Runoff Water Harvesting Contour Trenches and Pits in Hilly areas [Uganda]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: JOSELINE KASHAGAMA
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Nicole Harari, Maximilian Knoll, Yacime Khadraoui
Zimbibilo
technologies_3455 - Uganda
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Wazebekwa Dickson
+25671 3029283
Wanale Highland Farmer Organisation
P.O Box 931 Mbale
Uganda
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - Uganda1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
17/10/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
The trenches constructed in these regions address the problem of soil conservation to act as flow barrier (restricting the flow velocity within the safe limit from soil erosion point of view) and facilitate water conservation.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
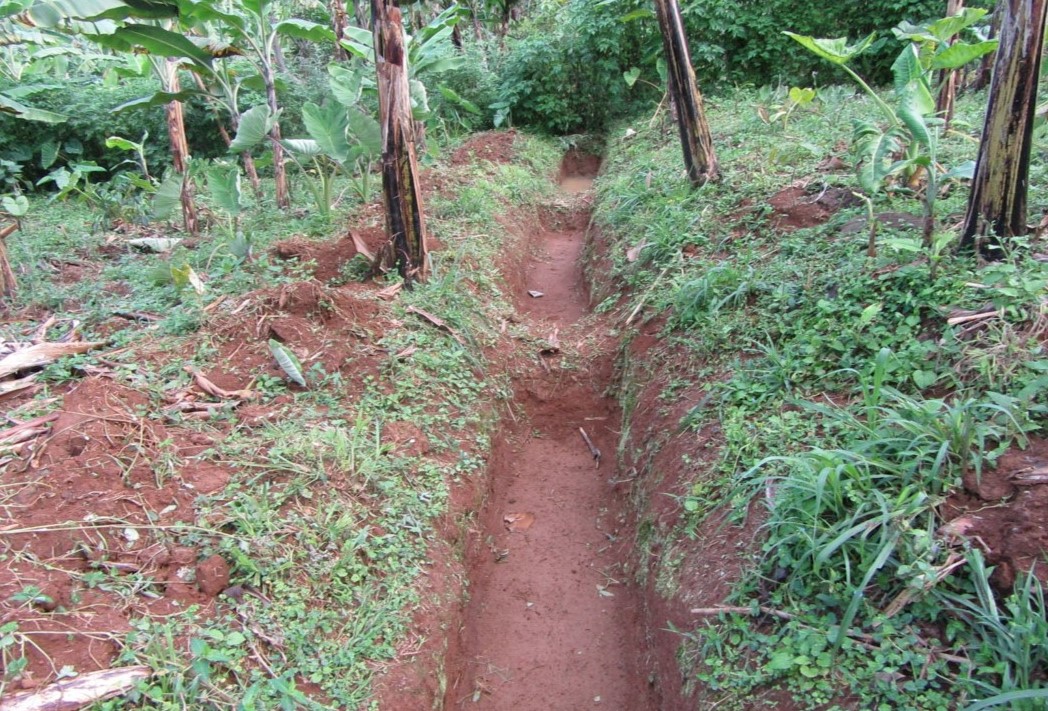
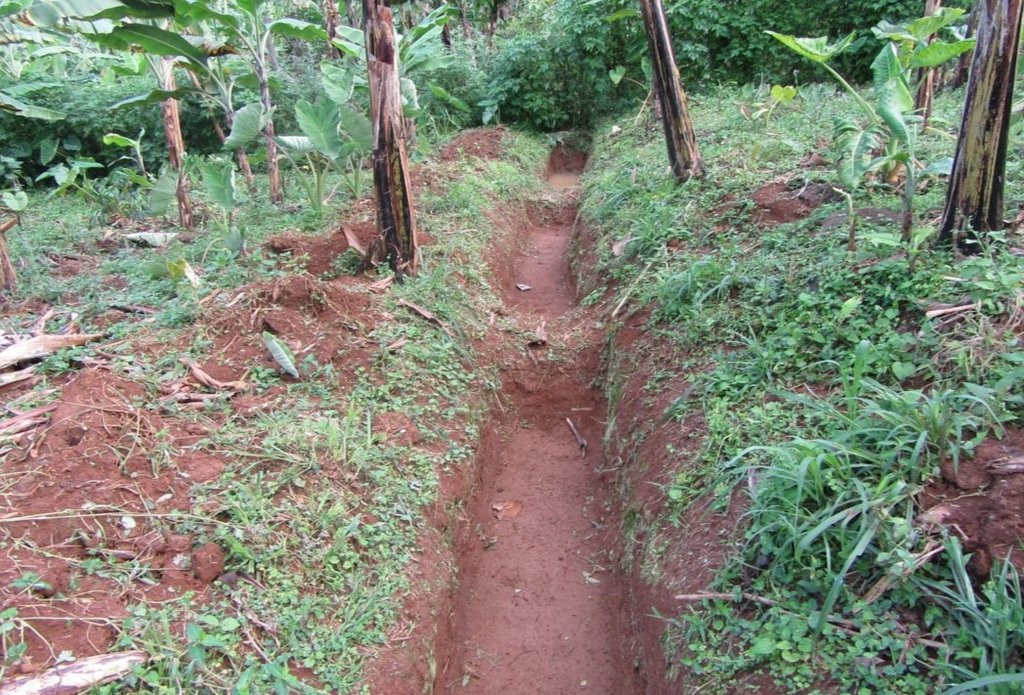
A contour trench and pit are an excavated ditch/pit along a uniform level across the slope of land in the top portion of catchment to trap runoff water.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
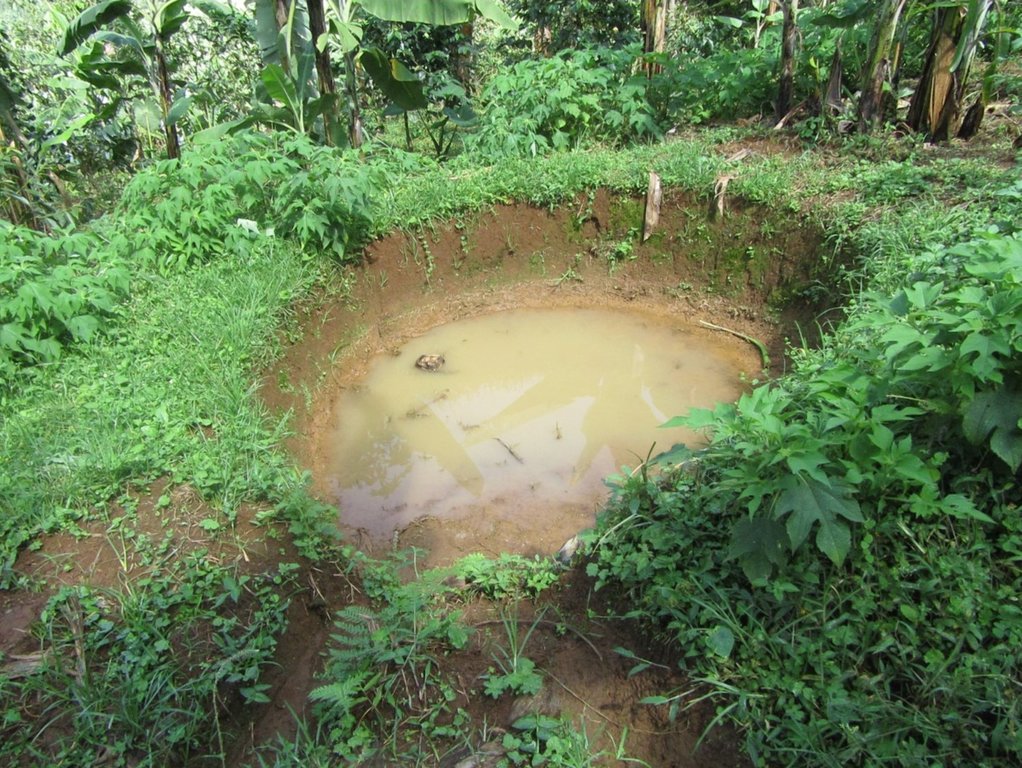
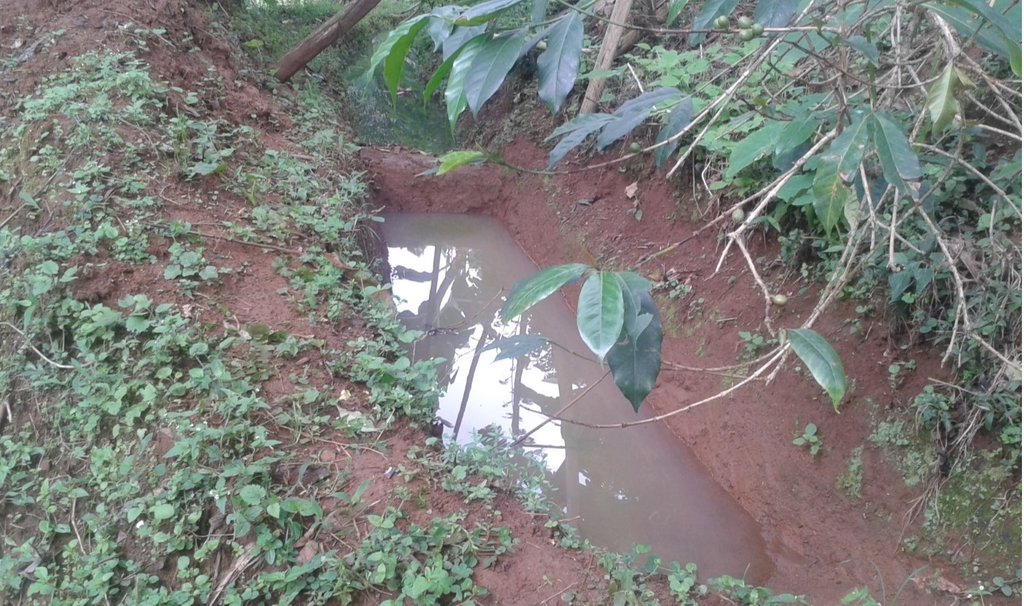
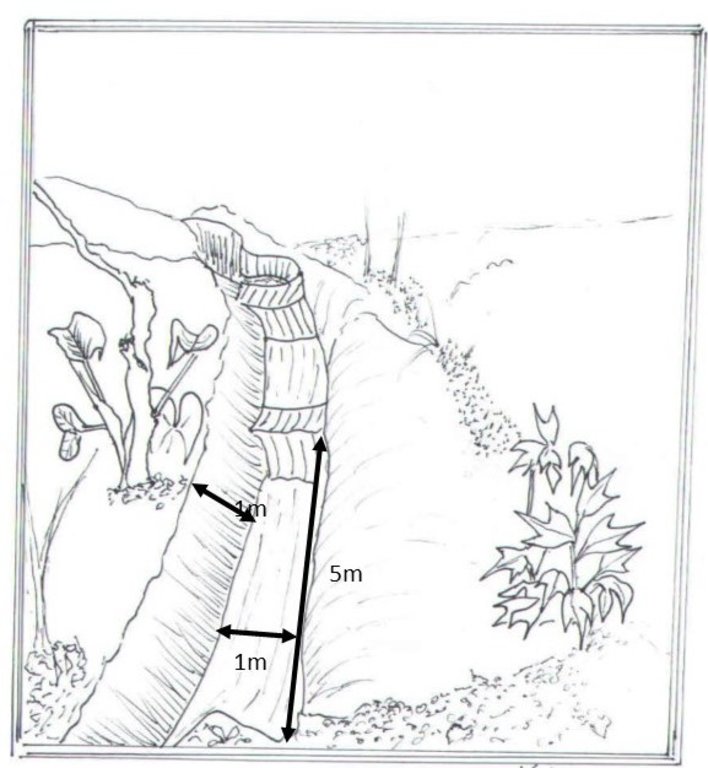
Water harvesting is the deliberate collection and storage of water that runs off on natural or manmade catchment areas. Catchment includes rooftops, compounds, rocky surface or hill slopes or artificially prepared impervious/ semi-pervious land surface. The amount of water harvested depends on the frequency and intensity of rainfall, catchment characteristics, water demands and how much runoff occurs. Contour trenches and pits are one of the oldest and most commonly used water management systems in the hilly areas of Mbale district. Contour trenches and pits are ditches dug along a hillside and run perpendicular to the flow of water. Their main objective is to slow down and attract runoff water which infiltrates into the soil which is used as soil moisture for crop cultivated after a rainfall event.These trenches and pits are constructed and maintained during the dry season. The size of the trenches is based on the slope and soil type. Bulabuli subcounty in Mbale district being a hilly area has trenches which are 5 metres long and 1 metre in width and depth. The materials needed in the construction of the trenches and pits are a hoe and spade. For maintenance they should be checked for build up soil, leaves and branches before the rainy season.The major advantages of rainwater harvesting are that it is simple, cheap, replicable, efficient, sustainable and adaptable and can be applied on any soil type and terrain. It can be implemented in small-scale, easily maintained and requires low investements which suites the rural community in Mbale district. Rainwater harvesting also has been shown an advantage as it reduces soil erosion, improves soil fertility and increases agricultural productivity as it reduces damage on the crops hence increases income and improves livelihood.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Date:
17/10/2017
Location:
Wanale subcounty Mbale district
Name of videographer:
Joseline Kashagama
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Uganda
Region/ State/ Province:
Eastern Uganda
Further specification of location:
Wahura village, Bunazoma Parish, Wanale subcounty
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
1989
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Irish Potatoes, Coffee and bananas

Settlements, infrastructure
- Settlements, buildings
Remarks:
Land users home
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Water is trapped from the streams flowing from the hills which is diverted into the farmlands
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Two rainy seasons between March to May and June to August or October
Livestock density (if relevant):
Cows and goats
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
- water harvesting
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 km2
Comments:
Most of the farmers in Wanale sub county constructed the trenches and pits as a way to combat soil erosion since the area is hilly
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
- Wr: riverbank erosion

physical soil deterioration
- Pw: waterlogging
- Ps: subsidence of organic soils, settling of soil

water degradation
- Hs: change in quantity of surface water
- Hp: decline of surface water quality
- Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
The technology reduced further land degradation by controlled run off water hence soil and water conservation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Trenches of 5metres long and one metre in width and depth while the pits are 4metres deep and 5metres in diameter. The materials needed in the construction of the trenches and pits are a hoe and spade. Contour trenches are dug along a hillside and run perpendicular to the flow of water.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Trench Line
Specify volume, length, etc. (if relevant):
Length
other/ national currency (specify):
Ugandan Shilling
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
3600.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
5000
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plan according to the topography of the area | Structural | Before the on set of rains |
| 2. | Purchase the materials need | Structural | Before the on set of rains |
| 3. | Measure and indicate | Structural | Before the on set of rains |
| 4. | Construction of the Trenches and pits | Structural | Before the on set of rains |
Comments:
The establishment activities are done during the dry season.
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Man Power | Trenches | 58.0 | 4000.0 | 232000.0 | |
| Equipment | Handhoe | piece | 3.0 | 10000.0 | 30000.0 | |
| Equipment | Spade | piece | 3.0 | 15000.0 | 45000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 307000.0 | |||||
Comments:
The land user bore all the costs since it was self innovative.
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of soil and other sediments from the trenches | Management | Annually before on set of rains |
Comments:
Once the trenches and pits are constructed, the land user is only left with digging out the soil that has build up in the trenches.
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | Trenches | 58.0 | 1500.0 | 87000.0 | |
| Equipment | Handhoe | pieces | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| Equipment | Spade | Pieces | 2.0 | 15000.0 | 30000.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 137000.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
The land user bore all the costs
Comments:
The maintenance costs are lower since less labour is need to maintain the structures. The land user doesn't have to buy the equipments again since they had been purchased at the beginning during the construction of the trenches.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
2064.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Wanale sub county receives high rainfall because of its high altitude
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
There's constant flow of streams from the hills which supports agriculture throughout the year
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Wanale hills is standing at the height of 6,864 ft
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
excess
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Yes
Specify:
There' s soil erosion in the hilly areas of Wanale which pollutes the water sources in low land areas
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
There's high adaptation of contour trenches in the area
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- low
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Most of the land is arable land and less occupied with natural forests
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
The land user is highly educated (University Level)
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
There is a lot of land fragmentation due to the high population and inheritance of land among the male children.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Reduced crop failure due to soil and water conservation
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
The soil is kept moist and it is a source of water for the crops after rains.
land management
Comments/ specify:
Promotes soil and water conservation and salinity of low ground water bodies through control of soil erosion.
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
Through increased crop production hence increased sales
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
Source of on farm income to those who provide labour in the digging of the trenches and pits
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
Increased productivity due to reduced crop failure
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Through knowledge sharing in their farmer groups
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
Reduced soil erosion hence reduced land slides
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Comments/ specify:
Reduced sheet erosion as a result of trenches trapping runoff water
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Water is trapped in the trenches which infiltrates into the soil and also used for irrigation
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
Soil is trapped in the trenches and also reduced soil erosion through reduced water runoff
soil accumulation
Comments/ specify:
Soil trapped in the trenches is removed and put into the field
salinity
Comments/ specify:
Reduces salinity of water bodies due to reduced soil erosion
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
Soil cover or mulch and top soil are conserved
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
Comments/ specify:
Ground cover is conserved since sheet erosion is controlled
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
Comments/ specify:
Controls flooding to low lands since some water is diverted into the trenches and pits
landslides/ debris flows
Comments/ specify:
Reduced land slides since water is trapped in the trenches and also the water speed is reduced
drought impacts
Comments/ specify:
Water trapped in the trenches and pits is used for crop irrigation
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
Water trapped in the trenches and pits can be used for spraying and making organic manure mixture from animals
downstream flooding
Comments/ specify:
Water is trapped in the trenches hence reduced runoff and water logging in low areas
downstream siltation
Comments/ specify:
Soil is trapped in the trenches
groundwater/ river pollution
Comments/ specify:
Soil erosion is controlled hence controlled salinity of water souces
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
Run off water is trapped hence reduced erosion and flooding in low land areas
damage on public/ private infrastructure
Comments/ specify:
Controlled soil erosion reduces land slides which would have blocked the roads affecting the transport system and maintenance costs
Comments regarding impact assessment:
Contour trenches are mainly dug to control soil erosion which slow down and trap run off water which infiltrates into the soil.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | very well | |
| annual rainfall | decrease | very well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | very well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | very well |
| landslide | very well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extended growing period | very well |
| reduced growing period | very well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
The trenches maintained after two rainy seasons and readily available cheap labour hence low maintenance cost.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- more than 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
Landowners have knowledge about the advantages of trenches and there’s readily cheap labour. Availability of Farmer groups in the area hence collective knowledge sharing.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Reduces soil erosion |
| Improves agricultural productivity through infiltration of the water collected in the trenches and pits |
| water can be used for irrigation and spraying after rains |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Prevents pollutants from draining into the low land water bodies |
| Reduces salinity of ground water |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Trenches silt up and need regular maintenance | Regular maintenance |
| Accidents may occur through drawning | Controlled movement of children |
| The trenches and pits are habitats for mosquitoes |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Increases land fragmentation since these trenches divide the land into small pieces of land |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1
- interviews with land users
1
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
4
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Importance of Continuous Contour Trenches (CCT) in Maharashtra by Nitin Bajirao Borse M.V.P.Samaj’s (2016) Arts, Science and Commerce College, Ozar (MIG) Affiliated to SP Pune University
Available from where? Costs?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308666186_Importance_of_Continuous_Contour_Trenches_CCT_in_Maharashtra
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Soil and water conservation Trenches
URL:
https://ecoursesonline.icar.gov.in/mod/page/view.php?id=2197
Title/ description:
Infiltration Trenches (water Absorption Trenches)
URL:
http://www.catchmentguidelines.org.mw/en/technical-guidelines/water-harvesting-and-storage/infiltration/infiltration-trenches-water-absorption-trenches
Title/ description:
Water Portal / Rainwater Harvesting / Groundwater recharge / Contour trenches
URL:
http://akvopedia.org/wiki/Water_Portal_/_Rainwater_Harvesting_/_Groundwater_recharge_/_Contour_trenches
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules