Retention ditches [Kenya]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Paul Kahiga
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Mitaro ya ruji (Mbeere)
technologies_1244 - Kenya
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Gathenya Mwangi
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Home Patrick
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Chege Timothy
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Omwange Abamba
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Kimengich Baobab
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Wamuongo Jane
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Karanja Andrew
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
Kenya
SLM specialist:
Namirembe Sara
World Agroforestry Centre
Kenya
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - KenyaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
KARI Headquarters (KARI Headquarters) - KenyaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Jomo Kenyatta University (Jomo Kenyatta University) - Kenya1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
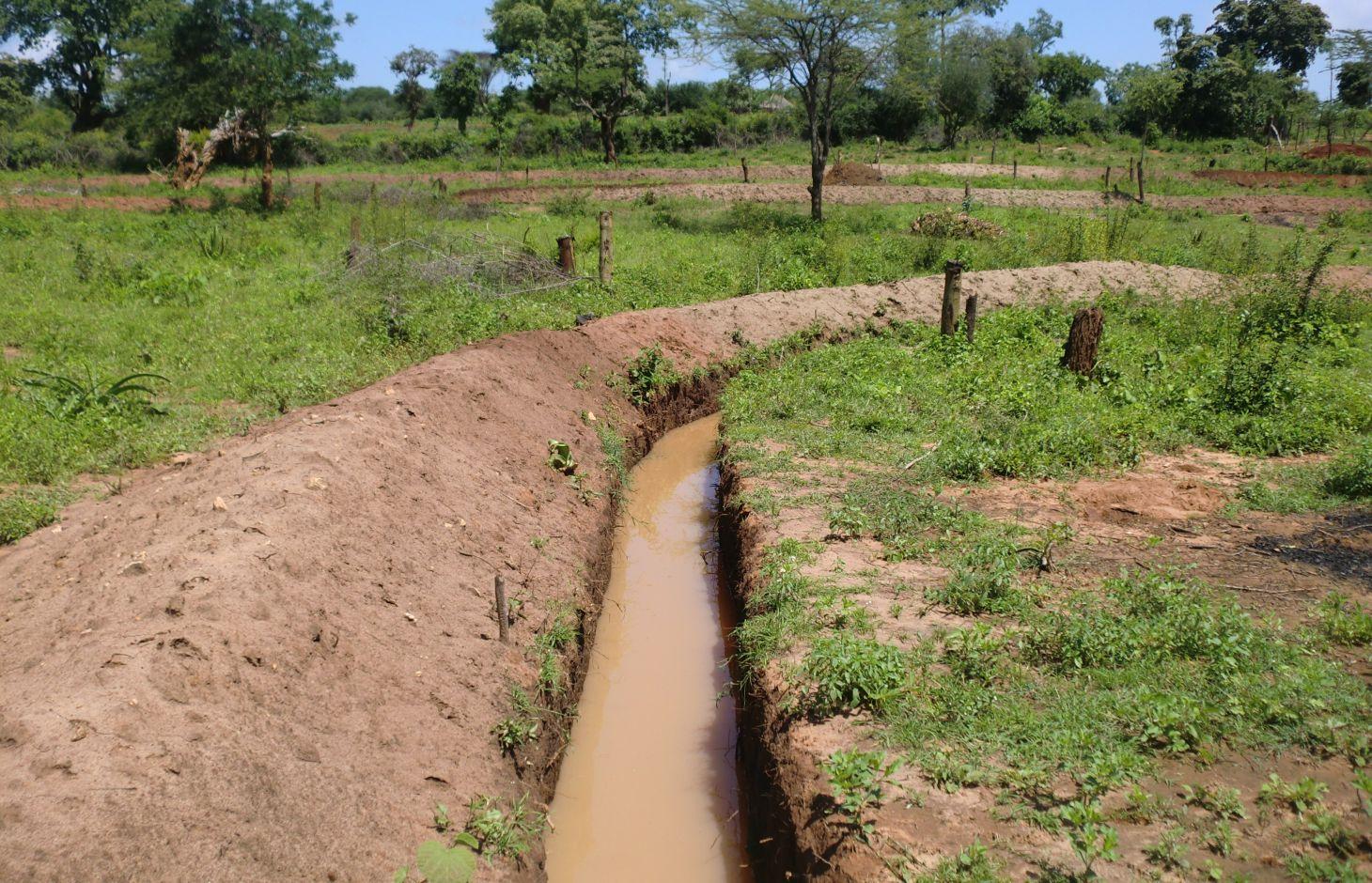
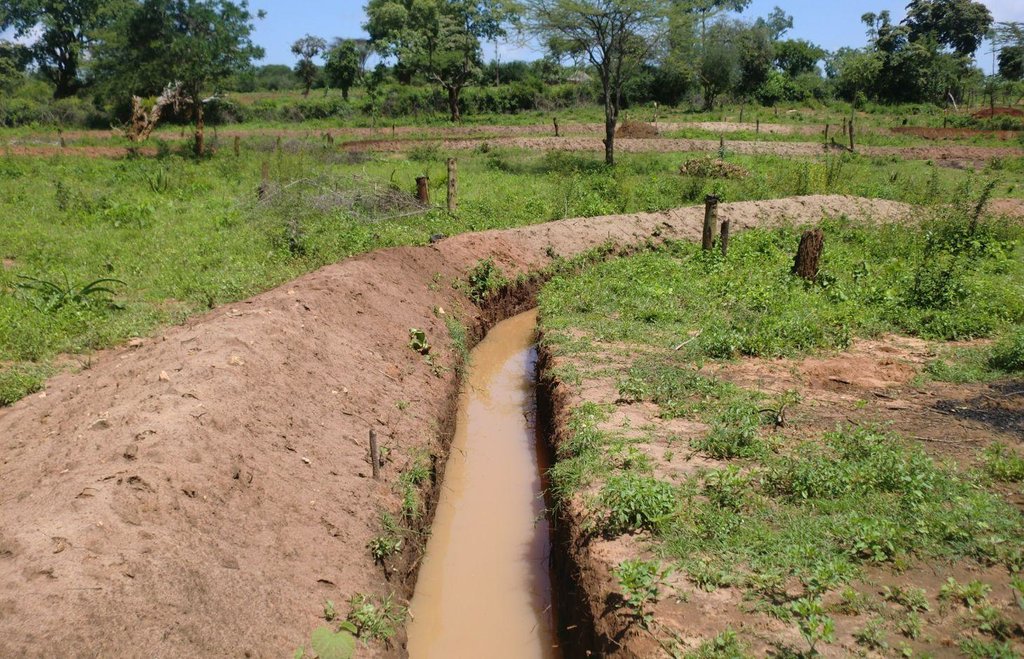
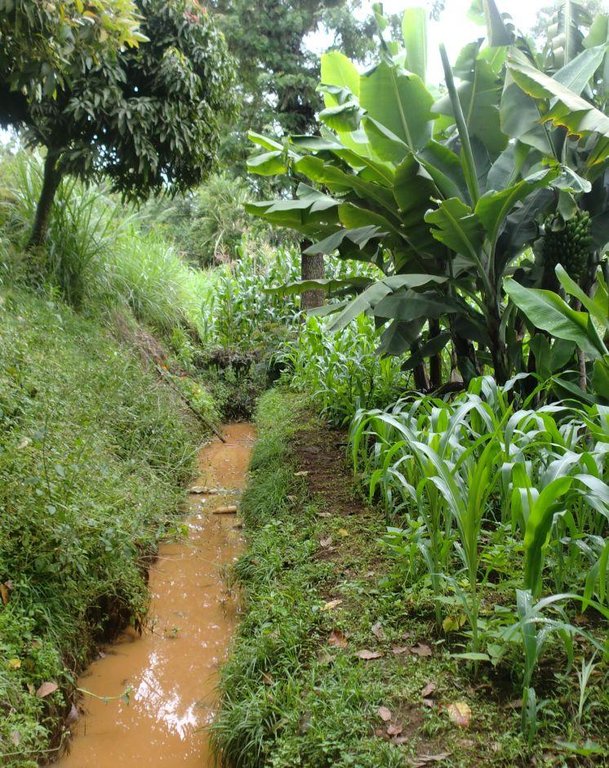
Retention ditches, also called infiltration ditches, are larger ditches designed to catch and retain all incoming runoff for infiltration into the soil.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Retention ditches, also called infiltration ditches, are larger ditches designed to catch and retain all incoming runoff for infiltration into the soil. They operate like contour furrows, increasing the supply of water made available to crops planted in and adjacent the ditch, while also reducing soil erosion. However, they handle much more water. Retention ditches are in essence water harvesting and conservation structures
Purpose of the Technology: They are commonly used as an alternative to diversion ditches if there is no places to discharge runoff or if there is a need , as in semi –arid areas , to harvest water , e.g. for bananas.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: When constructing the ditches, the soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. This structure can be stabilized further by planting grass on it. On soils with lower infiltration rate, or on slopes, the ends can be left open to allow excess water to drain out.
Natural / human environment: Retention ditches are normally constructed on relatively flat areas with closed ends and wide and deep enough to hold all the runoff expected. They are often found on steep slopes in humid area under small scale farming where there is no opportunity to discharge runoff to a waterway. Retentions ditches can be useful where soils are permeable, deep and stable. However, retention ditches are not recommended for areas with shallow soil, those prone to land slides or where soil salinity is a possibility.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Kenya
Region/ State/ Province:
Eastern
Further specification of location:
Mbeere
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
Retention ditches technology not practiced by many farmers although some collaborate with the local agricultural extension officer from the ministry of Agriculture to show them the guidelines of construction.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): To reduce soil erosion and retain runoff for infiltration.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Inadequate water for irrigating the farm.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- water diversion and drainage
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), poverty / wealth, labour availability
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
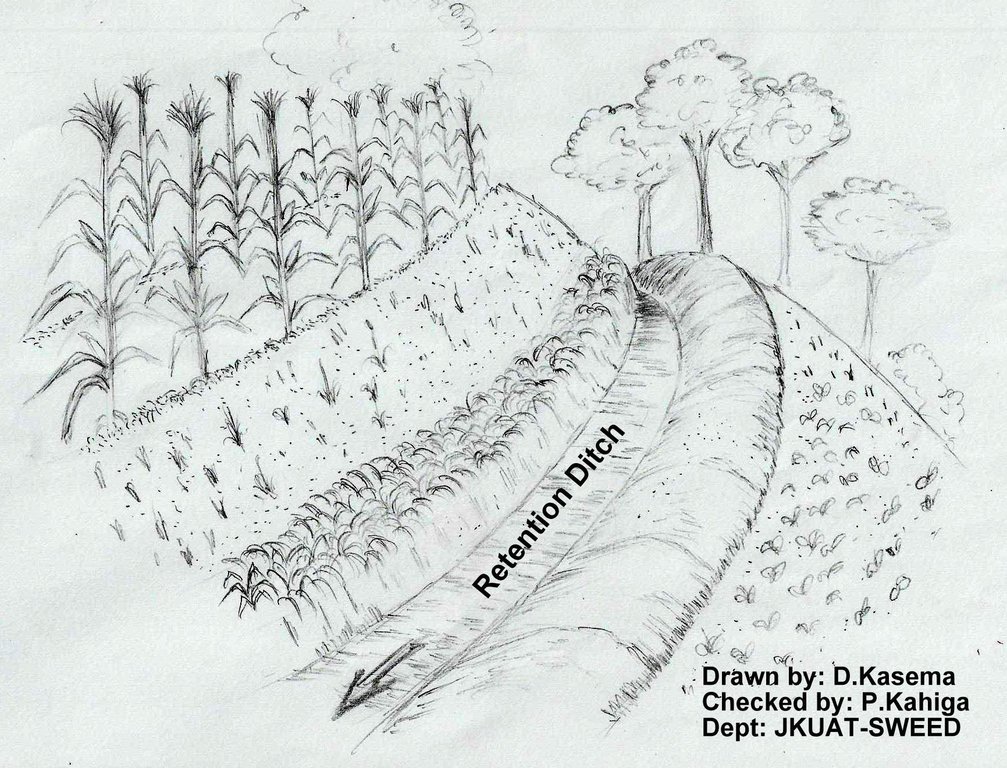
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
A technical drawing showing a retention ditch. The run-off ponds within the ditch giving it time to infiltrate.
Location: Ntharawe. Eastern Province
Date: 27/10/2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (In implement this technology the farmers collaborates with an Agriculture extension officer in order to assist in making the retention ditches.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Water scarcity triggers farmers to look for better means of soil conservation and retention ditch plays an important role to satisfy crop water requirement.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 6
Spacing between structures (m): 30
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Author:
Paul Kahiga, 8444-00300 Nairobi
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Kshs
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
100.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5.00
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing of vegetation | before the rain starts |
| 2. | Marking contours | After vegetation clearance |
| 3. | Digging the ditches | after marking the contours |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 130.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1.3 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of excess sediments | once after rainy season |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 80.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.8 | |||||
Comments:
in the month of June 2012
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
slope of the land, labour and availability of a technical person to assist in laying down of the contours
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
risk of production failure
land management
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
Soil
soil moisture
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
waterborne pests
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Comments:
stabilization of the up-slope using grass which is also fed to animals
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Retains runoff and improves soil moisture |
| It is a water harvesting technology for crops in dry areas |
| Reduces soil erosion by wind |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Prevents movement of machinery within the farms | leave some passages that can allow movement of machinery within the farm. |
| The retained water can habour mosquitoes and other water borne pests | Spraying with appropriate insecticides. |
| labour intensive to construct and to maintain | |
| Regular maintenance of the ditches. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
19/09/2012
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules