Rip-ploughing, oversowing [South Africa]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Insaai (Afrikaans)
technologies_1372 - South Africa
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
De Wet Saroné
Hattingh Asterid
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Ripploughing and oversowing (sodsowing) of extensive grazing land in order to improve productivity of a semi-arid rangeland.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
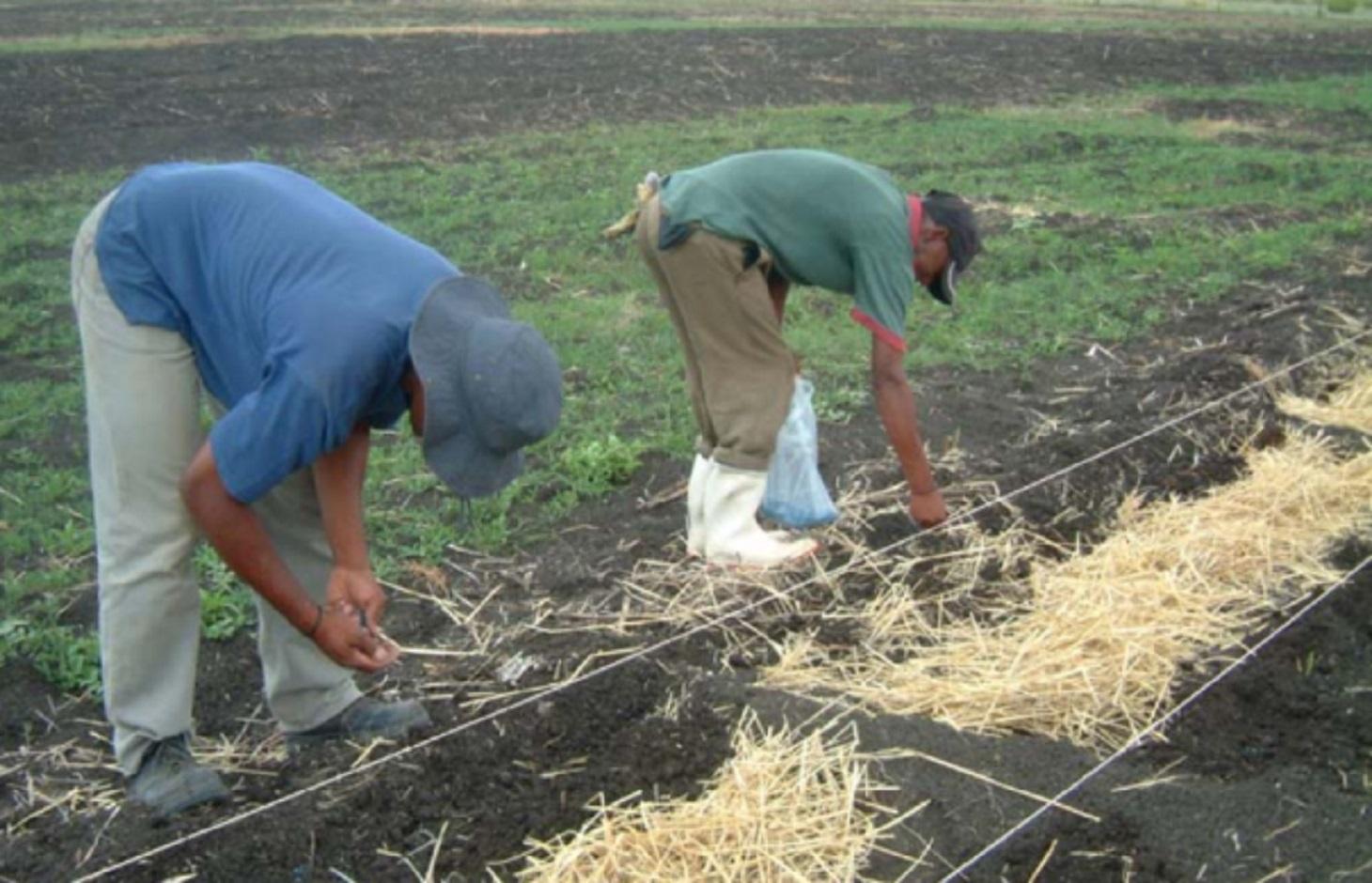
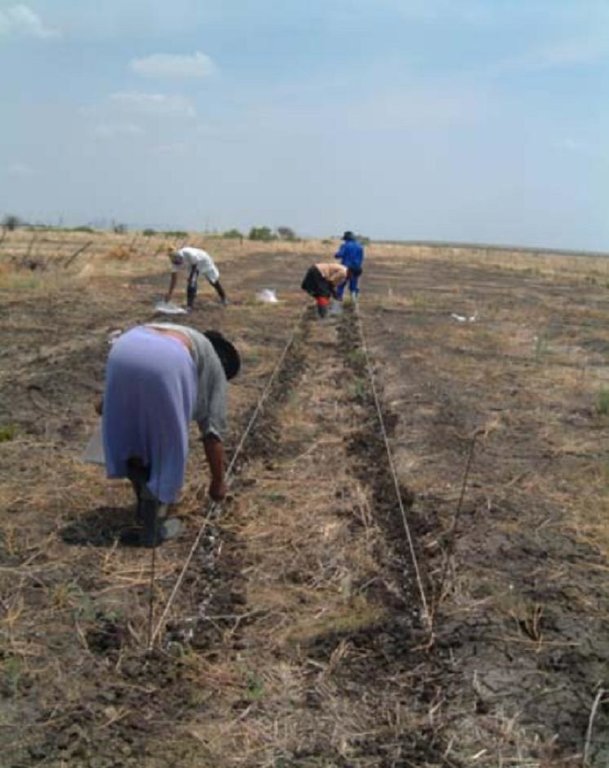
Description:
A pasture characterised by the unpalatable Cymbopogen plurinoides grass species was rip-ploughed to a depth of 20, 15, or 7 cm to uproot the unfavourable grass species.
Coated and uncoated seeds of more palatable grass species were hand sown into the furrows and the soil kicked over the seeds.
Grazing has been excluded for the past four years, giving the sown-in grass species the opportunity to establish and credit the soil seed bank.
The purpose of the technology was threefold: First, the success of rip-ploughing as a restoration technology was researched. Secondly, the suitability of coated or uncoated seeds was established. Thirdly, the suitability of the technology for restoration purposes was researched. This was done in the summer of 1995/96. The frequency and density was measured in the following years up to 1999. The density was measured with a 1 x 1 square meter; and tillers, vegetative and reproductive plants were distinguished.
The purpose of the frequency measurement is to establish the percentage a grass species contributes to the grass community. The density measurement gives the amount of rooted plants in a square meter. Distinction between the life stages indicates the self-sustainability of a population. Seed bank analyses are also added.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
South Africa
Region/ State/ Province:
North West Province
Further specification of location:
Madikwe, Koster, Potchefstroom
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
0.1
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.1 km2.
The localities are not strictly basin, except Kromspruit & Tweefontein. Davidkatnagel has no slope. Totiuskraal lies between the watershed and basin.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Lennof Reynecke (fellow student) & Klaus Kellner (lecturer)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Semi-nomadic pastoralism
- Ranching
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing or rather mismanagement led to i) dominance of the unpalatable grass species at Koster, and ii) bare soil at Totiuskraal, Davidkatnagel and Krompspruit.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Erosion/overgrazing making area unsuitable for grazing because of lack of vegetation of appropriate palatability and nutrition.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Kromspruit; Davidkatnagel
Ranching: Totiuskraal; Koster
Grazingland comments: Area closure only followed on incentive of researchers. Koster duplicated area enclosure on own initiative afterwards.
Type of grazing system comments: Area closure only followed on incentive of researchers. Koster duplicated area enclosure on own initiative afterwards.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved plant varieties/ animal breeds
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures

structural measures
Comments:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
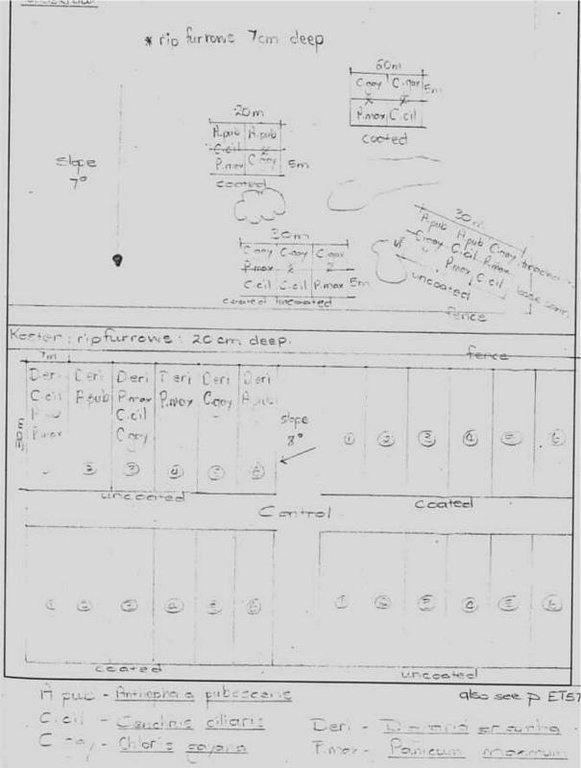
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Site plan for rip-ploughing and hand sowing of palatable grasses.
North West
Date: 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 100
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Grass species: Anthephora pubescens, Digitaria erlantha, Chloris gayana, Cenchrus ciliaris, Panicum maximum
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 8.00%
Change of land use type: Area close for plant establishment
Change of land use practices / intensity level: After plant establishment grazing occurs as in 2.4.3.3
Author:
Sarone de Wet
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
ha
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
8.30
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedbed reparation | Summer |
| 2. | Sowing of seeds | Summer |
| 3. | Enclosing site | Summer |
| 4. | Debushing were necessary | Early Summer |
| 5. | Area enclosure | From start for 2 years |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Constructing seed beds and | persons/day/ha | 36.0 | 8.3 | 298.8 | |
| Equipment | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 308.8 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 308.8 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grazing excluded | /Continuously |
| 2. | Grazing | Spring (Apr-Sept) /After 2 y for a week; then after regrowth |
| 3. | Rotation grazing | Late summer after 2nd year / Once a year for winte |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
For Koster, in terms of seeds and tractors; as well as final credit after 3 years measured in R/ large stock unit.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour and transport; equipment (gasoline).
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
430mm and 520 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms: Hill slopes for Totiuskraal, footslopes for Koster and valley floors for Davidkatnagel; Kromspruit
Altitudinal zone: 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l. for Totiuskraal
Slopes on average: Flat for Davidkatnagel, gentle for Kromspruit and moderate for Koster; Totiuskraal
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil texture: All sites actually; sandy clay loam: the soil is evenly textured but has a high clay content
Soil fertility is very high
Topsoil organic matter: Medium for Koster and poor for Kromspruit, Davidkatnagel and Totiuskraal.
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium for Koster and poor for Kromspruit, Davidkatnagel and Totiuskraal.
Soil water storage capacity: medium - high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, very poor
40% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (Koster).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Totiuskraal).
20% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (Kromspruit; Davidkatnagel).
Off-farm income specification: Farmers have extra-farm occupations for the Totiuskraal area
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence for Kromspruit; Davidkatnagel and commercial for Totiuskraal; Koster
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
Not large enough to be economically viable
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
Perennial grass species
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
Perennial grass species
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Able to carry more livestock in a sustainable way
Other socio-economic impacts
input constraints
Comments/ specify:
Labourers expect more money
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Explained beforehand
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
Difference in goal
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
excess water drainage
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Compared to none treated site
soil cover
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
Vegetation cover binds soil
Other ecological impacts
winter forage
Bush encroachment
Comments/ specify:
Easy establishment
palatability draw animals
Comments/ specify:
If not controlled - overgrazing
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
Comments/ specify:
Vegetation bind soil; denser covering of soil
wind transported sediments
Comments/ specify:
Vegetation cover ~100%
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
30 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
Comments:
30 land user families have adopted the Technology
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
25% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: One land user applied the technology to another part of his farm.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Vegetation cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? Rotational grazing |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Establishment of perennial grass cover How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing management; not graze to seed production stage. |
|
Increase of perennial grass production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing management |
|
Find suitable seed mixtures for different habitats How can they be sustained / enhanced? Literature study on habitat preferences |
|
Seed bed preparation enhance establishment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Know exact depth of sowing of seeds. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Implementation in communal areas mostly | Brainstorm on implementation without gasoline needed. |
| Communication with landuser | Contact on monthly basis built friendship |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Veld management in South Africa, Tainton. 1985.
Available from where? Costs?
From researcher
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules