Community approach of groundwater recharge in Lalitpur,Nepal [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Vu Jal Uttpati-Nepali
approaches_2481 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Bhattarai Saddikshya
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Shakya Anish Ratna
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Shrestha Shiwani
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Rajendra Shakya
980842772
Nyakhachowk,Lalitpur
尼泊尔
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakha Chuke Tole for … [尼泊尔]
Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakka Chuke tole for Domestic use.
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
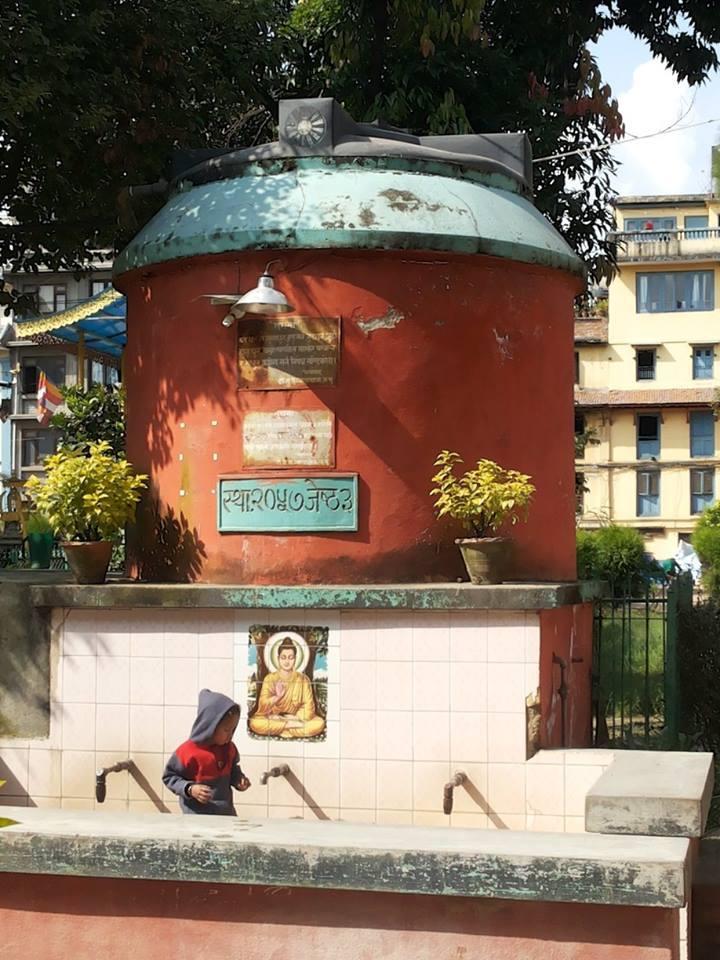
Groundwater recharge by rainwater for domestic purpose in Lalitpur,Nepal
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Bagmati
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lalitpur
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2001
2.7 方法的类型
- 最近的本地倡议/创新
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities
Recharge of the ground water
providing water for domestic use like drinking,cleaning etc
long term supplement of water
livelihood improvement
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: conflict over resource use
lack of technical knowledge
lack of cash to invest in SLM
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
wells are considered as place where God lives especially Hindu myth,so any change in water system of well is considered unauspicious
Treatment through the SLM Approach: awareness of public is the only treatment
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Some Financial problems
Treatment through the SLM Approach: collection of money from households
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: community ownership meant no hinderance to development
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
lack of tools and technology
Treatment through the SLM Approach: consultancy with experts
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Residence of the locality. Both gender
- 地方政府
Local leaders
provided fund-Lalitpur sub-metropolitan municipality
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
USaid,Indian embassy
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 自我动员 | local people felt the deficiency of water; they need to solve the problem so formed a committee to investigate and solve the problem |
| 计划 | 自我动员 | resident engineers and local people cooperated to solve problem |
| 实施 | 自我动员 | The implementation was according to the planning |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | monitoring of water level and quality were done on weekly basis |
| Research | 无 |
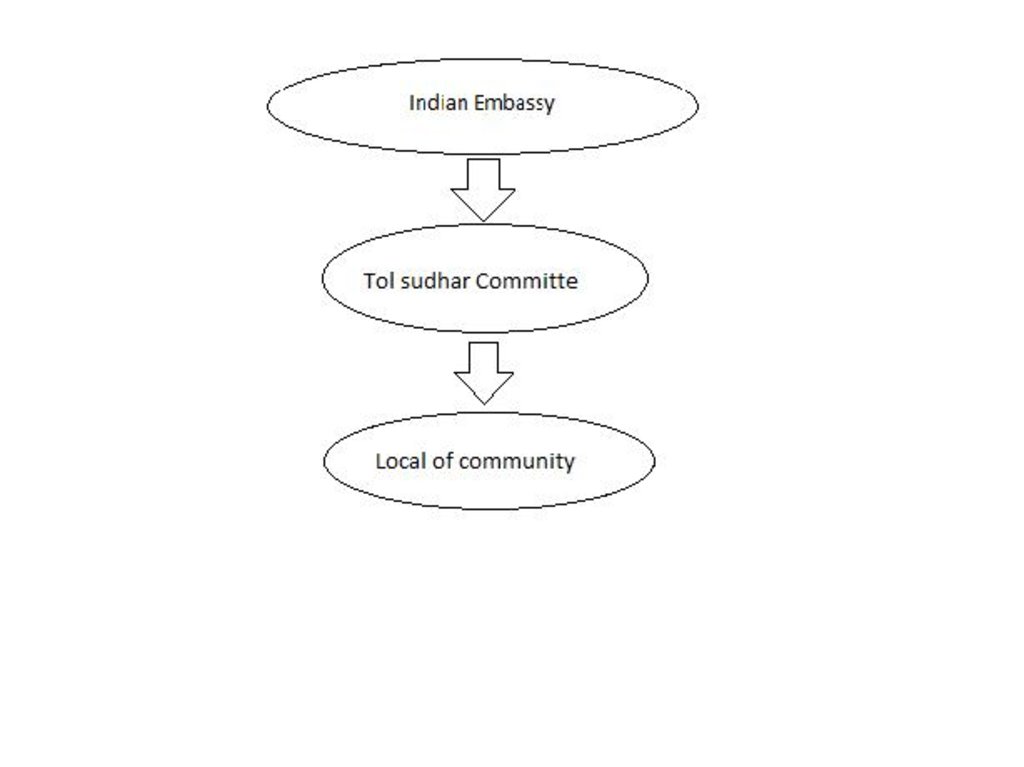
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
The Indian embassy donated materials, the tol sudhar committee gave some financial inputs which was then provided to the local community for the initiation of the project
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 仅限土地使用者(自主)
解释:
problems were registered;investigation was done by the local community;decision was made by the local people
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). local people along with the help of some specialist,engineers from the same locality
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
- local people
培训形式:
- learning by doing
涵盖的主题:
ground water recharge
sustainable use of water
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在固定中心
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: committee in every locality; Key elements: agenda formation, meetings and discussions, final decision making
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; its a national issue
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,少许
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Water user
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by land users through measurements; indicators: Water user
technical aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Water user
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Water user
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Water user
area treated aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Water user
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Water user
management of Approach aspects were monitored by None through observations; indicators
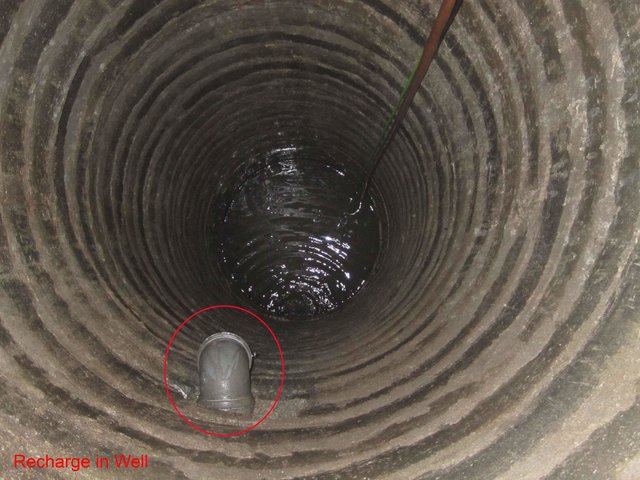
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: a hand pump was replaced by a recharge well
water is being collected with a motor,stored in tanks and distributed daily
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: water resisting plants were planted instead of demanding plants around recharge area
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 经济/市场营销
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
local people with technical knowledge
Research was carried out on station
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 2,000-10,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government: 10.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc): 10.0%; local community / land user(s): 80.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 机械 | 充分融资 | motors, drill machines |
- 建筑
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Cement, bricks | 充分融资 | |
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
there was no hinderance The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. the approach creates a framework for future use
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
many places of Kathmandu and neighbouring sub urban cities have adopted this approach
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
better quality of water resource was available
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
no dependence on tank water suppliers where people have to pay a lot and no dependence on pipeline water of government
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
increase groundwater level
- 环境意识
water deficiency results conflicts
- 美学改进
water for life
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
better water facility
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
as approach is local initiative with local knowledge
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
local participation sufficiency of water resources increase quality of life (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: regular monitoring and evaluation Active participation of committee) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
local people are themselves responsible self motivation and local participation is high (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: increase in awareness regular maintenance active participation of the committee ) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| recharge can degrade the aquifer unless quality control of the injected water is adequate | treatment of water using filters and locally available materials like charcoal,gravels,chips |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakha Chuke Tole for … [尼泊尔]
Ground Water Recharge in Nyhakka Chuke tole for Domestic use.
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
模块
无模块