Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakha Chuke Tole for domestic use. [Nepal]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1655 - Nepal
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Bajracharya Reena
Kathmandu university
Nepal
SLM specialist:
Maharjan Satish
Kathmandu university
Nepal
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Kathmandu University (KU) - Nepal1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [Nepal]
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
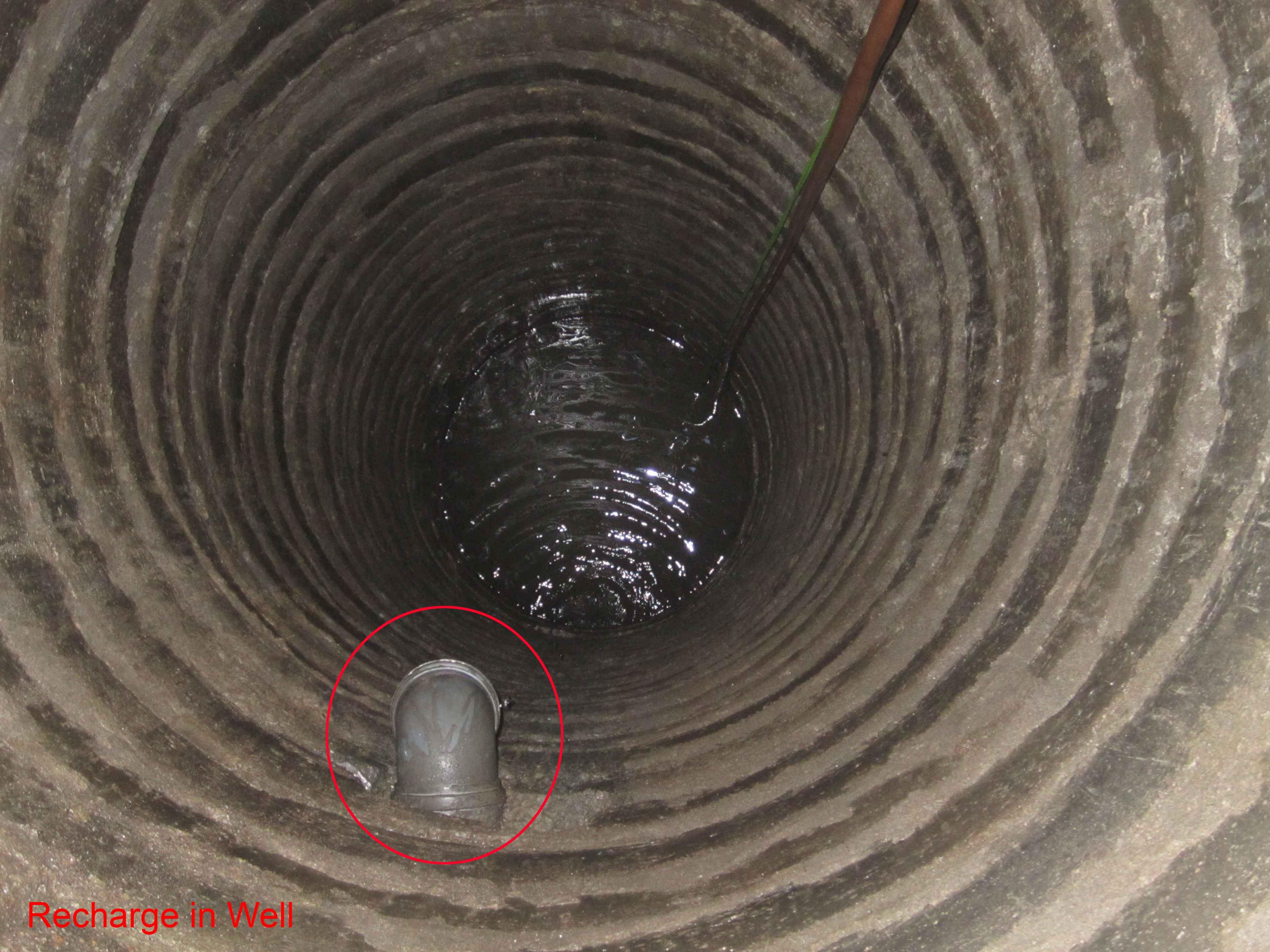
Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakka Chuke tole for Domestic use.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Due to increasing population and urbanization along with unmanaged settlements in and around the core city areas in Lalitpur existing ground water dries up while the water levels in well is decreasing alarmingly. However with initiation of rainwater recharge programs in areas in 2009
locals from around 150 houses around nyakha chuke tole and adjoining areas in lalitpur get their water supply with sucessful replerishment of their underground aquiter through rainwater harvesting.the dugwells are being sucessfully replerished due to rainwater recharge system.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is mainly applied to replerish ground water aquiter to support around 20 different committee in Lalitpur.
This aims to make people aware of the recharge mechanism and augument ground water level.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The credit for implementing this technology must go to local people participation. It is only because of the cooperation among themselves that make them realize current alarming problem and made them collect money for implementing recharge system.They have done it with external material support such as food-work, payment, subsidized machinery.
Regarding maintenance activities , women living around nyhakha chure tole are responsible for cleaning areas where technology has been implemented. Besides , water content in dug well are tested every six months to make sure that water is suitable for drinking that is free from ions and other chemicals . As well as different machine such as pump are checked every six months and are replaced if damaged, with the money collected from different house hold.
Natural / human environment: The implementation of this technology or system has made availability of water for various domestic use by supplying the water in each and every houses.It also has helped increasing harmony and mutual understanding among the people living there by. In past years people use to fight for getting water. there were fight between two locality for water . Ground water recharge system has increased water sources . There is proper distribution of water. Now people do not have to disturb their sleep for getting water like before.this has even helped to improve living standard and health of people.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Nepal
Region/ State/ Province:
Nepal
Further specification of location:
Lalitpur
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Map
×3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- Protect ground water
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- rice
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- citrus
Comments:
major cash crop (CA): Rice
major cash crop (CP): Potato
major cash crop (CT): Orange
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

other
Specify:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development, population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify) (unmanaged settlements.), land tenure, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
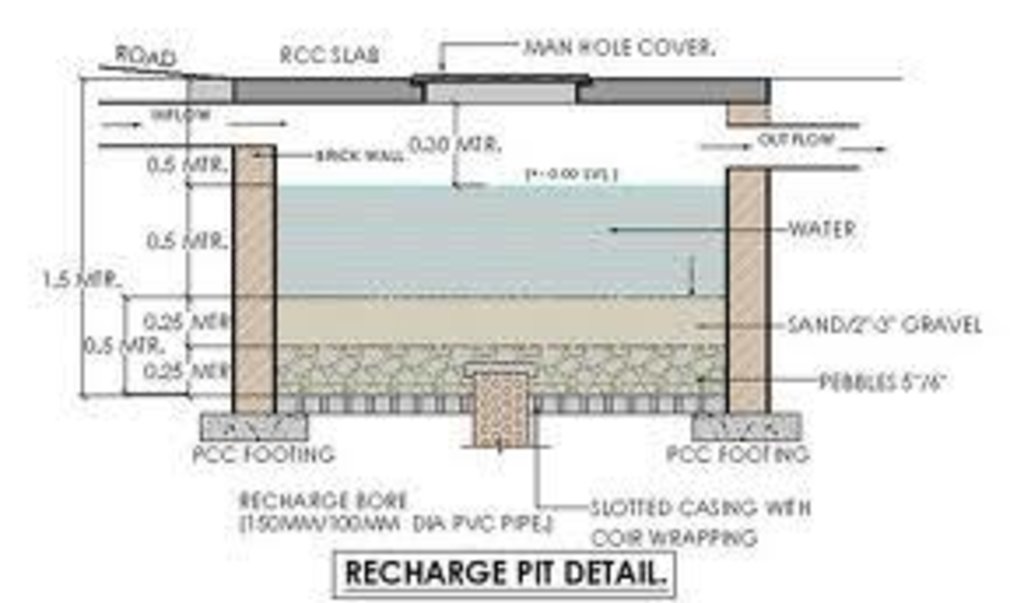
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
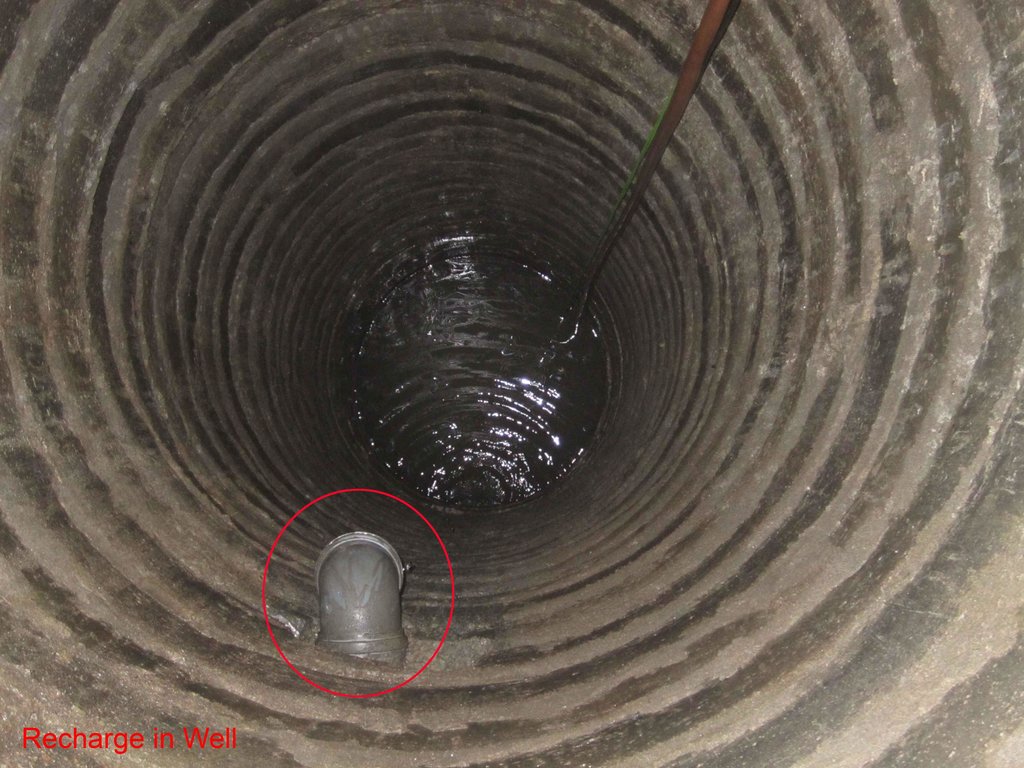
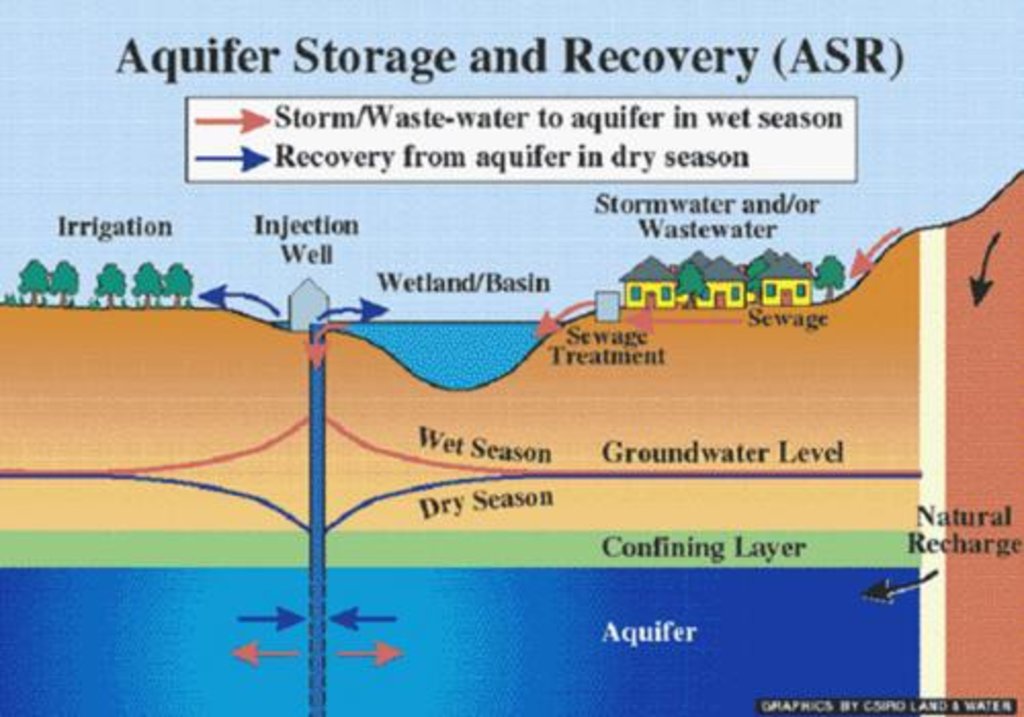
Underground water from dug well is drawn to stone filter through electrical pump. Water is purified in wash stone filter. purified water is pumped and drawn to surface water tanks from where water is distributed and supplied to people.
Location: nyakha chuka tole. lalitpur
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 200ft
Structural measure: rechargewell
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20ft
Structural measure: dugwell
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 29ft
Structural measure: underground
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15ft
Structural measure: water tank
Construction material (earth): used for construction
Construction material (stone): used for purfying
Construction material (concrete): used for construction
Construction material (other): used for construction
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Water harvesting system
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | dug well | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 2. | underground water tank | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 3. | recharge well | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 4. | others | 8hrs for 7 days |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Dug well | pieces | 1.0 | 124.0 | 124.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Underground water tank | pieces | 1.0 | 257.0 | 257.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Recharge well | pieces | 2.0 | 28.5 | 57.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Others | unit | 1.0 | 128.5 | 128.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 566.5 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 566.5 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | electricity | every month |
| 2. | dump | every month |
| 3. | others | every month |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other | Electricity | month | 1.0 | 18.57 | 18.57 | 100.0 |
| Other | Dump | month | 2.0 | 85.5 | 171.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | others | ,onth | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 206.57 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 206.57 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
labour and constructing wells are the most determinant factors affecting the cost.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1114.00
Agro-climatic zone
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
Level of mechanization: tractor
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- group
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
irrigation water availability
irrigation water quality
demand for irrigation water
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
health situation
cultural opportunities
recreational opportunities
community institutions
national institutions
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
livelihood and human well-being
Comments/ specify:
The Technology helps providing pure water for drinking which is one of the basic factor for drinking
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
water quality
harvesting/ collection of water
surface runoff
groundwater table/ aquifer
evaporation
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
| local windstorm | not known |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | not known |
Comments:
proper drainage system
better plantation
diversity
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
The establishment and maintainance cost is not so high compared to benifit and facility that are provided by the technology which has solved the problem of water in more than 200 household in one locality
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
150 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
Comments:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: the technology have been developed traditionally with local knowledge. therefore locals manage and maintain the pumps, controlbox.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: water is basic fundamental needs of life. peoples are also searching for alternatives for minimizing and solving the problems.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
now people dont need to disturb their sleep for collecting water How can they be sustained / enhanced? further educating people about benifit of ground water recharge we can make them participate in various program of maintainance and development of this technology |
| water supply is easily facilitated |
| local participation |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
there is proper supply of water in each and every houses How can they be sustained / enhanced? making all people aware of recharge mechanism, we can enhance this technology and supply water to people |
| peace and unity among people |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| land investment is required even different modern technology should be made available to purify water and make them iron free | government should make their concerns regarding such problems |
| participance from local communities is not enough for such large investments and implementing new technology |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| in some places the % of iron is high which makes the water unsuitable for drinking | different water purifying technology should be applied such as pets, sand, gravel etc |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [Nepal]
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
- Compiler: Sabita Aryal
Modules
No modules