Controlling of soil erosion during crop production [South Africa]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Ursula Gaemperli
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff
technologies_950 - South Africa
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Mahlakoane Francis
Department of Agriculture & Environment, Northern Province
South Africa
SLM specialist:
Mashatola Mokgwakgwe Boy
South Africa
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Dept. of Agriculture, Northern Province (Dept. of Agriculture, Northern Province) - South Africa1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
The technology that applies contouring, mulching and intercropping in SWC.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Agronomic technology is used to control soil erosion during the crop production period, i.e. method that is employed to improve soil fertility, conserve water and protect from soil erosion while the land is under crop production.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is to keep the fertility of the soil stable by protecting the soil from soil erosion and water loss.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment is either done by planting strong root crops in between cultivated areas, or leaving the soil uncultivated, with a mulch cover on the soil surface. This will be maintained by keeping the intercrop strong and healthy while using zero or minimum tillage without removal of left over material on the soil surface.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
South Africa
Region/ State/ Province:
Limpopo Province
Further specification of location:
Sekhukuneland
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
10.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 10 km2.
Soil conservation measures were constructed (contour banks), then but was looked after until 1980's.
2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Western World
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- Prevent water loss
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- legumes and pulses - beans
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb

Grazing land
- cattle
Comments:
Major cash crop and major food crop: Maize
Other: Groundnuts & dry beans
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Silting and low infiltration rate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Injudicious cultivation.
Other grazingland: intensive grazing land
Grazingland comments: Cattle graze in the cropland during winter periods.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize mixed with groundnuts.
Maize mixed with dry beans
Type of grazing system comments: Cattle graze in the cropland during winter periods.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Water supply: Also rainfed for cattle
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- minimal soil disturbance
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A7: Others
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: contour planting / strip cropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, contour ridging
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
Comments:
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
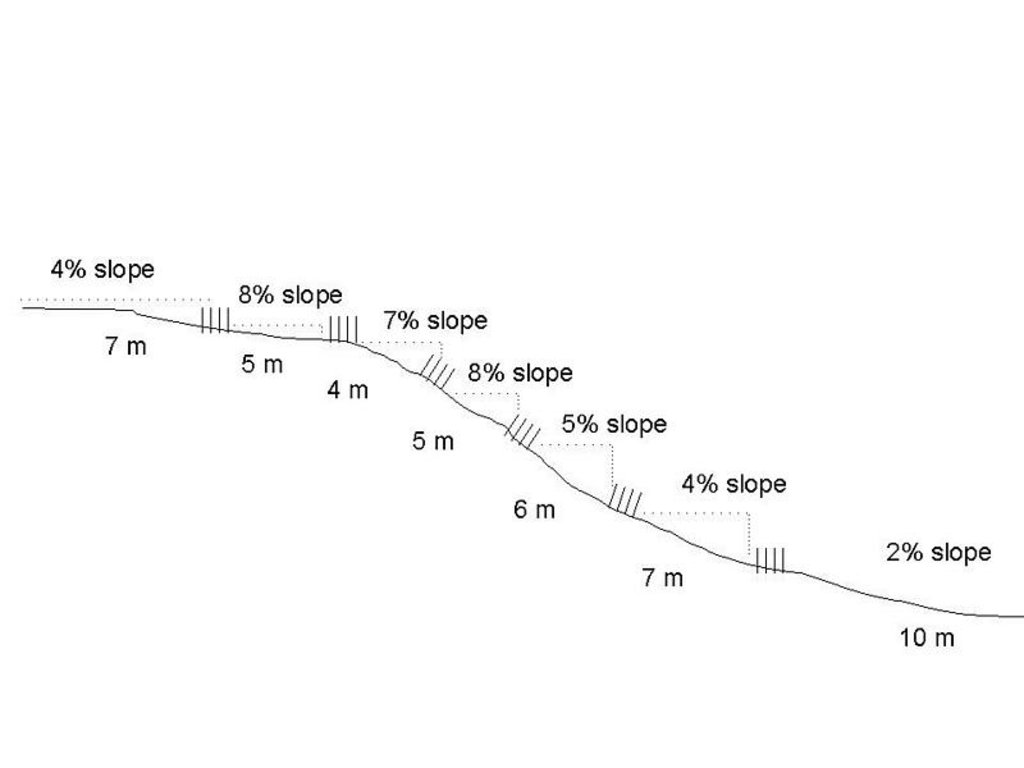
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical drawing off slope
Location: Mahlanga. Northern Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert
Author:
Mokgwakgwe Mashatola
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
6.00
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | persons/day/ha | 100.0 | 6.0 | 600.0 | 10.0 |
| Equipment | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| Construction material | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 825.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 825.0 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conventional tillage | early in rainy season / once a year |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Conventional tillage | persons/day/ha | 20.0 | 6.0 | 120.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 120.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 120.0 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: tractor/gallion
Grass strips per ha.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
The voluntary labour was at minimal, therefore labour affected the cost significantly.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Altitudinal zone: 1490 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil texture: Gravely loamy to sandy
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- very poor
- poor
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
1% of the land users are average wealthy.
66% of the land users are poor.
33% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
For CA (1-2 ha): 1 ha/ household
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Maize production & legume crops improved in good seasons
production area
land management
Other socio-economic impacts
input constraints
Socio-cultural impacts
community institutions
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
40
Quantity after SLM:
10
excess water drainage
Comments/ specify:
More water entered the soil
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Less clay was eroded
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
Not a priority in this case
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
0.5
Quantity after SLM:
0
Comments/ specify:
More soil was trapped
Other ecological impacts
soil fertility
Comments/ specify:
Less fertilisers was washed away
soil erosion locally
waterlogging
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
downstream flooding
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
350 households cover 80 percent of the area stated
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
97% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
350 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Soil protection How can they be sustained / enhanced? Involve land-users right from the beginning and allow them to run the SWC on their own |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Control soil erosion effectively How can they be sustained / enhanced? Involve land-users right from the beginning and allow them to run the SWC on their own |
| Conserve moisture |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Implementation | Implement with the land users and allow the land users to own the technology |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Sustainable land use plan for Nebo-district
Available from where? Costs?
Department of Soil Science, University of the North
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules