Home Garden (Pomelo, Lemon, Supplementary Crops) [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Be Gechkim
- Editors: Navin Chea, Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Reviewers: Nicole Harari, Nimul CHUN, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
Mixed Cropping
technologies_2099 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
Ouk Sophoeurn
Farmer
Cambodia
Acting Chief of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries ,Preaek Prasab District Office:
Official of Chetr Borei district office of agriculture, forestry and fisheries:
Saravuth Ly
Chetr Borei district office of agriculture, forestry and fisheries
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
Because they grow crop don’t use chemical fertilizer and get high yield
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
This technology involves the cultivation of crops around the house, including pomelos, lemons and other supplementary crops, with solely the application of cattle and chicken manure as fertilizer, whilst abstaining from the use of chemicals. The purpose of this technology is to obtain various products, generate a household income especially from the lemon trees as it is a long-term crop which provides a continuous supply of daily produce and is also relatively easy to grow, as well as to establish a comfortable environment for people to live in.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
A home garden is the practice of planting different crops around the house such as a variety of vegetables, herbs, fruit trees, and other annual crops for the family’s daily consumption as well as for commercial purposes. Home gardens have been set up in Cambodia and in many countries all over the world, albeit they might be named differently (Helen Keller International/Cambodia., 2003). This technique provides both economic and environmental benefits: generating household incomes and regulating the micro-climate by creating a desirable and ambient temperature around the house which makes the lives of family members more comfortable. More importantly, the technology provides opportunities for marginal groups like women, children, aging people and the disabled, to carry out agricultural work that contributes to an increase in household income (Landon-Lane C., 2012; Helen Keller International, 2010).
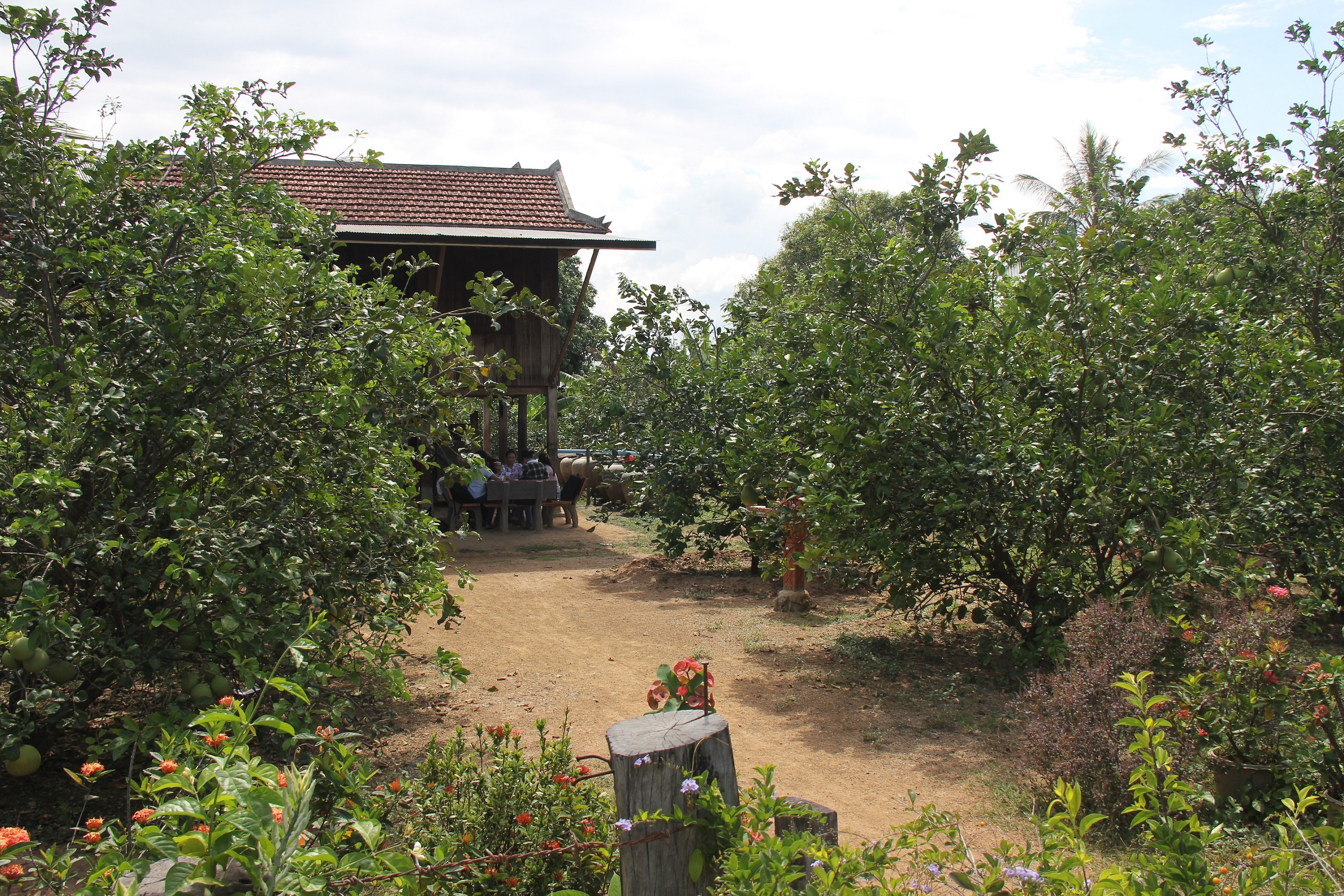
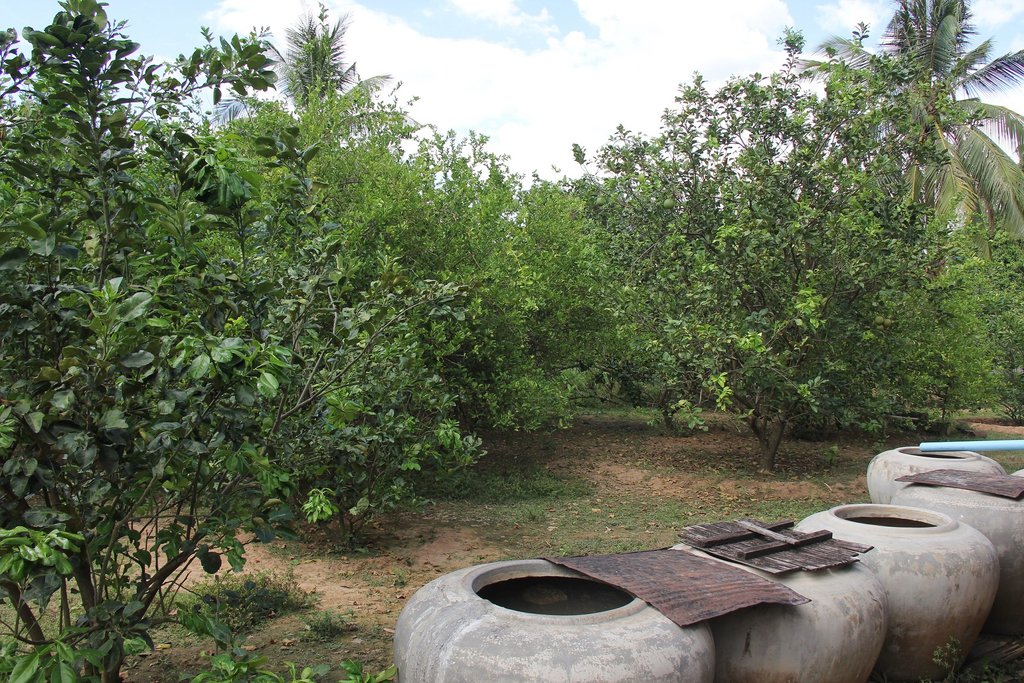
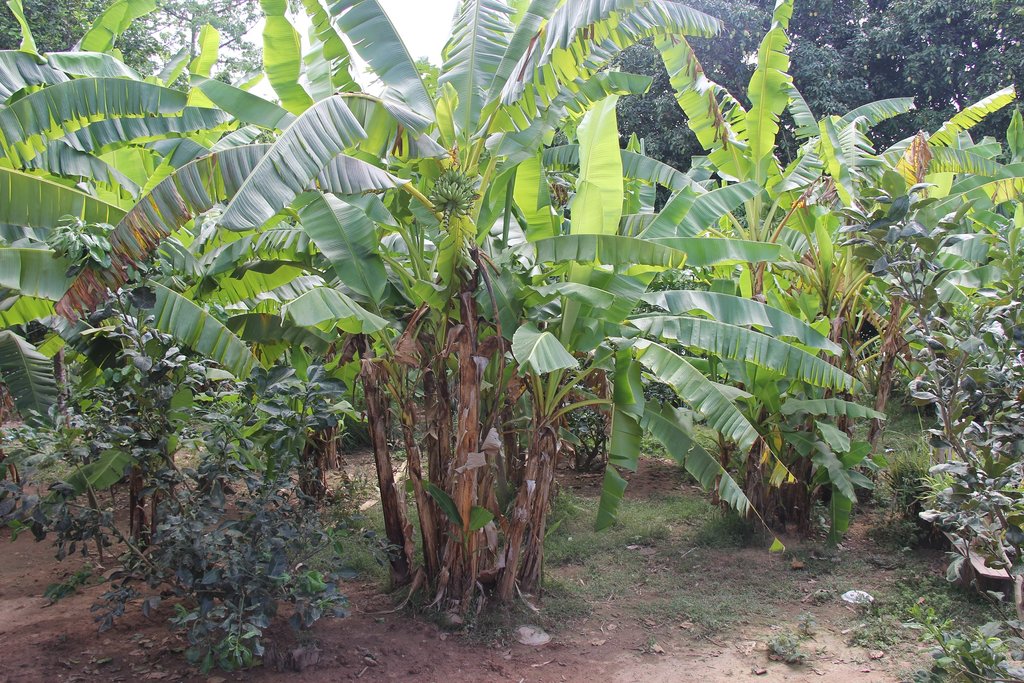
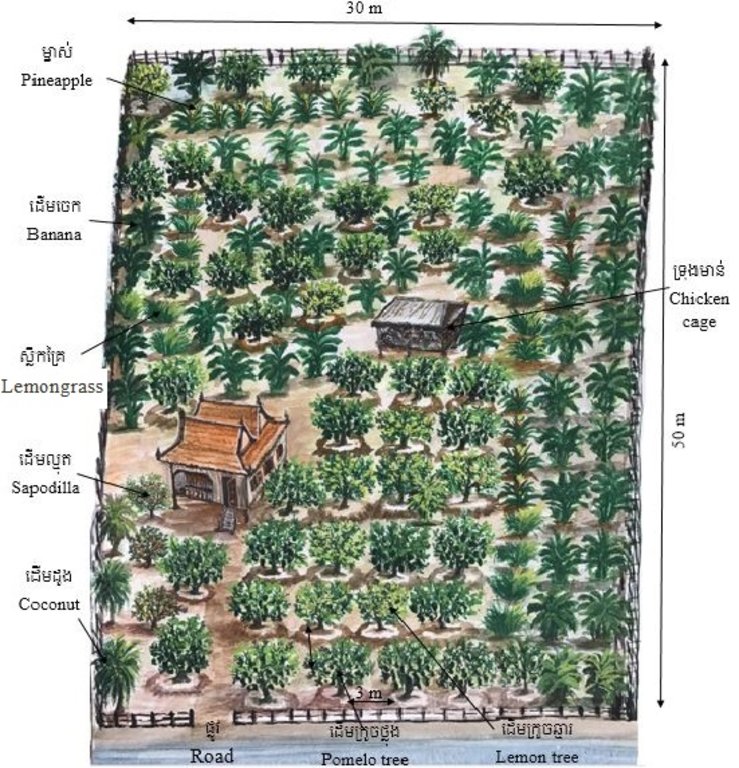
Home garden technique is being applied at Samraong village, Sambour commune, Sambour district, Kratie province, where the farmer is growing pomelo (30 trees) and lemon (10 trees) as the main crops for sale and other supplementary crops (banana, pineapple, pomegranate, lemongrass, coconut, mango and jackfruit mainly for household consumption. The technology is being implemented in an area of 1500 square meters (30x50 meters), with the Mekong River being located behind the house.
In order to plant the pomelo and lemon trees, the farmer digs 0.6 x 0.6 meter square pits that are 0.5 meters in depth. There is a distance of three meters from one pit to another to allow ample space for the trees to fully spread their branches. Animal manure is also added into the bottom of the pits. In addition, the farmer builds a small circular dike around the trunk of each pomelo and lemon tree in order to avoid water run-off while watering, and furthermore this can retain some water during rainfall. This technology only applies cattle and chicken manure, and avoids the use of chemical fertilizers.
Through the implementation of the home garden technology involving the cultivation of lemon and pomelo trees as the main produce as well as other supplementary crops, the farmer can gain many benefits. These include improving the farmer’s daily income, creating greenery around the house and providing a favorable living environment that can adapt to the rising temperature caused by climate change. Also the technology is preventing or addressing soil erosion, and providing an appropriate environment for poultry raising. This technology is not expensive as the farmers are able to start implementing it on a step by step basis depending on the availability of labor and resources or they are also able to do it during their spare time.
Farmers can harvest lemons on a daily basis (around 10 to 15 kg per day) and also other supplementary crops. The pomelo trees produce fruit once per year (around 30 fruits per tree on average). In addition, such crop diversification also creates a natural habitat for biodiversity underground, which is an important factor in enhancing soil nutrients and other aggregates. It also avoids the use of chemicals that could harm the health of the family.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
N/A
Name of videographer:
N/A
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
Samrorng Village, Sambo Commune, Sambo District, Kratie Province
Further specification of location:
Village land
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2010
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Learn to do this from other farmers
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- citrus
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Long term crop
Comments:
Pomelo and lemon which can be harvested from the 3rd year and continue for about 15 years.
Livestock density: 20 chickens, cage size 3 x 5 = 15 square meters
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- mango, mangosteen, guava
Comments:
Before the farmer was growing mango trees.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
The farmer pumps water from the Mekong River behind her house.
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated pest and disease management (incl. organic agriculture)
- home gardens
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
Comments:
As structural measures of small the dikes 10 cm in height are piled ub around the tree.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

biological degradation
- Bl: loss of soil life

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Getting shadow for the soil and supporting the increase of beneficial species
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
The total land area of the technology is 1500 square meters (30 m x 50 m), with the Mekong River behind the house. Within the home garden around the house, there are 30 trees of pomelo and 10 trees of lemon, together with another supplementary crops such as banana, coconut, lemongrass, coconut and pineapple. The space between lemon and pomelo trees is three meters and a small circular dike around the trunk of each pomelo and lemon tree is made to prevent water run-off. The other supplementary crops are scattered amongst the pomelo and lemon trees especially at the backyard and along the fence. The farmer used a pumping machine to pump the water from the river which was then connected with a pipe for irrigation.
Author:
Mr. Khuon Sophal
Date:
07/04/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1500 square meters
other/ national currency (specify):
Riel
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20000 /day
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy pomelo it at Koh Trong | Dry season |
| 2. | Buy Lemon along road | Dry season |
| 3. | Buy equipment, pump machine, pipes | Dry season |
| 4. | Buy tools: hoe, shovel, basket | Dry season |
| 5. | Ridge of the row for plantation | Dry season |
| 6. | Plant the crops | Rainy season |
| 7. | Constructing small dikes around the tree trunks | Dry season |
Comments:
Growing in raining season could damage the plant due to muvh of rainfall.
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Digging hole (own self) | day | 10.0 | 20000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Pumping machine and pipe | set | 1.0 | 2000000.0 | 2000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Hoe | piece | 4.0 | 20000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Shovel | piece | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Basket | piece | 5.0 | 10000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Buy soil to fill | Small trucks | 100.0 | 25000.0 | 2500000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Pomelo seedlings | Tree | 30.0 | 40000.0 | 1200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Lemon seedlings | Tree | 10.0 | 15000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Cattle Manure | Sack | 20.0 | 3000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 6255000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1563.75 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Puting fertilizer 3 times per year | Early, middle and lately year |
| 2. | Weeding | Every week |
| 3. | Watering | Every 3 days |
| 4. | Pick out some pomelo if it is too much | For the first fruiting |
| 5. | Spray mosquito killer to kill ants | In rainy season during no rain |
| 6. | Pomelo harvesting | In May |
| 7. | Lemon harvesting | Everyday |
Comments:
When the plant grows big, weeding can be reduced.
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Put fertilizer (done by the farmer herself) | day | 10.0 | 20000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Weeding | times | 32.0 | 14000.0 | 448000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Harvesting | hours | 635.0 | 2500.0 | 1587500.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Gasoline for pumping mechine | liters | 608.0 | 3000.0 | 1824000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Manure | Sack | 30.0 | 3000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 4149500.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1037.38 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
អត់មាន
Comments:
Everyday for lemons can be piked, which concludes in average an hour per day.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
They use own labour and only natural fertilizer, so that they get more income and reduce costs.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1138.20
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
The average annual rainfall in 2015 is 1138.2 mm, in 2014 is 1696.5 mm, in 2013 is 1661.8 mm.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Department of Meteorology, Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology (2015)
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
The weather is warm and humid with 2 different seasons: dry and rainy seasons.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Sandy clay along river bank
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Sandy clay along river bank
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Yes
Regularity:
episodically
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
The famer use water from the Mekong River for drinking and for irrigation.
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
The land user is 45 years old.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
She has another 10 ha of paddy fields and crop land which she keeps uncultivated for 10 years.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Increase around 20% if compare to previous productions of mango trees.
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
Crop quality of both pomelo and lemon are increase slightly because there are enough water if compared to other place.
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
Pomelo and lemon are higher demand that lead to increase household income by getting higher price.
product diversity
land management
Comments/ specify:
The dike construction around tree trunks is keeping water for longer time.
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Comments/ specify:
Water irrigation still demanded because beside of pomelo and lemon she planted as other crop mango trees.
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
Not using pesticides
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Additional profit of around 20%
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
Farmer received additional revenue after this practice
workload
Comments/ specify:
The workload has decreased because previously she irrigated by hand, but now she is using a pump machine.
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
She is obtainin higher yields
health situation
Comments/ specify:
She does not use chemicals or other toxic elements at all.
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
The land user got knowledge about efficient water protection by dike construction around tree trunks and also about the positive effect of using of animal manure.
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Because of dikes around the trunks that preserve water for longer time.
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
Has been reduced by using natural fertilizers (chicken and cattle manure).
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
Can be reduced by using natural fertilizers (chicken and cattle manure).
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
Increasing nutrition because plant leaves fall to the ground.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
There is an increase as instead of chemical fertilizers animals manure is used.
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
Pest and disease are normal because this technique doesn't focus on that. And further there are no chemical or biotic fertilizers in use.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
groundwater/ river pollution
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local thunderstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | moderately |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | moderately |
| flash flood | moderately |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | moderately |
| insect/ worm infestation | moderately |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extended growing period | moderately |
| reduced growing period | moderately |
| sea level rise | moderately |
Comments:
The last a few years, there is no drought and floods
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
After 2-3 years they can harvest the fruits and it should continue for the next 15 years.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Comments:
There are 10 to 20 households which bought 1or 2 trees for cultivating them in the same way.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Easier to sell due to the high demand of lemons and pomelo which are not planted frequently. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The kind of crops that can stand for a long time, provide high yields, be harvested for many years and the lemon crop delivers produce on a daily basis. |
| There are lack of people growing pomelos and lemon trees in this area, so it is quite good for market demand. |
| Applying animal manure can attain high yields and produce high quality crops. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Labor is needed to take care of the plants and to do the watering on a regular basis. | When busy, just keep it going on or take sometimes to do it specially in the early morning and evening after doing the other primary work. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
One specific garden place
- interviews with land users
one specific person (land user)
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
3 experts
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
07/04/2017
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Helen Keller International/Cambodia, 2003. Handbook for Home Garden in Cambodia: The Complete Manual for Vegetable and Fruit Production. Phnom Penh: Helen Keller Worldwide.
Available from where? Costs?
file:///C:/Users/HTPP-ROYAL-INC/Downloads/Home%20_Gardening_Cambodia.pdf
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Landon-Lane C. (2012) Livelihoods grow in gardens. Rome: Rural Infrastructure and Agro-industries Division Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Available from where? Costs?
http://www.fao.org/3/a-i2463e.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Galhena D.H, Freed R., and Maridia K.M. (2013) Home Gardens: a promising approach to enhance household food security and wellbeing.
URL:
https://agricultureandfoodsecurity.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/2048-7010-2-8
Title/ description:
Helen Keller International (2010) Homestead Food Production Model Contributes to Improved Household Food Security, Nutrition and Female Empowerment-Experience From Scaling-up Programs in Asia (Bangladesh, Cambodia, Nepal and Philippines). Nutrition Bullein 8 (1).
URL:
http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/wa_workshop/docs/Homestead_Food_Production_Nutrition_HKI.pdf
Title/ description:
World Vegetable Center (2016) Home Garden in Cambodia. Retrieved on May 14 2017 from
URL:
https://avrdc.org/home-gardens-cambodia/
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules