Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
- Editores: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Kaqayb Galka Dadwayne
approaches_6718 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Persona(s) de referencia clave/s
Especialista MST:
Omer Ahmed
+251910061493
ahmdomr1954@gmail.com
Natural Resource Department of Somali Regional State Bureau of Agriculture
Somali Regional State, JigJiga
Etiopía
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
22/03/2023
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST
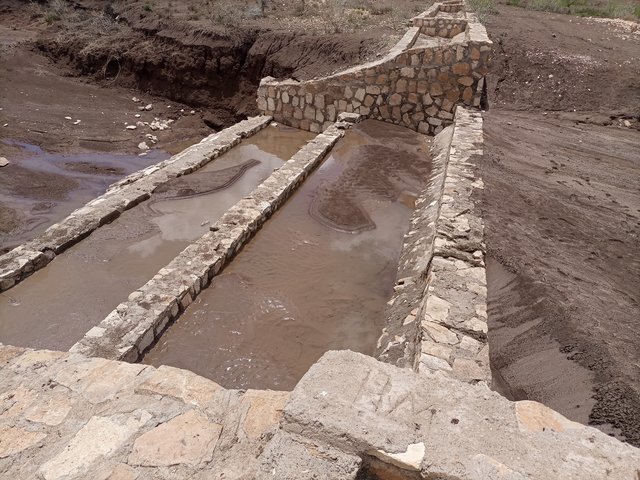

Double Basin Masonry Check Dam [Etiopía]
A double basin masonry check dam is a physical structure that helps to stop gully formation or further development of gullies in dry valleys. It rehabilitates small to a medium-sized deep gullies that are eating into the heart of adjacent land.
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
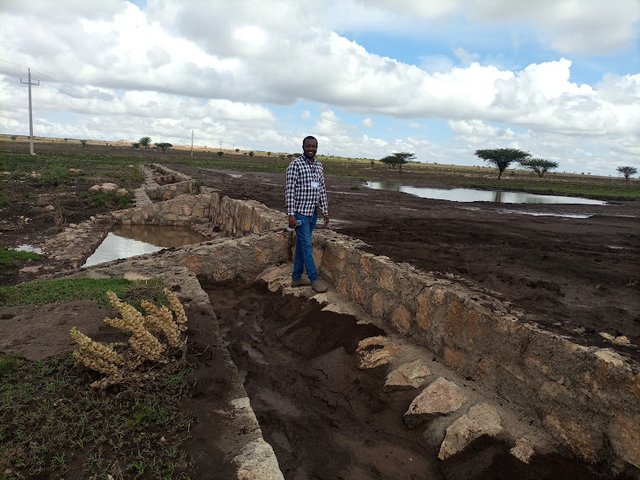

Water Spreading Weirs [Etiopía]
Water Spreading Weirs are designed to protect the degradation of agricultural fields and rangelands. They contribute to soil and water conservation and enhance the productive use of dry valleys for food crops and livestock fodder production via the harvest and spread of runoff water and fertile soils.
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Participatory rehabilitation and productive use of dry valleys is an approach employed to rehabilitate degraded and degradable land. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Participatory rehabilitation of degraded and degradable dry valleys engages the community at the grassroots through consultation. It is operationalised through the Lowland Soil Rehabilitation Project with local development partners from kebele, district, regional agricultural bureaus, and other relevant stakeholders.
Technical experts from the district and region are involved in reconnaissance, observation and joint selection of the intervention sites. The team conduct a survey, then profile and design the technologies required, along with the project engineer. The approach optimises the participation of the community and agricultural actors, allowing the development of a sense of ownership and accountability through training and awareness-creation exercises. In turn this encourages them to take care of and maintain the structures.
This approach combines top-down and bottom-up methods. At the grassroots, the local agropastoral communities are mobilized by local extension agents and made aware about the SLM intervention that the project and partners strive to put in place – including the physical structures in the farmers' fields and communal lands. The procedures include a site visit, a survey/ observation, and the identification of the intervention site based on the specific topographic features and drainage system of the catchment. Then, detailed field data is collected and a profile analysis is made to develop the design and get approval after stakeholders’ consultation and review of the details of the implementation design. The approach is complemented by satellite imagery and ground truthing. Following this, the next stage is identification of masonry experts, provision of training, and supply of construction materials and tools. Building the masonry works involves both skilled and unskilled labour.
The woreda NRM expert (focal person) facilitate the process at the grassroots through the development agents. The community gives their consent and support to the objectives of the project implementation. Therefore, they are involved in local decision-making and overseeing the technology that is being put in place.
The agropastoral community is the end user and benefits from the positive consequences of the intervention which is a result of better management of soil and water for productive uses of the dry valley. However, because of a lack of awareness, and the agropastoralists conventional livelihoods practice traveling with their livestock, there is a lack of participation in the day-to-day implementation activities. That limits their active contribution in implementation. Of course, local elders value the consultative experience which confirms a sense of self-worth and acknowledges their role in ownership of the land and as the ultimate decision-maker for development intervention operating in their areas.
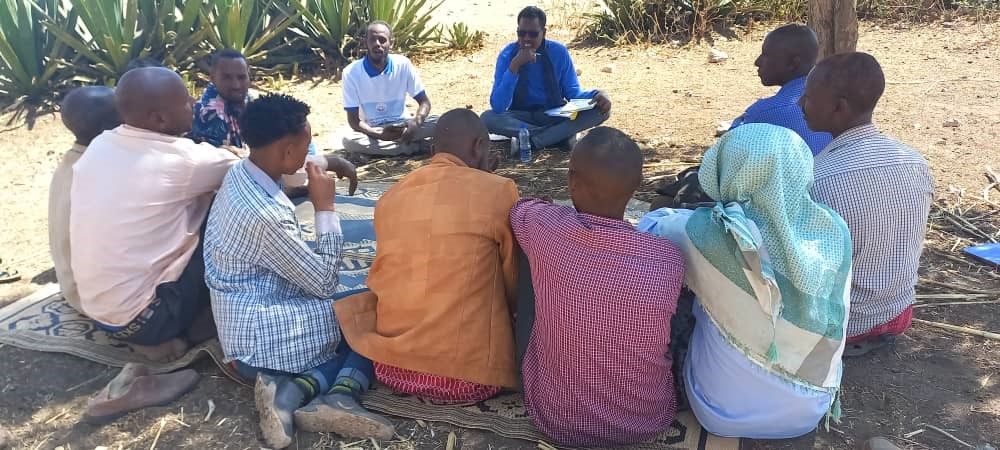
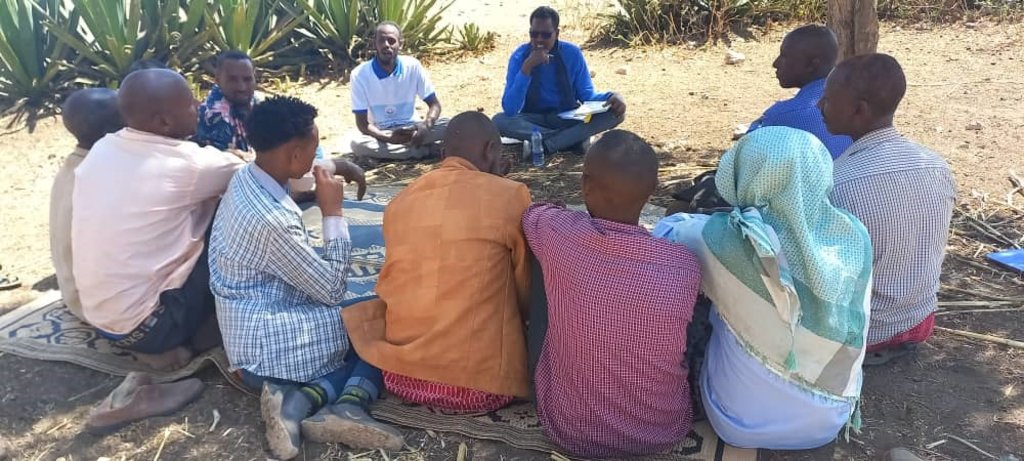
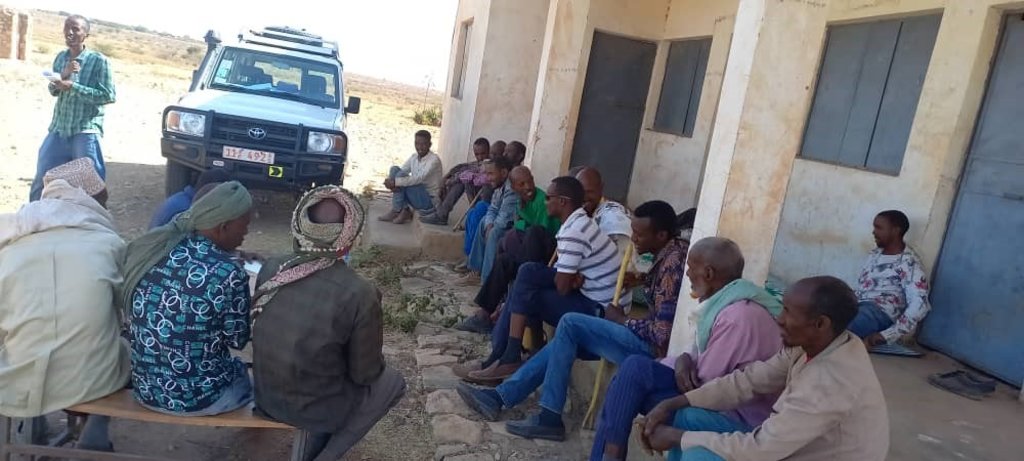
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
Comentarios generales sobre las fotos:
Photos (undated) obtained from project staff of community engagement taking place at the beginning of the project implementation.
2.4 Videos del Enfoque
Comentarios, descripción breve:
Video of the approach was not documented.
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Somali
Especifique más el lugar :
Amadle kebele, South Jijiga district
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
2021
Comentarios:
The project termination date is not indicated.
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
To engage the community and other stakeholders in making participatory decisions on the rehabilitation of the dry valley.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- facilitan
Access to finance promotes intensive awareness creation and participation of the community to implement the technology at a larger scale. Also, it allows supporting the maintenance and other follow on actions that ensure sustainability.
entorno institucional
- facilitan
Setting up the local institution such as an agropastoralist group enables the effective implementation of dry valley rehabilitation technologies/practices.
colaboración/ coordinación de actores
- facilitan
Coordination of actors enables the identification of useful actors and cross-fertilize experiential knowledge for documentation and further uses. Also, it enables acknowledgment of the contribution of different actors.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- facilitan
Having SLM knowledge enables efficient and effective implementation of dry valley rehabilitation technologies.
carga de trabajo, disponibilidad de mano de obra
- facilitan
Labour in the agropastoralist area is the limiting factor for the effective implementation of SLM practices. Therefore, the availability of labor or manpower is pivotal for the proper implementation of the SLM.
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Agropastoralist.
Participatory planning and decision making, sources casual laborer and oversee the technologies/practices.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
Natural Resource Management experts.
Facilitate stakeholders' participation, provide technical support, and backstopping services, and monitor the development during and after the implementation of the technologies.
- sector privado
Contractor to perform the engineering works.
Building/constructing the physical structures.
- GIZ project
GIZ (bilateral cooperation) projects.
Provide financial and technical support to the government partner organizations to promote the proper implementation of the rehabilitation of dry valley.
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | interactivo | Agropastoralists involve in allowing peers to understand SLM-related intervention. |
| planificación | interactivo | Land users involve in participatory planning and decision-making exercise. |
| implementación | apoyo externo | Skilled and unskilled laborers are sources from neighboring urban areas and the intervention kebeles. |
| monitoreo y evaluación | apoyo externo | SLM experts and extension agents support in monitoring and evaluation of the intervention activities. |
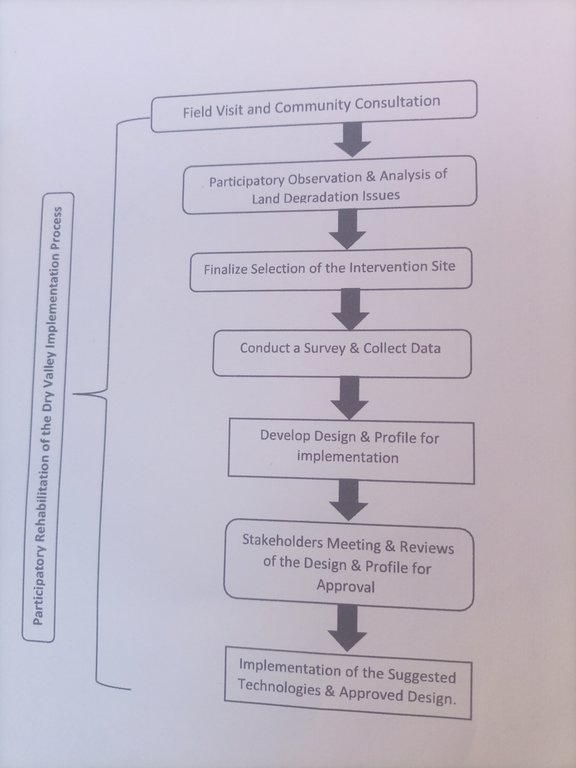
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
Descripción:
The sketch describe the process of implementing Participatory Rehabilitation of Dry Valleys.
Autor:
Gerba Leta
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- principalmente por especialistas MST en consulta con usuarios de tierras
Explique:
The communities are consulted, however, selection decision is made by the SLM experts of the partner organizations in consultation with the project SLM specialists.
Especifique las bases que sustentaron la toma de decisiones:
- la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- personal de campo/ consejeros
Forma de capacitación:
- en el contexto de trabajo
- reuniones públicas
Forma de capacitación:
- Masonry workers
Temas avanzados:
Dry Land Rehabilitation and Produce Use of the rehabilitated land. Basically, the training is on the SLM practices which are suitable for agropastoralist areas with special emphasis on the physical structure.
Comentarios:
SLM experts from partner organizations and masonry workers were trained to assist in the implementation of SLM practices for dry land rehabilitation.
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
Describa/ comentarios:
Advisory services related to SLM are infrequently given. As the agropastoralists are mobile looking for feed and water, particularly during the dry period, advisory services have not been provided on regular basis.
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, un poco
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
Describa la institución, roles y responsabilidades, miembros, etc.
Stakeholders from government and bilateral organization (project) do make ad hoc meeting during planning and evaluation, this brings actors together but need to establish a sustainable institution that stands on its own and can be working beyond the project's lifetime. Particularly, a land users (agropastoralist) group is essential to oversee the technology placed on their land so that sustainability of the intervention can be ensured.
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- financiero
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
- equipo
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
The equipment refers to the technical tools that can be used by the partner experts - but not farm tools. The latter is expected during which the agropastoralist resumes the productive use of the rehabilitated land which is currently in the initial years of implementation and not yet associated with the productive uses of it.
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
The monitoring and evaluation are part of the project implementation that enables the implementers to track the development and engage the end users to enable them to sense the benefits. The land users started to benefit from the structure such as fetching drinking water both for human and their livestock, though, it is an indirect benefit from the intervention.
Si respondió que sí, ¿la documentación se utilizará para monitoreo y evaluación?
Sí
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
No
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 2,000-10,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
No specific data on budget allocation for SLM at the district level. However, Local Subsidy Contract (LSC) was used to assist the woreda implement and follow-up the development of the intervention.
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
No
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
Comentarios:
There is no subsidy system supplied to the land users. Labor contribution is on a pay basis in cash. As the area is characterized by food insecurity and drought-prone by virtue, free labor is not expected. Basically, skilled and unskilled labor imported from the nearby town. Thus, it is impossible to assign this role to the land users.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
5.5 Otros incentivos o instrumentos
¿Se usaron otros incentivos o instrumentos para promover la implementación de Tecnologías MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque empoderó a los usuarios locales de tierras, mejoró el involucramiento de las partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Local land users consulted and informed regarding the benefits of SLM for the degraded and potentially degradable lands to ensure rehabilitation and its productive use. This may give motivation and a sense of self-worth as land owner.
¿El Enfoque facilitó la toma de decisiones basada en evidencia?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Beyond the approach, the land users can learn from the actual function of the technologies.
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Consultation with the land users motivates them to build trust in the intervention.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la coordinación e implementación efectiva en costos de MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
In the long run, it can assist land users mobilize casual laborers.
¿El Enfoque movilizó/mejoró el acceso a recursos financieros para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de los usuarios para implementar MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The approach creates an opportunity for land users to engage in the initial implementation process through which their awareness is raised.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el conocimiento y capacidades de otras partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Through stakeholders meeting and training opportunities created by the project.
¿El Enfoque construyó/ fortaleció instituciones, colaboración entre partes interesadas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
It builds collaboration between stakeholders.
¿El Enfoque mitigó conflictos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Involve them in the awareness creation training.
¿El Enfoque mejoró la equidad de género y empoderó a las mujeres y niñas?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Women are involved in the community meeting and/or consultation. Also benefited from the technology as it creates the opportunity to fetch drinking still water closer to their residence.
¿El Enfoque alentó a jóvenes/ la siguiente generación de usuarios de tierras a involucrarse con MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
It provides knowledge to the young generation through exposure to evidence based intervention.
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque resultó en mejor seguridad alimentaria/ mejoró la nutrición?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The technology implemented using the participatory approach believed to rehabilitate degraded lands and enhances productive use of the rehabilitated lands for growing various crops, and supply feeds to the livestock.
¿El Enfoque mejoró el acceso a los mercados?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque llevó a un acceso mejorado a tierra y saneamiento?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The technology implemented using this approach creates land users temporal access to still as well as groundwater regardless.
¿El Enfoque llevó a un uso más sostenible/ fuentes de energía?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque mejoró la capacidad de los usuarios de tierras a adaptarse a los cambios climáticos/ extemos y mitigar desastres relacionados al clima?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
In the future, when the productive use of dry valley is effected, post the rehabilitation efforts, land users certainly develop an adaptation to climate change and associated disasters through participatory approach.
¿El Enfoque llevó a oportunidades de empleo, ingresos?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
It improves generation of income from the production of food and feed crops.
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
Food crops and livestock feed production are increased as the technology reduces the intensity and effects of erosion and conserves soil and water.
- incremento de la renta(bilidad), proporción mejorada de costo-beneficio
Over time, the technology/approach improves the productive use of rehabilitated land for crop and livestock production that increases overall benefits.
- reducción de la degradación del suelo
As the structure stops heavy movement of the soil with runoff, it absolutely reduces the rate or speed of erosion and land degradation.
- reducción del riesgo de desastres naturales
The water harvested and spread on the farmland reduces the risks of crop failure and can be used for spate irrigation. Furthermore, the structure reduces the speed of runoff and retain the top soil moving away.
- conocimiento y capacidades mejorados de MST
The exposure to training and collective action and lesson learnt from the outcome of the implementation enhance knowledge and skills of the land users and experts.
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- incierto
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
As maintenance of the structure such as in cases of check dam is resource demanding, it is less likely for the land users to maintain/repair on their own. Rather early combining the physical structure by biological barriers or perennial forage or tree planation may ensure sustainability of the technology/land use. Furthermore, it demands time and labor from the agro-pastoralists.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Creates stakeholders awareness on SLM, and productive use of rehabilitated dry valley. |
| Improves coordination between agricultural actors in line offices, and other stakeholders collective action. |
| Enhances participatory decision making on the development and use of the rehabilitated lands. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| It creates evidence based lesson learning to replicate similar practices across the region. |
| It improves SLM implementation capacity of the development partners (agricultural offices) and the land users at local level. |
| It encourages the government respective department to allocate matching fund for SLM operationalized by development partners. |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Time and energy/labor demanding to integrate efforts of experts from different organizations. | Nurture proper joint planning for collective action. |
| Shortage of financial and material resources to put the structure in place. | Find and generate sources of resources and promote efficient use of the available budget. |
| Improper participation of stakeholders (dropout of experts) | Enforce participation through adopting binding by-laws to all. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Recurrent droughts displace the land users while looking for water and feed to their animals. | Ensure representation to the community, and assess enabling environment that reduce temporal displacement of the land users. |
| Relatively low participation of the land users in the conception and implementation of the approach as well as the technology intended to rehabilitate the dry valley. | Promote land users participation through intensive capacity building and awareness creation by gender and various categories of the community. |
| Lack of forming agro-pastoralist group who are believed to share knowledge, skills and labor for collective oversee and maintenance of the technology when damage is encountered. | Promote the development of a local institution that allows not only for the use of the land but also to oversee the gaps, report the issues, and involve in participatory fixing activities. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
Three individuals
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
Four
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Problems and landscape approach for ecological rehabilitation in the dry valleys of Southwest China. Dong, Y. & Liu, S. (Undated)
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shiliang-Liu-5/publication/221354340_Problems_and_Landscape_Approach_for_Ecological_Rehabilitation_in_the_Dry_Valleys_of_Southwest_China/links/574129be08ae9ace84160bec/
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Supporting local planning and the importance of mapping
URL:
https://dream.vandermeijde.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/220620_planningandmapping_Roden.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Double Basin Masonry Check Dam [Etiopía]
A double basin masonry check dam is a physical structure that helps to stop gully formation or further development of gullies in dry valleys. It rehabilitates small to a medium-sized deep gullies that are eating into the heart of adjacent land.
- Compilador: GERBA LETA

Water Spreading Weirs [Etiopía]
Water Spreading Weirs are designed to protect the degradation of agricultural fields and rangelands. They contribute to soil and water conservation and enhance the productive use of dry valleys for food crops and livestock fodder production via the harvest and spread of runoff water and fertile soils.
- Compilador: GERBA LETA
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos