Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien [Tunisia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Donia Mühlematter
- Editor: Hichem Khemiri
- Reviewers: Alexandra Gavilano, Donia Mühlematter
Agroforesterie
technologies_3722 - Tunisia
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: Aug. 21, 2019 (inactive)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: Aug. 21, 2019 (public)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: May 30, 2018 (inactive)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: May 30, 2018 (inactive)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: May 28, 2018 (inactive)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: May 28, 2018 (inactive)
- Le système d’Agroforesterie pour la protection des terres et l'amélioration des revenus des exploitants dans les zones montagneuses.de Nord Ouest Tunisien: May 28, 2018 (inactive)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Tunisia
SLM specialist:
Tunisia
land user:
Tunisia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Office de Développement Sylvo-Pastoral du Nord-Ouest (ODESYPANO) - Tunisia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Projet de développement des zones montagneuses du Nord … [Tunisia]
Le projet de développement des zones montagneuses de Nord Ouest Tunisien est mis en oeuvre par l'Office de développement sylvo-pastoral de Nord Ouest en adoptant une approche participative et intégrée afin de promouvoir le développement socio-économique et agro-écologique des zones montagneuses.
- Compiler: Donia Mühlematter
2. Description of the SLM Technology
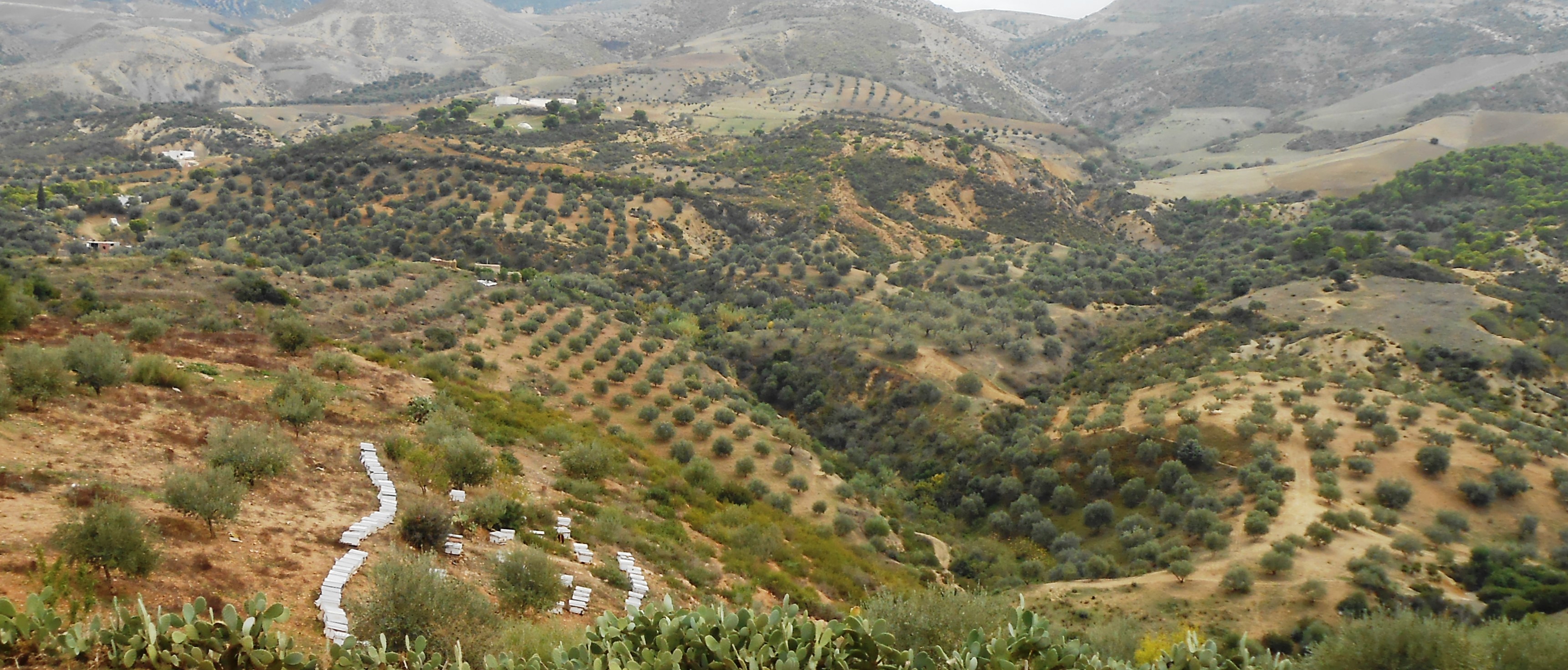
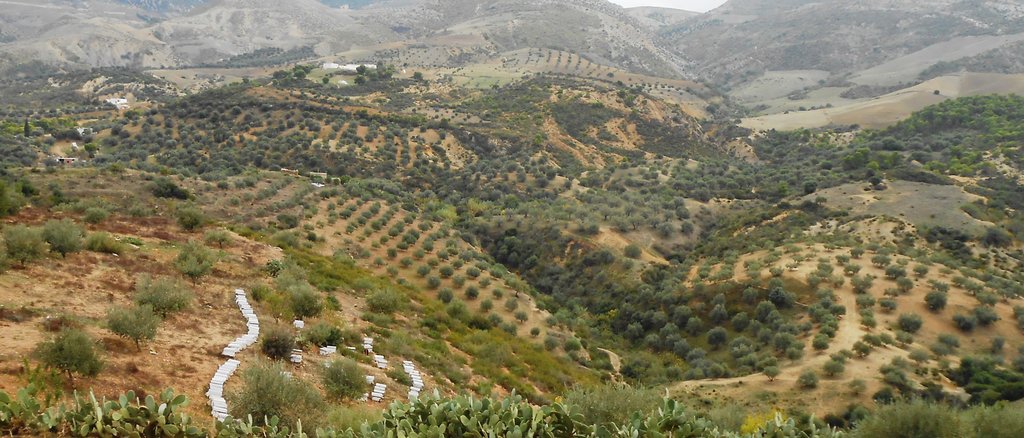
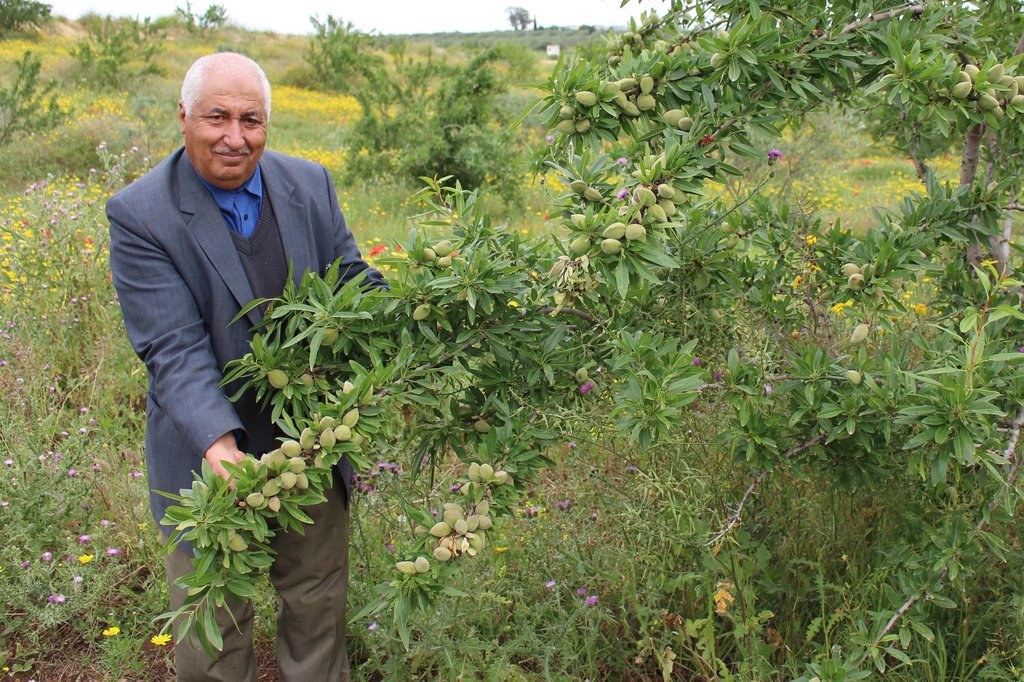
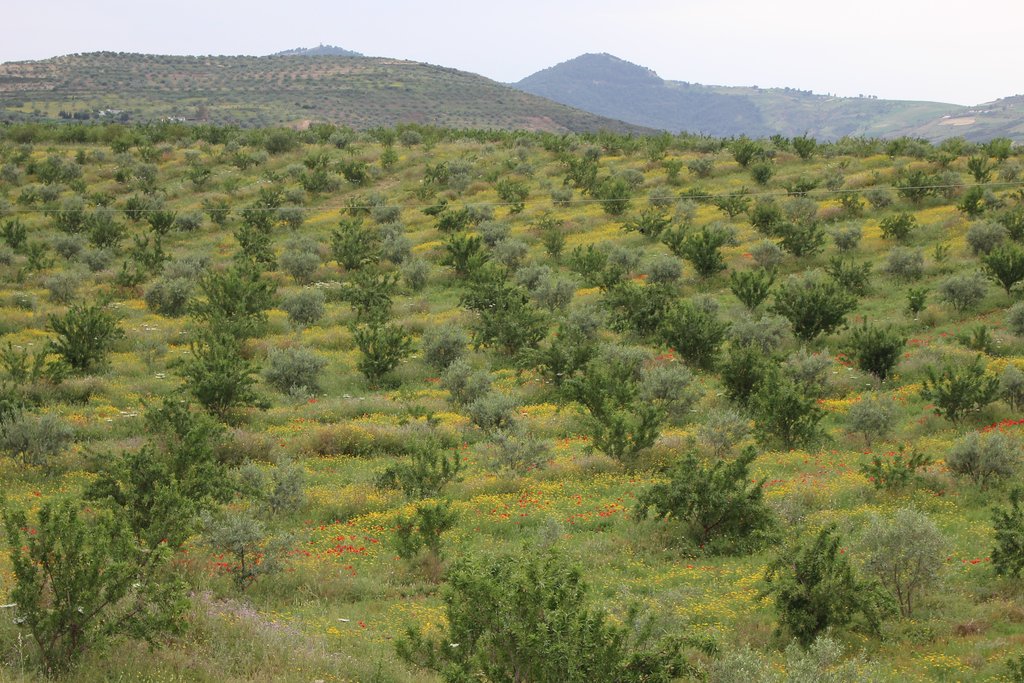
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tunisia
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- reduce risk of disasters
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Ranching
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing

Forest/ woodlands
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- integrated crop-livestock management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A3: Soil surface treatment

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level
- M7: Others
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Date:
14/05/2018
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
2.45
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 100.0 | 3.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 100.0 | 2.0 | 200.0 | |
| Plant material | None | None | 100.0 | 2.2 | 220.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 3.0 | 50.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 870.0 | |||||
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 100.0 | 2.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 100.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 2.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 400.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
crop quality
fodder production
fodder quality
animal production
risk of production failure
product diversity
production area
land management
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
farm income
diversity of income sources
workload
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
community institutions
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
soil crusting/ sealing
soil compaction
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
invasive alien species
animal diversity
beneficial species
habitat diversity
pest/ disease control
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
landslides/ debris flows
drought impacts
impacts of cyclones, rain storms
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
fire risk
wind velocity
micro-climate
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
damage on neighbours' fields
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | dry season | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local thunderstorm | very well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | very well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | well |
| landslide | very well |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Yes
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- changing markets
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Projet de développement des zones montagneuses du Nord … [Tunisia]
Le projet de développement des zones montagneuses de Nord Ouest Tunisien est mis en oeuvre par l'Office de développement sylvo-pastoral de Nord Ouest en adoptant une approche participative et intégrée afin de promouvoir le développement socio-économique et agro-écologique des zones montagneuses.
- Compiler: Donia Mühlematter
Modules
No modules