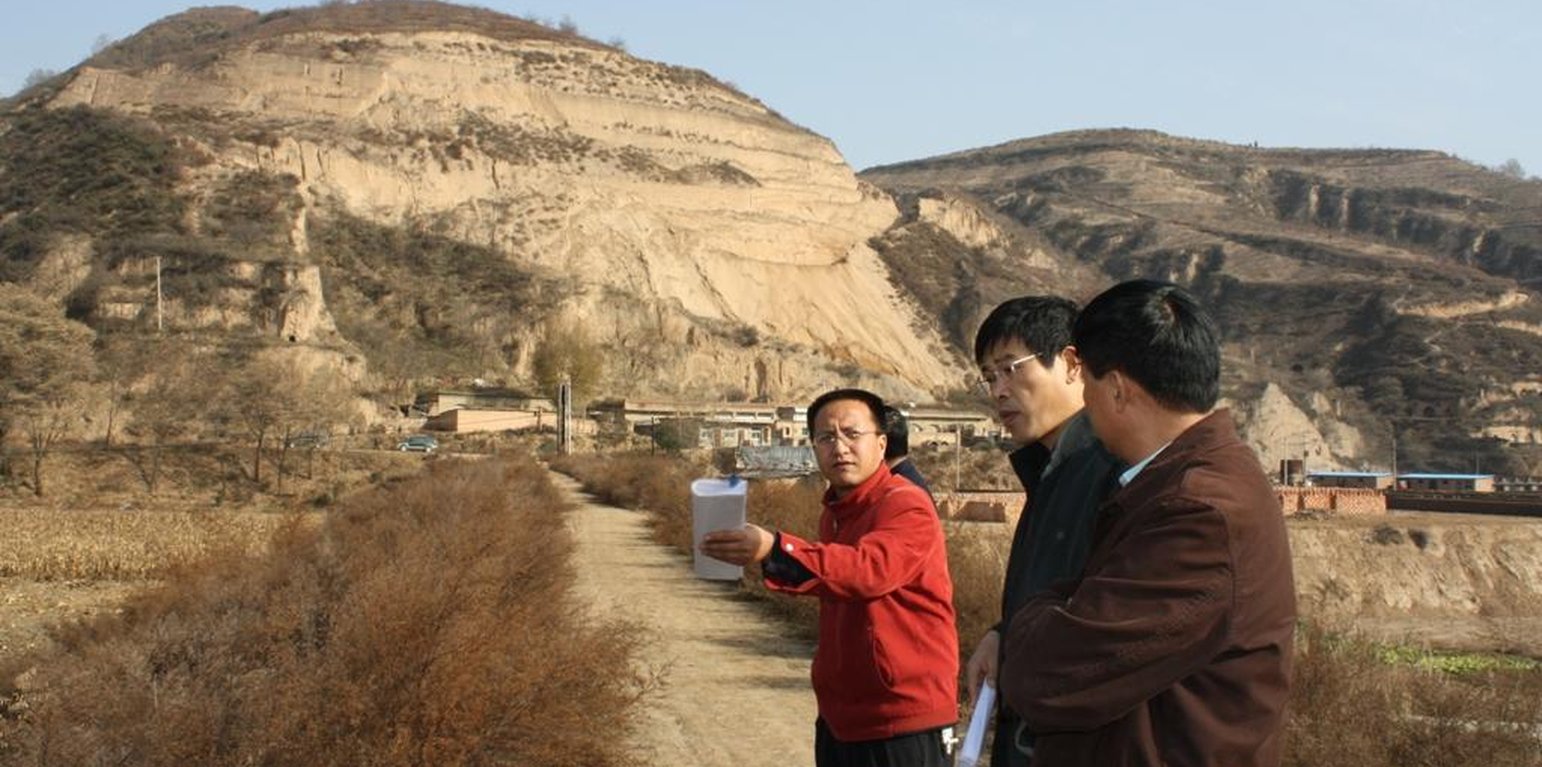




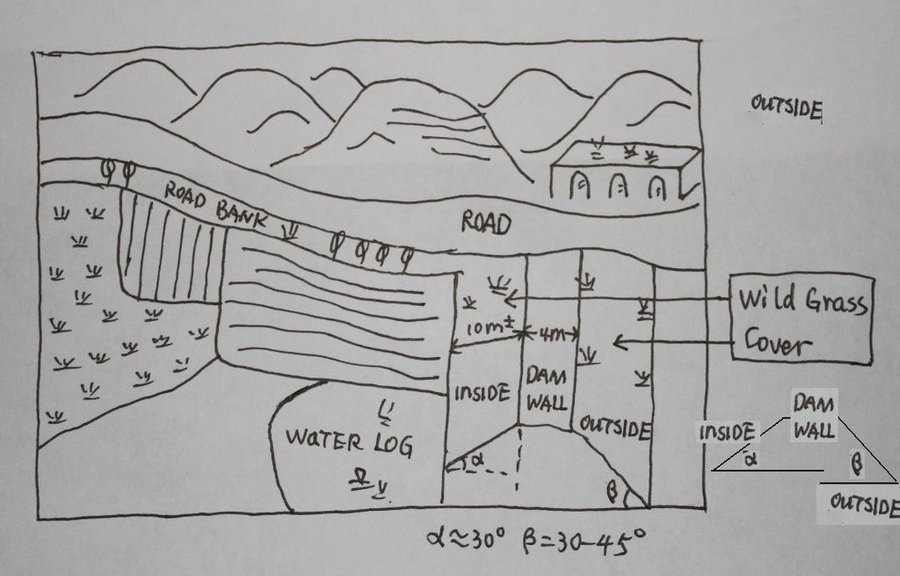
The check dam is a small dam designed to reduce flow velocity, control soil erosion, and allow to settle on the bed of the valley. The whole system includes main body of dam, spillway, overflow and supporting measures. The check dam for land is a small dam mainly for land after it is filled up by the sediment from upstream area, from several years to 20 years in common, it could be flat land in the valley, not mainly for water collection (different from reservior).
Purpose of the Technology: Check dams in the Loess Plateau are very common. There are many advantages. The check dam could not only reduce the erosion of the gullies, furthermore it retain the sediment in the flow and this decreases the sediment of the Yellow River. The check dam is good quality land for the soils because of the sedimentation of organic matter and other nutrients from topsoil . In this region soils are deep and very fertile because most soil is from the top soil upstream. The soil moisture of check dam is also much better than in any other places in the watershed because the flood should go away from its surface and the water inflitration is great in raining seasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment needs enough money because it has to be safe enough, and the maintenance cost is not so high. The catchment with great soil erosion is better when we considered the formation time of land.
Natural / human environment: The controlling area of check dam for land varies greatly from 30 square km or more. Since the "Grain for Green" Project of China in 1999, the soil erosion on the slope decreased. The time from reservoir to land need more time because there is less and less sediment from upstream and the sedimentation changed slowly.
Lugar: Yanhe River Basin, Shaanxi Province, China
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados: un solo sitio
Difusión de la Tecnología: aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 10-50 años atrás
Tipo de introducción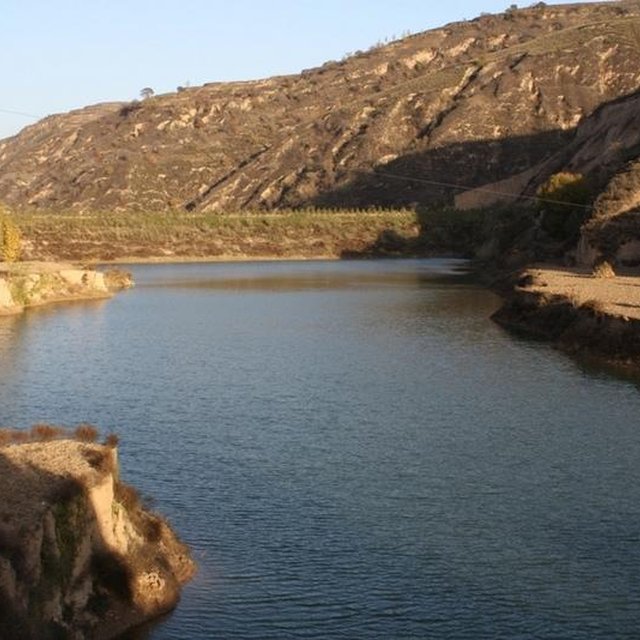




| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Building the wall/ field survey and planning | Person/day | 180,0 | 8,8 | 1584,0 | 90,0 |
| Building the wall/ field survey | Machine/hrs | 75,0 | 43,8 | 3285,0 | |
| Material de construcción | |||||
| Stone | m^3 | 40,0 | 26,35 | 1054,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 5'923.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | -2'729.49 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| check annualy the dam wall | Person/day | 15,0 | 8,8 | 132,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 132.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | -60.83 | ||||
Cantidad antes de MST: 600
Cantidad luego de MST: 6000
Cantidad antes de MST: 4500kg/ha
Cantidad luego de MST: 2500kg/ha
In extreme year with great rainfall, low yield of check dam land
Cantidad antes de MST: 950
Cantidad luego de MST: 59
Cantidad antes de MST: 200 kg
Cantidad luego de MST: 350 kg
Cantidad antes de MST: 8 m
Cantidad luego de MST: 4-6m
Cantidad antes de MST: 12-16%
Cantidad luego de MST: 16-22%
Cantidad antes de MST: 60t/ha/yr
Cantidad luego de MST: 5t/ha/yr
Sediment from slope decelerate the process of building arable land. In other words the economic function can not appear soon.
Cantidad antes de MST: 2events/yr
Cantidad luego de MST: nearly no