Санитарно-гигиеническая и сельхозяйственное значение эко-санитарных туалетов. [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: MIZROBSHO AMIRBEKOV
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
Ахамияти санитари-гигиени ва кишоварзии хочатхонахои хушк
technologies_3735 - Tajikistan
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Санитарно-гигиеническая и сельхозяйственное значение эко-санитарных туалетов. : Aug. 19, 2019 (inactive)
- Санитарно-гигиеническая и сельхозяйственное значение эко-санитарных туалетов. : June 18, 2018 (inactive)
- Санитарно-гигиеническая и сельхозяйственное значение эко-санитарных туалетов. : Aug. 19, 2024 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihood ProjectName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
SDC Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation) - Switzerland1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
15/05/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
Технология направлено на экосанитарных норм и развитие органического и экологического производство сельского хозяйства
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
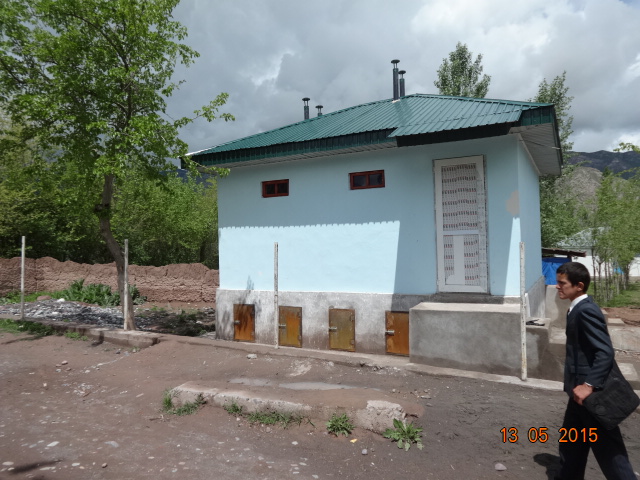
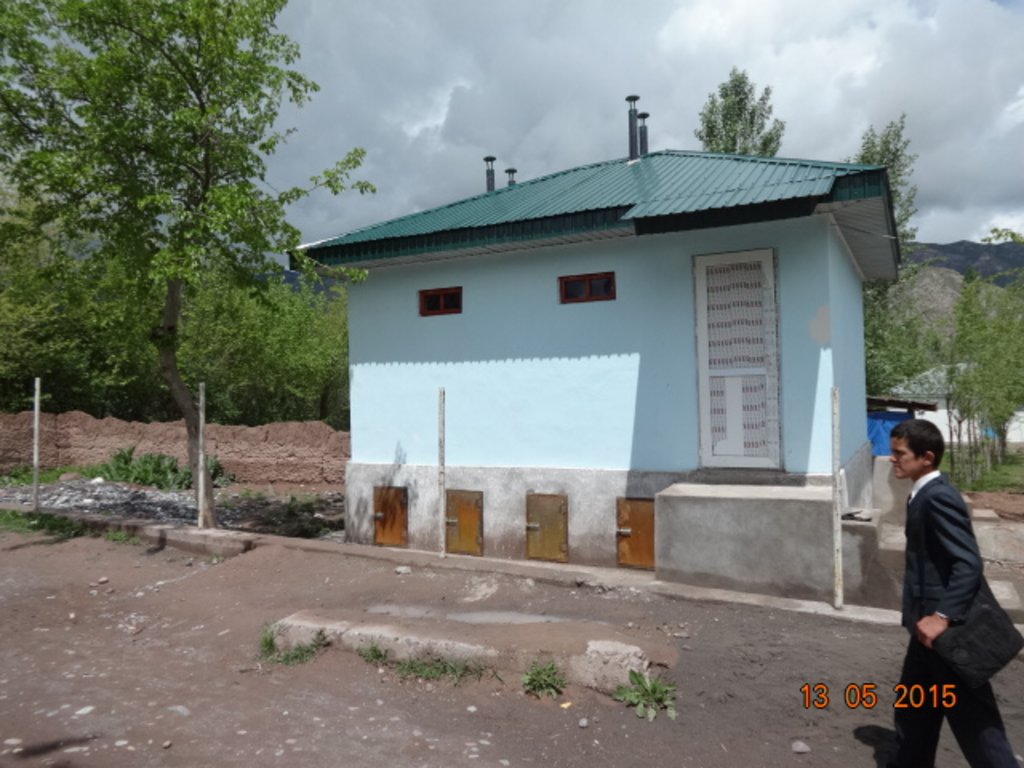
Технология использование экосанитарные туалеты состоит в том, что протцесс выполнение туалета идёт с раздельным сбором урины и фекалий и их последующимиспользованием в качестве удобрений. Практика внедрения и работы экосанитарных (или «сухих») туалетов показала их важное значение врешении проблемы загрязнения человеком окружающей среды на бытовом уровне.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
При финансирование SDC (Шведцарское Агенство по развития) в условиях горных регионах Таджикистана начались строительство экосанитарные туалеты. Данный момент эти туалеты строились во всех районах Горно-Бадахшанской Области и группа районов Раштской долины-Файзабад, Нурабад, Сангвор, Рашт, Точикабад и Ляхшский район.
Экосаны позволят отказаться от выгребных ям, существенно снизить загрязнение грунтов и водоносных горизонтов на территории частных поселений, уменьшают использование питьевой воды для санитарии и минимизируют количество сточных вод, что создает хорошие предпосылки для преодоления потребительского подхода и перехода граждан к активному участию в решение проблемы уменьшения отходов и стоков, как и общегозагрязнения природы.
С целью обучение использователей данных туалетов со стороны Фонда Ага-Хана были организованы специальные тренинги на местах, создавались макеты эко-санитарных туалетов и на основе этого было доведено до жителей село технология строительство и использование туалетов в быту и одновременно владельцам туалетов былы обучены технологические требование по приготовления и использованием компостов как удобрении в систему земледелии.
Для запуска технологии необходимо первый очередь иметь обученный и подготовленный персонал, которой он хочет по желании иметь данную технологию и можеть его использовать. Использователи дольжны знать как используется туалет в первое время до запольнение очки, и как надо переходить к использование второму точку. Для его хорошего поддержания еще необходимо иметь практического знания исползования почвы или другого выда компостируемого материала. На третем варианте использователя необходимо знать технология использования мочесобирательного сектора эко-санитаных туалетов. Иногда использователи не имеют достаточного практического опыта и занания использование технологических процессов туалета и могуть отказаться от его содержания.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
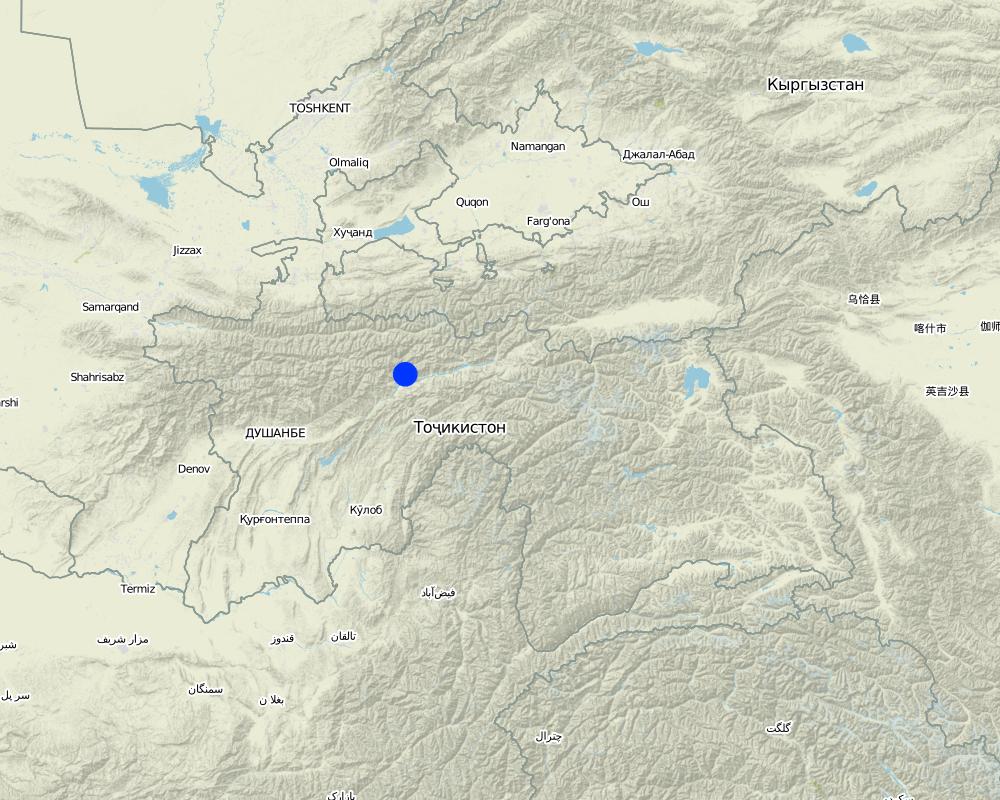
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Гармский район
Further specification of location:
Шуль
Comments:
Село Шул находится в Раштском районе.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Экосанитарный проект
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Картофель, овощей, садоводство

Grazing land
Extensive grazing land:
- Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism
Comments:
В регионах, где применяется технология фермеры в асновном занимаются земледелием, выращивают картофелЬ овощей, зерновых и бобовых, содержать домашный скот. Из-за того, что у фермеров мало доступа к минеральным удобрением они охотно используют компость подготовленной в экосанитарных туалетов и покрывают своё нуджу в удобрениях.
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
До применение технология фекалий не применялись как удобрений. потому что сельские фермеры не имели информация о данной технология. После применение техноллогия фермеры начали использоват компосты приготовляемый в экосанитарных туалетов.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
В условиях Раштский район все пахотные земли являются орошаемые. Богарные земли используются как пастбища.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Природно-климатические условия региона позволяет получить только одно урожай в течение сезона.
Livestock density (if relevant):
два крупного и более 5 овец и коз на 1 гектар.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- integrated soil fertility management
- ground water management
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
Из-за малого обёма приготоленного компоста в экосанитарных туалетах производство компостов ограниченно и по этому причину фермеры не имеют возможность применять компость на всю култивируемые площады.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

structural measures
- S8: Sanitation/ waste water structures

management measures
- M6: Waste management (recycling, re-use or reduce)
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wo: offsite degradation effects

chemical soil deterioration
- Cs: salinization/ alkalinization

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
- Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities

biological degradation
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bl: loss of soil life
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
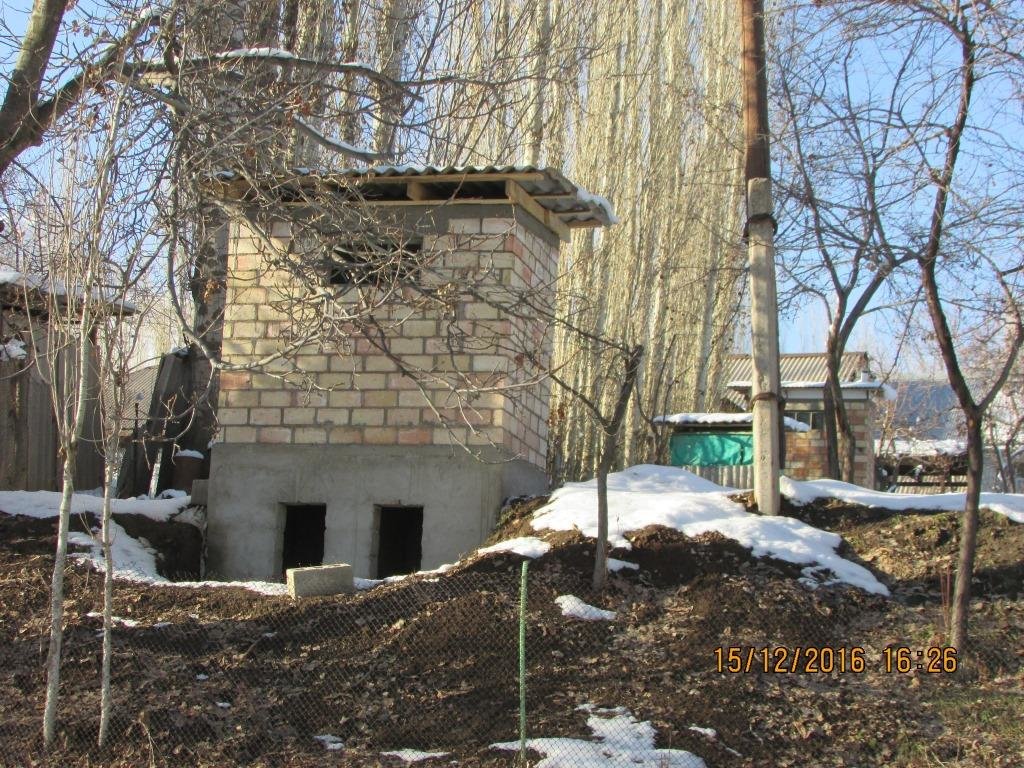
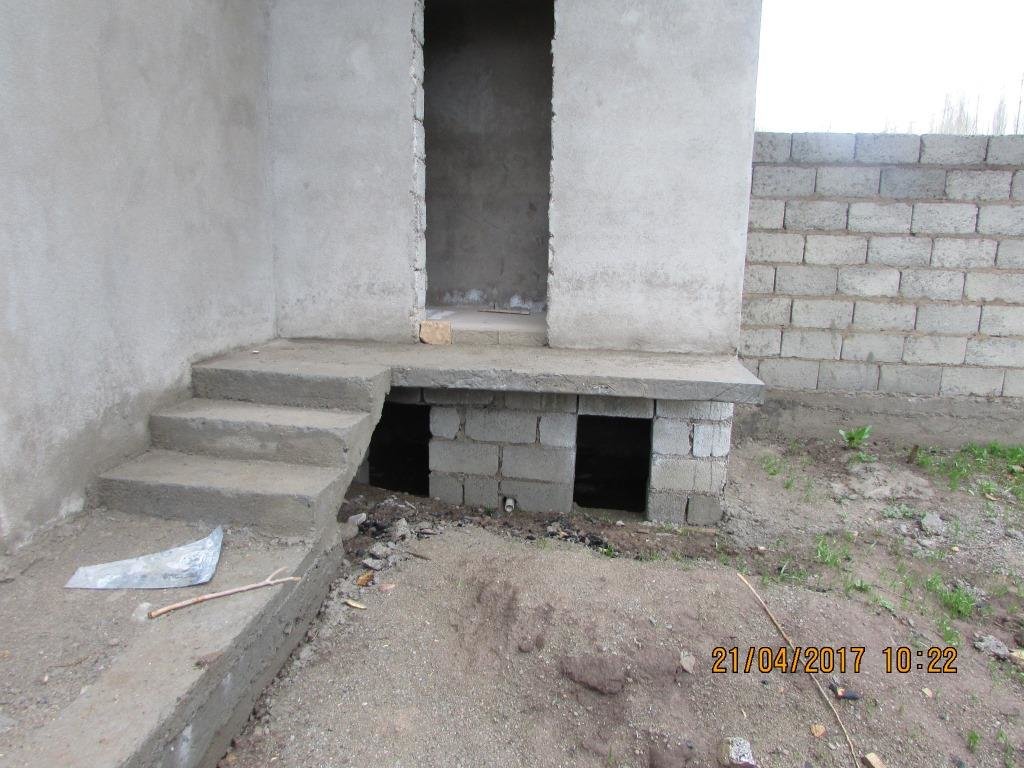
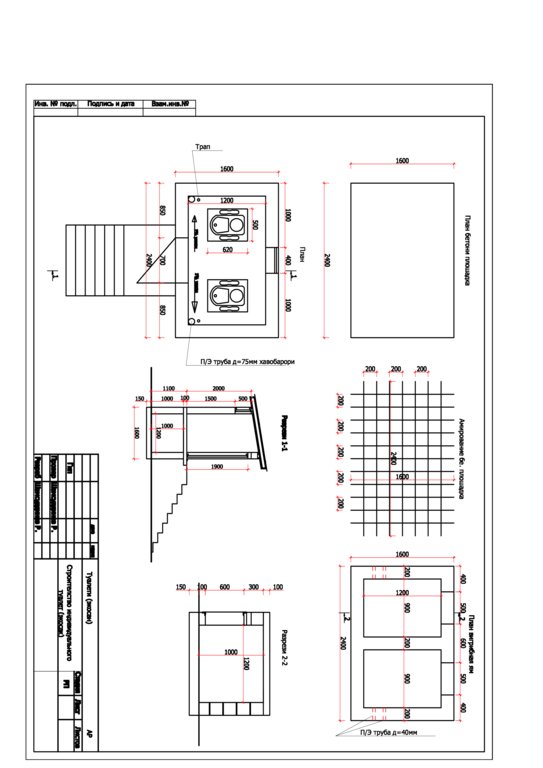
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Длина помещения зависить от число точек, которой использователь оставляет, однако число точек не можеть быть меньше двух. Потому, что один экплатируется до его заполнение и пользователь переходить к второму. Длина туалета из двух точек должень составить 2.5 м , высота погребных ям составляет 1.5 м высота обслуживаемой части туалета составляет 2м.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
ам.долл
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.9
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3.4 долл сша
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Выбор местности | Structural | 10 дней |
| 2. | составление проект и смета | Structural | 10 дней |
| 3. | Подбор строительных материалов | Other measures | 10 дней |
Comments:
Перед строительством туалета необходимо подобрать соответствующего места и на втром плане необходимо составить проект и смета, согласно требованием использователья. на третьем необходимо подготовыть строительных материалов.
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Составление проект и смета | чел. дни | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | |
| Labour | Строительство объекта | чел.дни | 20.0 | 20.0 | 400.0 | 20.4 |
| Equipment | Унитазы | шт | 2.0 | 20.0 | 40.0 | |
| Construction material | Цемент | кг | 200.0 | 5.6 | 1120.0 | |
| Construction material | Цементные блоки | шт | 500.0 | 0.52 | 260.0 | |
| Construction material | Жесть | шт | 6.0 | 5.6 | 33.6 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 1953.6 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Расходы покрывались за счёт донорских вложений
Comments:
Шведцарское агенство по развитии финансировал реализацииипроекта в Рашстском районе Таджикистан
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Эксплуататция туалета | Management | периодически |
| 2. | Очиска | Management | После заполнение и компостирование |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Очиска помещения | день | 365.0 | 1.0 | 365.0 | 365.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 365.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Факторы влияющие на стоимости проекта в основном являются место где строится туалет, в отдалённых местностях из-за транспортного расхода стоимость увеличивается, на втором на стоимость проекта влияет выборку мтериалов, если проект строится вместо кирпича за счёт бутобетонного камня и местных материалов и в этот момент стоимость проекта снижается. Если использователь хочеть иметь туалет с нескольким очком и в этот момент стоимость проекта увеличивается.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1000.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Сезонные
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Гармский
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
климат месности является умеренно влажное, зимой снег, осень и весной дожди
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Технология применяется вне зависимости релефа местности
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Почвы местности составляют темные серозёмы, небогатые гумусом
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Вода для орошение земел вполне достаточно, питевая вода не проблемачитно
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Регион иммеет очень богатя биоразнообразия
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Земли используются как долгосрочная аренда, фермеры в основном выращивают картофель и занмаются садоводством.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Фермеры имели допольнительный органической удобрении
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Санитарно-гигиенская |
| Селхозяйственная |
| Экологческая |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Санитарно-гигиеническая |
| Экологическая |
| Селхозяйственная |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Адаптация людей в сельской местности | Обучение |
| Приготовление компостов при использование туалета | Обучение |
| Технология использование туалета | Обучение |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Пока сельские люди не имеют опыта польного использования туалета | Обучение |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
При проведение технические мониторинги проектов
- interviews with land users
Проведение опрос использователей туалетов
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Платформа знаний по устойчивому управлению земельными ресурсами в Таджикистане
URL:
https://slmtj.net
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules