Banquettes en terre irriguée combinées à l’agroforesterie [Morocco]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Chkirni Malika
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Gudrun Schwilch, Isabelle Providoli, Donia Mühlematter, Alexandra Gavilano
Qanderte (ⵇⴰⵓⴷⴰⵕⵟ) القندرت
technologies_2165 - Morocco
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Banquettes en terre combinées avec de l’Agroforesterie.: Sept. 5, 2019 (inactive)
- Banquettes en terre irriguée combinées à l’agroforesterie: June 2, 2021 (inactive)
- Banquettes en terre irriguée combinées à l’agroforesterie: April 14, 2021 (inactive)
- Banquettes en terre irriguée combinées à l’agroforesterie: April 16, 2021 (inactive)
- Banquettes en terre combinées avec de l’Agroforesterie.: Jan. 3, 2018 (inactive)
- Banquettes en terre irriguées combinées à l’agroforesterie: Oct. 26, 2022 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Moha Ahdour
Agriculteur
Morocco
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Projet de Gestion Participative et Intégrée des Bassins Versants pour la Lutte contre l’Erosion (FAO/GPC/MOR/050/SWI)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royaume du Maroc, Haut Commissariat aux Eaux et Forêts et à la Lutte Contre la Désertification (Royaume du Maroc) - Morocco1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
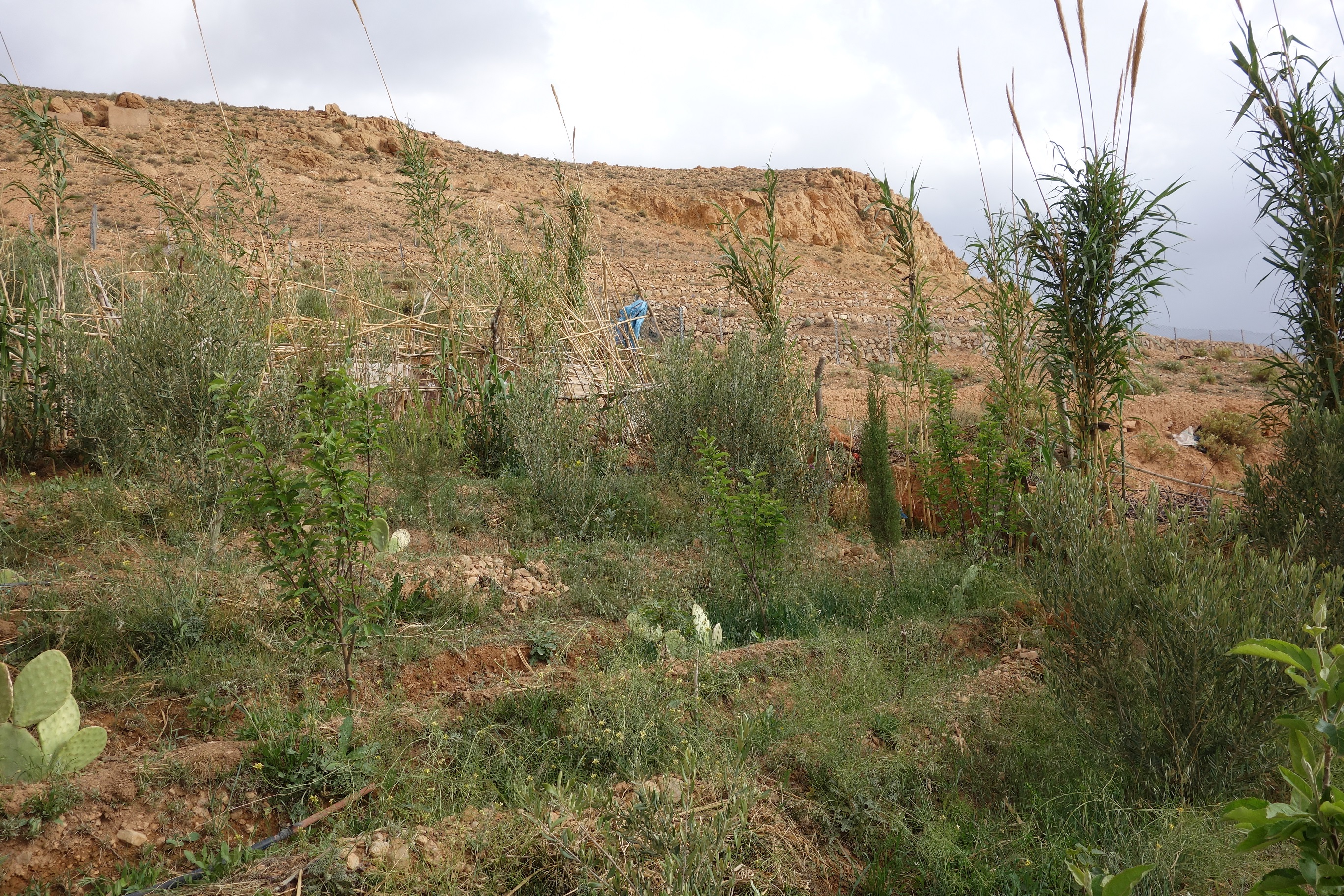
Les banquettes, combinées avec des plantations à base d'espèces forestières et fruitières, ont pour objectif de lutter contre l'érosion hydrique qui menace les habitations et les infrastructures de base en aval de la parcelle.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
La récurrence de périodes de sécheresse et de violentes averses estivales provoque l’accélération de l’érosion hydrique sous toutes ses formes et des inondations qui compromettent sérieusement tout développement normal de la zone. Pour lutter contre l’érosion hydrique, un exploitant du Douar de Flilou a pris l'initiative de mettre en place une parcelle de plantations anti érosives en s’inspirant d’un projet pilote mis en place par la FAO à proximité.
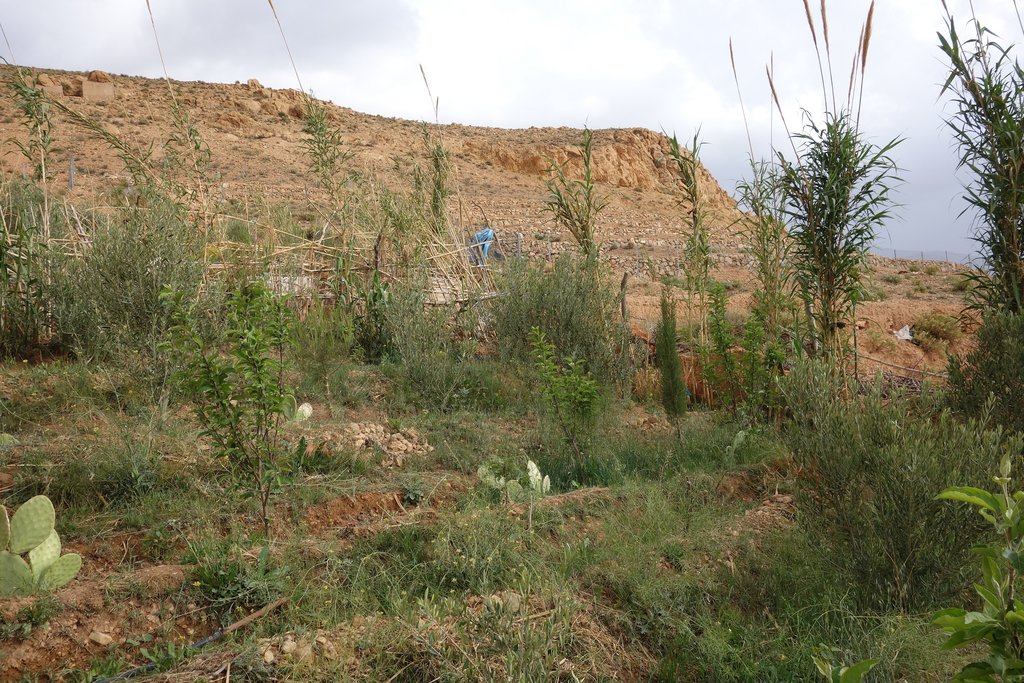
Des banquettes traditionnelles ont été établies grâce à la construction de talus en pierre qui suivent les courbes de niveau.
Le but de ces structures est de fractionner les pentes et de diminuer l’importance duruissellement pour contrôler l’érosion, augmenter l’infiltration et la quantité d’eau stockée dans le sol et accumuler les sédiments érodés.
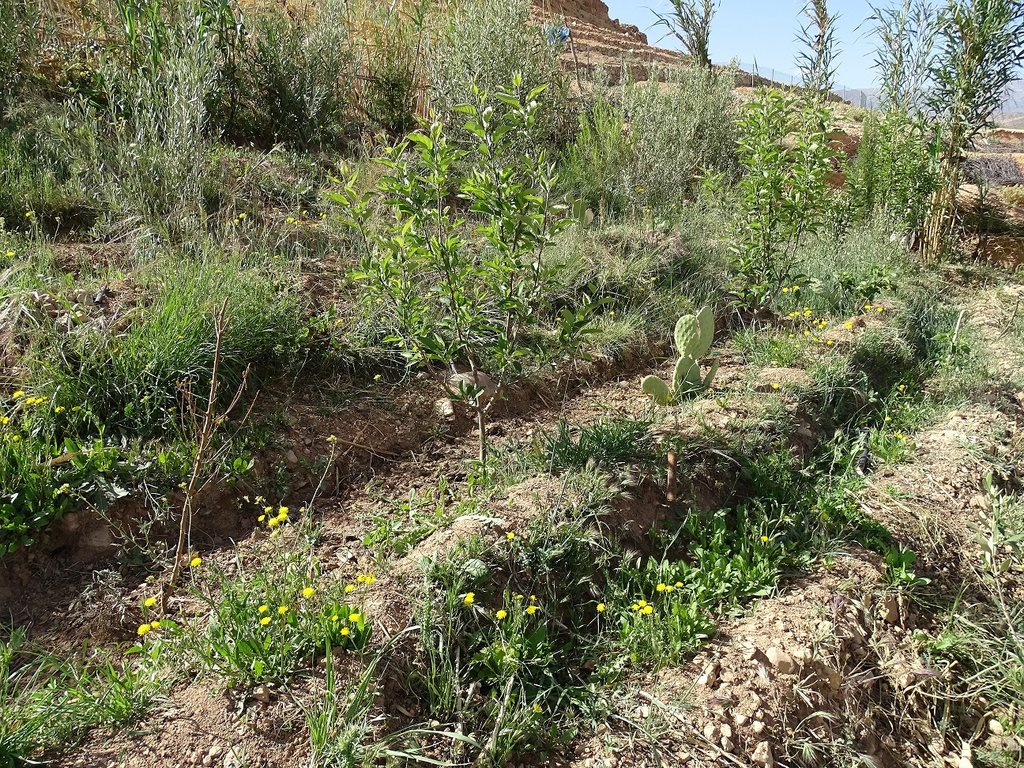
Des cultures diversifiées sont installées sur ces banquettes. La plantation des légumineuses aide aussi à améliorer la fertilité du sol. Des structures de collecte des eaux ont été développées pour améliorer encore les rendements des plantations d’arbres fruitiers en particulier. Un des inconvénients de cette technologie est qu’elle nécessite un entretien très fréquent.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Morocco
Region/ State/ Province:
Midelt
Further specification of location:
Qcer Flylou
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
Une superficie inferieur à 0,1 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2011
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- vegetables - other
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- agave / sisal
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- figs
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
- olive
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1

Forest/ woodlands
Type of tree:
- Pinus species
- Populus species
- Chêne vert (cf. Quercus ilex), roseau
Comments:
Principaux produits/ services: Olivier, figue, pommier, chênes vert ,pin d’Alep, gave, roseau, légumes, peuplier...
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Comments:
Au passé la parcelle a été un terrain de parcours accidenté et maintenant la parcelle est devenu agro-forestière.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Valorisation des eaux pluviale pour assurer l 'irrigation des plantations (eaux des seguia).
Et également, il assure l'irrigation par un tuyau bronché de sa maison vers la parcelle.
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- cross-slope measure
- ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

structural measures
- S1: Terraces
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
- M3: Layout according to natural and human environment
- M5: Control/ change of species composition
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
- Wm: mass movements/ landslides
- Wo: offsite degradation effects

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil
- Eo: offsite degradation effects

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
- Bl: loss of soil life
- Bp: increase of pests/ diseases, loss of predators

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
- Hs: change in quantity of surface water
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
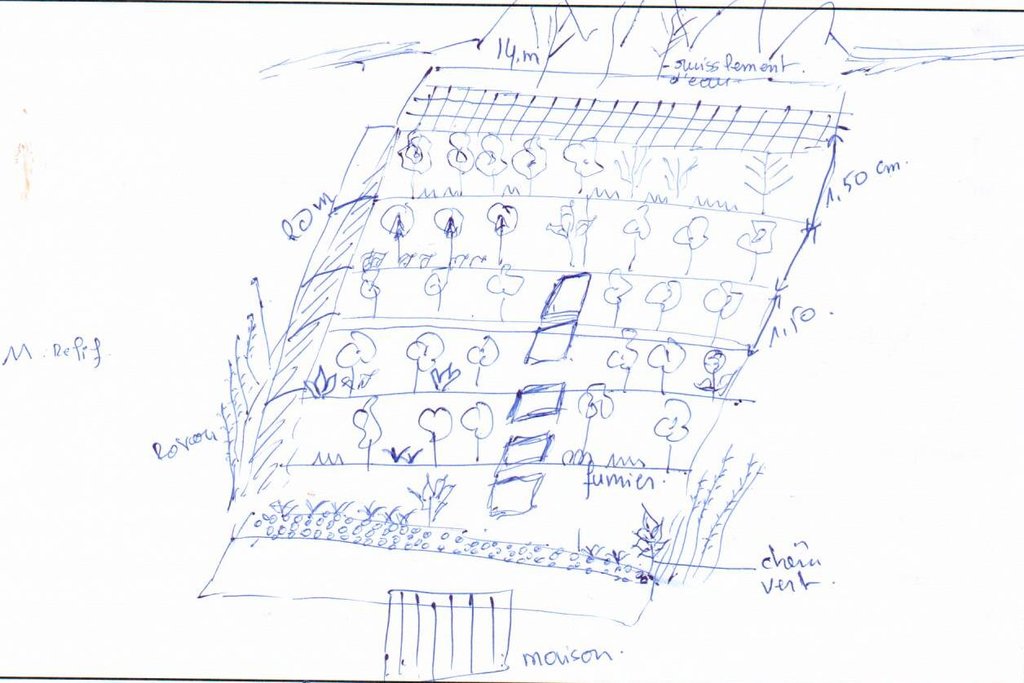
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Longueur de la parcelle : 20 m
Largeur de la parcelle : 14 m
Espace entre banquettes: 1.50 cm
L'espace entre les arbres est très faible (moins d'1 mètre).
Author:
chkirni malika
Date:
03/05/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
280 m2
other/ national currency (specify):
Dirhams
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
10.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
80 dirhams
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation des banquètes | Novembre |
| 2. | Plantation des oliviers | Mars |
| 3. | Plantation des figuiers | Mars |
| 4. | Plantation des roseaux | Mars |
| 5. | Plantation des pommiers | Mars |
| 6. | Plantation de chêne vert | Avril |
| 7. | Plantation du pin d’Alep | Avril |
| 8. | Plantation des cyprès | Avril |
Comments:
Plantation des plantes de raisin , noyer, faux poivrier , raquette de figue de barbarie...
Ainsi des cultures des maraichage notamment persil ,oignions, fèves, tomates..etc
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Main d’ouvre de construction des banquettes | Jours | 60.0 | 80.0 | 4800.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | plantation des oliviers | plants | 70.0 | 7.5 | 525.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | plantation des pommiers | plants | 14.0 | 8.0 | 112.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Engrais 18/46 | kg | 50.0 | 4.2 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 5647.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 564.7 | |||||
Comments:
Toutes les activités ont été à la charge de l’exploitant de terre. Les couts ont été calculés seulment pour 200 m2 et non pas par hectare.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cultures maraîchères | |
| 2. | Fertilsation du sol | deux fois par année |
| 3. | Entretien des banquettes | après l'hiver |
| 4. | Irrigation | deux fois par mois |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | main d'oeuvre | jours | 5.0 | 80.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Tuyau d’irrigation | M | 38.0 | 7.0 | 266.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Achat d’engrais | Kg | 50.0 | 4.2 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 876.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 87.6 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
La disponibilité de main d'oeuvre.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
pluvimétrie trés variable d'une année à autre.
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Un climat rude marqué par un hiver rigoureux et un été chaud, influencé par les amplitudes thermiques saisonnières et
journalières.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Il s’agit des calcaires, des calcaires dolomitiques et des marnes du jurassique. Cette série repose en discordance sur les terrains sous-jacents.
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Yes
Regularity:
episodically
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
La régénération d'autres espèces dégradés notamment le thym et l'armoise.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
C'est un agriculteur vieux.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
Bonne conduite des cultures par l’apport du fumier organique, ainsi que l'irrigation.
forest/ woodland quality
Comments/ specify:
L'irrigation des plantes forestiers facilite la bonne croissance de ces espèces par rapportaux plantations dans des terrains forestiers non-irrigués
product diversity
Water availability and quality
irrigation water availability
Comments/ specify:
L’exploitant a mis en place un système d'irrigation.
demand for irrigation water
Comments/ specify:
Dans le passé, c'était un parcourt dégradé et maintenant l'exploitant peut effectuer des cultures irriguées.
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
Diminution des charges en matière d’achat des intrants.
farm income
workload
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Mise en place d’une association par le projet FAO et collaboration avec la Direction Provinciale des Eaux et Forêts de Midelt pour renforcer et sensibiliter les populations quant aux effets bénéfiques de cette pratique.
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
harvesting/ collection of water
surface runoff
groundwater table/ aquifer
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
soil accumulation
soil crusting/ sealing
soil compaction
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
beneficial species
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
landslides/ debris flows
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
wind velocity
micro-climate
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
Comments/ specify:
Car il utilise l'irrigation.
downstream flooding
downstream siltation
buffering/ filtering capacity
wind transported sediments
damage on neighbours' fields
damage on public/ private infrastructure
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
Généralement se sont des impacts positives.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local hailstorm | moderately |
| local snowstorm | moderately |
| local sandstorm/ duststorm | moderately |
| local windstorm | moderately |
| tornado | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| heatwave | moderately |
| cold wave | moderately |
| extreme winter conditions | moderately |
| drought | moderately |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| landslide | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
Son voisin à été inspiré la technologie de M.Moha et il a fait la meme chose que lui.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Yes
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- changing markets
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
Diversification des espèces avec des arbres fruitiers et forestiers.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Avantage de point de vue esthétique. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| La lutte contre l'érosion hydrique. |
| La lutte contre la dégradation off-site (protection des habitations en aval). |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Les arbres sont plantés trop densément pour une production intéressante. | Une fois les espèces adaptées identifiées, couper les autres. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
Interview avec Mr. Moha.
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
03/05/2017
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
FAO/GCP/INT/093/SPA/2011-Monographie du sous-bassin versant d’Oued Outat
Available from where? Costs?
malika chkirni
Title, author, year, ISBN:
rainwater harvezting for drylands and beyond, Brad Lancaster,
Available from where? Costs?
https://www.harvestingrainwater.com/
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Monographie de la province de Midelt
URL:
https://magazine-geo.blogspot.com/2014/06/monographie-de-la-province-de-midelt.html
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules