. | Dig holes (2-3 ft) | Structural | During establishment |
| 5. | Plant suckers | Agronomic | During establishment |
| 6. | Water: dry season | Management | After estabslishment |
| 7. | Weeding | Agronomic | After estabslishment |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | persons | 3.0 | 5000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Hoe | Pieces | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Spray pump hire for a week | Pieces | 1.0 | 35000.0 | 35000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Panga | Pieces | 2.0 | 7000.0 | 14000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Seedlings | Kgs | 42.0 | 2500.0 | 105000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Pestcide | Litres | 0.5 | 15000.0 | 7500.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Fertilizer | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | ||
| Fertilizers and biocides | Organic fertilizer (weekly) | bags | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 246502.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing | Management | Around December every year |
| 2. | Spraying with herbicide against pests | Management | Every time they are observed |
| 3. | Weeding | Management | Twice a year |
| 4. | Watering | Management | During the dry season, when they are young |
| 5. | Fertilisation | Management | Twice a year |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour for on daily basis | Persons | 3.0 | 5000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Hire of spray pump for one week | Pieces | 7.0 | 5000.0 | 35000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 50000.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour takes the most of costs.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1500.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
March April at the on set of the forst rainy season and second rainy season on set in the month of August.
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
The flooding occurs during the month of excess heavy rains (Nov-Dec and March-May).
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Due to leaves litter.
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
due to grass cover and maintaining soil fertility.
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
Mangoes and oranges.
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
Only paying for for labour to do simple weeding.
farm income
Comments/ specify:
From sale of fruits.
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
Fruits - oranges and mangoes.
Selling mangoes and oranges and buying food.
national institutions
Comments/ specify:
Operation Wealth Creation (OWC) / National Agricultural Advisory Services (NAADS).
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Use of grass cover and littered leaves.
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
Conflicts caused by roaming animals searching for pasture.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Comments/ specify:
Due to grass cover.
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Due to grass cover.
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
Due to grass cover and leaves.
soil loss
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
Due to mulching.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
Due to permanent grass cover.
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
Due to allowed growth of the vegetation cover.
beneficial species
Climate and disaster risk reduction
landslides/ debris flows
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
Due to presence of vegetation cover.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | decrease | well | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | decrease | well |
| annual rainfall | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
| land fire | very well |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| insect/ worm infestation | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- more than 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 50-90%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Appropriate for small and large scale land users. |
| The technology can be replicated elsewhere by other farmers. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Good at providing income when mangoes and oranges are sold. |
| Appreciated by the land user due its ability to provide household income and fruits for consumption and sale. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Requires skilled labour at the time of establishment to dig the holes and applying the right spacing. |
Train family labour to acquire the skills. Use extension workers and expert farmers to provide the skills |
| The technology is liked by thieves since it provides income and food. |
Fencing to prevent intruders from piking the fruits without payment. Put in place strict byelws and harsh penalties for offenders. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Fruit trees are having canopies in close contact hence reduced fruiting with the spreading of branches. The technology is not well managed as would be expected. | The farmer should trim the branches. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
01
- interviews with land users
01
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules