Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakha Chuke Tole for domestic use. [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1655 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Bajracharya Reena
Kathmandu university
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Maharjan Satish
Kathmandu university
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [尼泊尔]
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakka Chuke tole for Domestic use.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
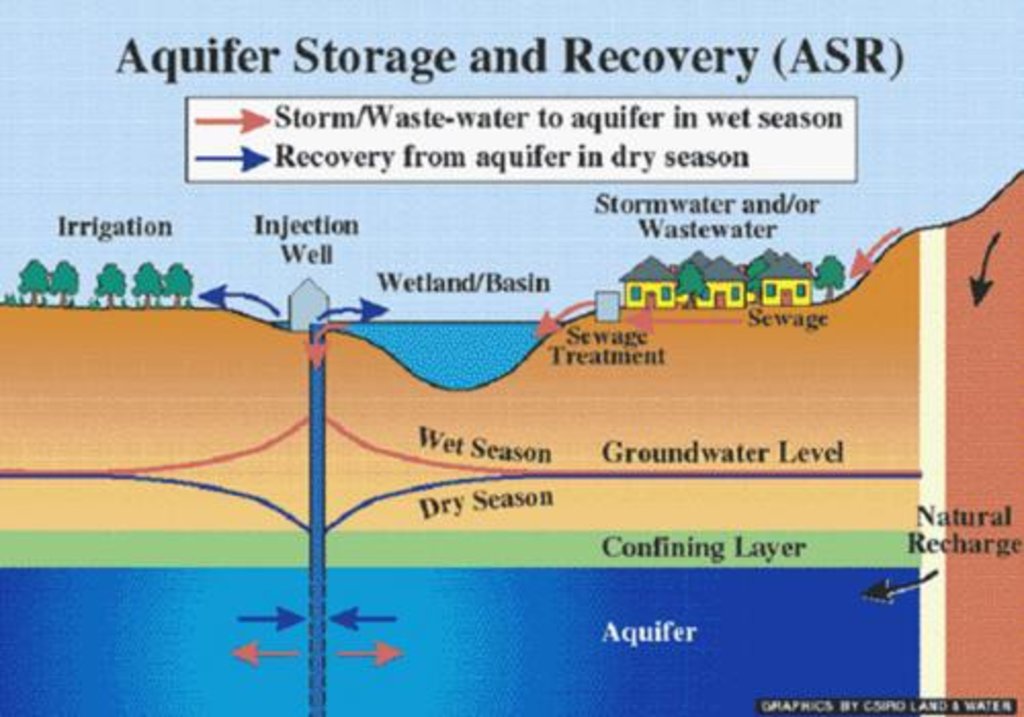
Due to increasing population and urbanization along with unmanaged settlements in and around the core city areas in Lalitpur existing ground water dries up while the water levels in well is decreasing alarmingly. However with initiation of rainwater recharge programs in areas in 2009
locals from around 150 houses around nyakha chuke tole and adjoining areas in lalitpur get their water supply with sucessful replerishment of their underground aquiter through rainwater harvesting.the dugwells are being sucessfully replerished due to rainwater recharge system.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is mainly applied to replerish ground water aquiter to support around 20 different committee in Lalitpur.
This aims to make people aware of the recharge mechanism and augument ground water level.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The credit for implementing this technology must go to local people participation. It is only because of the cooperation among themselves that make them realize current alarming problem and made them collect money for implementing recharge system.They have done it with external material support such as food-work, payment, subsidized machinery.
Regarding maintenance activities , women living around nyhakha chure tole are responsible for cleaning areas where technology has been implemented. Besides , water content in dug well are tested every six months to make sure that water is suitable for drinking that is free from ions and other chemicals . As well as different machine such as pump are checked every six months and are replaced if damaged, with the money collected from different house hold.
Natural / human environment: The implementation of this technology or system has made availability of water for various domestic use by supplying the water in each and every houses.It also has helped increasing harmony and mutual understanding among the people living there by. In past years people use to fight for getting water. there were fight between two locality for water . Ground water recharge system has increased water sources . There is proper distribution of water. Now people do not have to disturb their sleep for getting water like before.this has even helped to improve living standard and health of people.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Nepal
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lalitpur
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Protect ground water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- rice
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 柑橘属
注释:
major cash crop (CA): Rice
major cash crop (CP): Potato
major cash crop (CT): Orange
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

其它
具体说明:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development, population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify) (unmanaged settlements.), land tenure, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
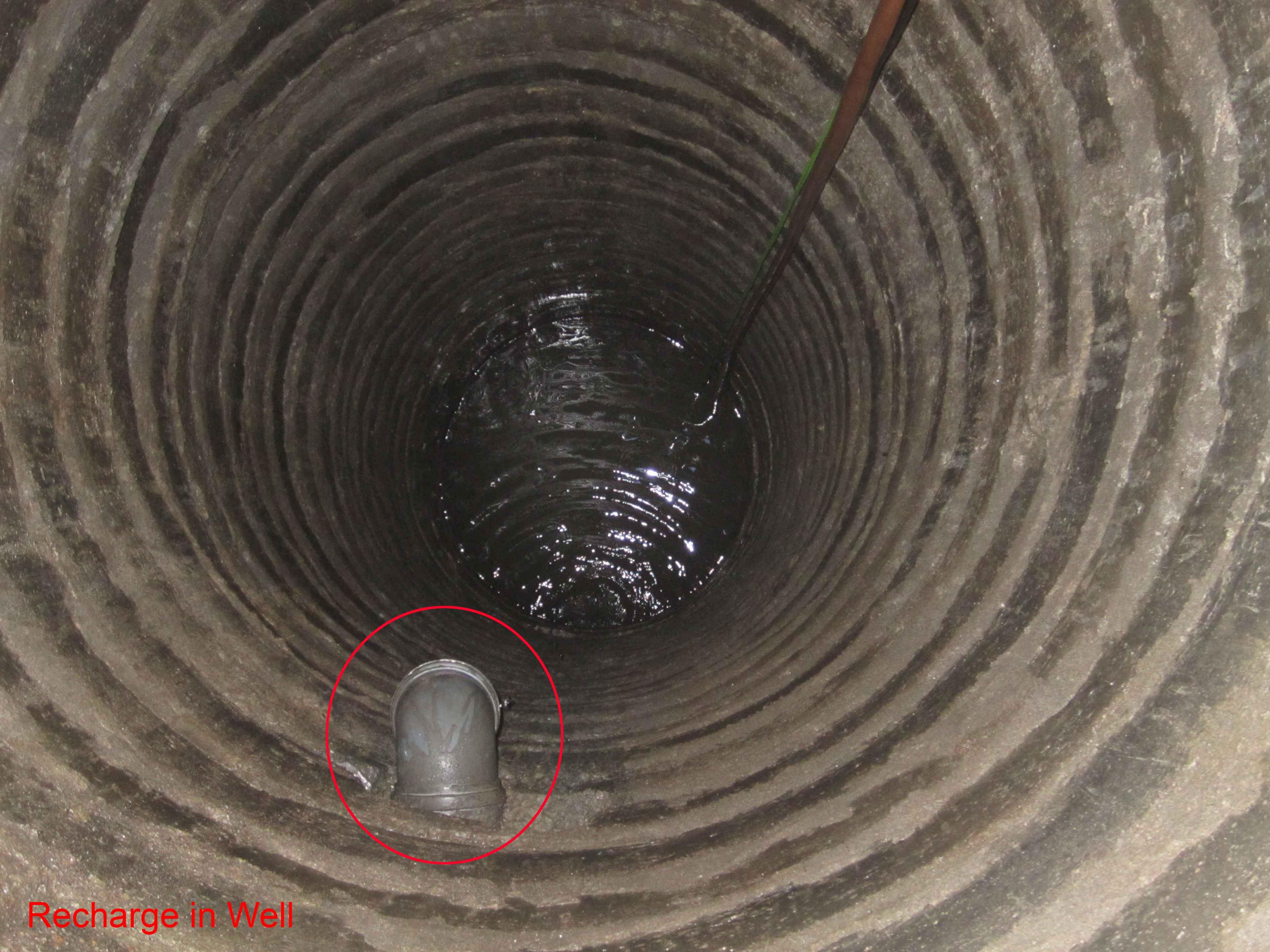
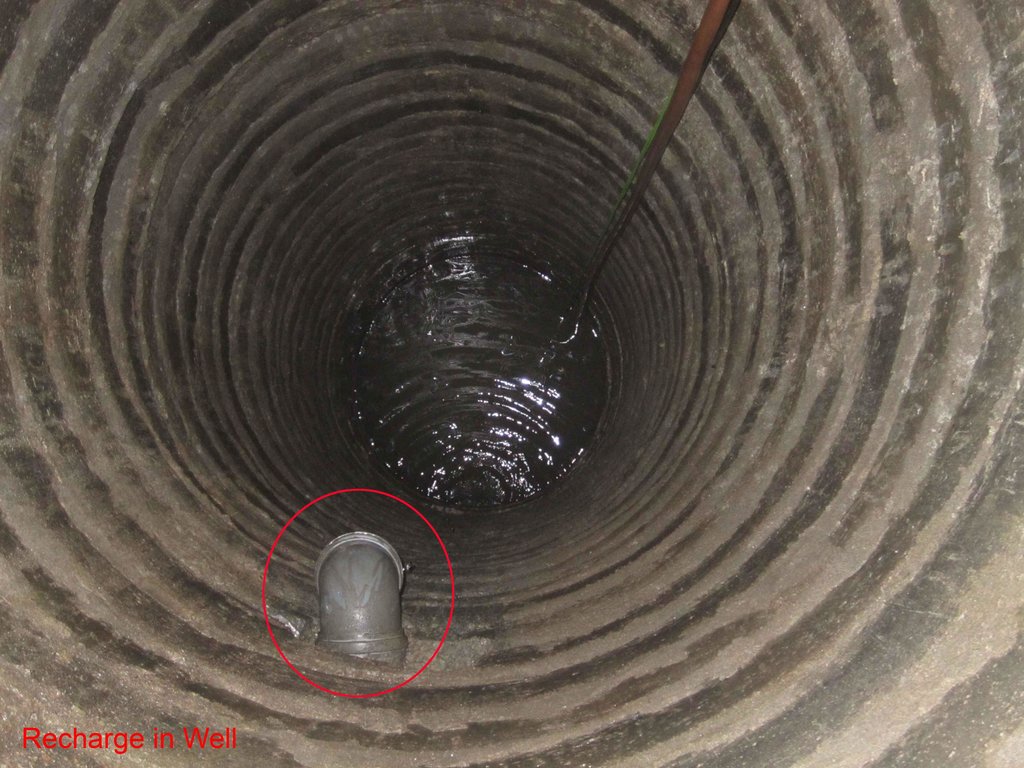
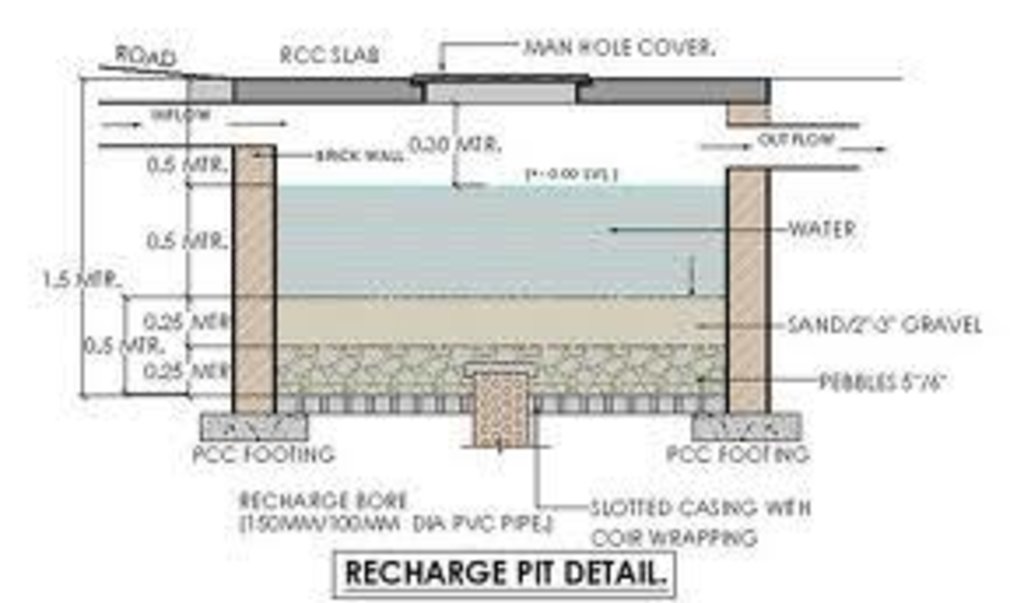
Underground water from dug well is drawn to stone filter through electrical pump. Water is purified in wash stone filter. purified water is pumped and drawn to surface water tanks from where water is distributed and supplied to people.
Location: nyakha chuka tole. lalitpur
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1ft
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1ft
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 200ft
Structural measure: rechargewell
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 20ft
Structural measure: dugwell
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 29ft
Structural measure: underground
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 15ft
Structural measure: water tank
Construction material (earth): used for construction
Construction material (stone): used for purfying
Construction material (concrete): used for construction
Construction material (other): used for construction
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Water harvesting system
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | dug well | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 2. | underground water tank | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 3. | recharge well | 8hrs for 7 days |
| 4. | others | 8hrs for 7 days |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Dug well | pieces | 1.0 | 124.0 | 124.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Underground water tank | pieces | 1.0 | 257.0 | 257.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Recharge well | pieces | 2.0 | 28.5 | 57.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Others | unit | 1.0 | 128.5 | 128.5 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 566.5 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 566.5 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | electricity | every month |
| 2. | dump | every month |
| 3. | others | every month |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 其它 | Electricity | month | 1.0 | 18.57 | 18.57 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Dump | month | 2.0 | 85.5 | 171.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | others | ,onth | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 206.57 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 206.57 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour and constructing wells are the most determinant factors affecting the cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1114.00
农业气候带
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
Level of mechanization: tractor
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The Technology helps providing pure water for drinking which is one of the basic factor for drinking
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
proper drainage system
better plantation
diversity
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
The establishment and maintainance cost is not so high compared to benifit and facility that are provided by the technology which has solved the problem of water in more than 200 household in one locality
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
150 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: the technology have been developed traditionally with local knowledge. therefore locals manage and maintain the pumps, controlbox.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: water is basic fundamental needs of life. peoples are also searching for alternatives for minimizing and solving the problems.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
now people dont need to disturb their sleep for collecting water How can they be sustained / enhanced? further educating people about benifit of ground water recharge we can make them participate in various program of maintainance and development of this technology |
| water supply is easily facilitated |
| local participation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
there is proper supply of water in each and every houses How can they be sustained / enhanced? making all people aware of recharge mechanism, we can enhance this technology and supply water to people |
| peace and unity among people |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| land investment is required even different modern technology should be made available to purify water and make them iron free | government should make their concerns regarding such problems |
| participance from local communities is not enough for such large investments and implementing new technology |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| in some places the % of iron is high which makes the water unsuitable for drinking | different water purifying technology should be applied such as pets, sand, gravel etc |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [尼泊尔]
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
模块
无模块